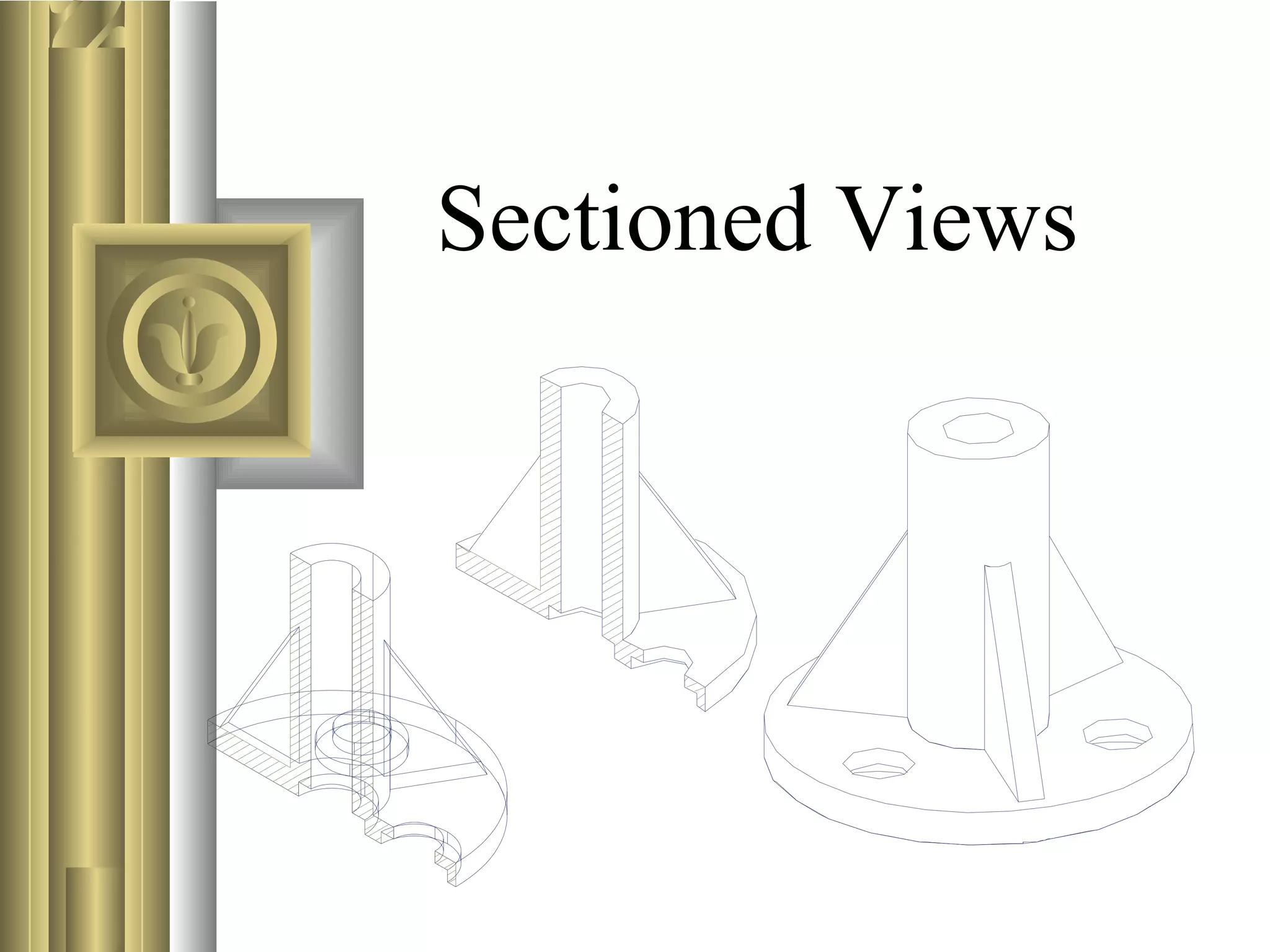
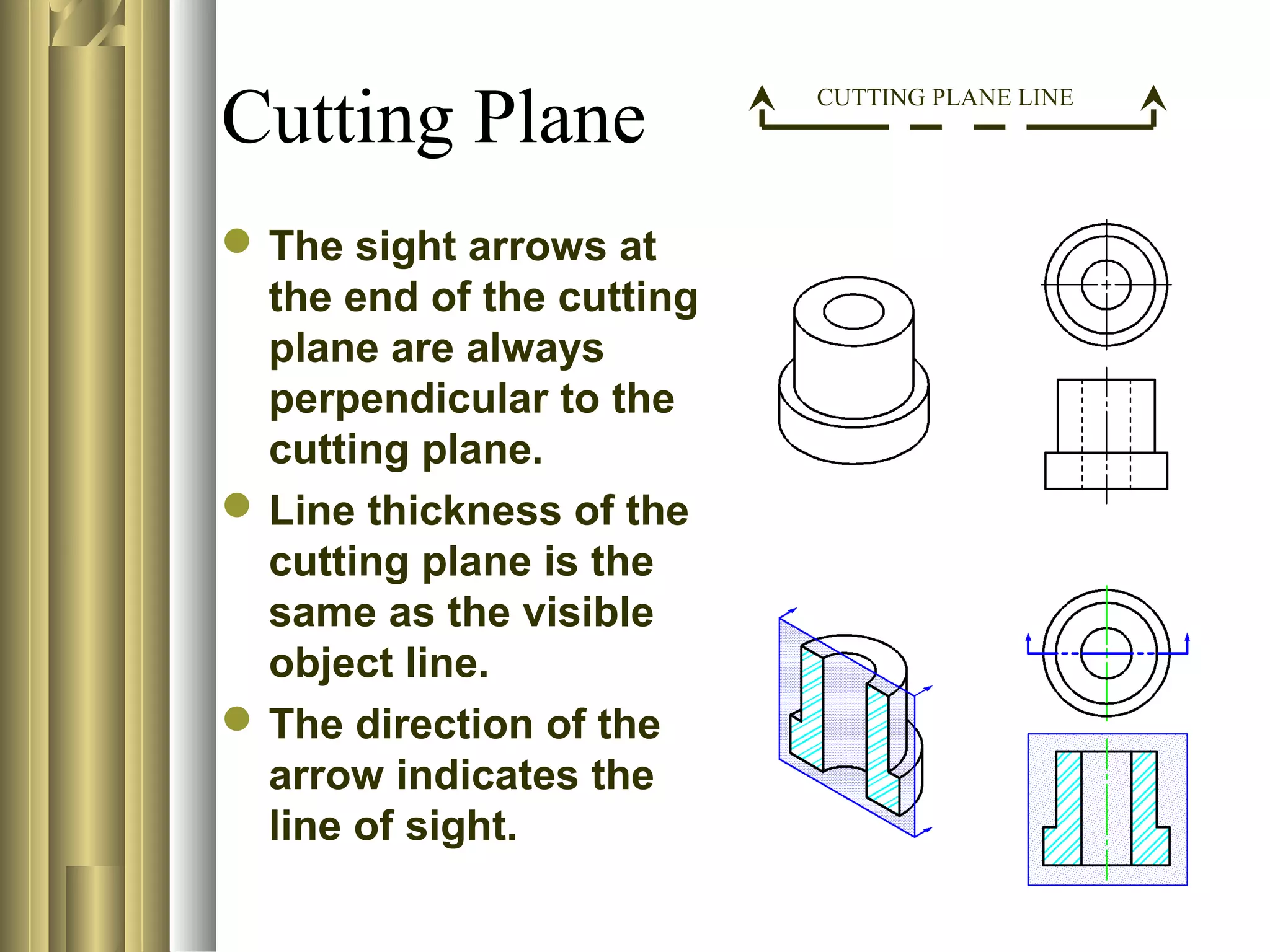
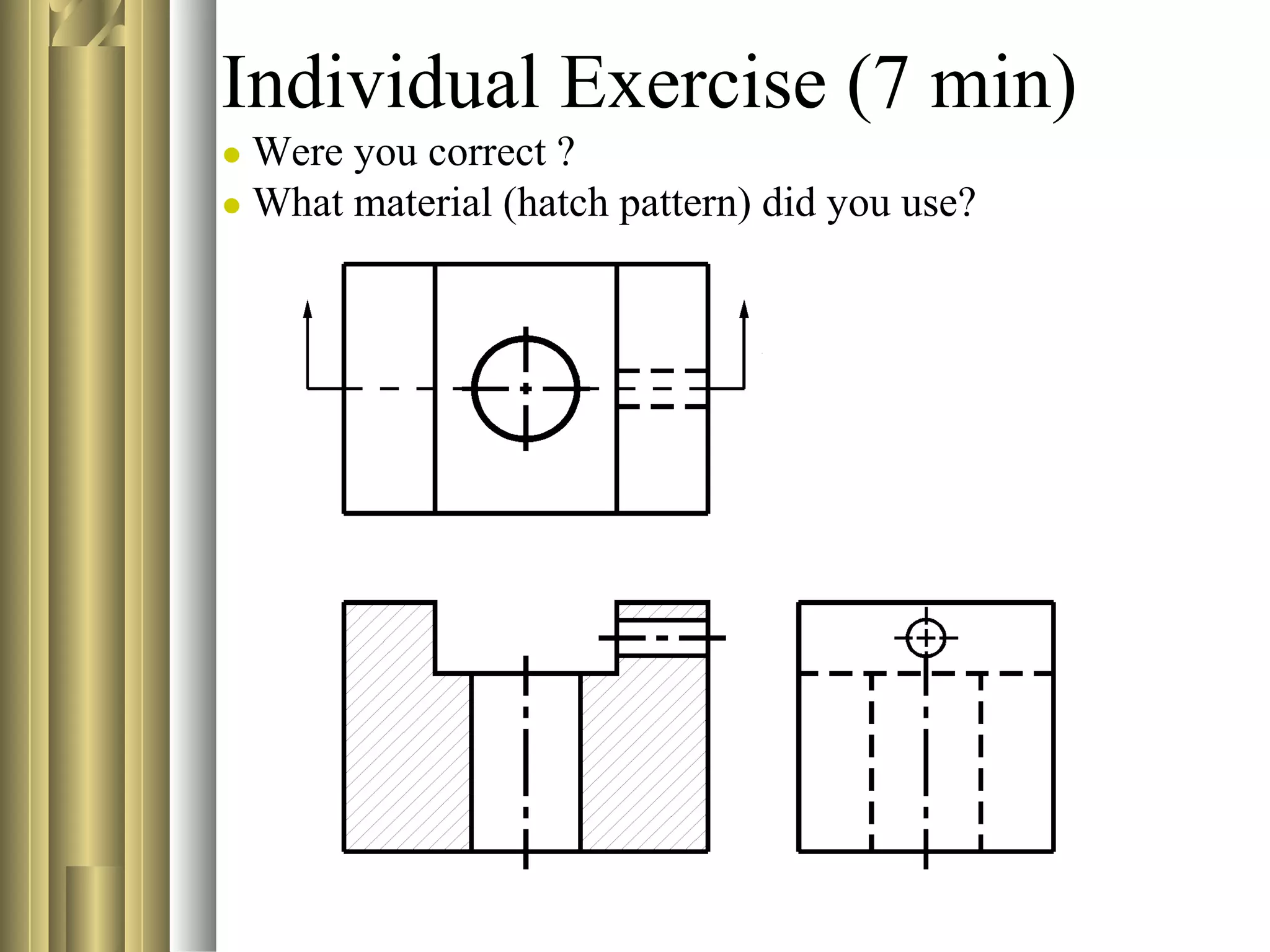
This document discusses section views and sectioning practices in technical drawings. It covers the following key points:
