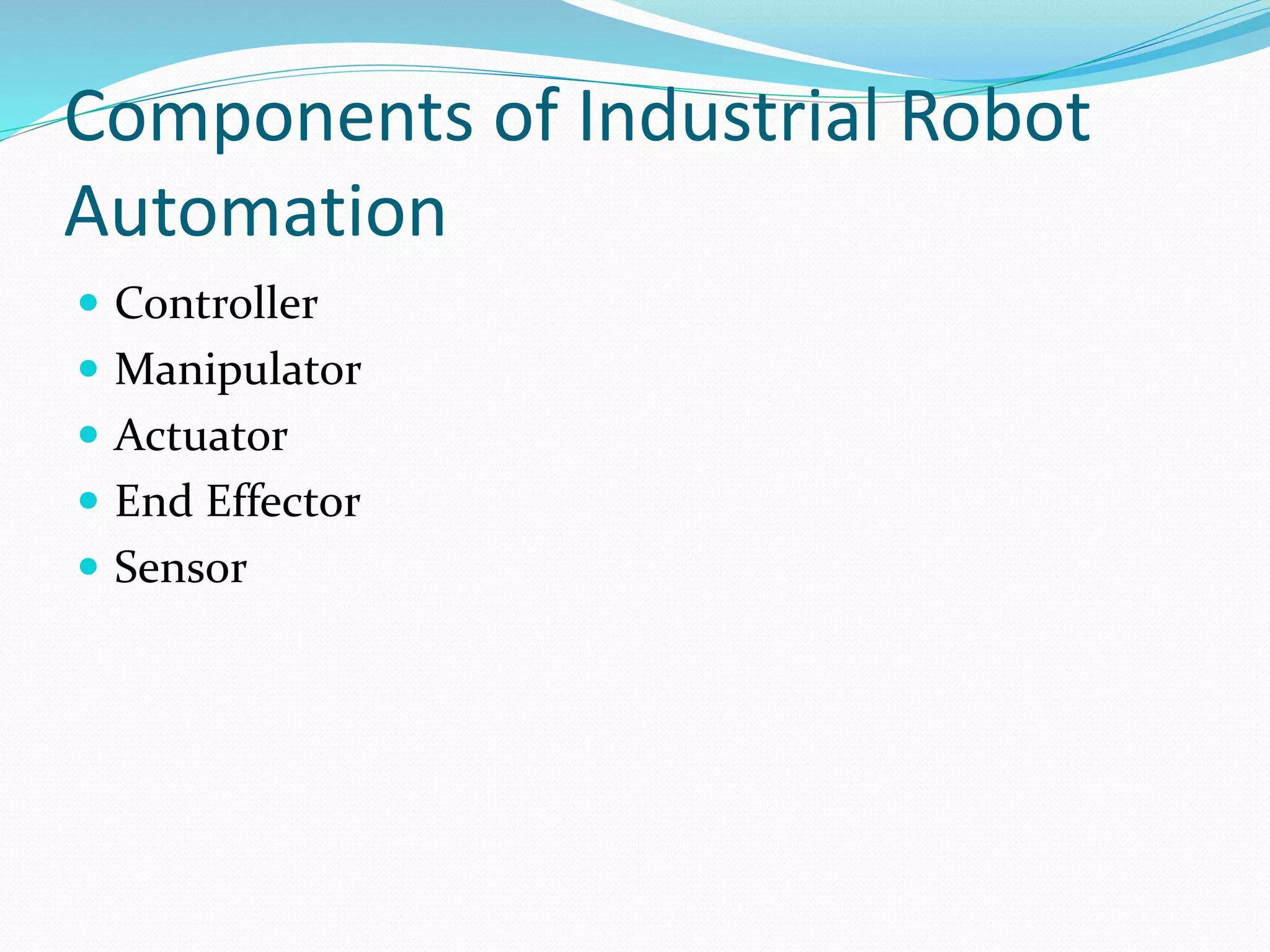
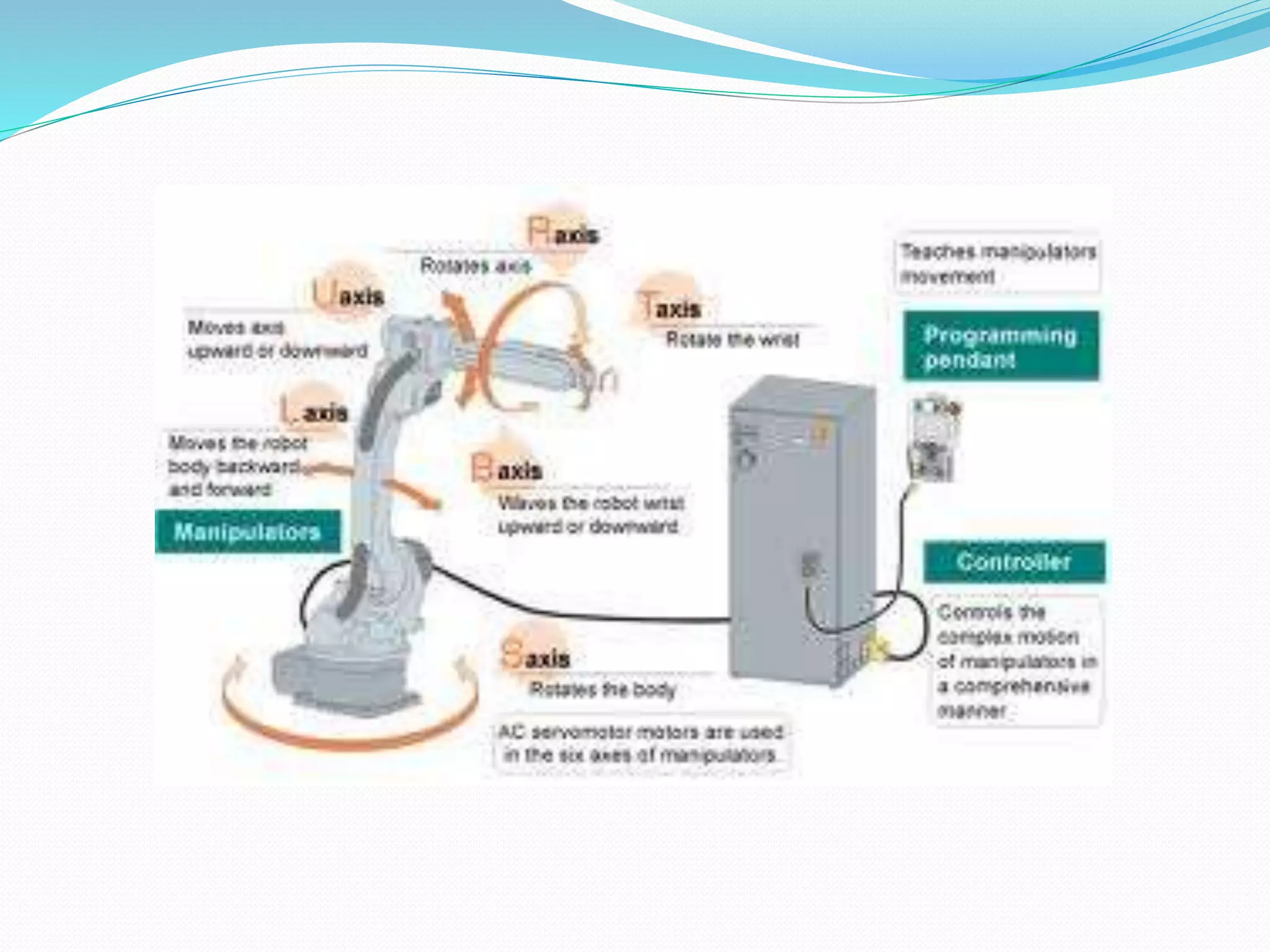
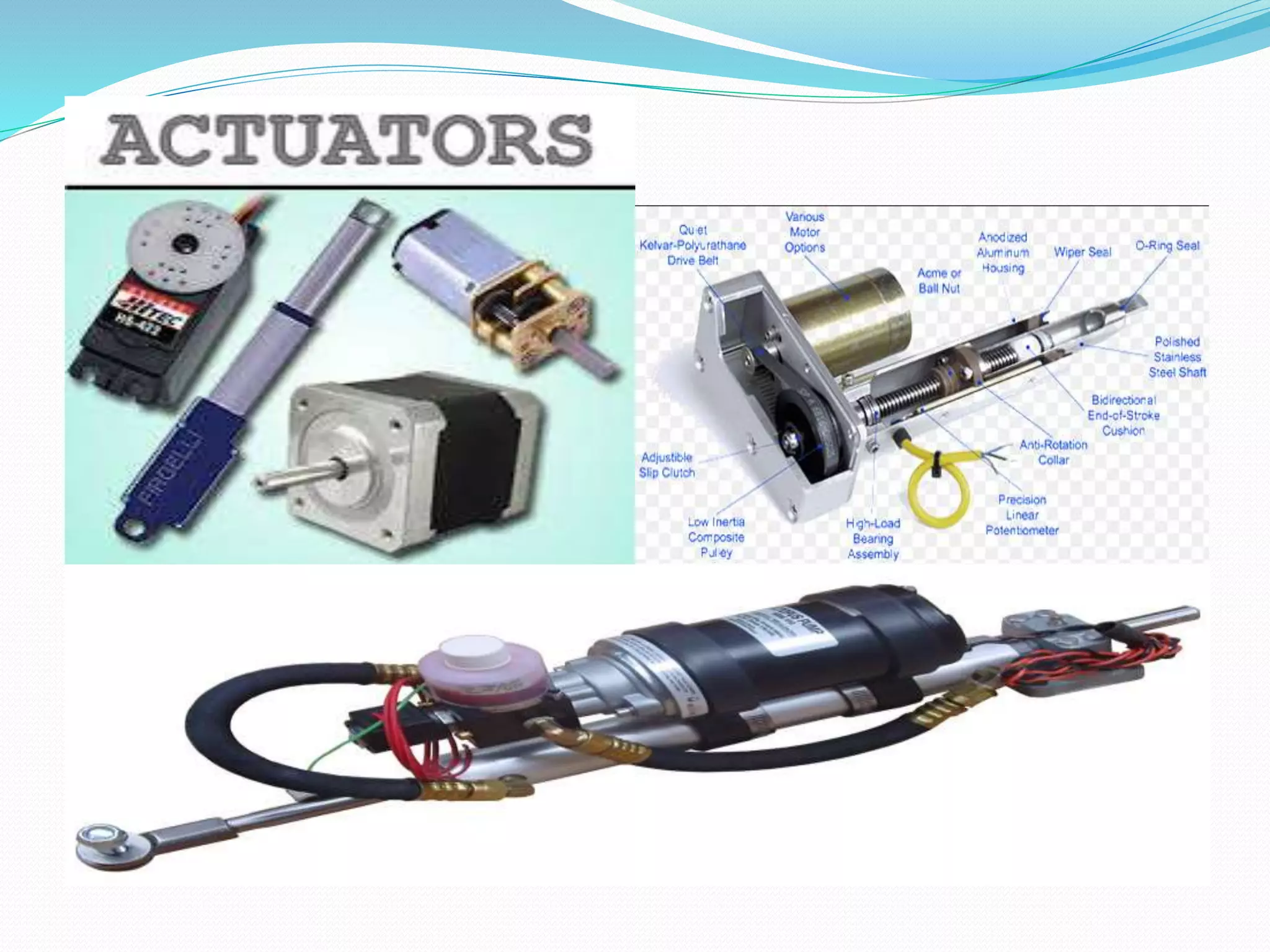
