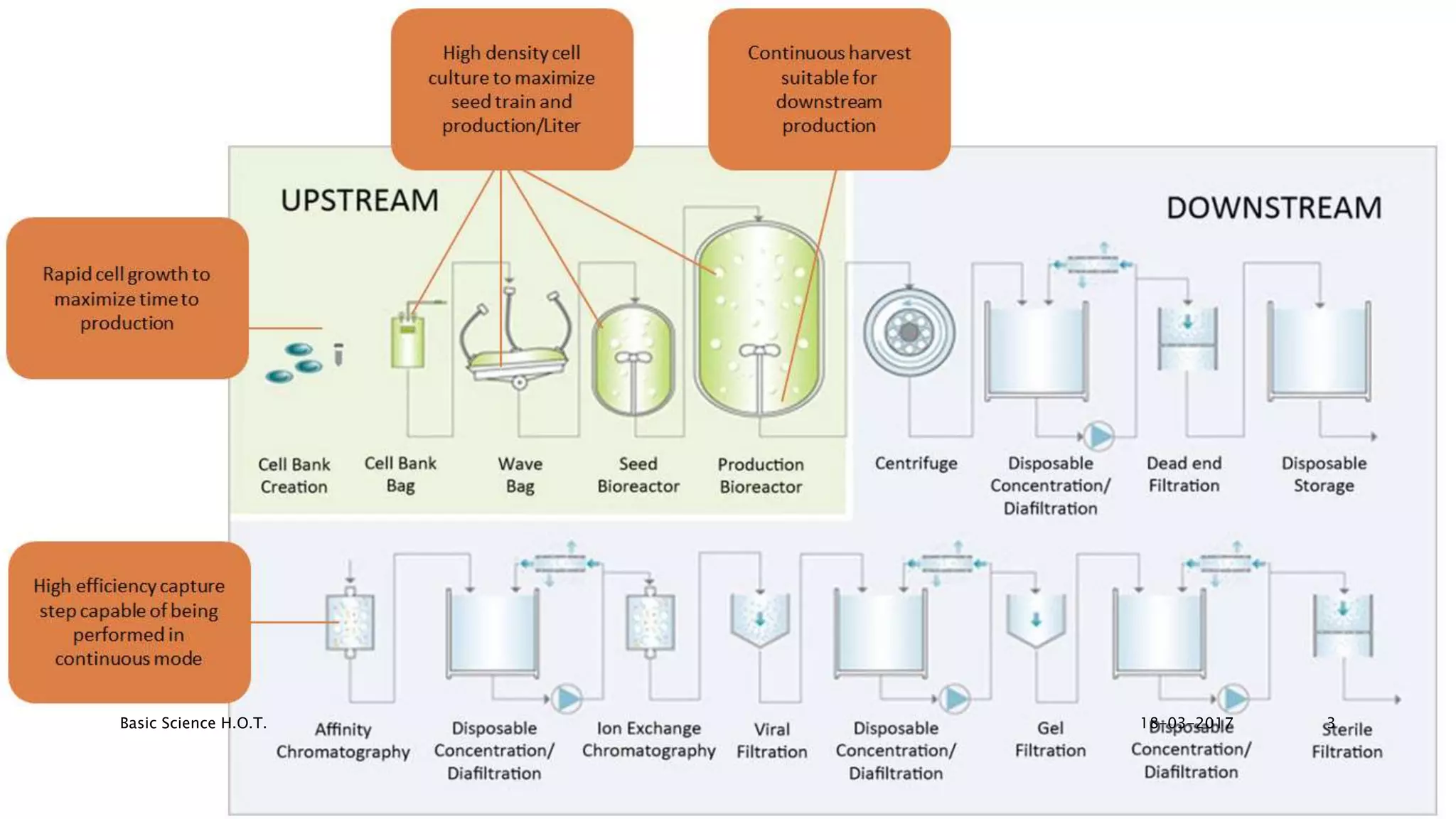
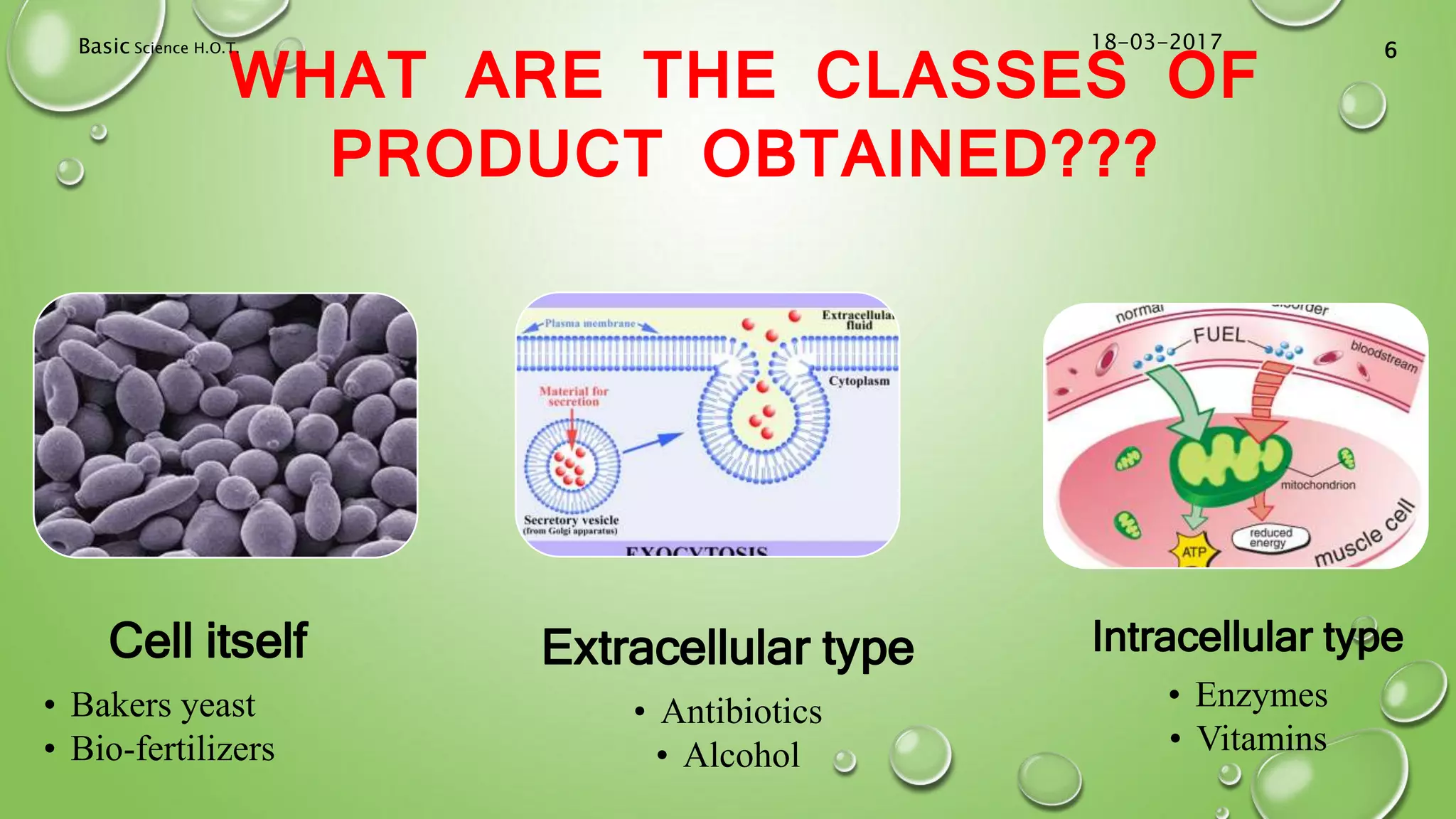
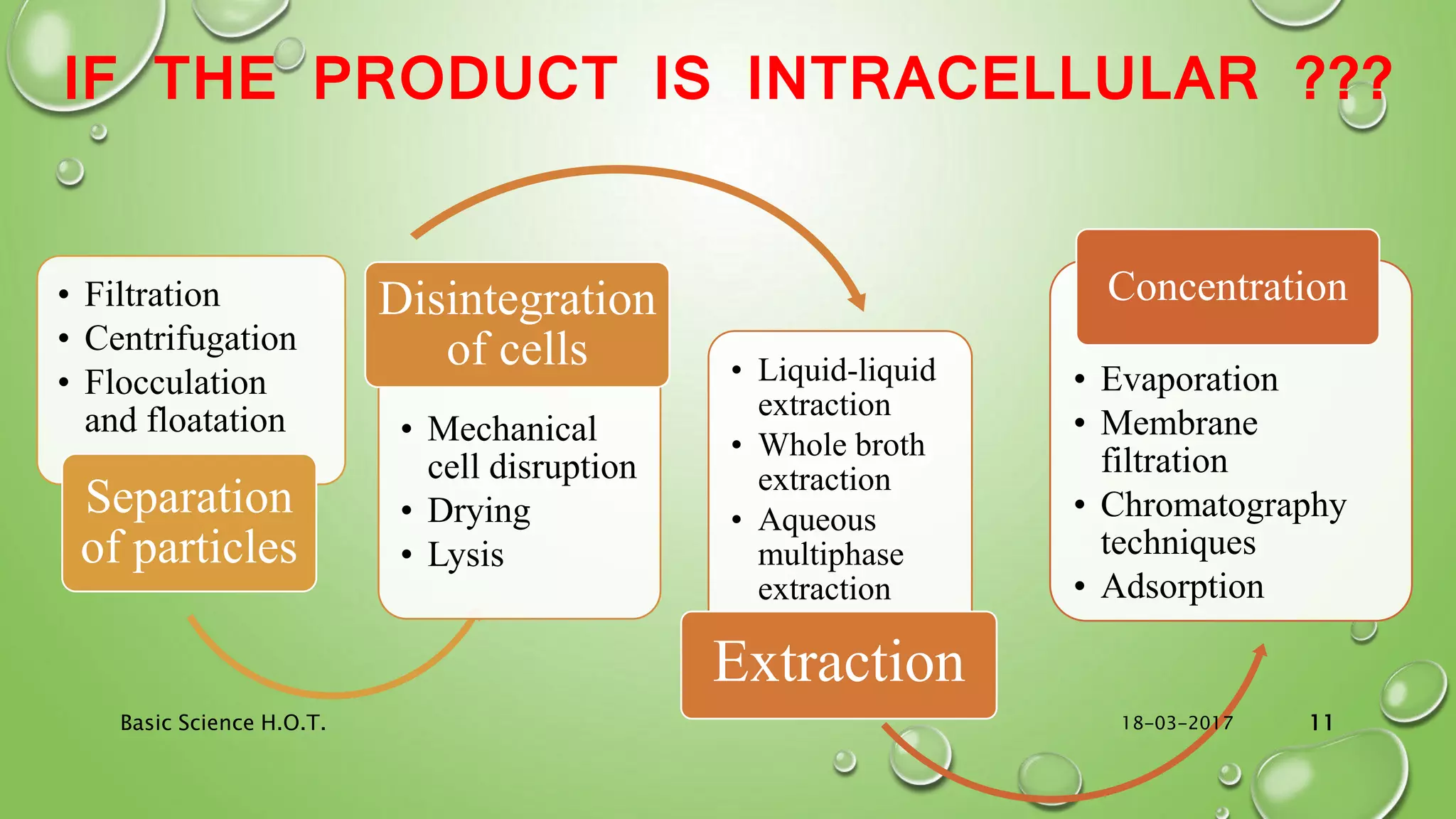
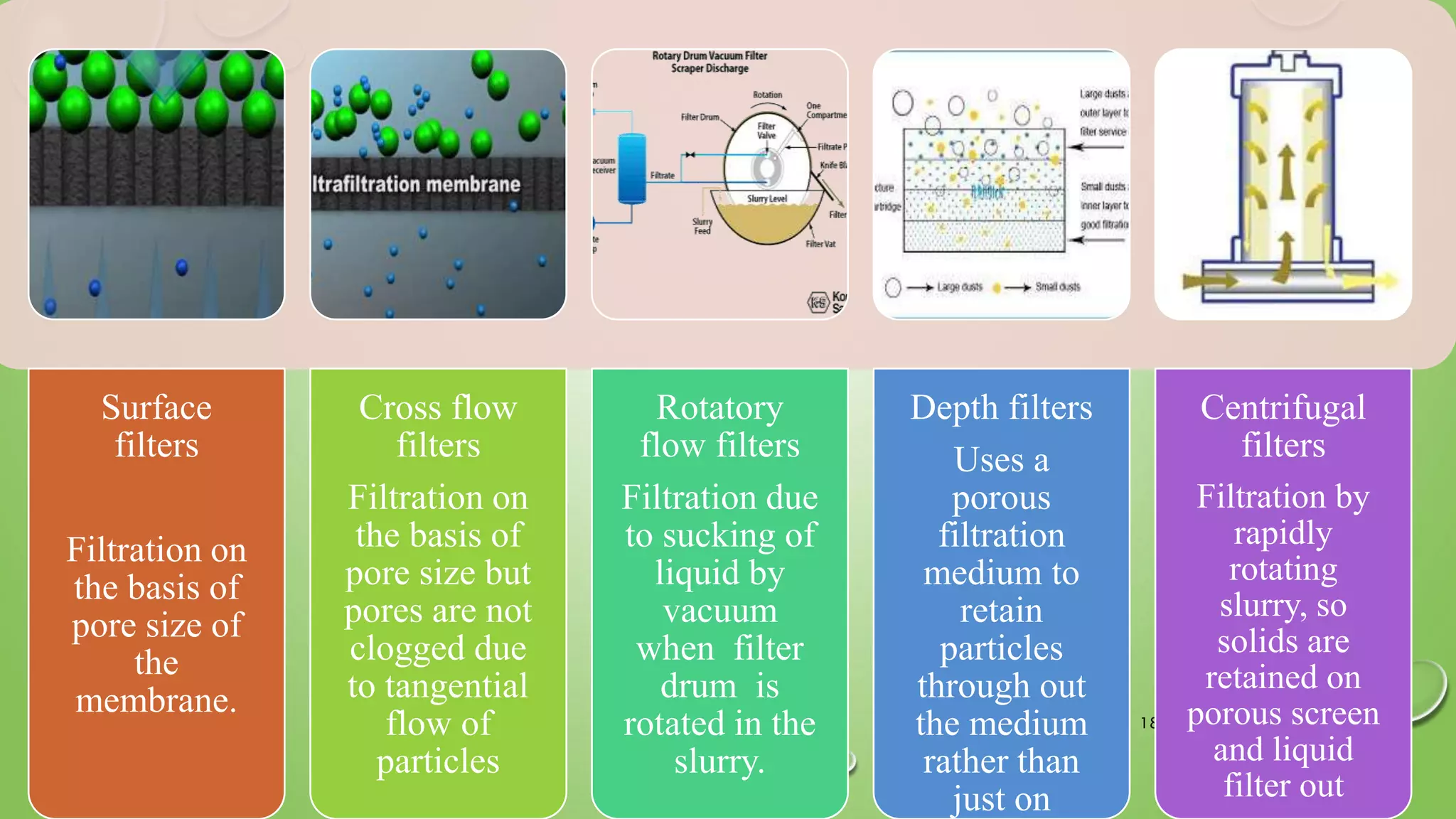
