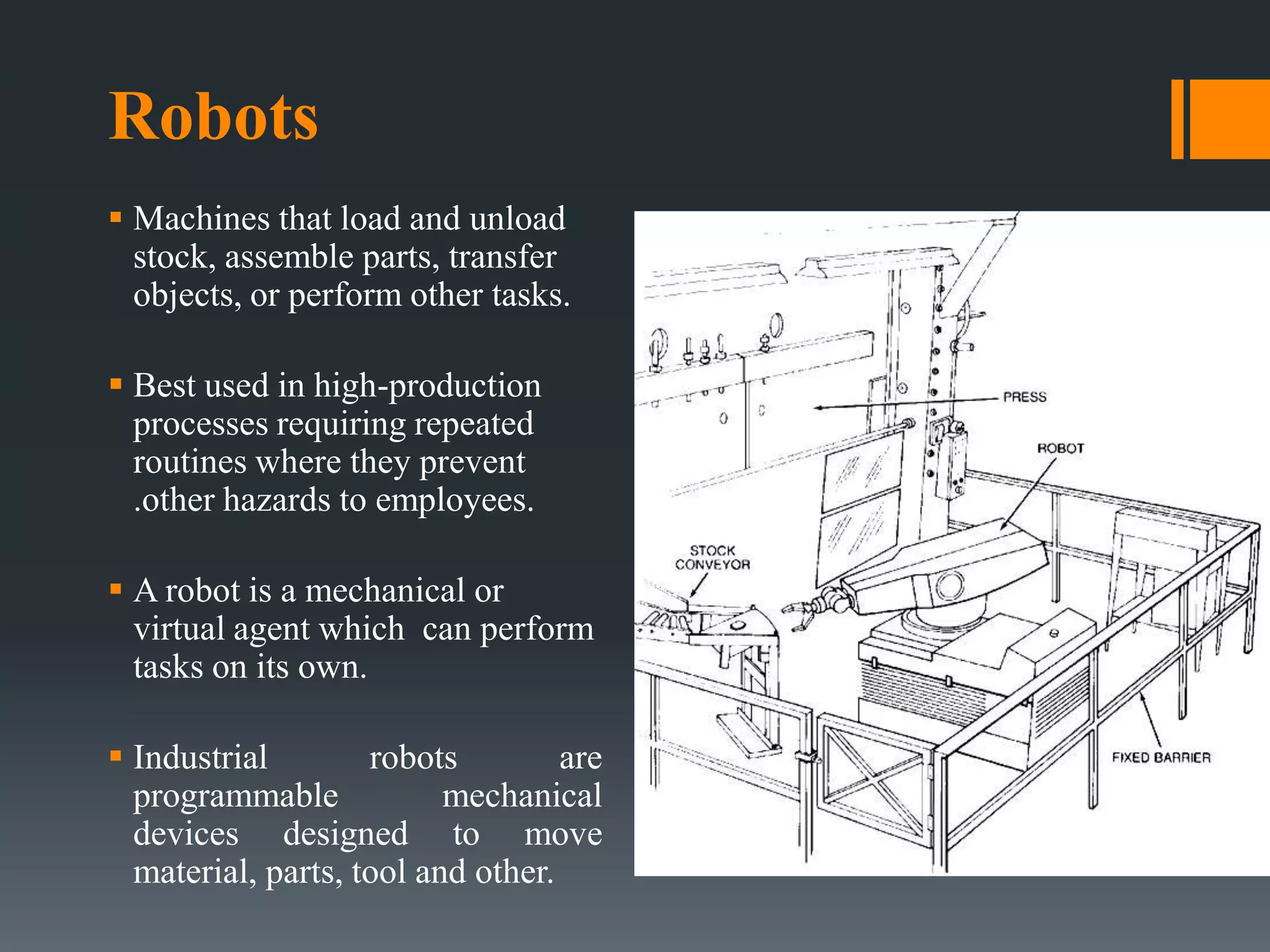
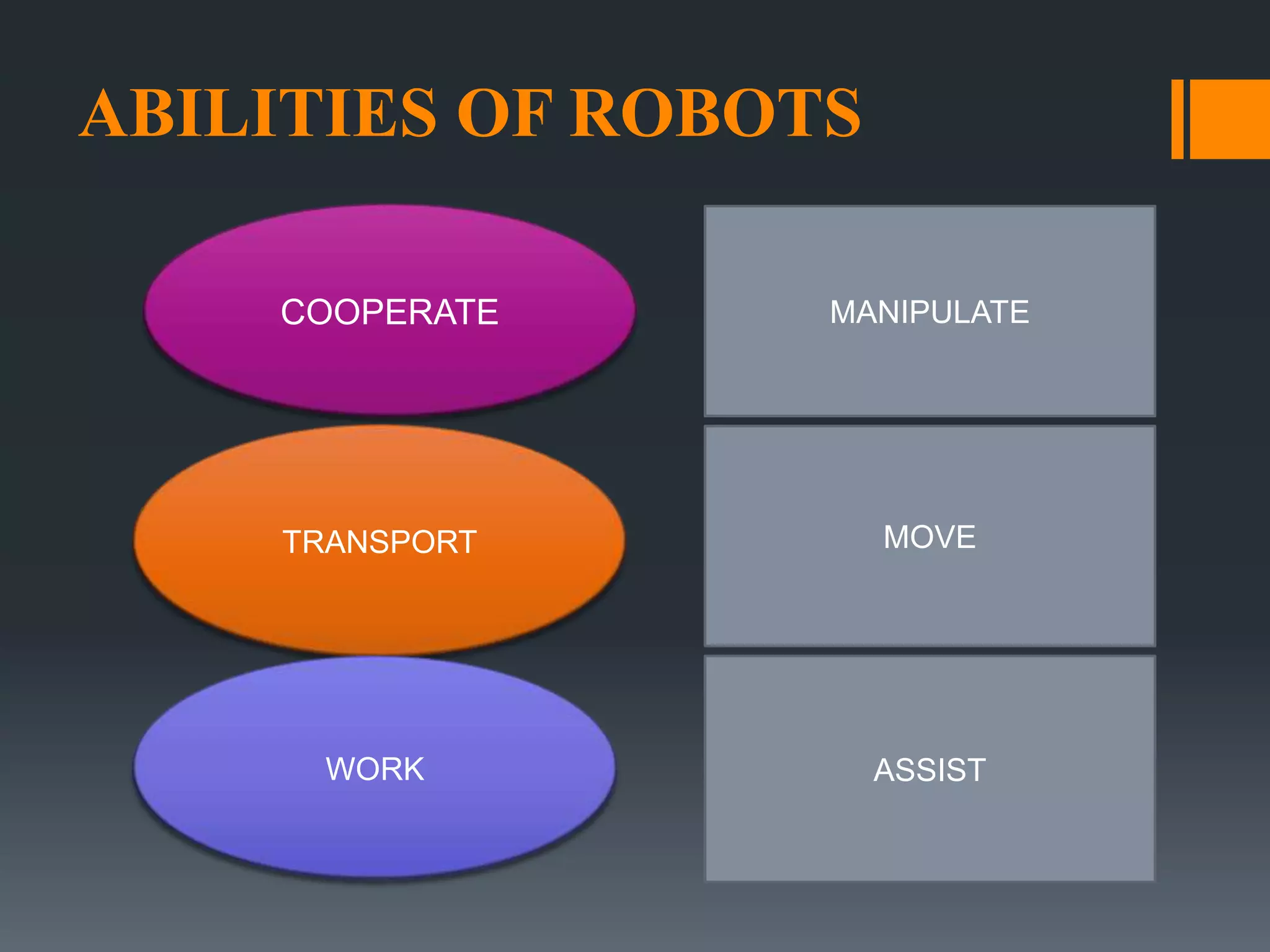
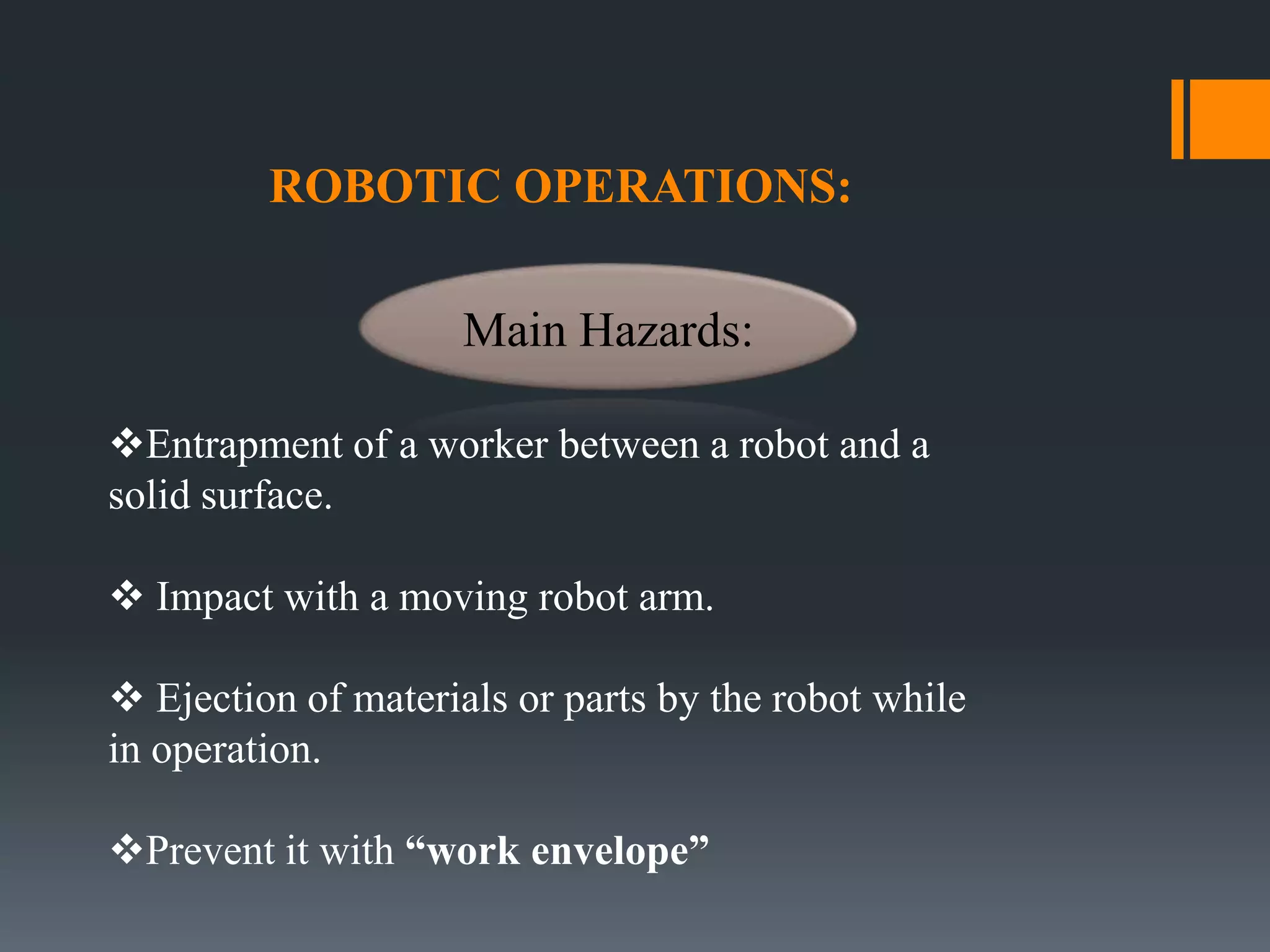
