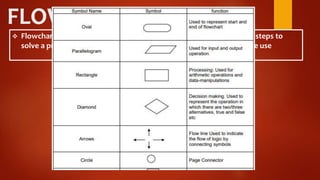
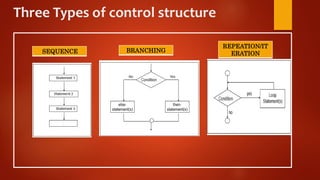
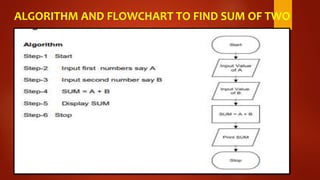
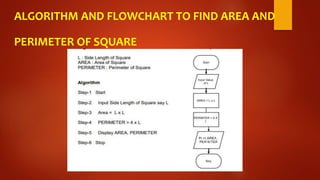
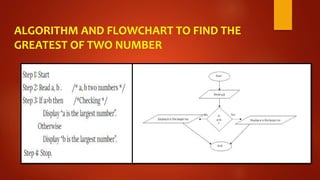
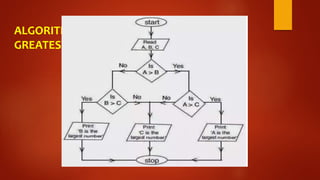
This document discusses algorithms and flowcharts. It defines an algorithm as a step-by-step process to solve a problem and a flowchart as a graphical representation of the steps using standard symbols. The document outlines the characteristics and advantages of algorithms, including being unambiguous, terminating in finite time, and easy to understand. It also discusses the history and advantages of flowcharts, such as being easy to analyze problems, develop programs, and maintain systems. Examples of algorithms and flowcharts are provided to find the sum of two numbers, area and perimeter of a square, and to determine if a number is even or odd.