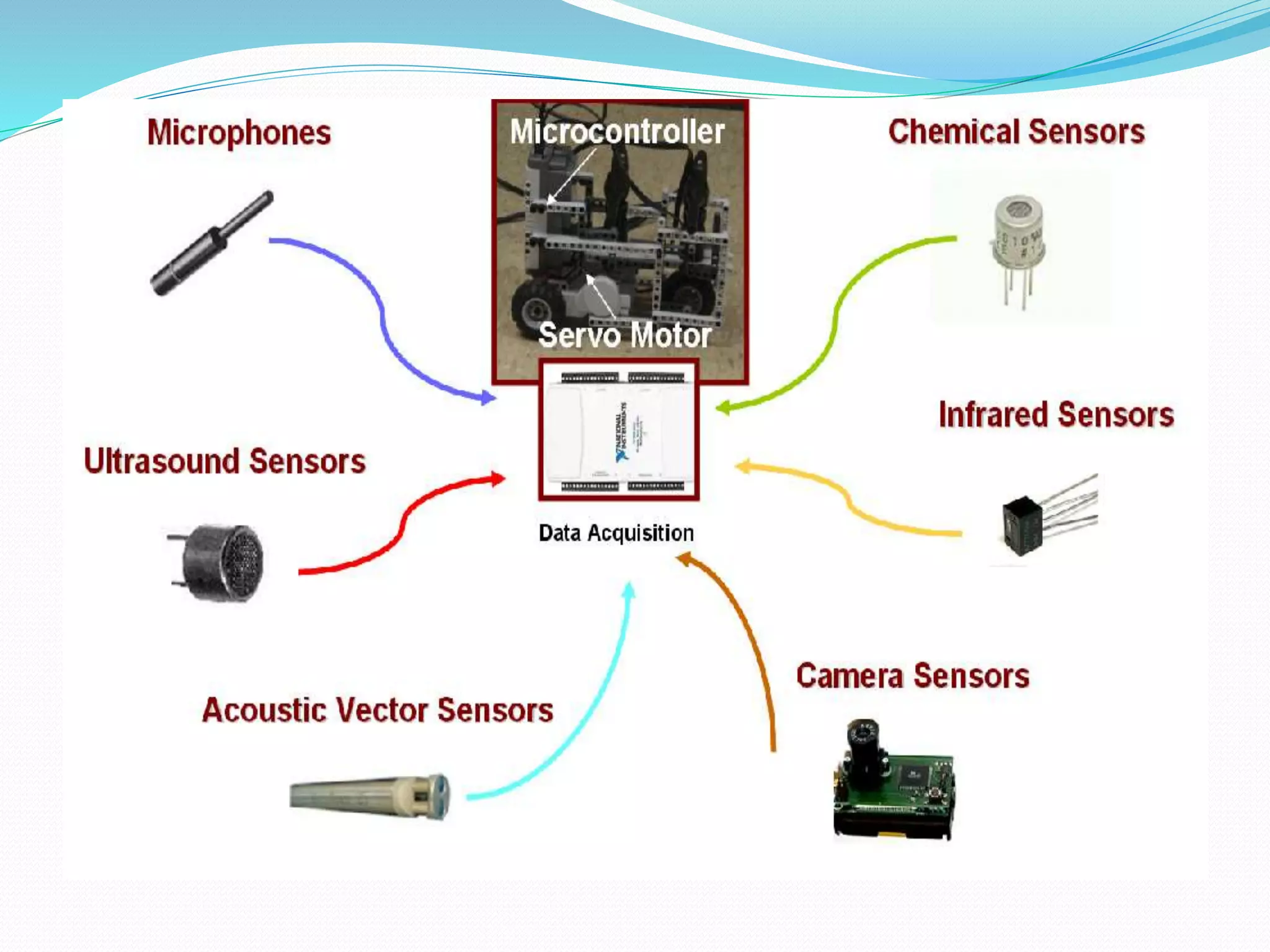
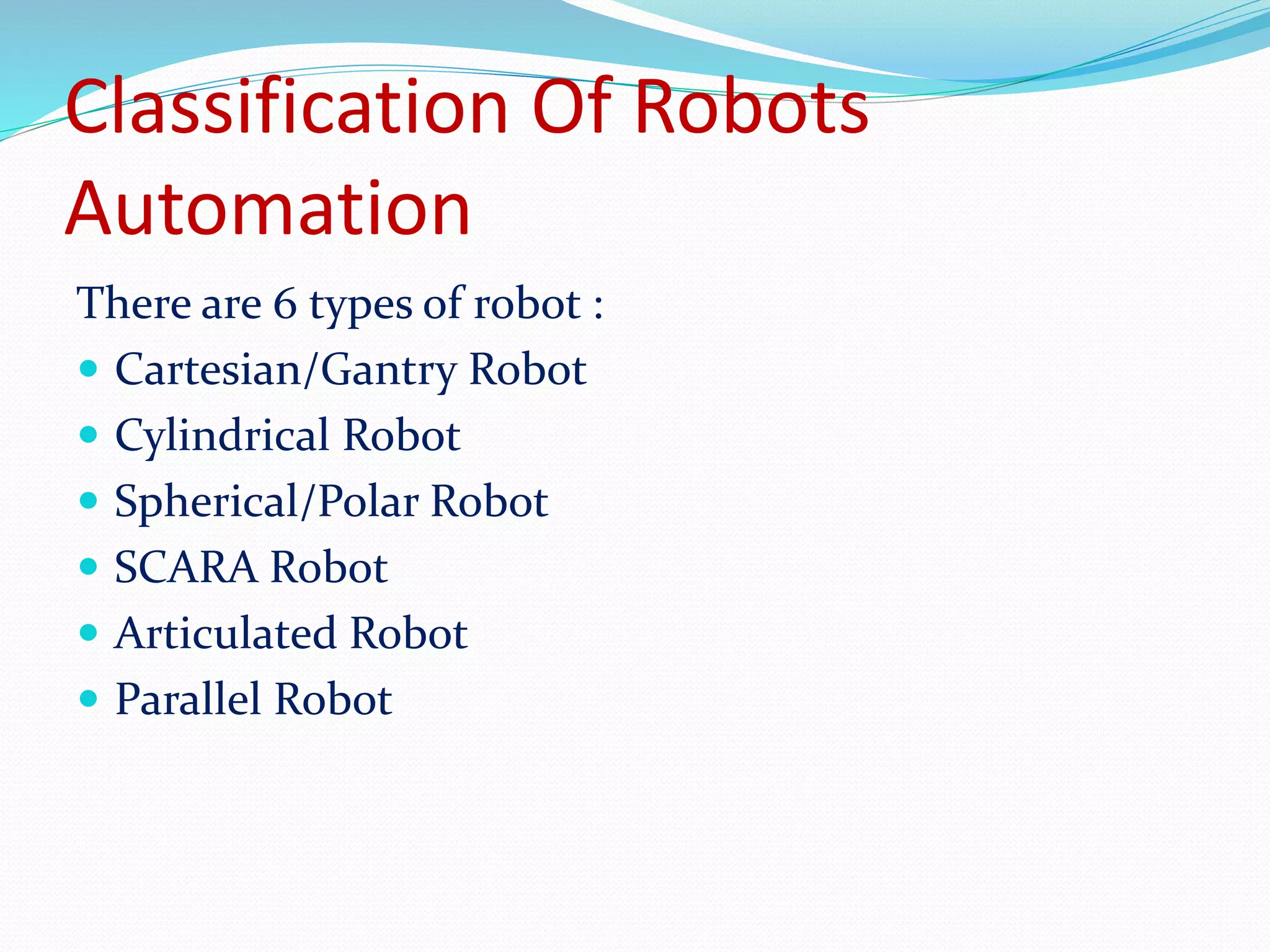
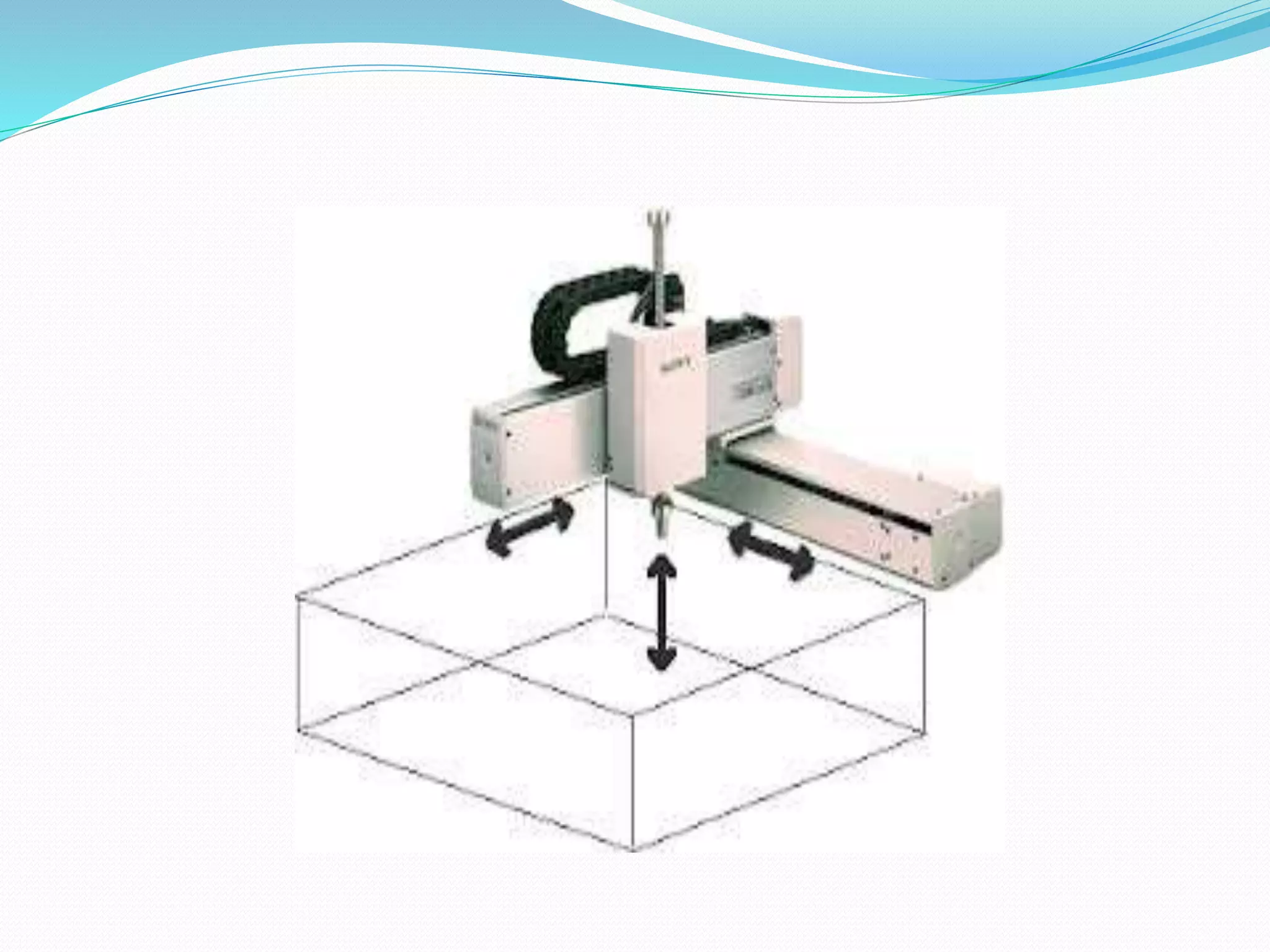
