Embed presentation
Download to read offline


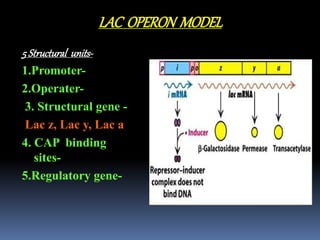
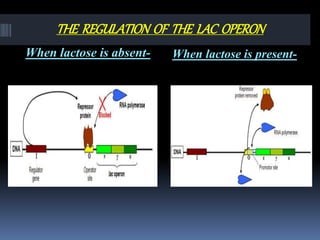
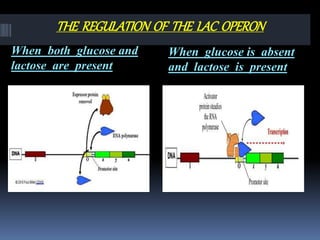

The document describes the lac operon system, which was the first operon described in 1961 and controls the catabolism of lactose in prokaryotes. The lac operon has 5 structural units - a promoter, operator, three structural genes (LacZ, LacY, LacA) that encode enzymes for lactose breakdown, CAP binding sites, and a regulatory gene. When lactose is absent, a repressor protein binds to the operator, preventing transcription of the structural genes. When lactose is present, it binds to the repressor and causes a conformational change that releases it from the operator, allowing transcription and the breakdown of lactose.





