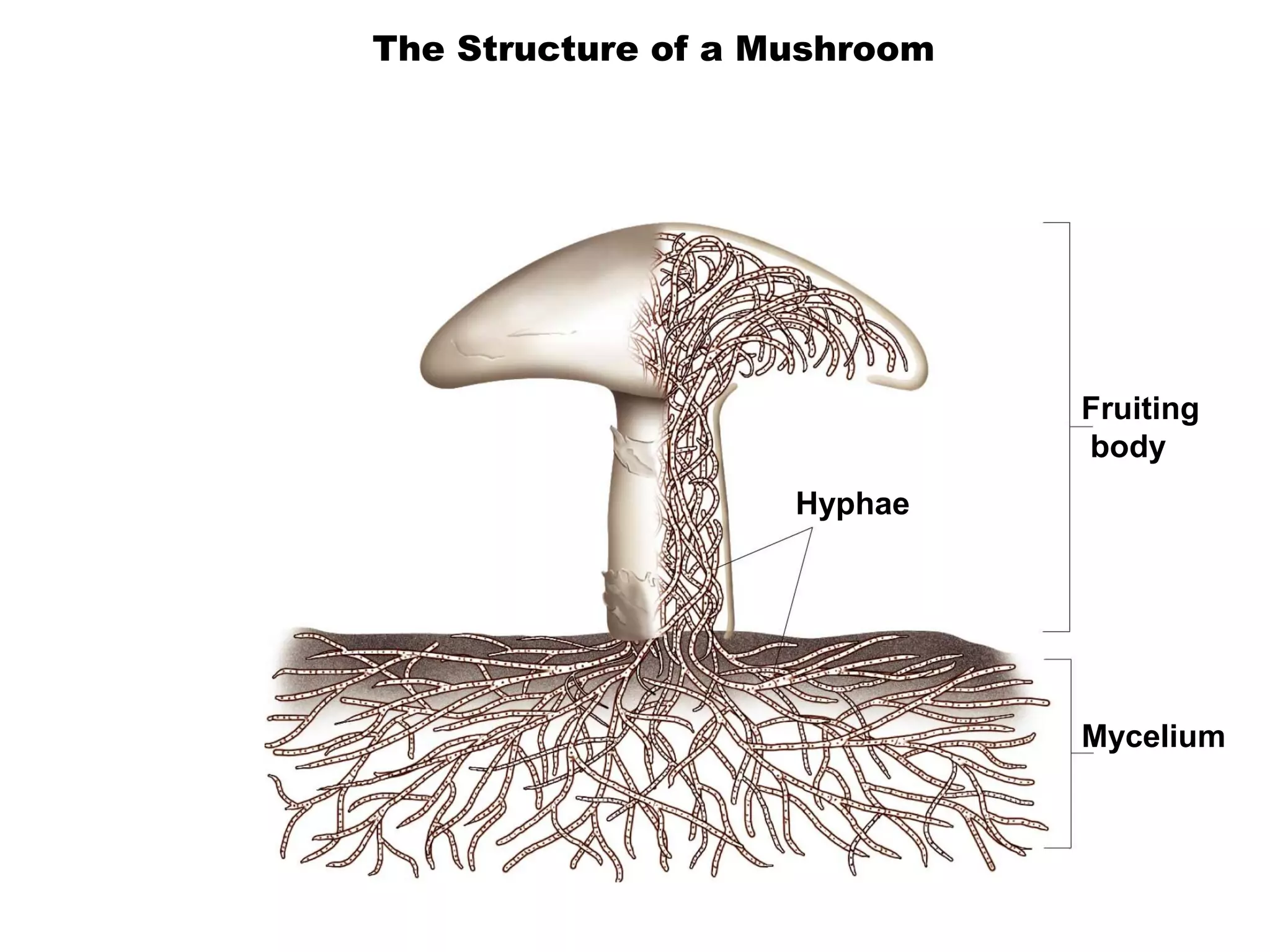
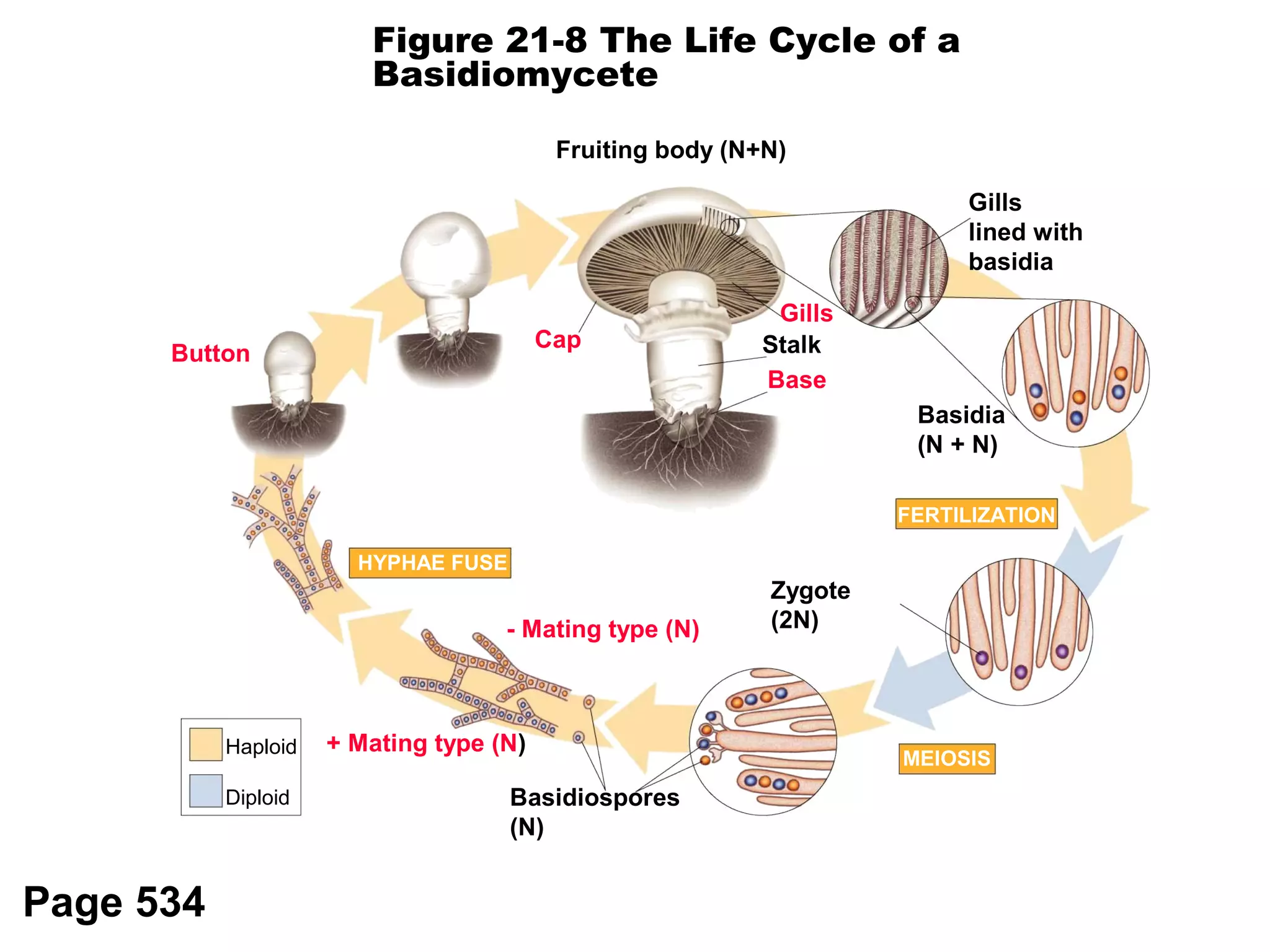
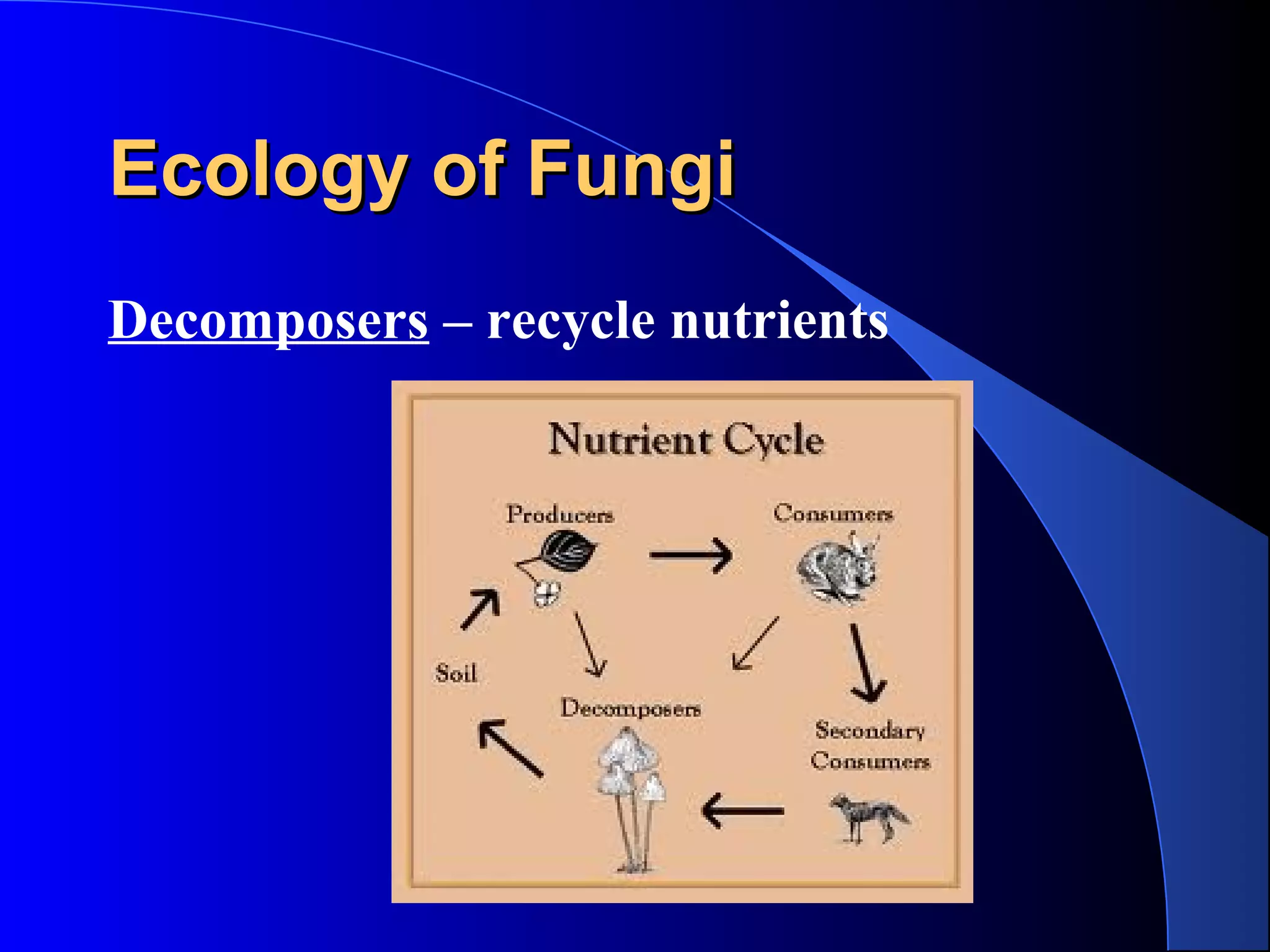