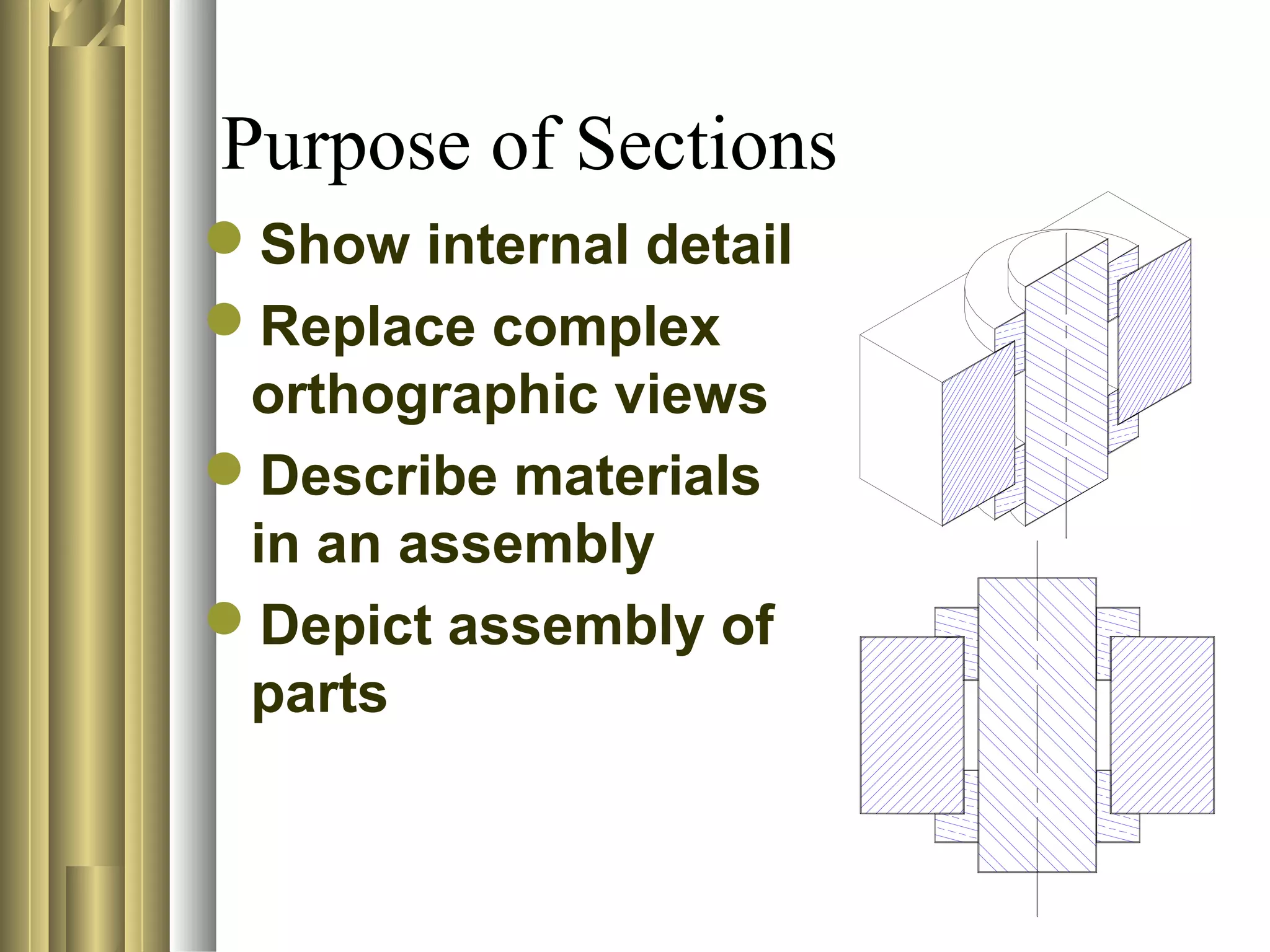
- The purpose of section views is to show internal details of an object, replace complex orthographic views, describe materials in an assembly, and depict the assembly of parts.
