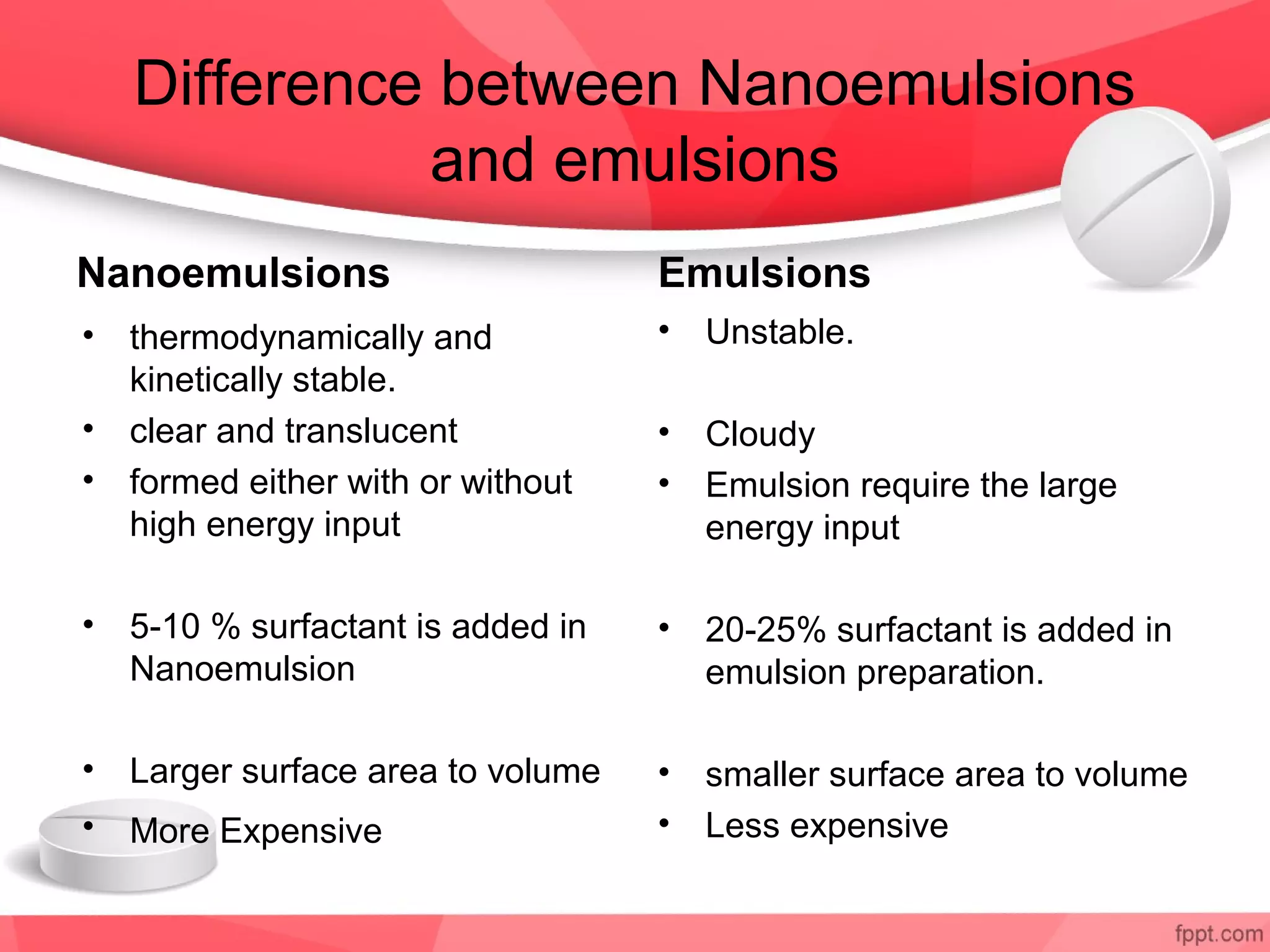
Nanoemulsions are emulsified oil and water systems with droplet sizes between 10-200 nm that are thermodynamically stable and optically clear. They can be produced using high-energy methods like high pressure homogenization or microfluidization or low-energy methods like solvent diffusion or phase inversion. Nanoemulsions have advantages over regular emulsions like improved stability, higher drug loading, and enhanced permeation and absorption of drugs. They have a variety of applications including cosmetics, antimicrobial products, targeted drug delivery, and oral or transdermal delivery of poorly soluble drugs.