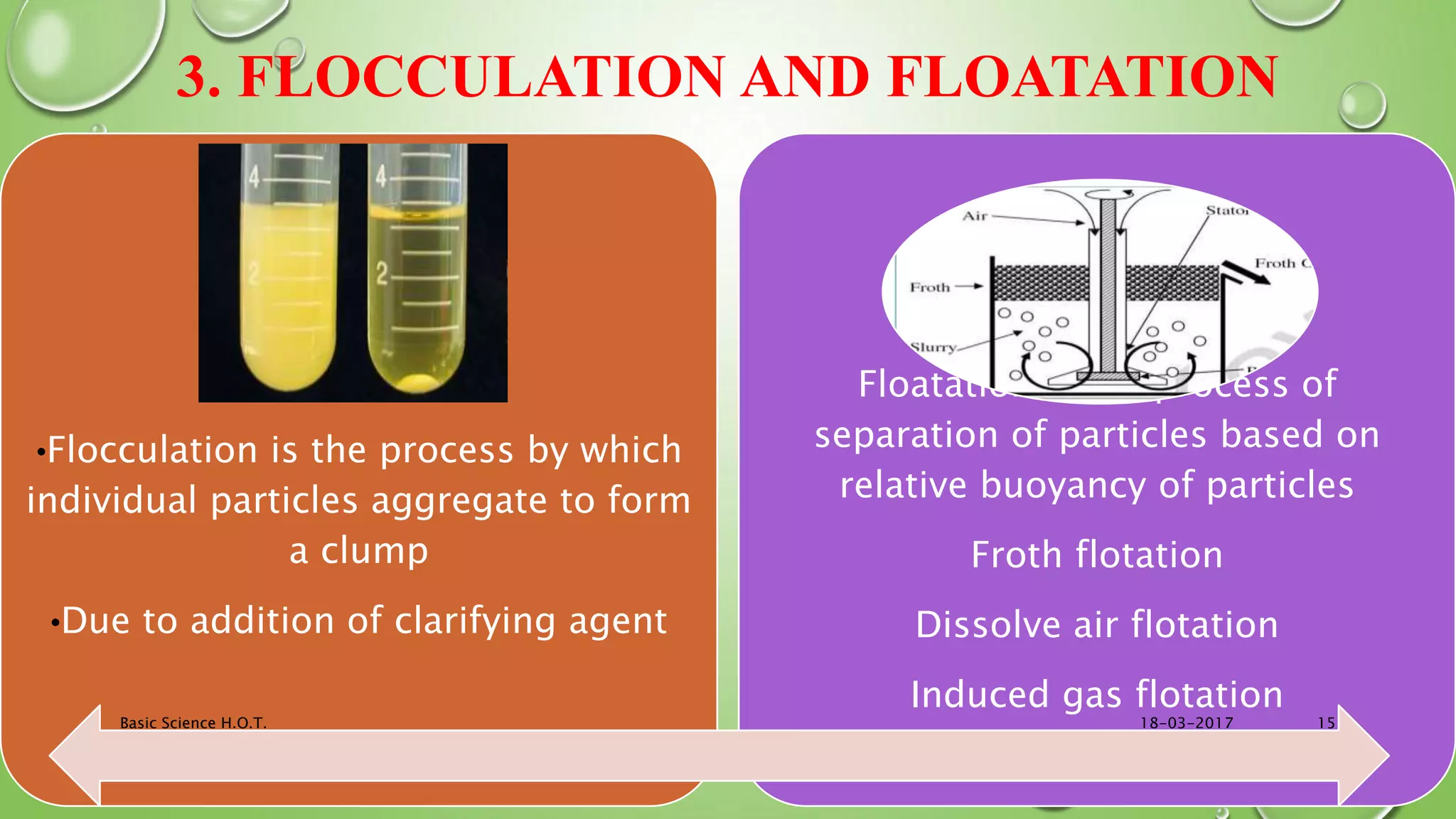
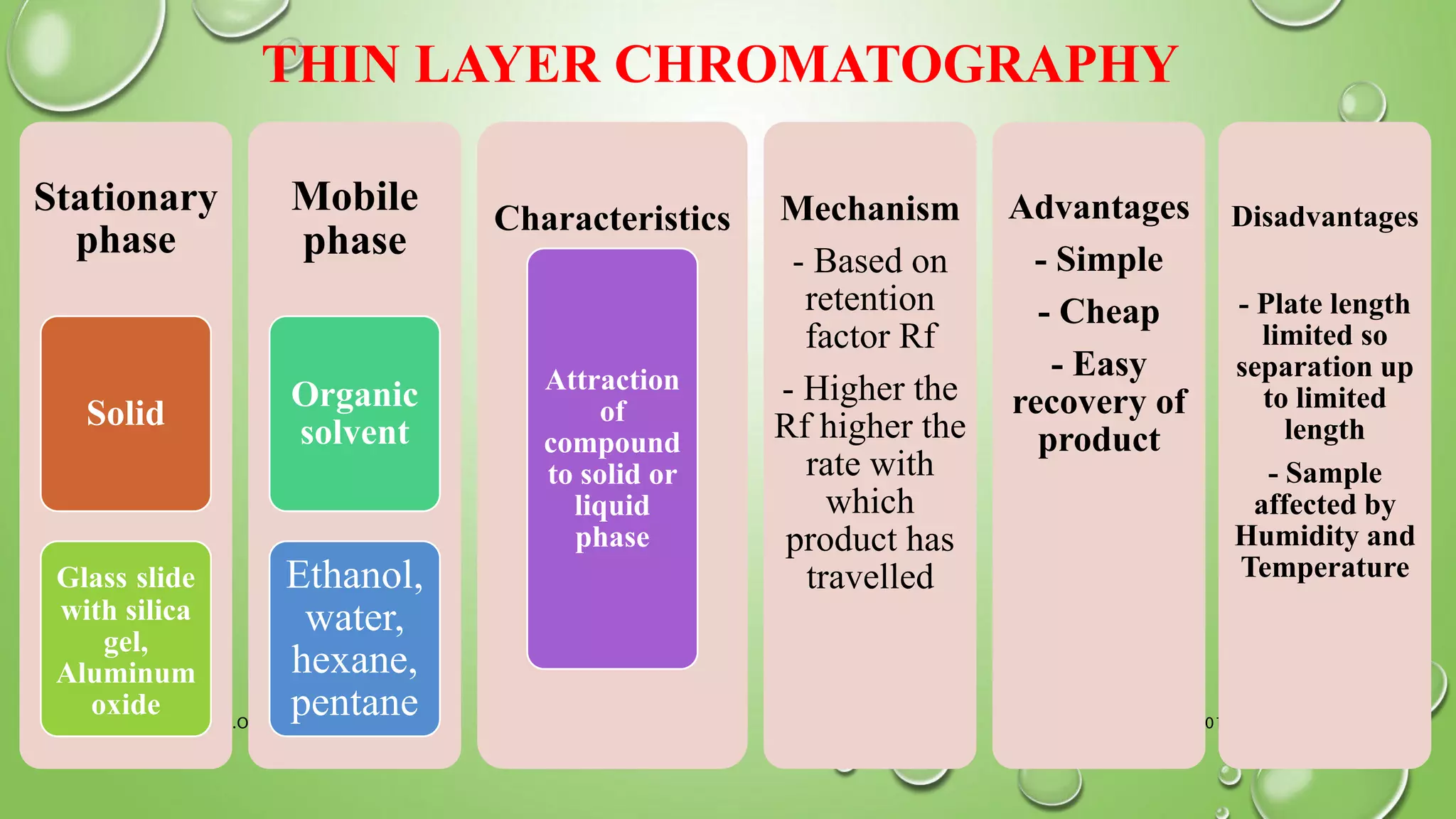
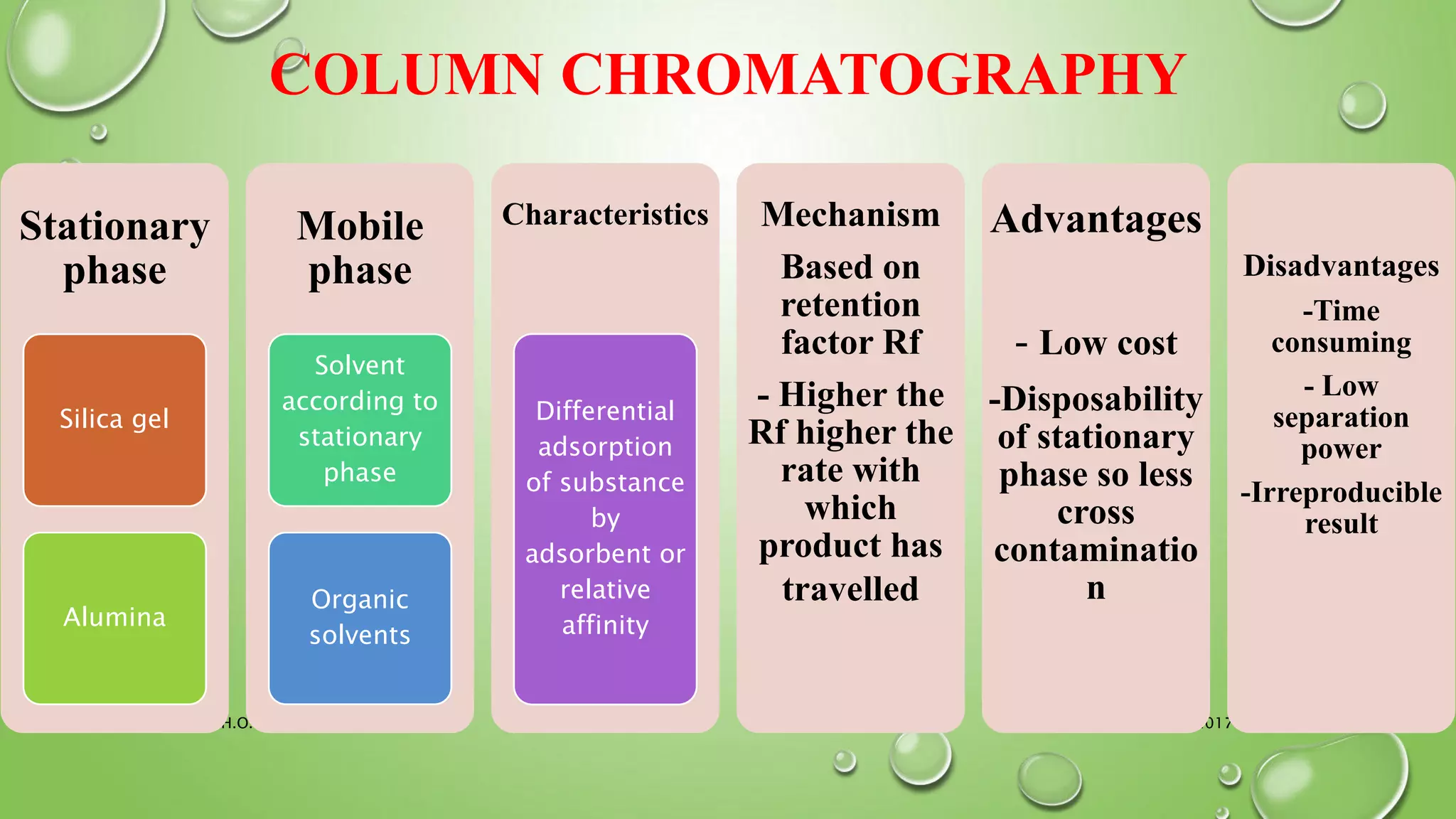
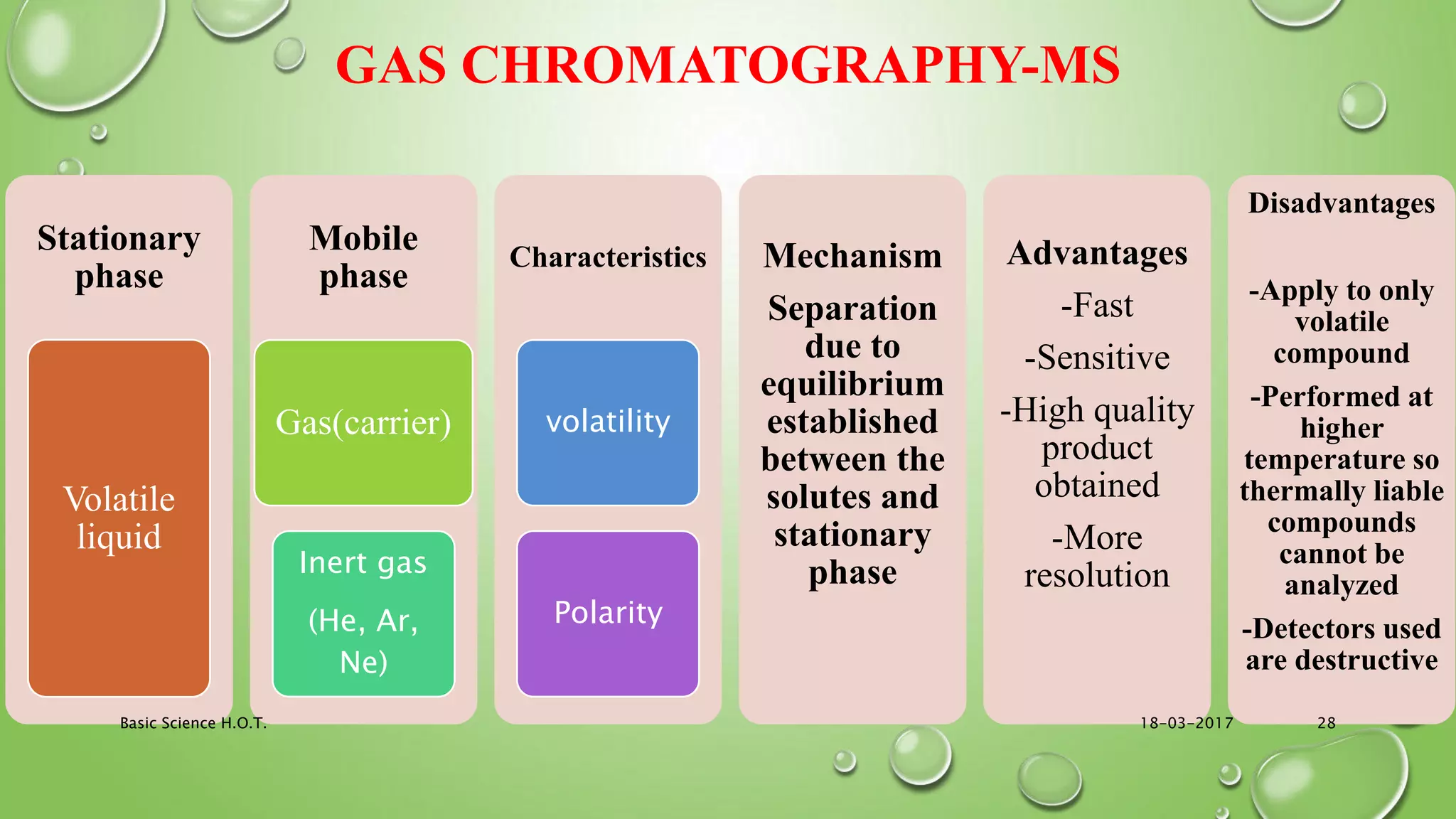