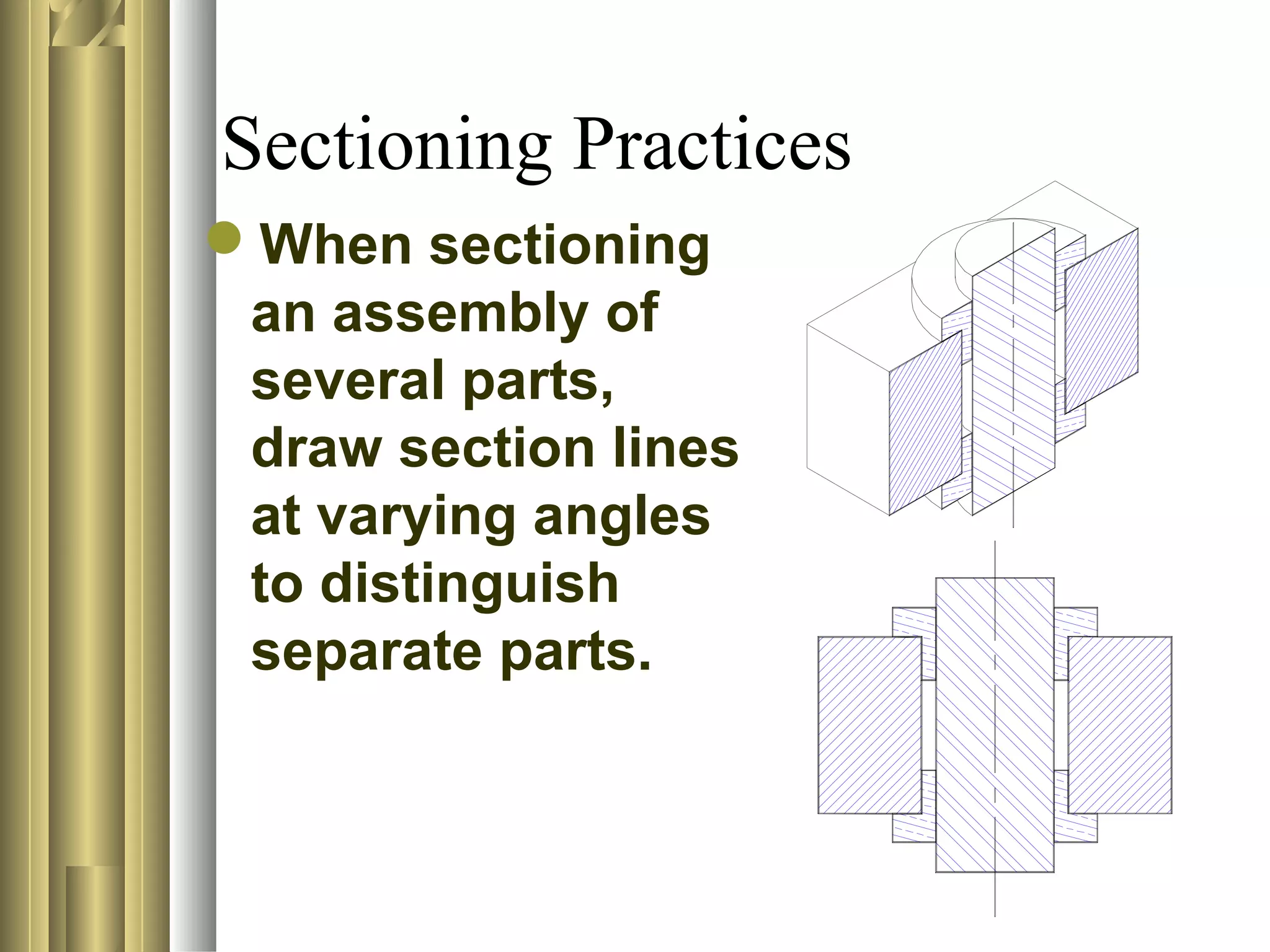
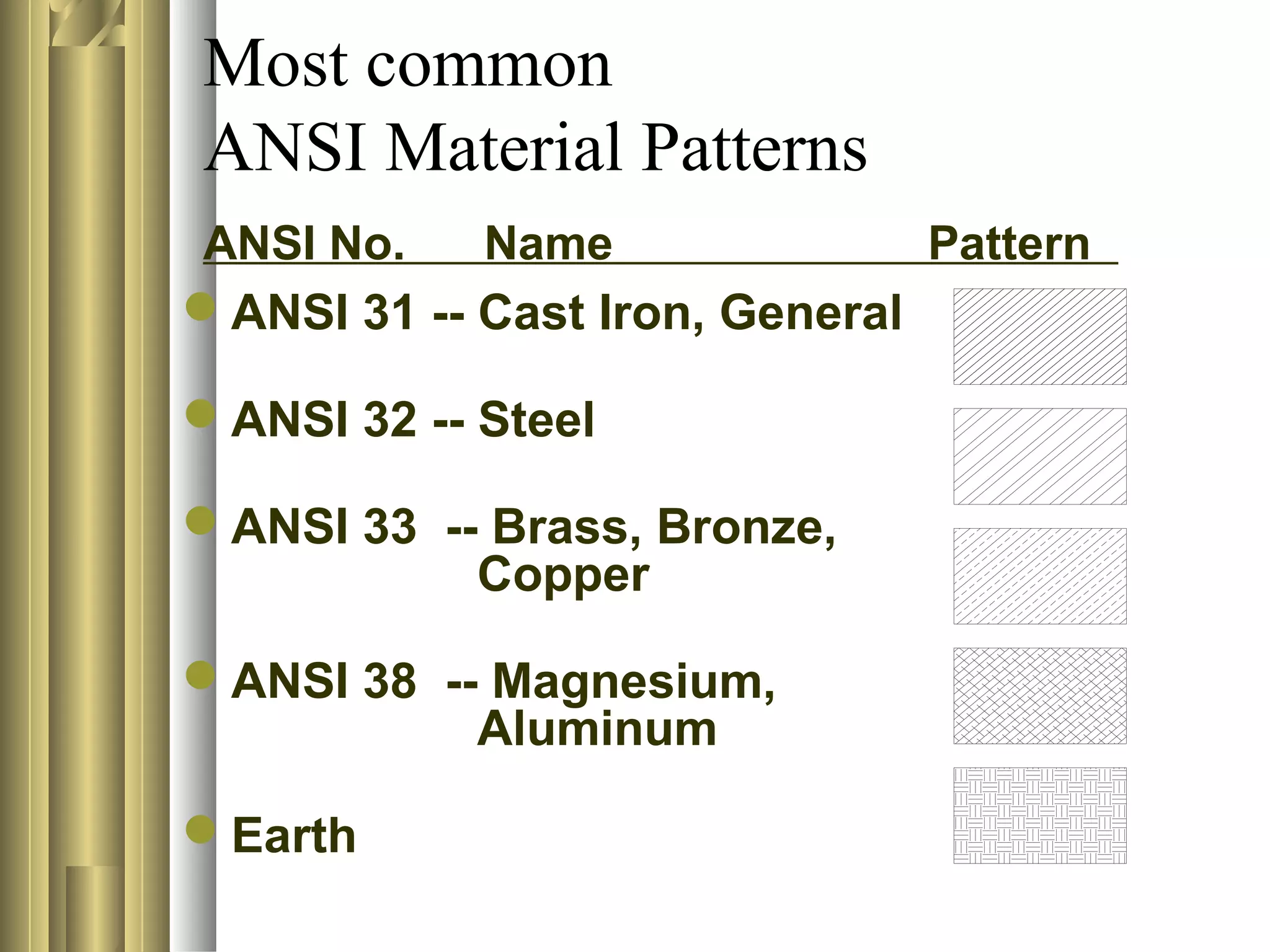
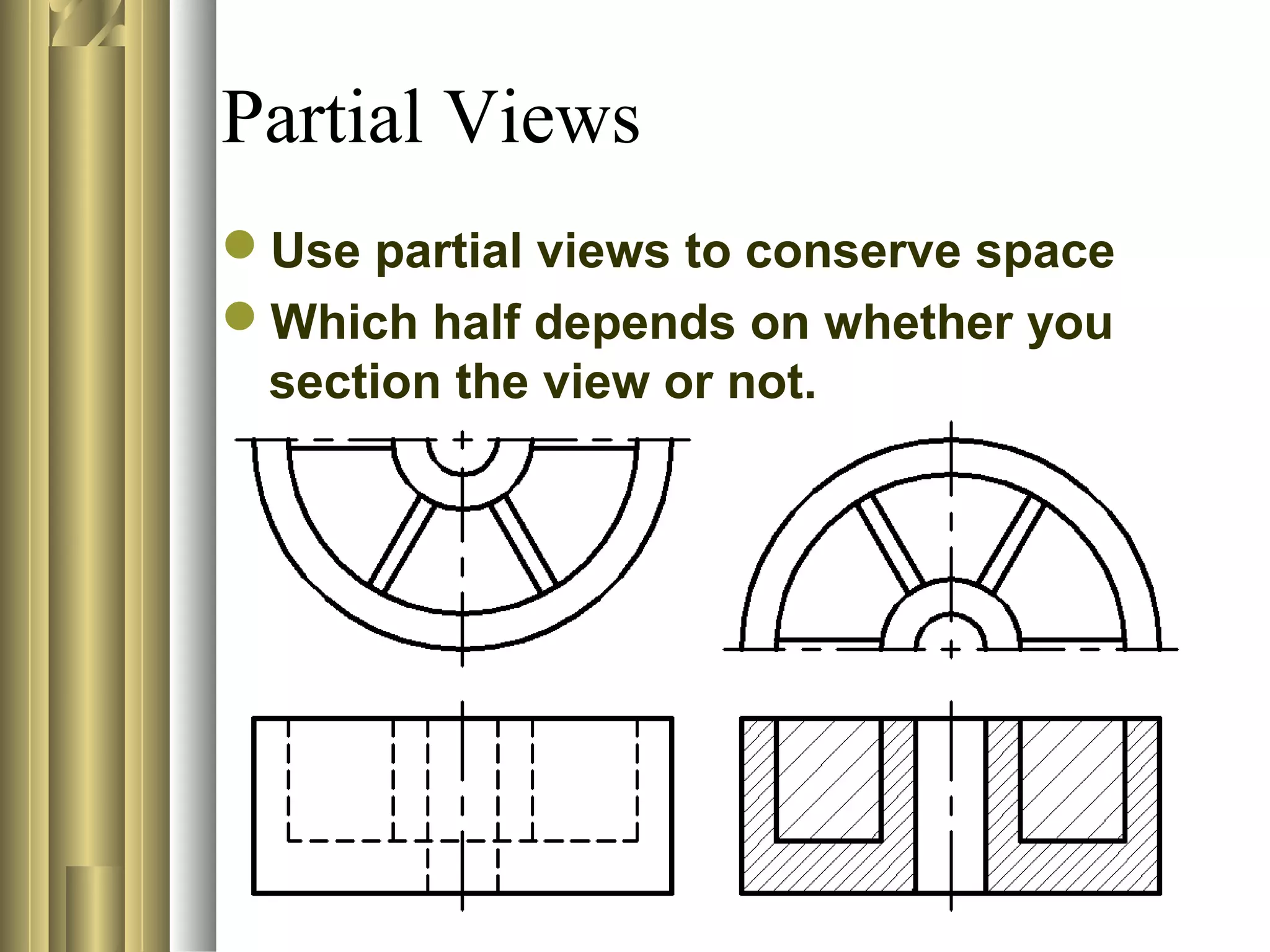
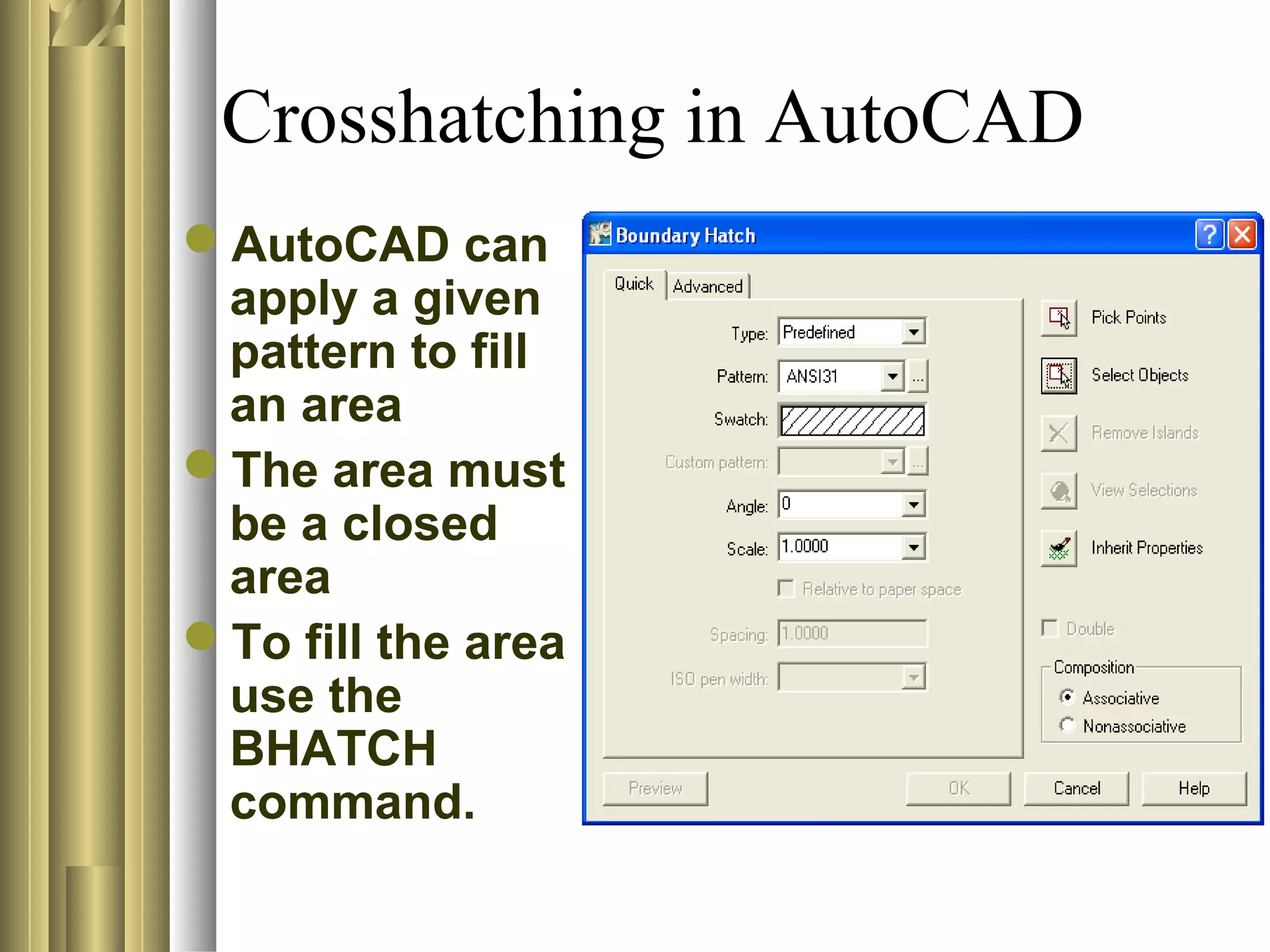
- Common sectioning practices include using different cutting plane angles for separate parts, standard hatch spacing and line thicknesses, and not drawing section or hatch lines parallel to boundaries.