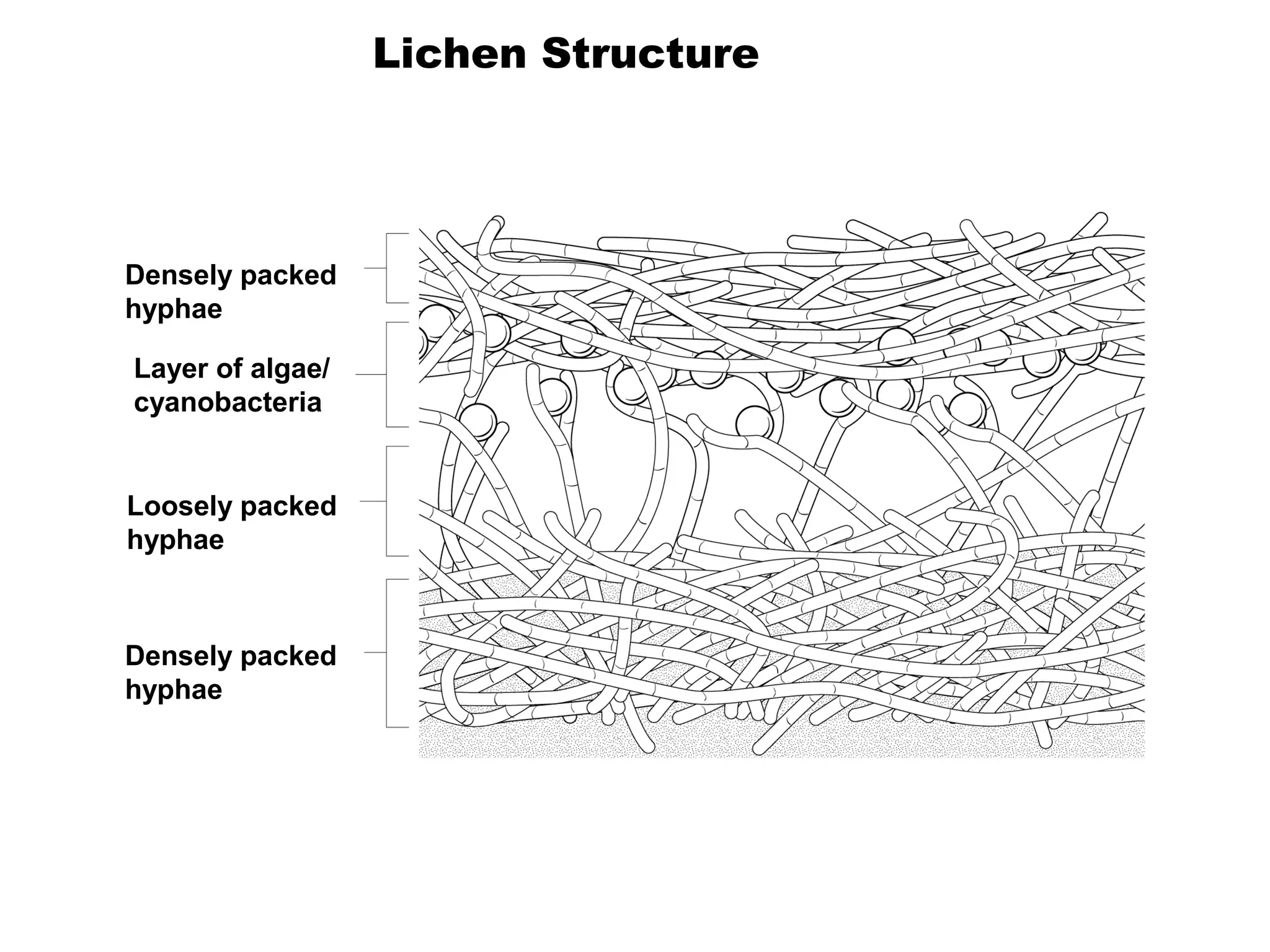
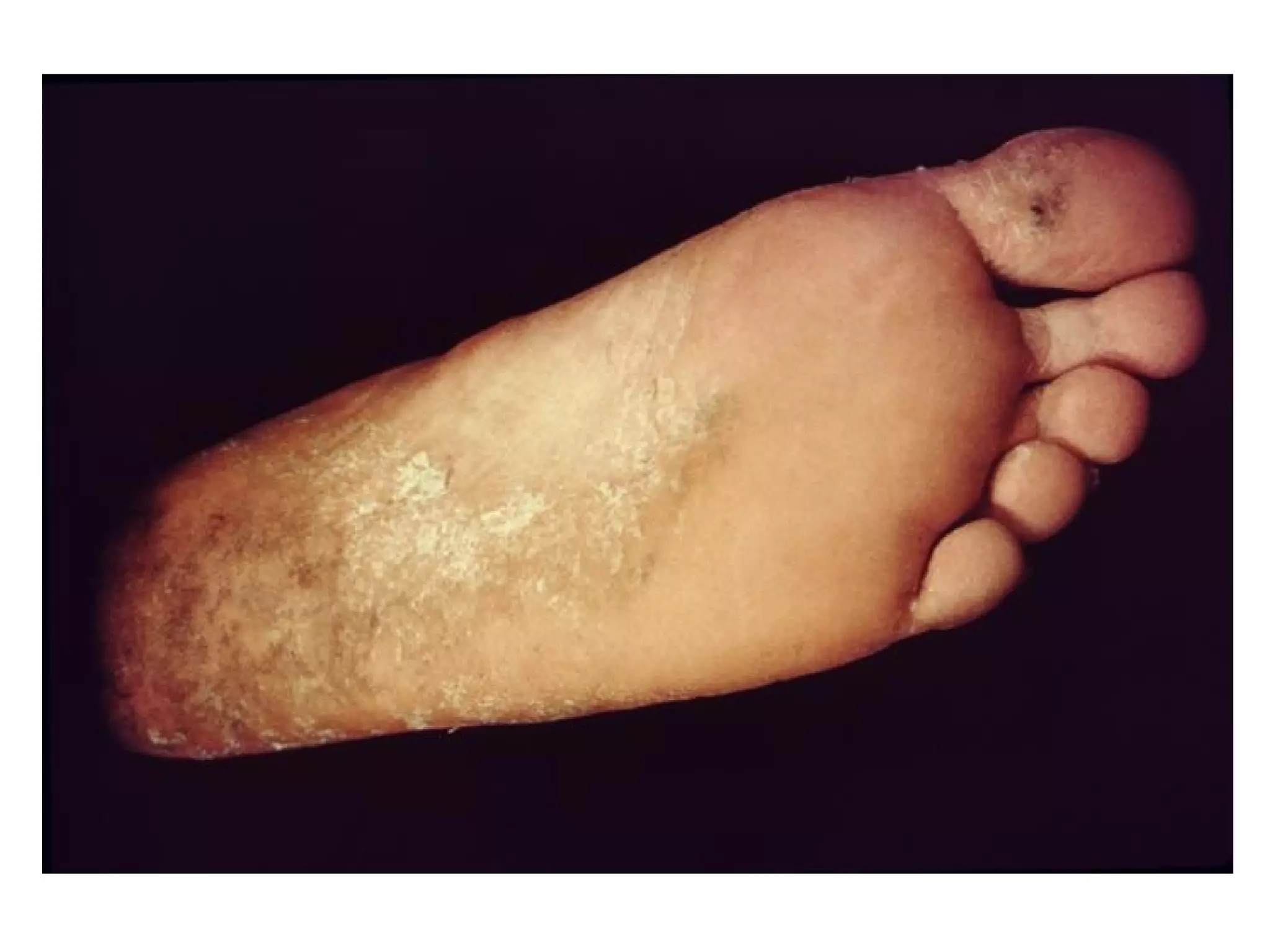
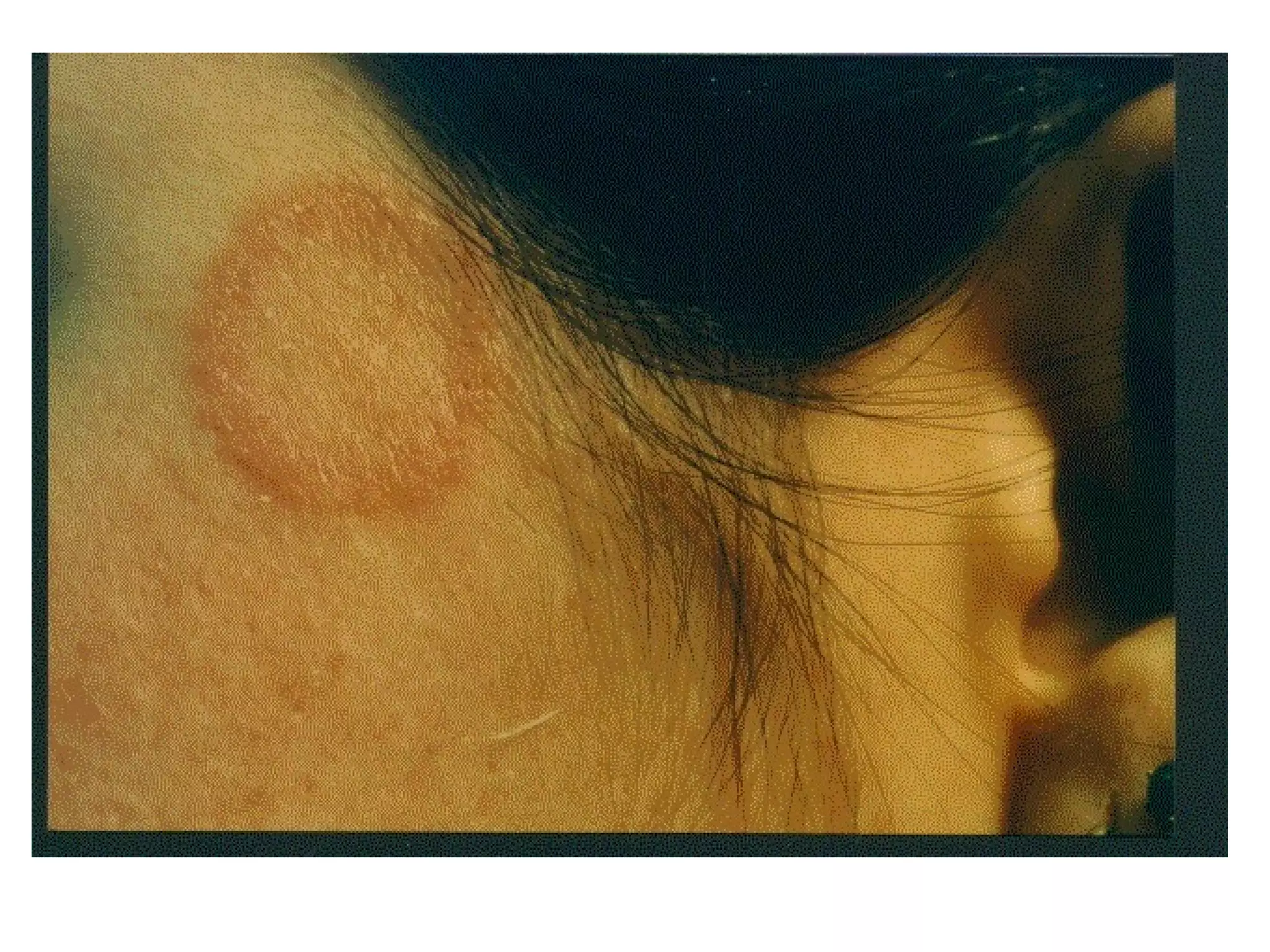