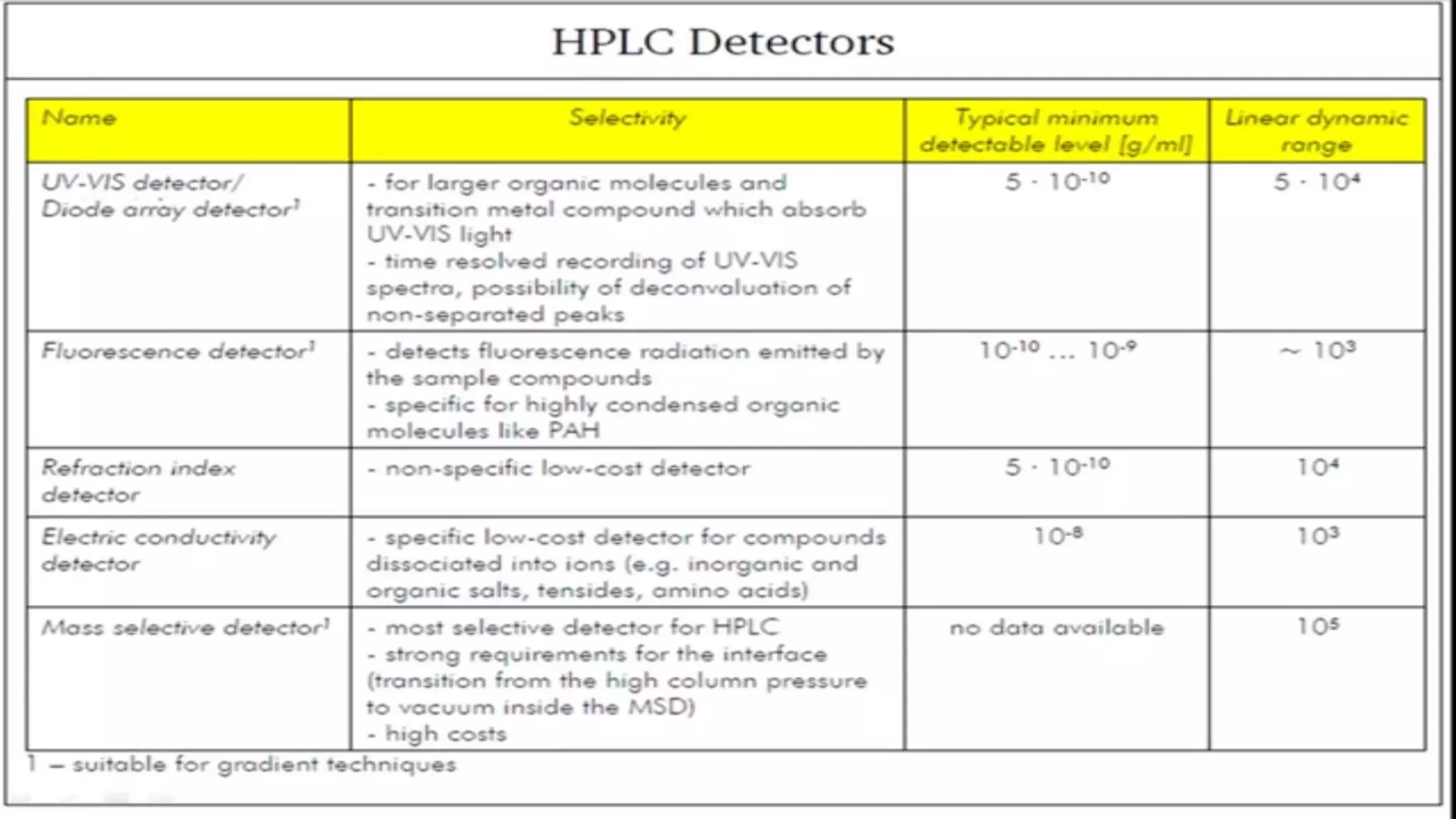
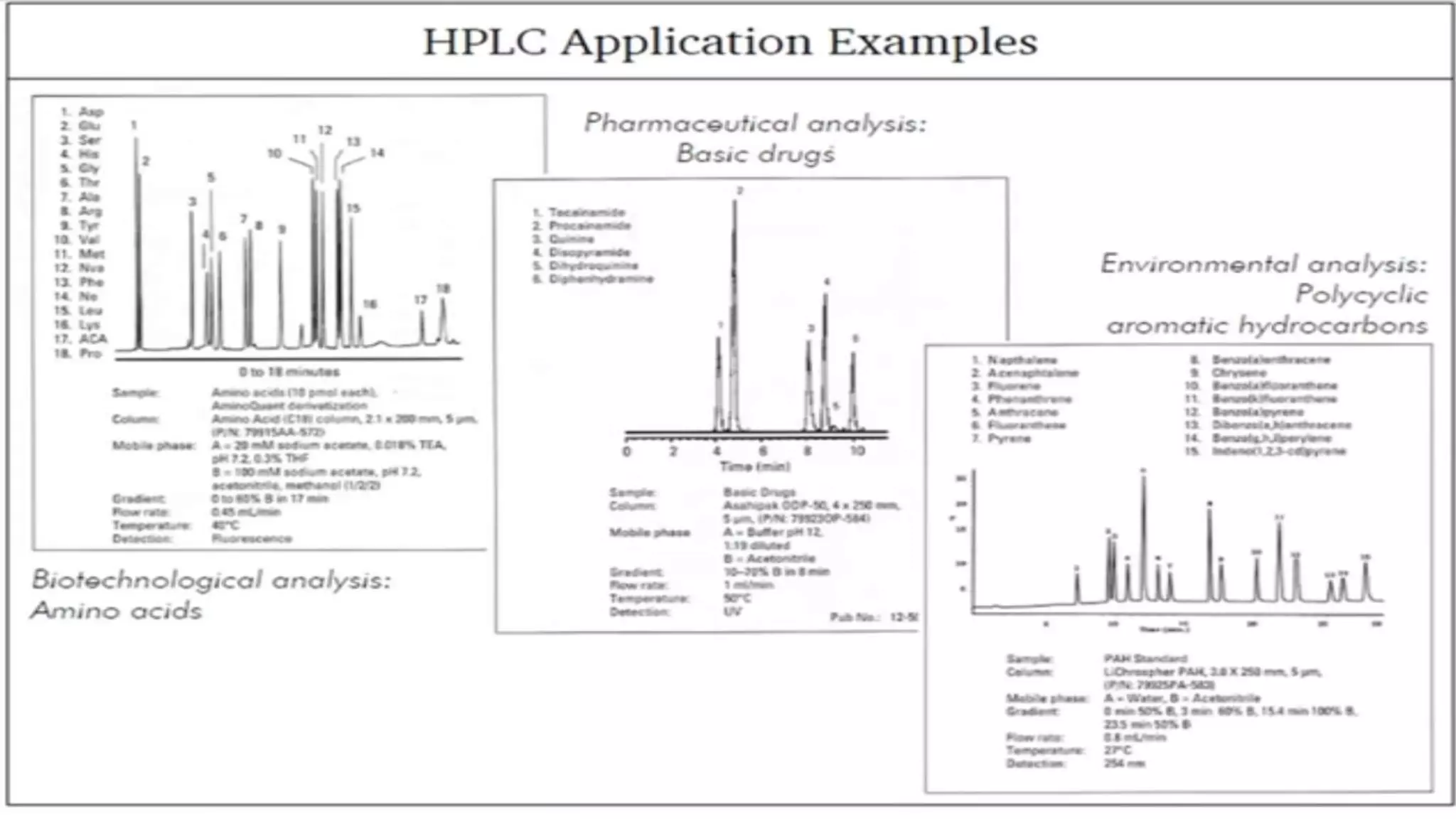
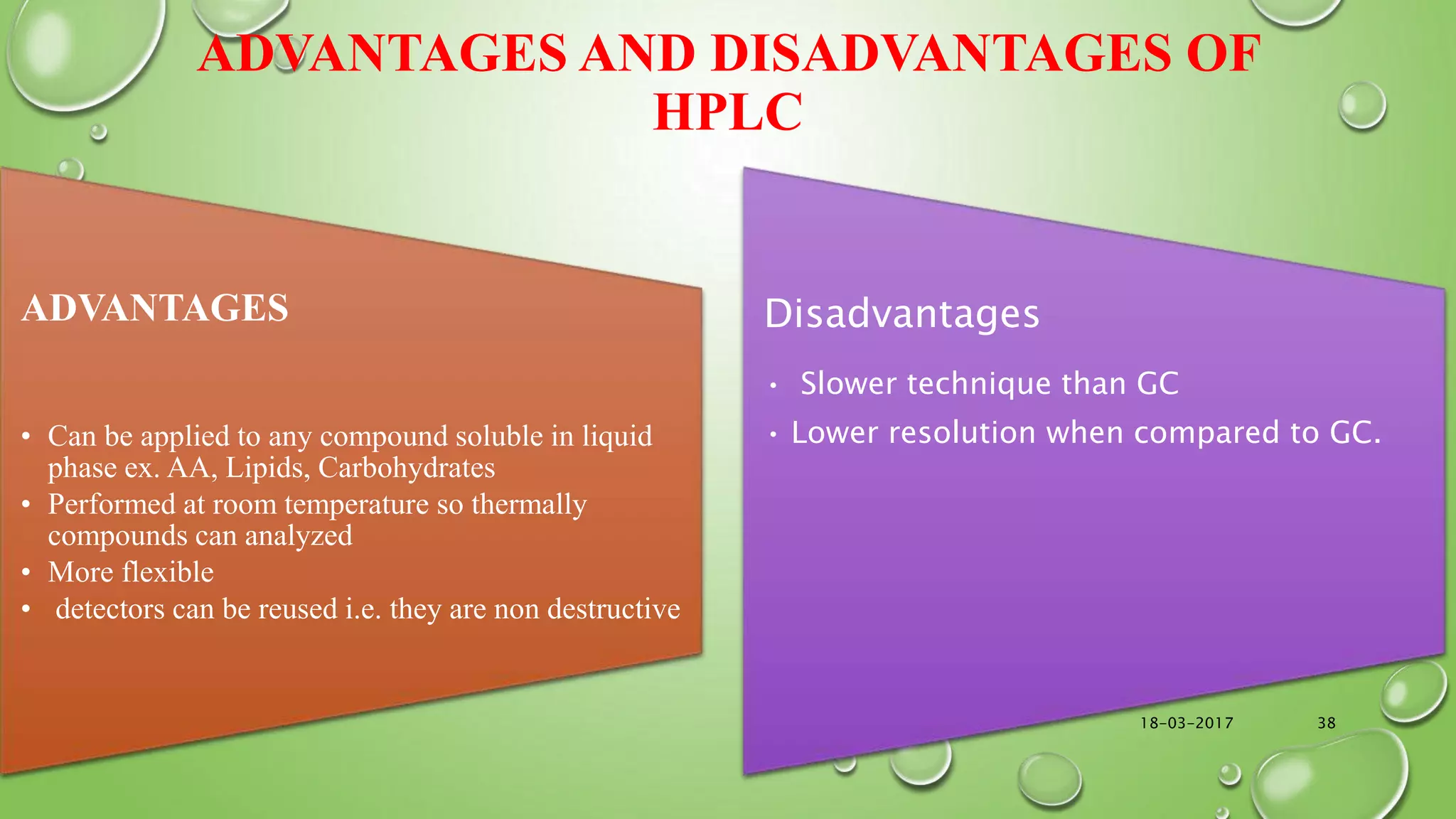
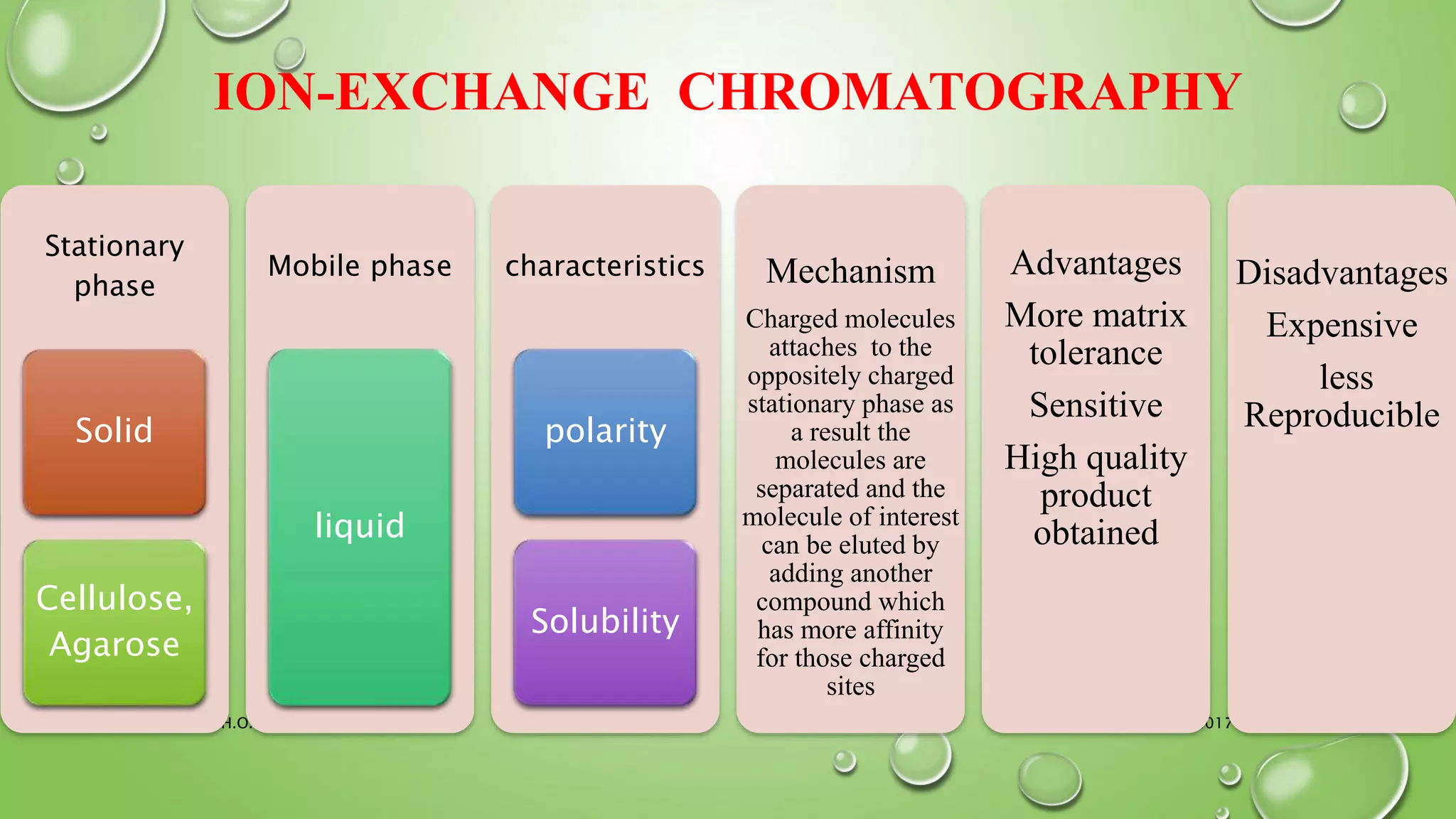
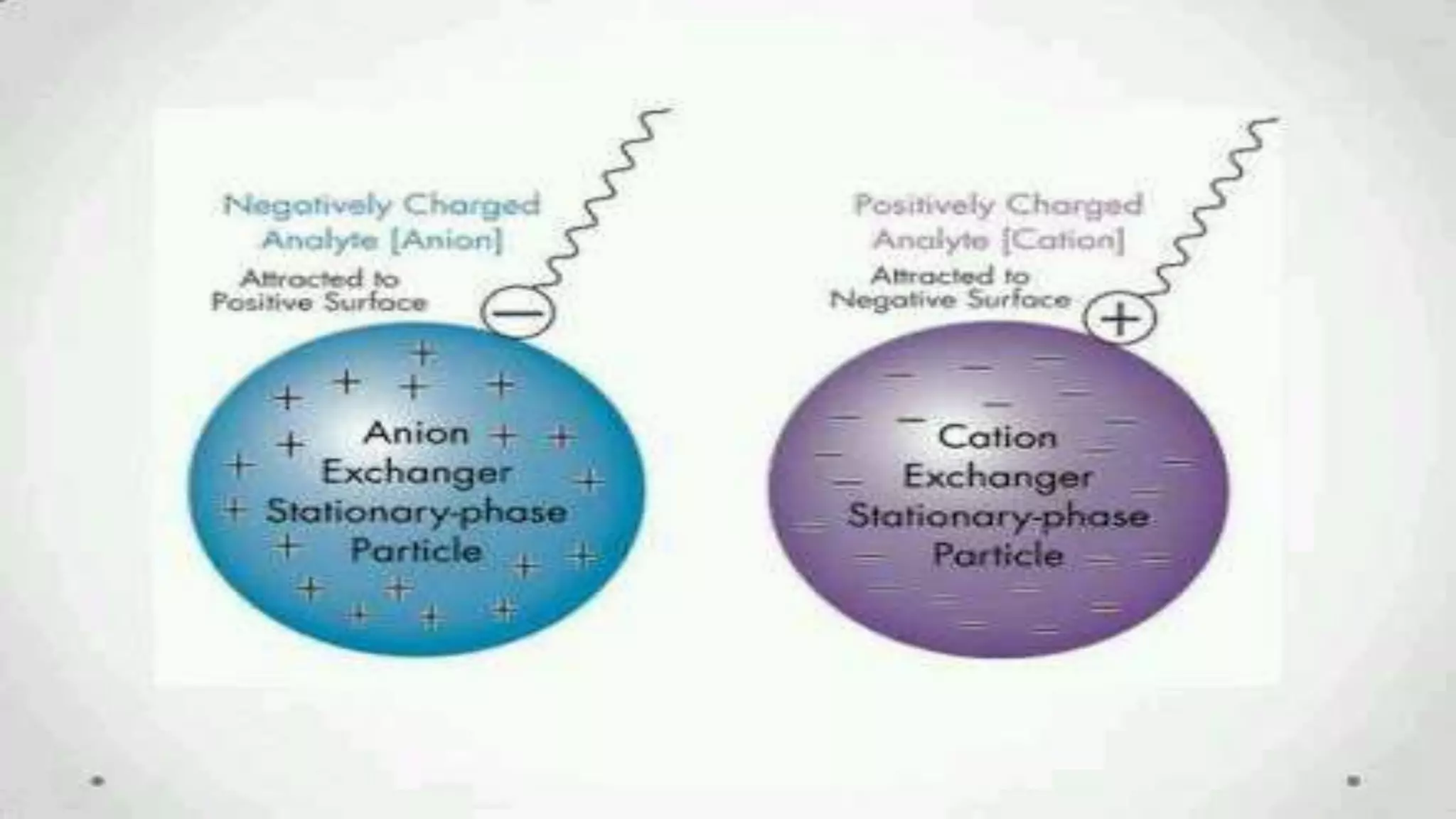
