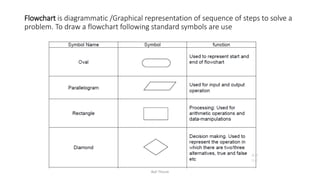
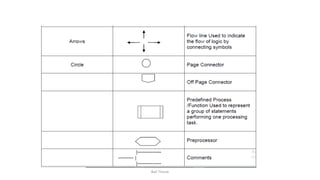
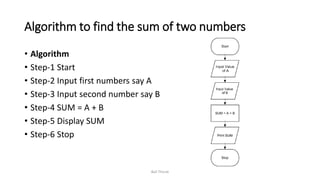
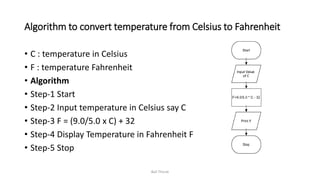
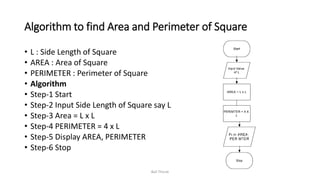
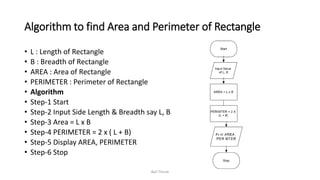
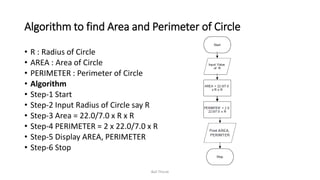
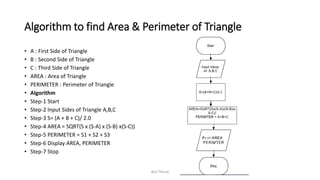
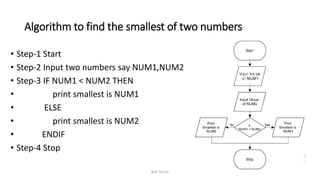
The document discusses algorithms and flowcharts. It defines an algorithm as a sequence of steps to solve a problem and lists their characteristics as having inputs, outputs, definiteness, and finiteness. Examples of algorithms are provided to find the sum of two numbers, convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit, and calculate the area and perimeter of shapes. Flowcharts are defined as using symbols to represent the sequence of operations to solve a problem. Advantages of both algorithms and flowcharts are given.