Embed presentation
Download to read offline

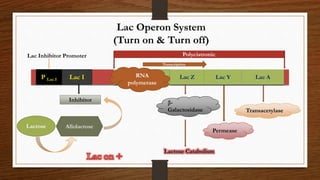

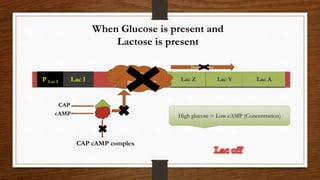


The document describes the lac operon system in E. coli for lactose catabolism. It explains that when glucose is absent and lactose is present, allolactose acts as an inducer by binding to the lac repressor and allowing RNA polymerase to transcribe the lac genes encoding β-galactosidase and other proteins for lactose metabolism. However, when glucose is present, even if lactose is also present, transcription is repressed due to low cAMP levels inhibiting the CAP-cAMP complex from activating transcription.