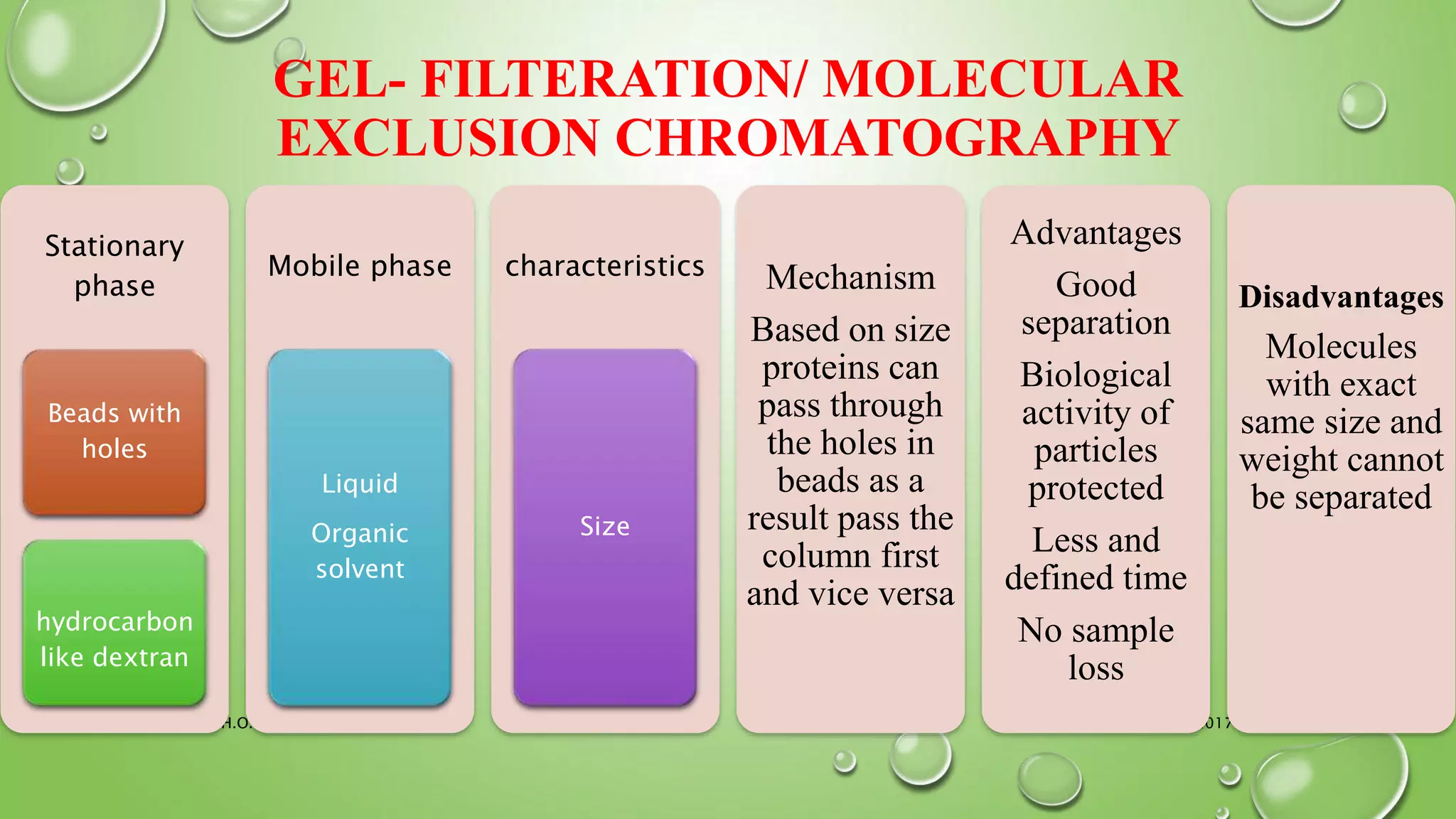
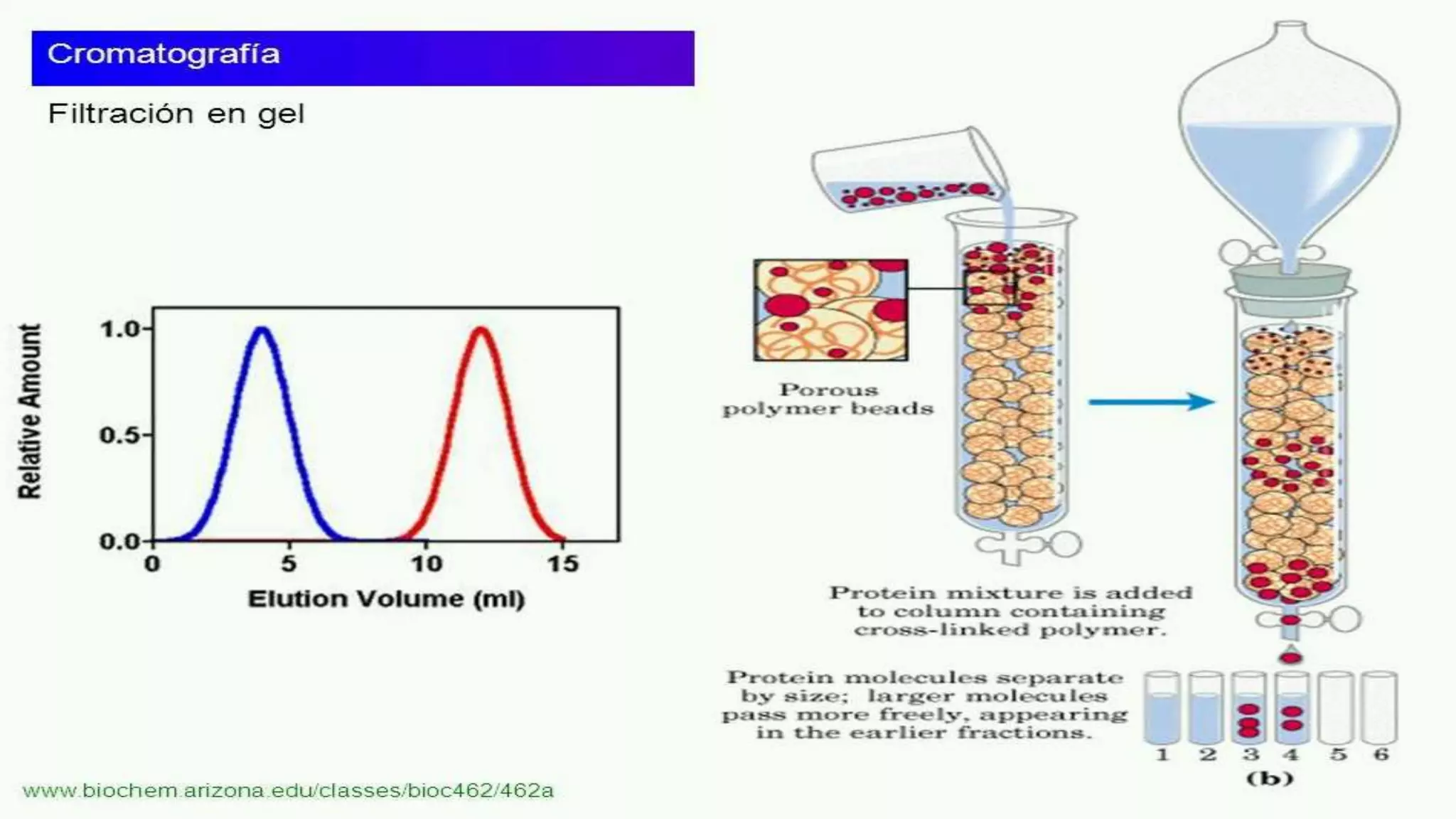
The document provides an in-depth overview of downstream processing processes used for the recovery and purification of biosynthetic products, particularly focusing on methods such as filtration, centrifugation, and chromatography. It elaborates on techniques for separating various types of products including intracellular, extracellular, and the cell itself, as well as methodologies for recovery of itaconic acid, highlighting its relevance in producing biopolymers. The document emphasizes challenges in improving recovery and purification methods to reduce production costs, detailing various physical and chemical properties of itaconic acid and different recovery techniques like crystallization, liquid-liquid extraction, and membrane separation.