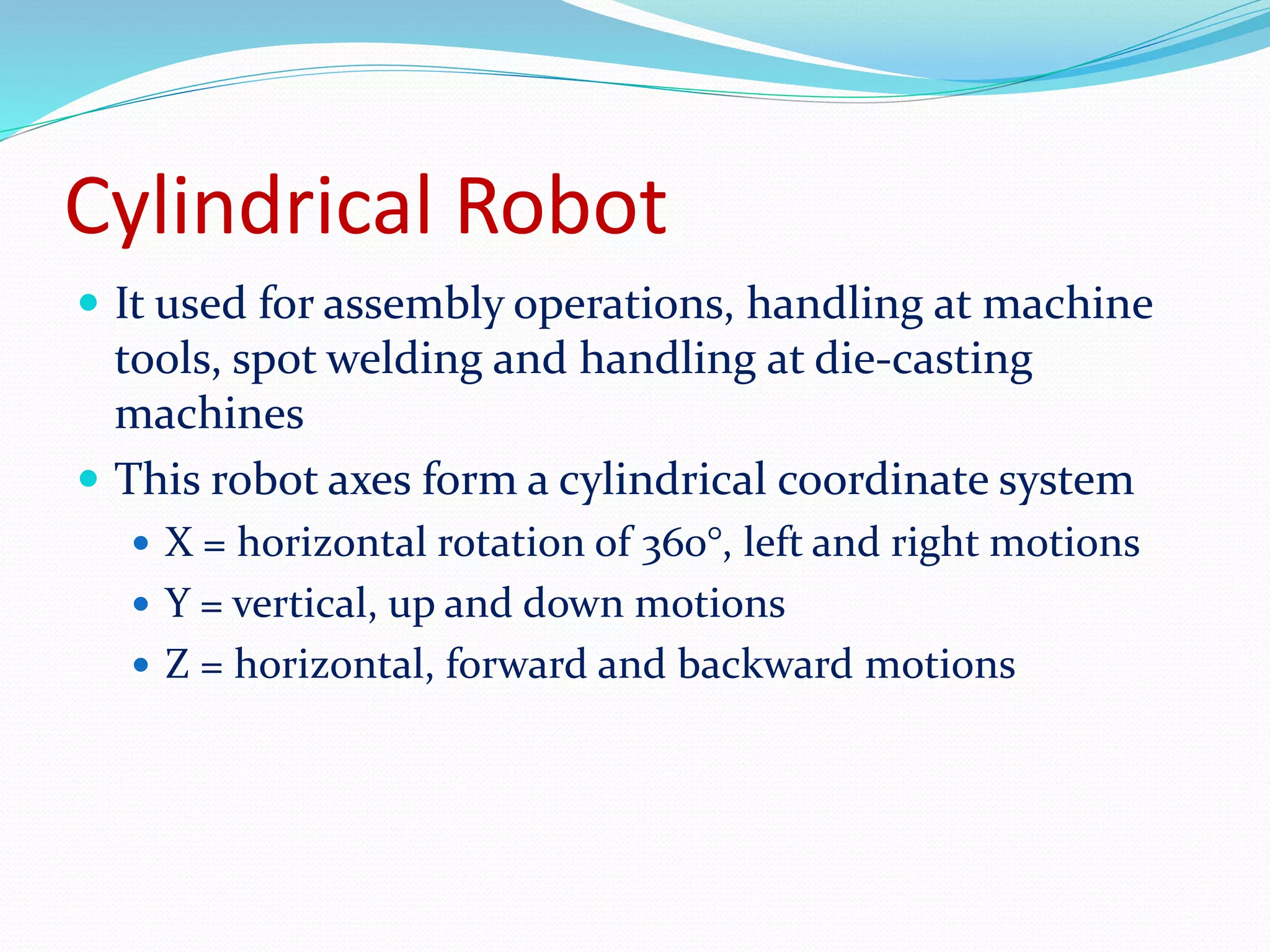
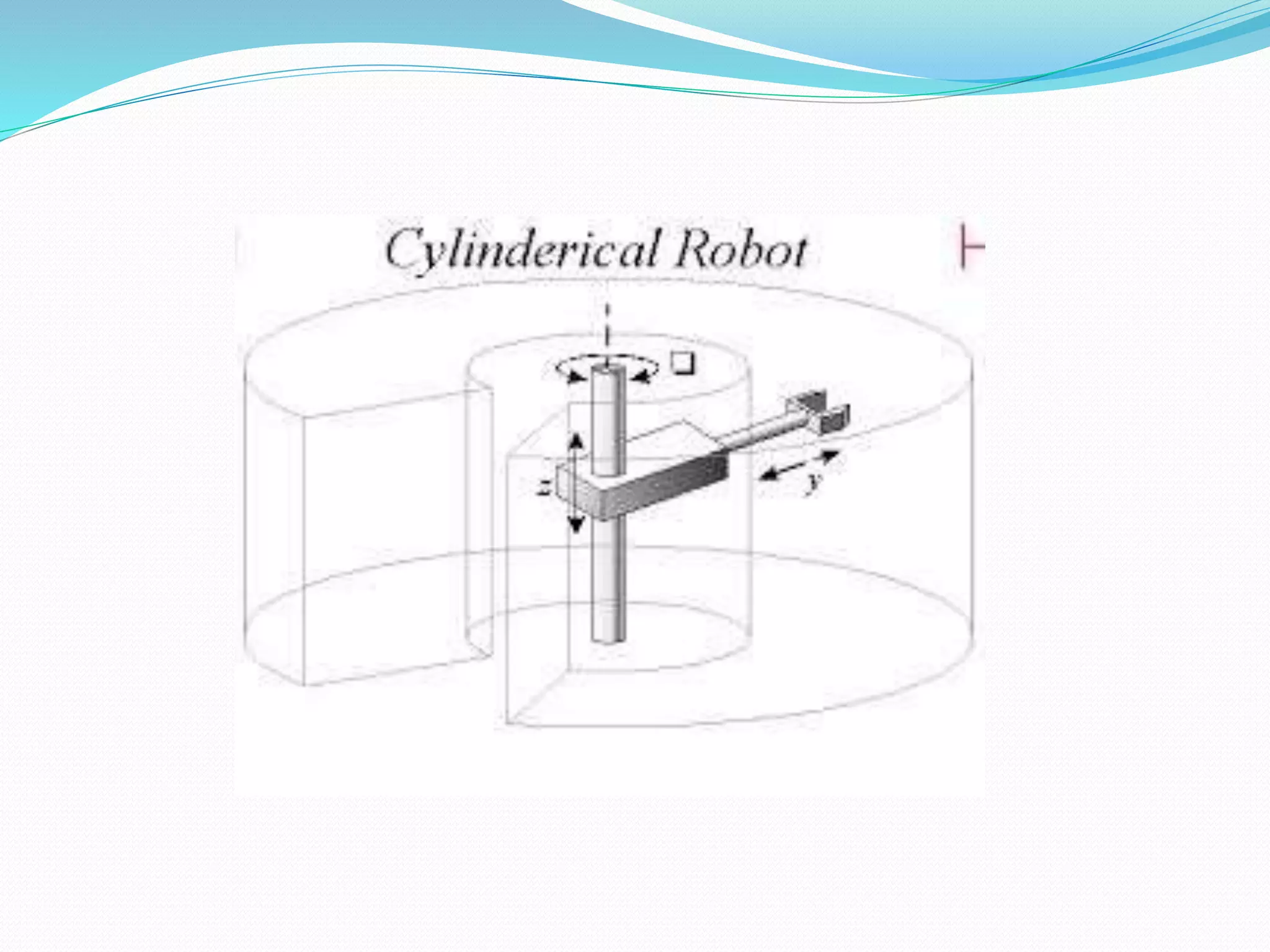
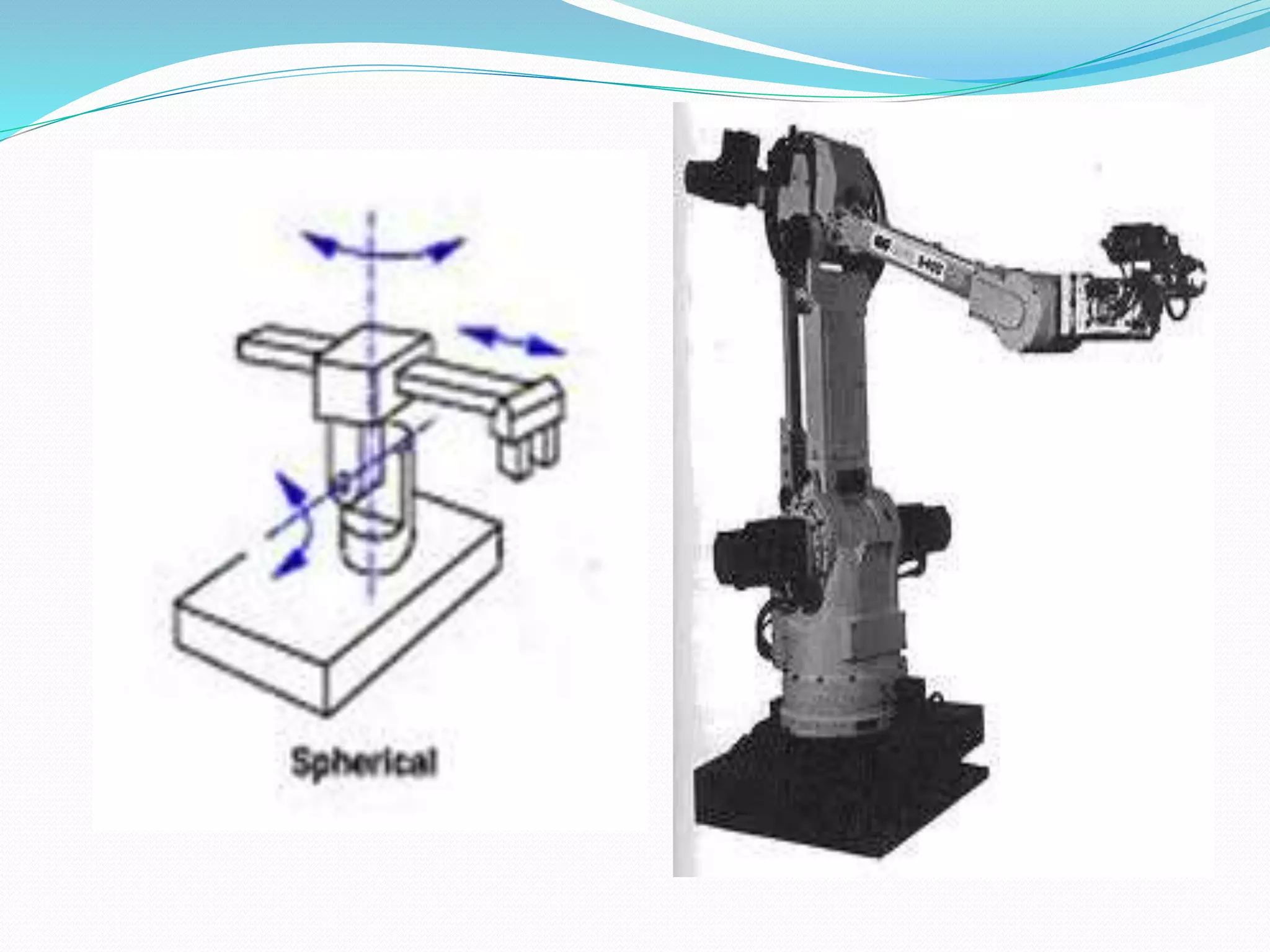
