Embed presentation
Download to read offline



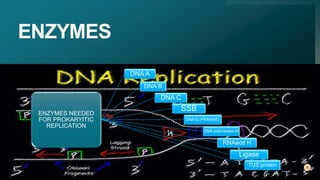

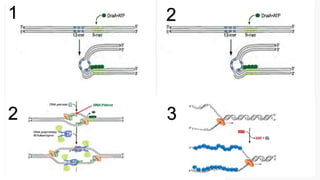
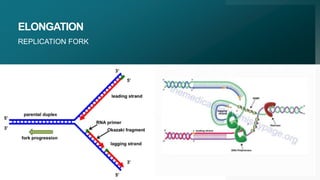
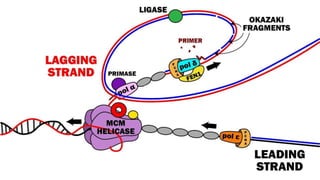
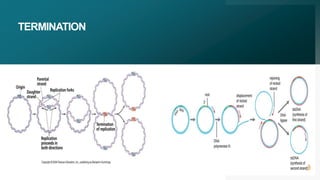
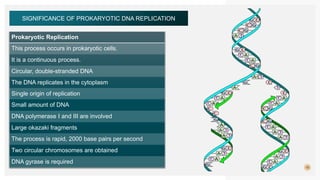

This document summarizes prokaryotic DNA replication. It describes prokaryotic replication as the process by which a circular, double-stranded DNA molecule in prokaryotic cells is copied to produce two identical molecules. The key steps are initiation at a single origin of replication, elongation of DNA strands by DNA polymerases, and termination resulting in two circular chromosomes. The replication occurs rapidly in the cytoplasm and requires enzymes including DNA polymerases I and III.