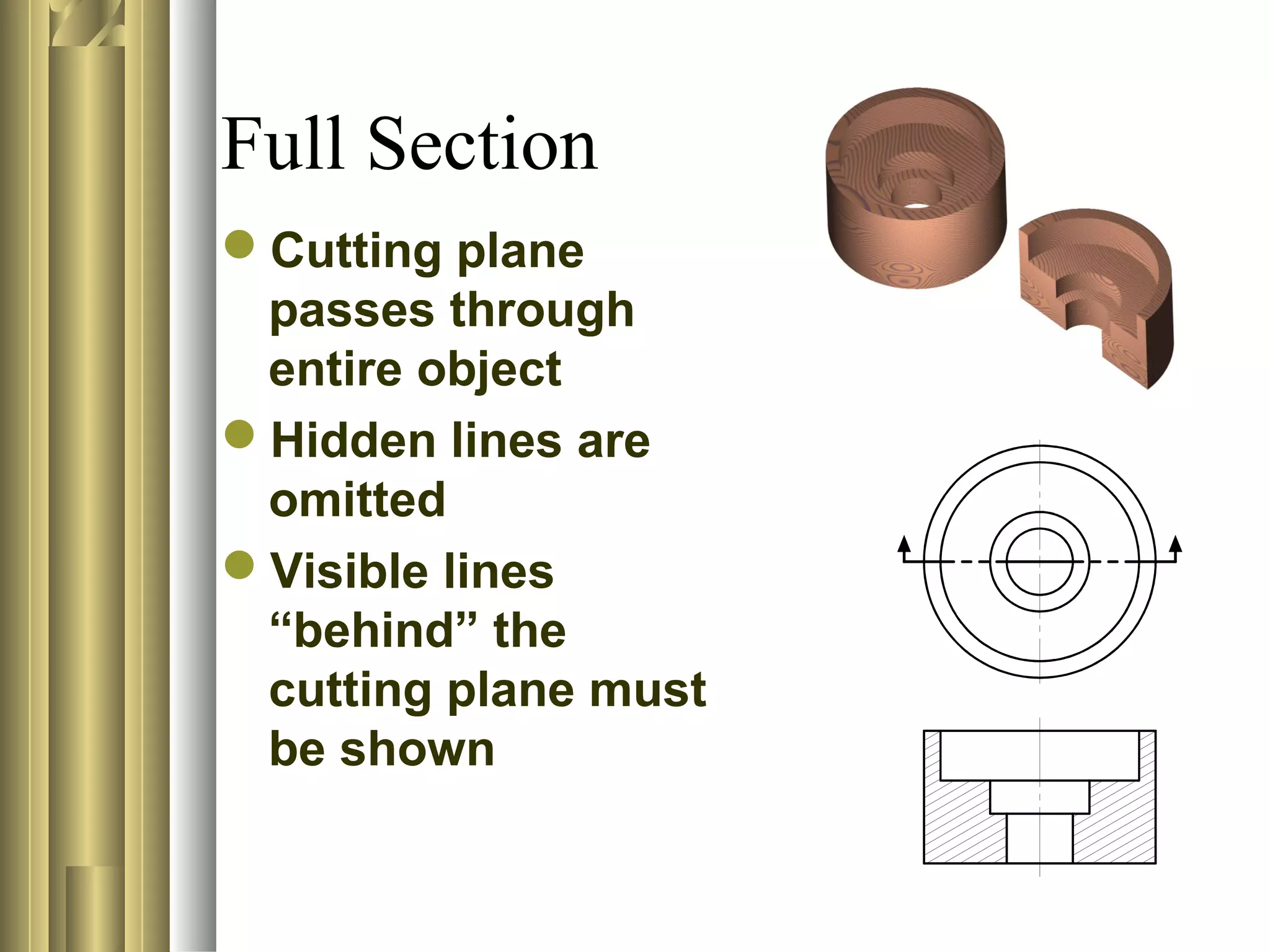
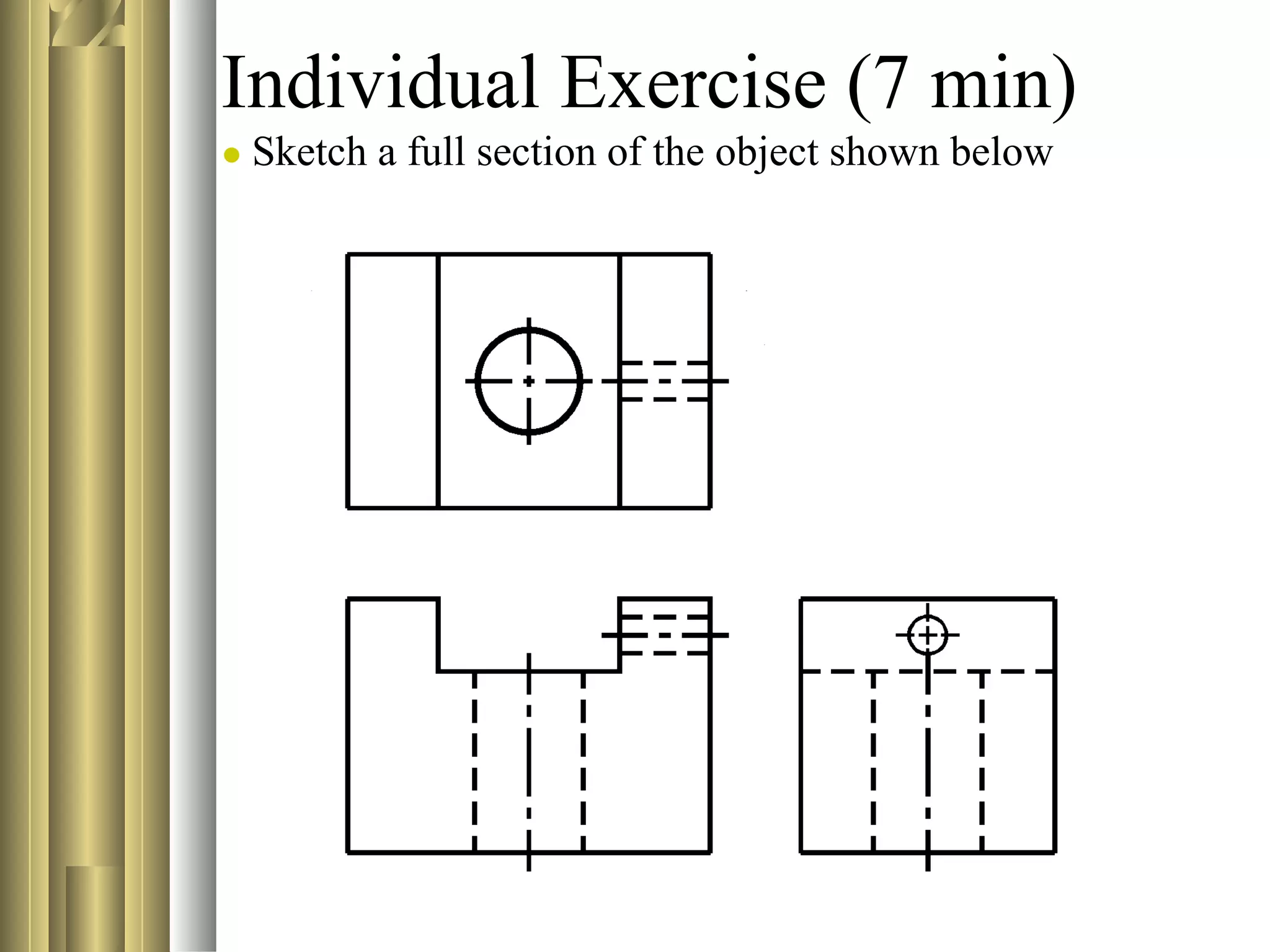
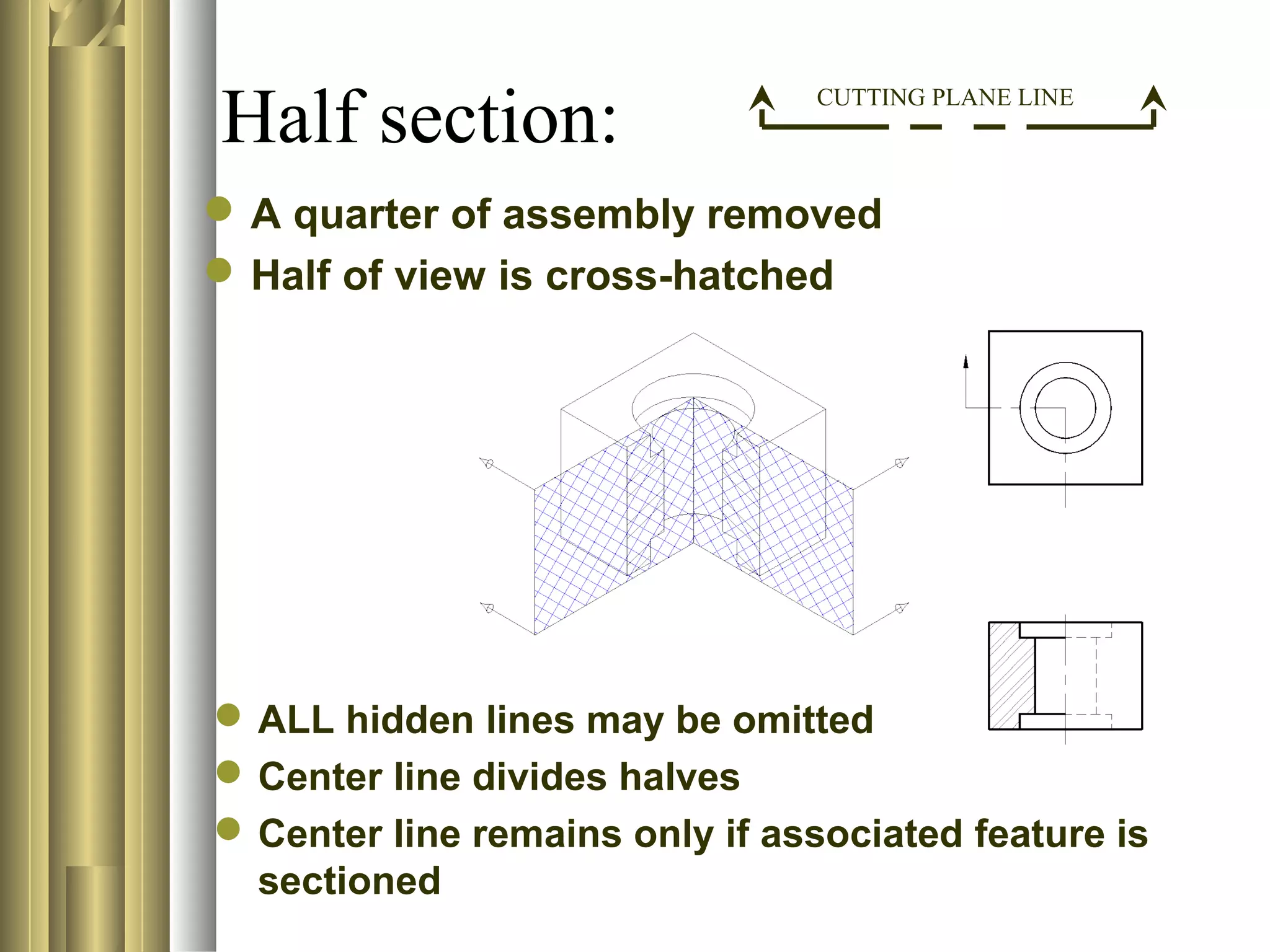