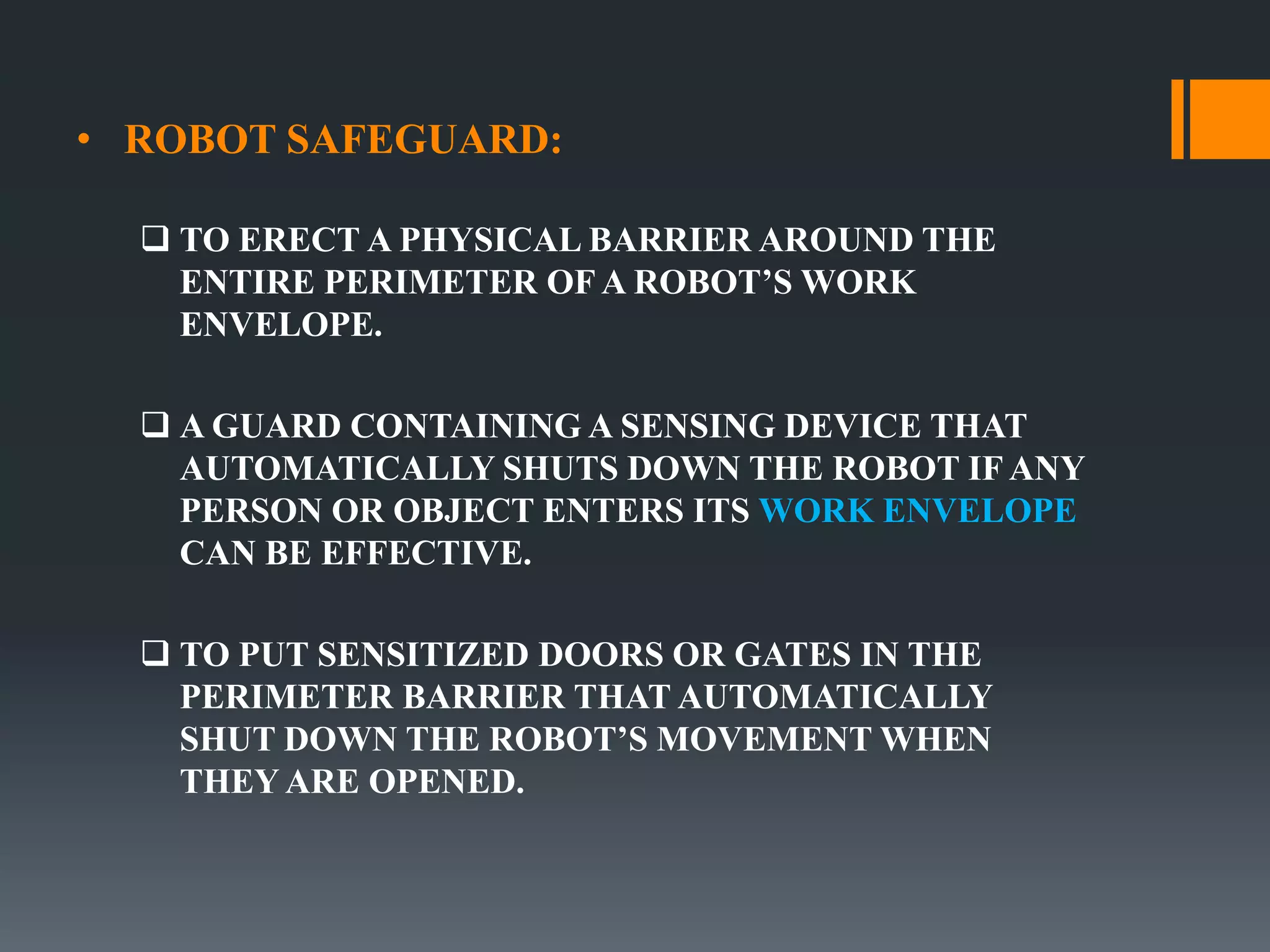
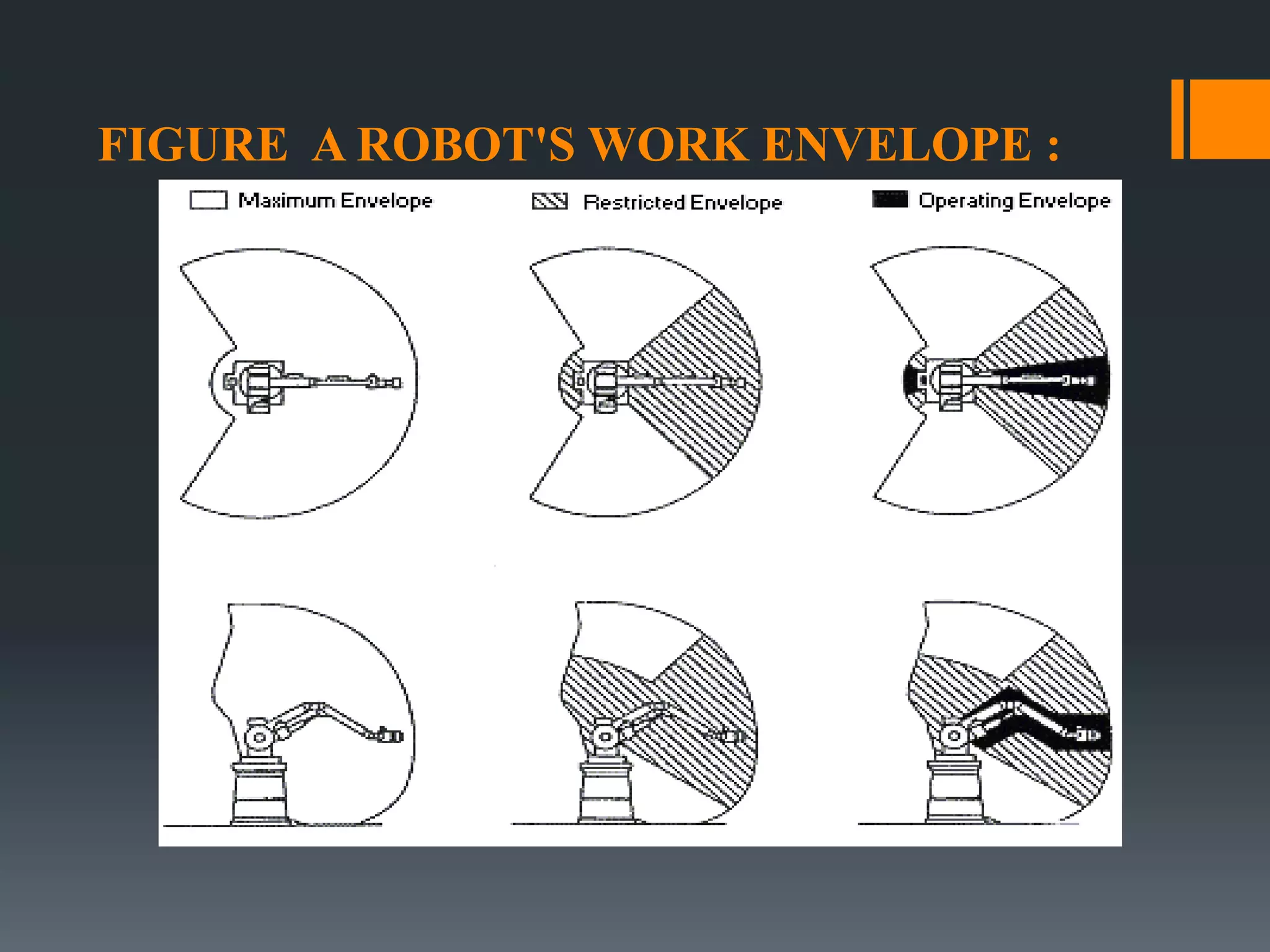
