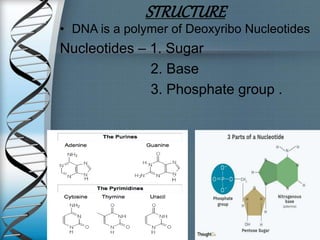
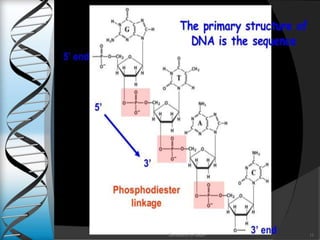
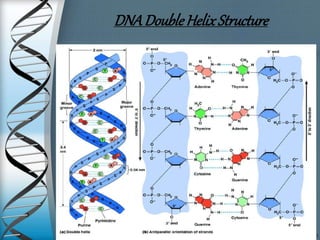
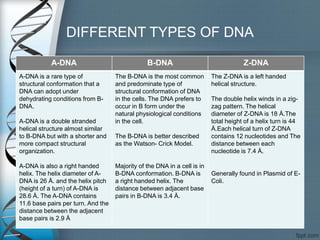
This document discusses the structure and types of DNA. It begins by introducing DNA and its components. DNA is made up of deoxyribonucleotides and carries genetic information found in chromosomes, chloroplasts, mitochondria and nuclei. The structure of DNA is a double helix formed from nucleotides containing a sugar, phosphate group and one of four nitrogenous bases. There are three main types of DNA structures: A-DNA, B-DNA, and Z-DNA. B-DNA is the most common form found in cells under normal physiological conditions. It is a right-handed double helix with 10.5 base pairs per turn and a diameter of 20 angstroms. A-DNA and Z-DNA are less common structures