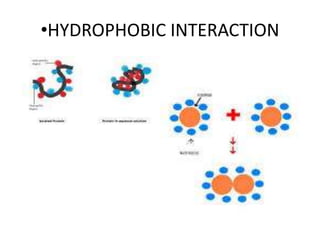
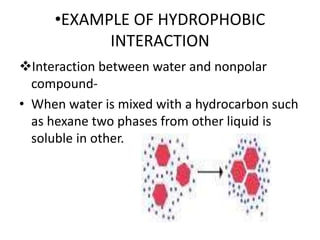
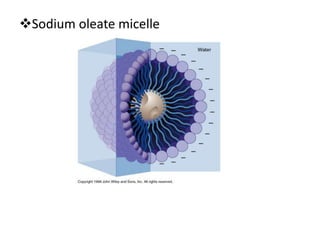
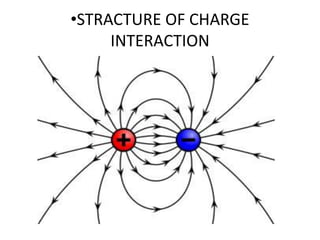
The document discusses hydrophobic interactions, defining them as the tendency of nonpolar molecules in a polar solvent, particularly water, to interact with one another. It highlights various types of molecular interactions, including van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, and examples such as sodium oleate micelles and protein stability. The conclusion emphasizes the weak nature of hydrophobic interactions compared to ionic interactions and hydrogen bonds, which are also influenced by the solvent properties of water.