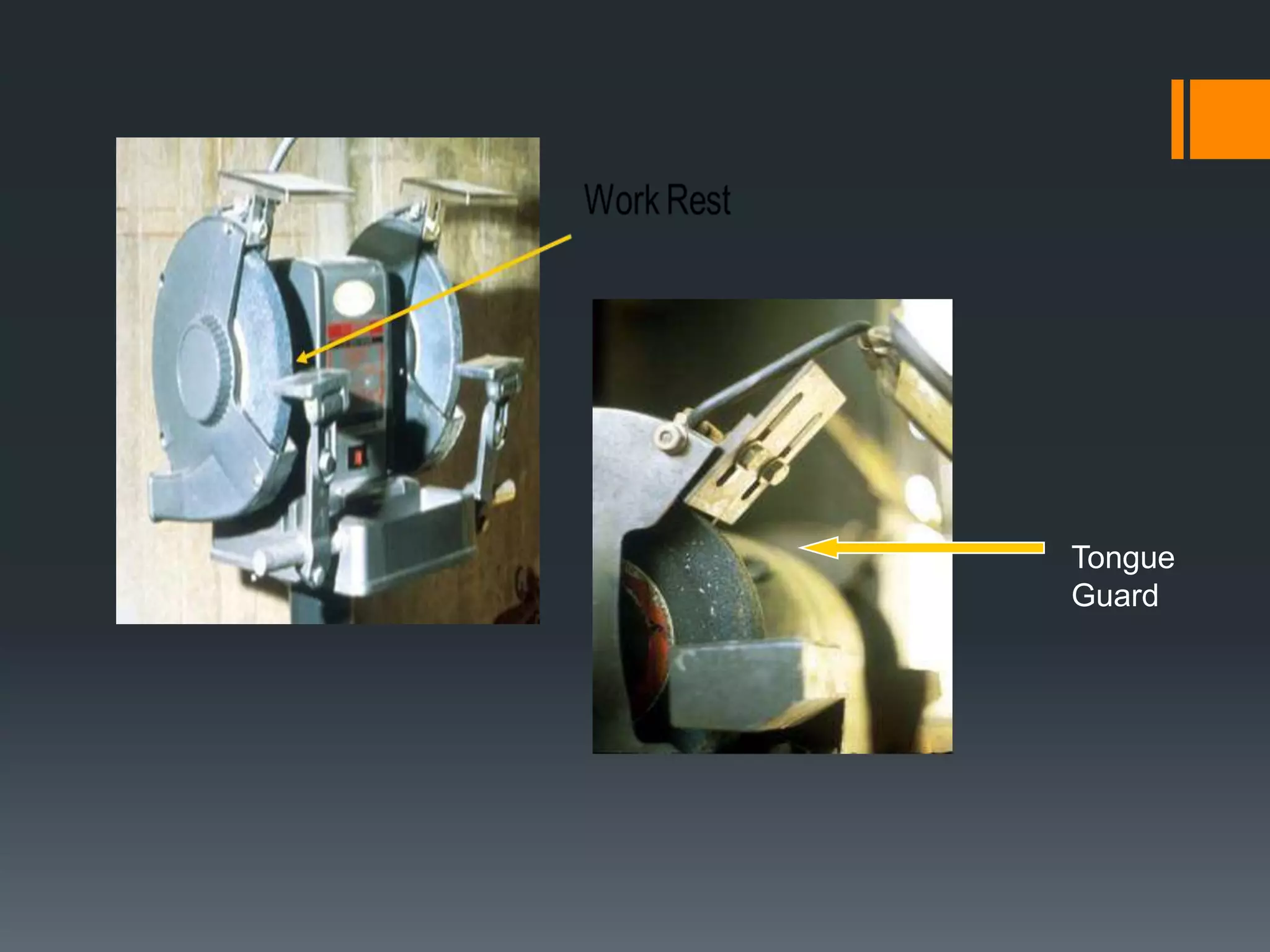
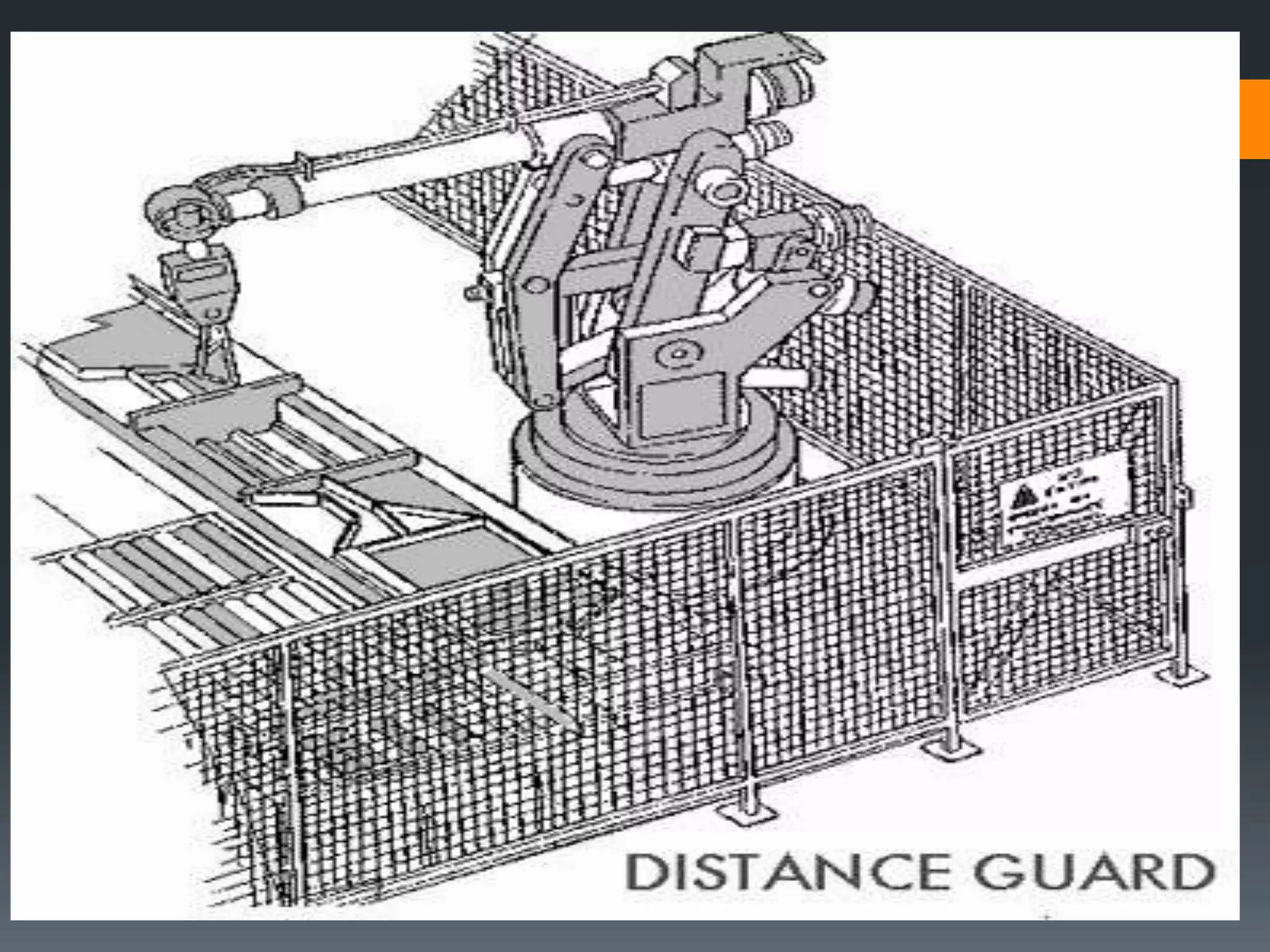
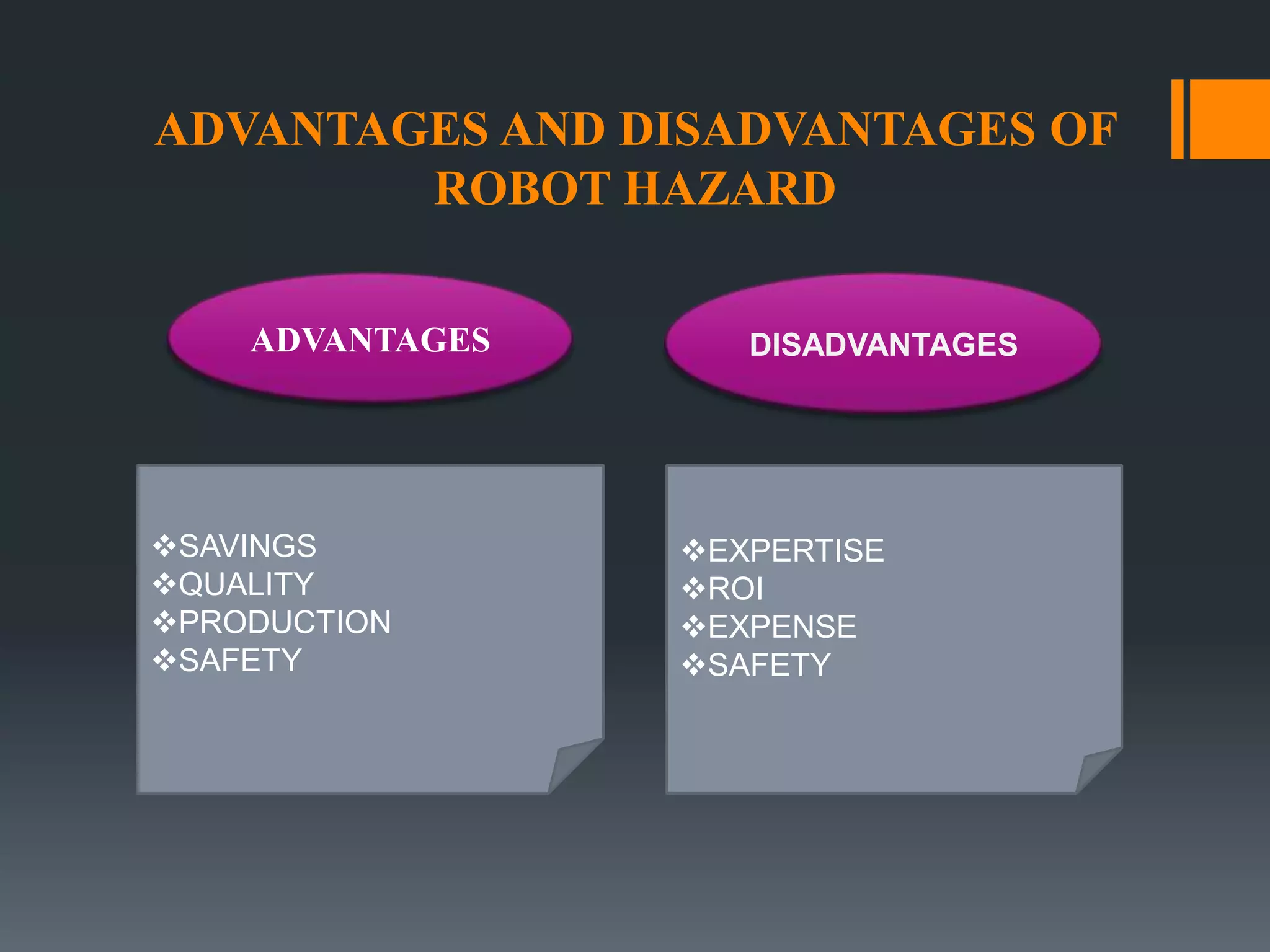
This document discusses robot hazards in the workplace and prevention methods. It describes the abilities and differences between robots and conventional machinery, sources of hazards, and ways to safeguard robots through establishing a physical work envelope and using sensing devices to automatically shut down robots if persons enter the envelope. The advantages of robots include improved quality, production, and safety, while disadvantages are the initial expense and ensuring proper expertise is developed for operation.