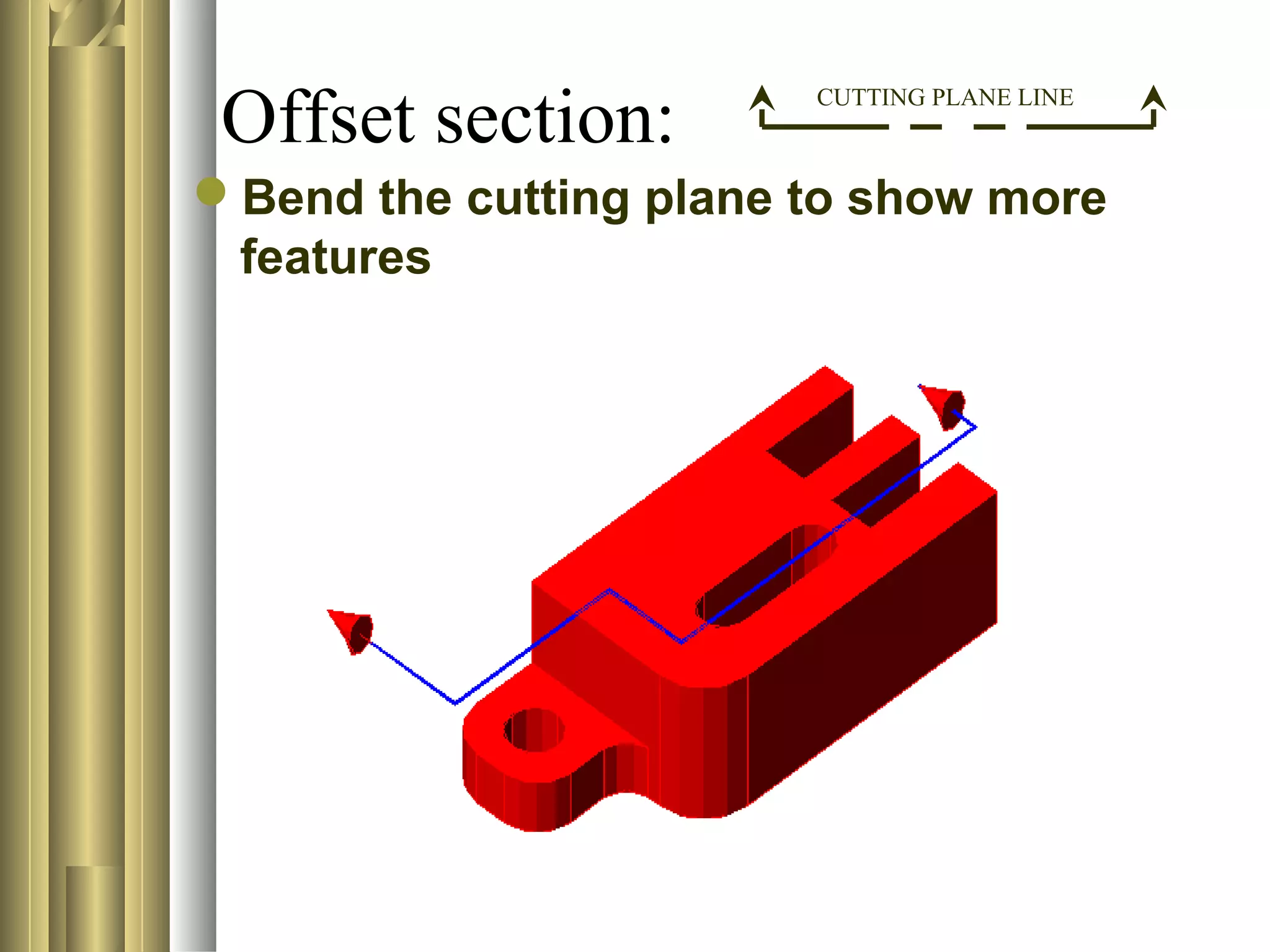
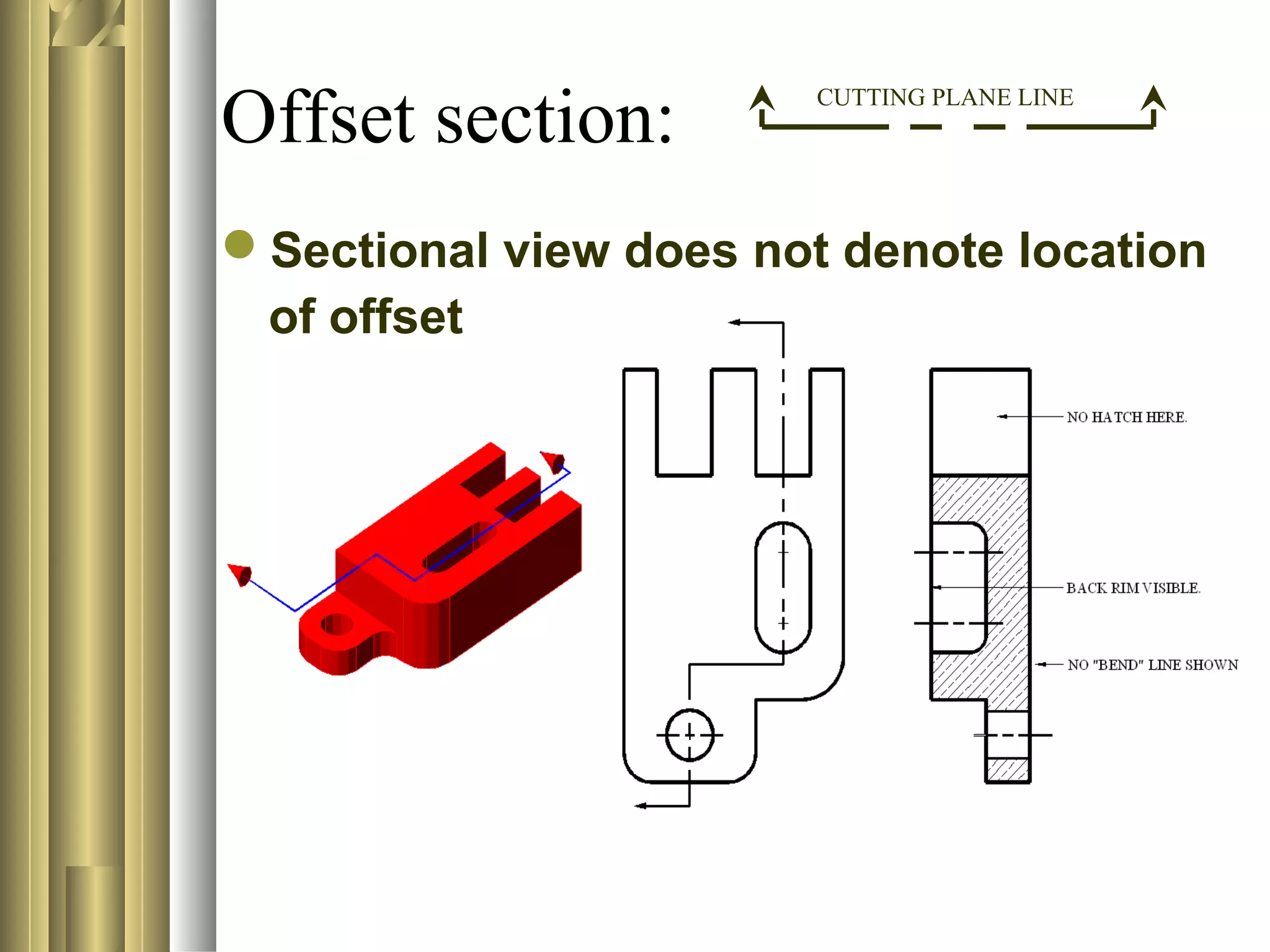
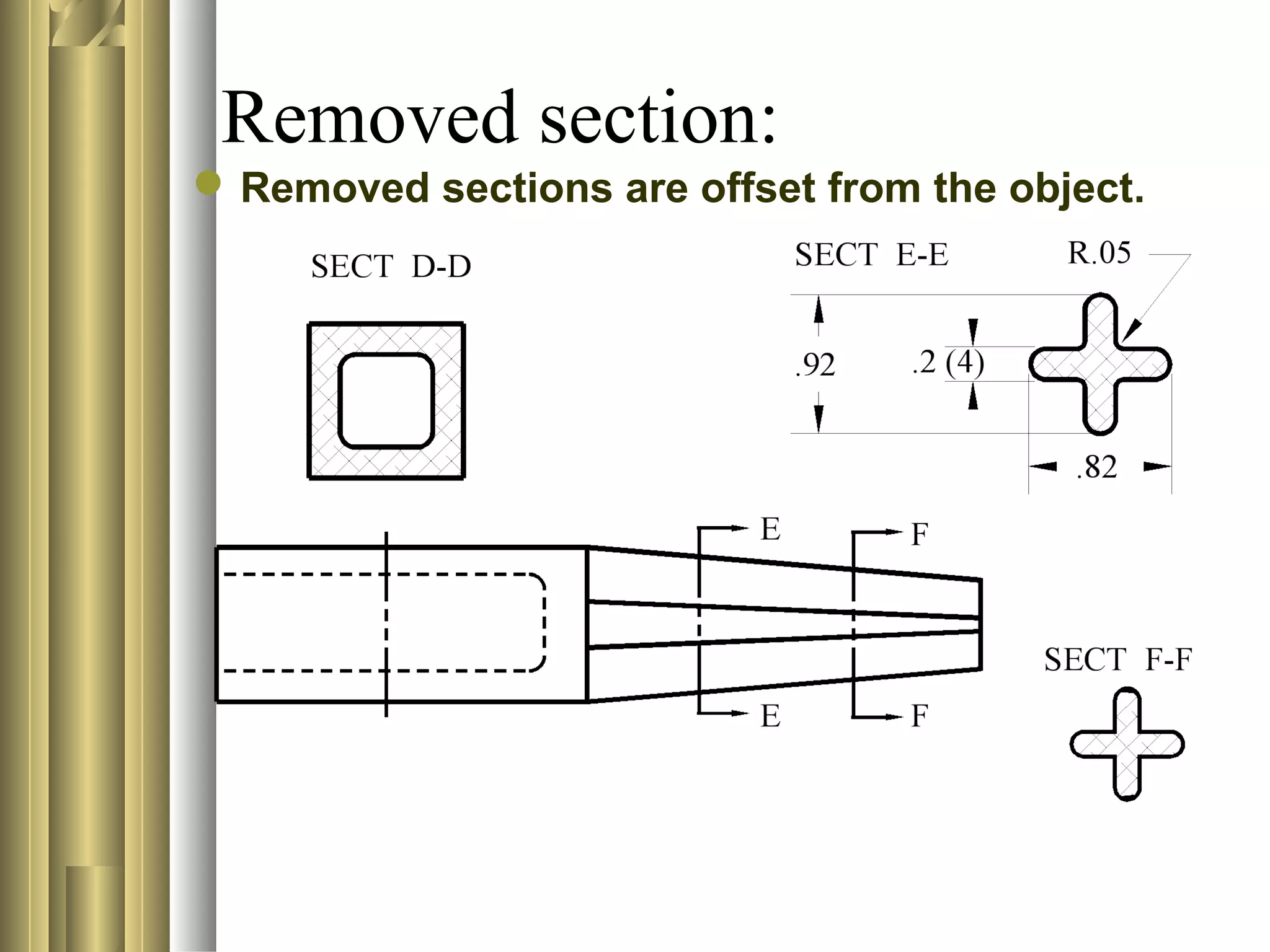