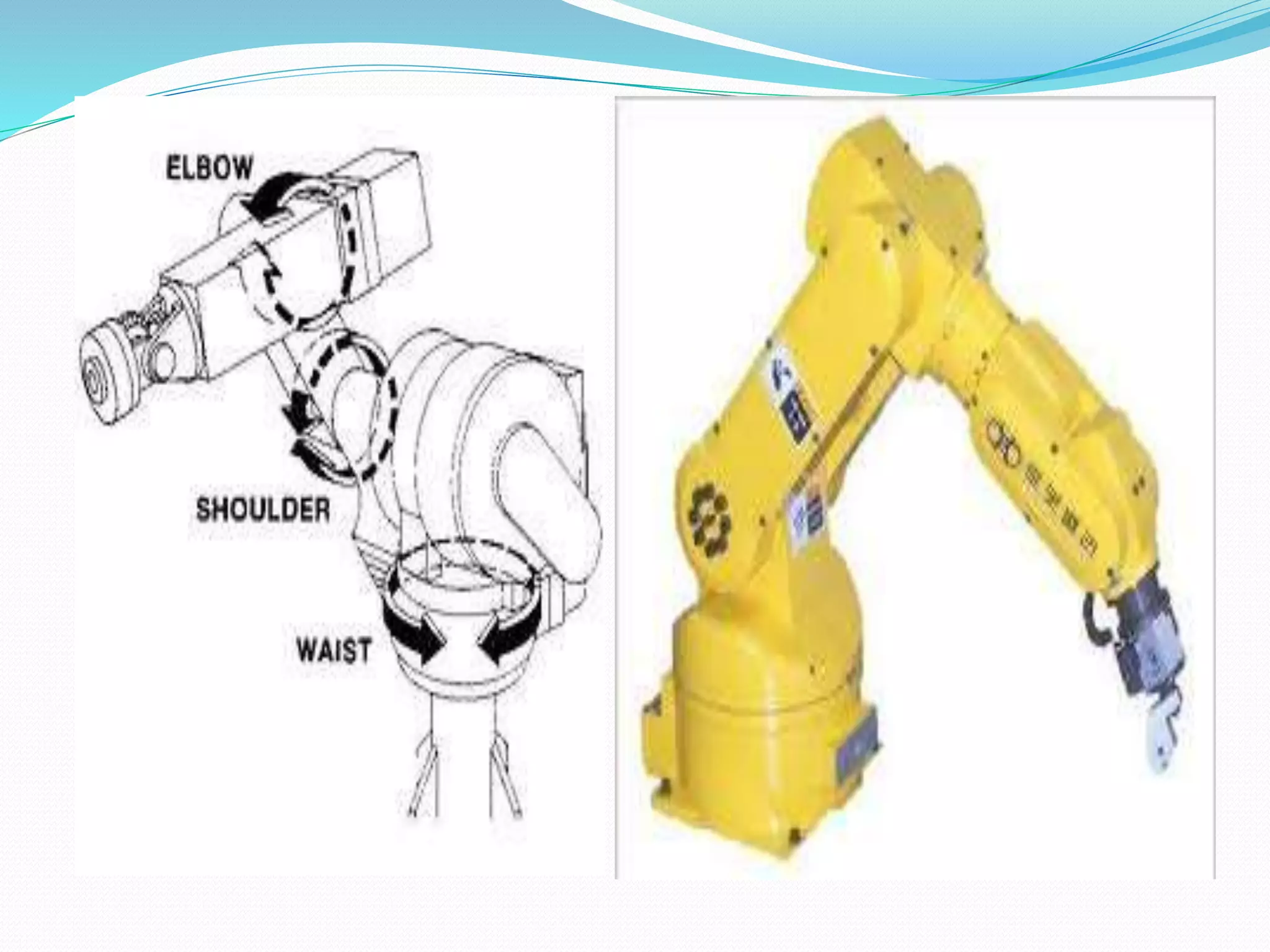
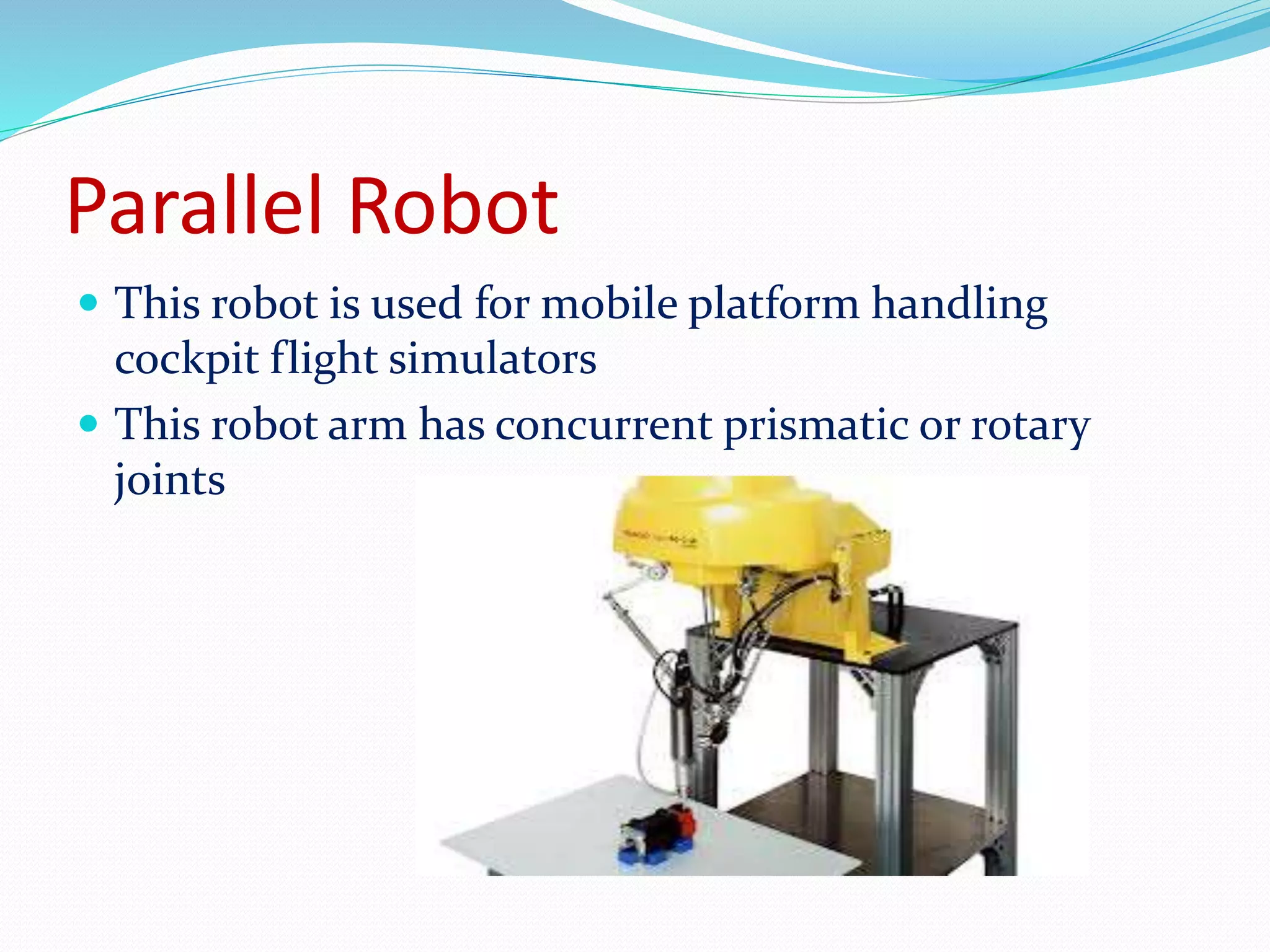
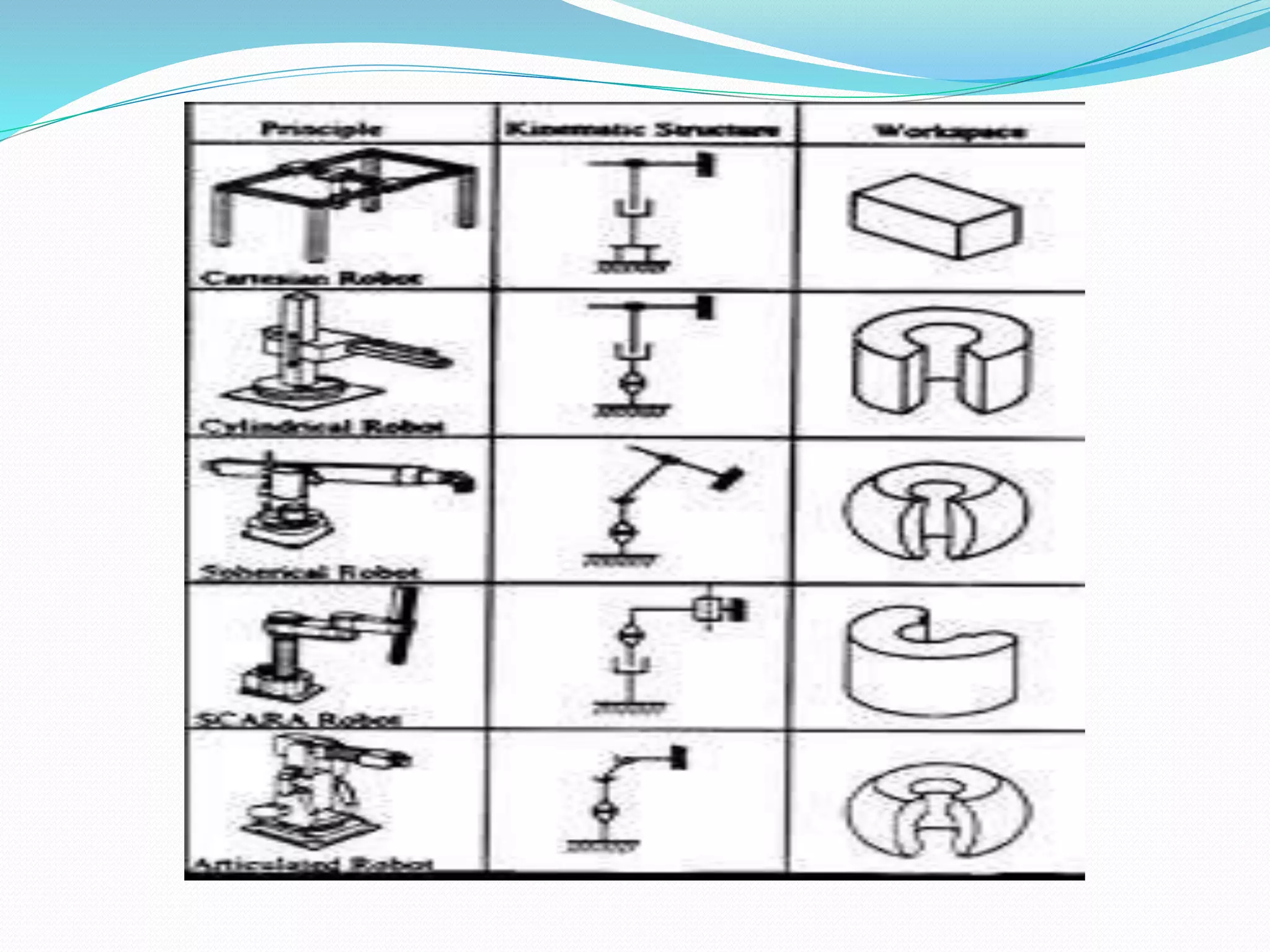
This document discusses the components and classification of robots. It describes the major components that make up industrial robots: controllers, manipulators, actuators, end-effectors, and sensors. It then explains the six main types of robot classification: Cartesian, cylindrical, spherical, SCARA, articulated, and parallel robots. Each classification is defined by the orientation and movement of its axes. The document provides examples of common uses for each robot type.