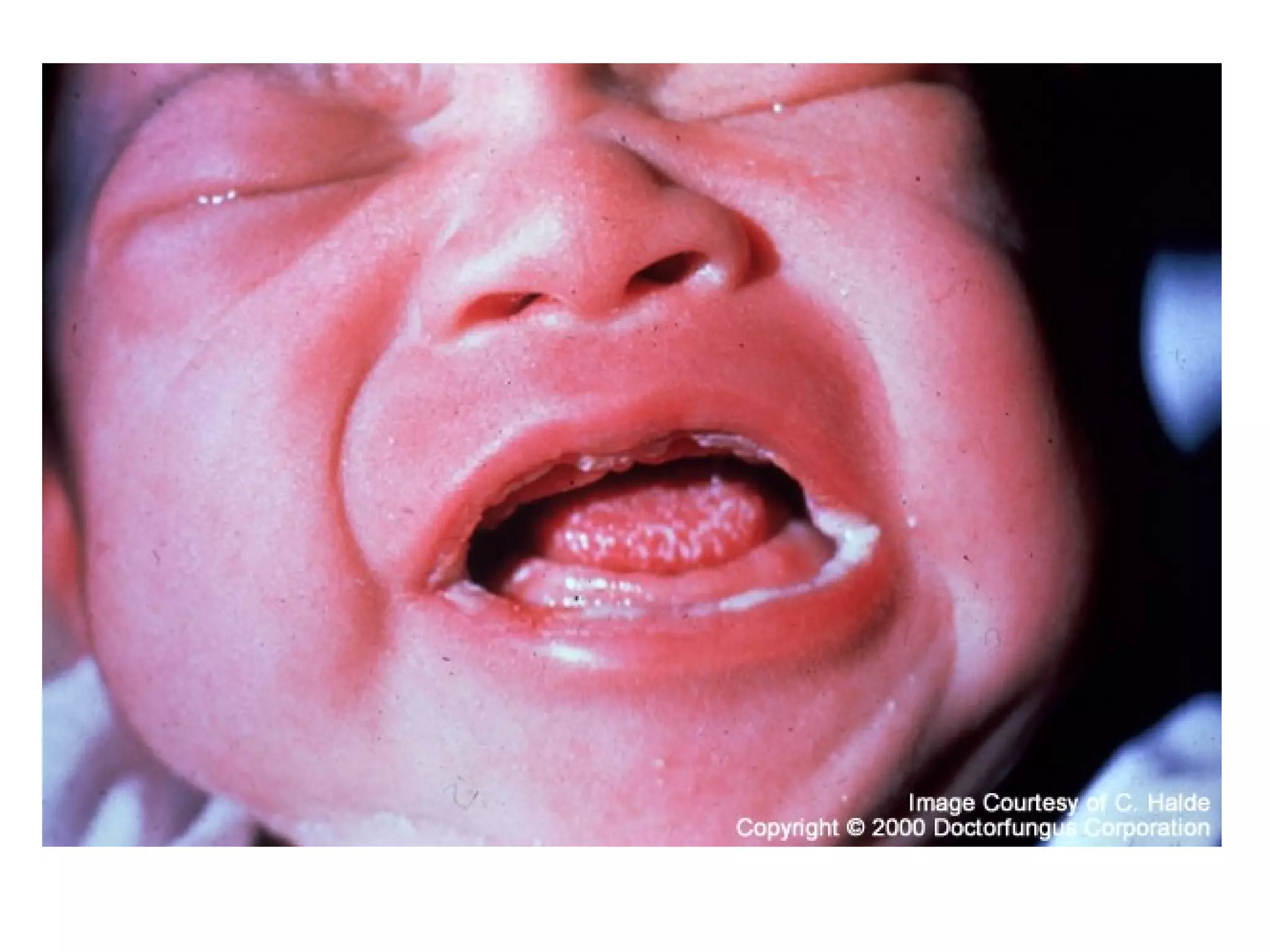
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that are classified into groups such as zygomycetes, ascomycota, and basidiomycota based on their structure and reproduction. They play important ecological roles as decomposers that recycle nutrients, form symbiotic relationships with plants and lichen, and are found in a variety of habitats. Fungi are also economically significant as sources of food, causes of crop damage and disease, and in industries like baking, brewing, and medicine production.