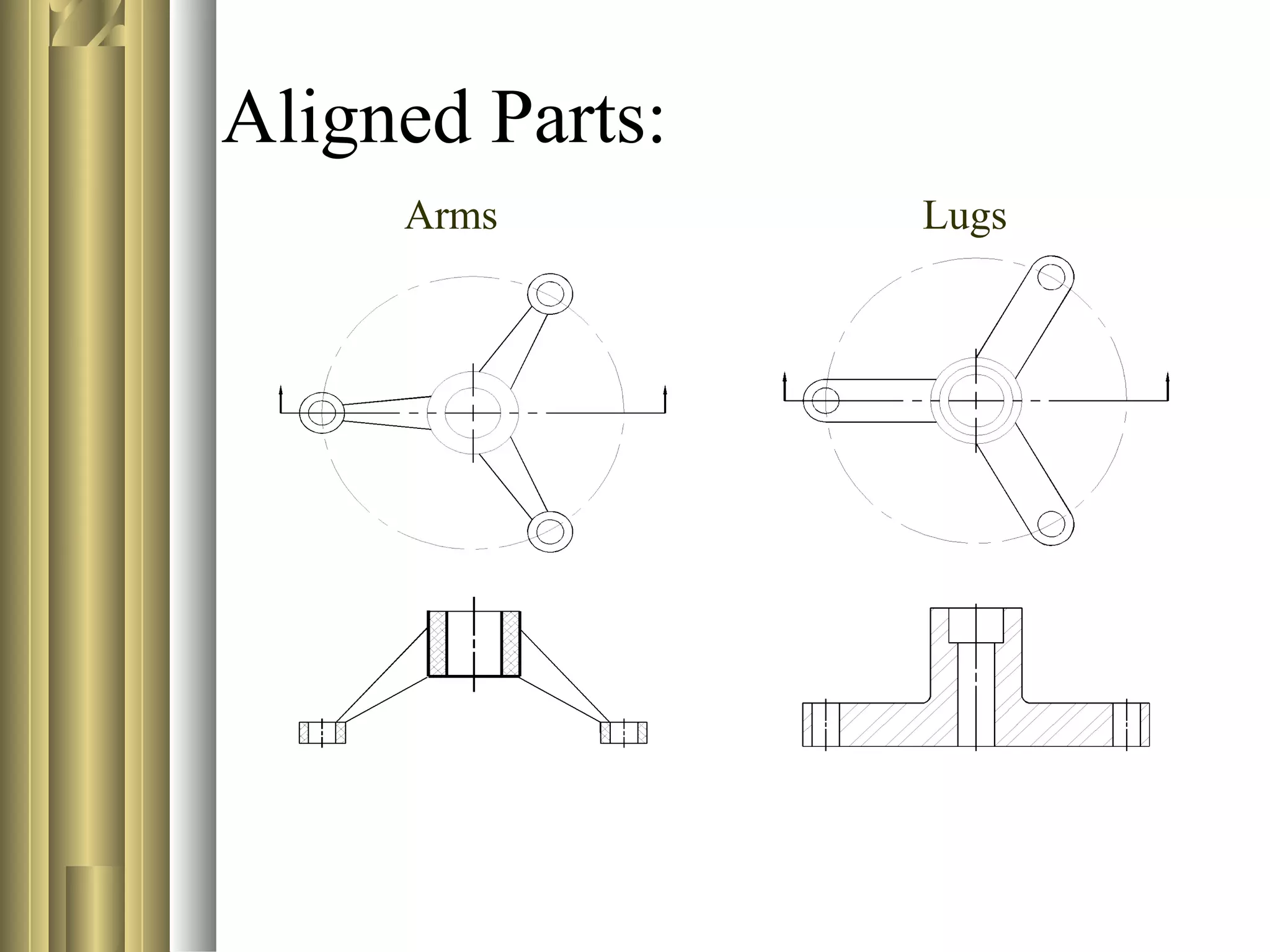
- Sectional view types include full sections, half sections, offset sections, revolved sections, removed sections, and broken out sections.
- Not all features get crosshatched, even if the cutting plane passes through, such as ribs, webs