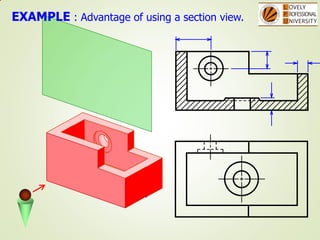
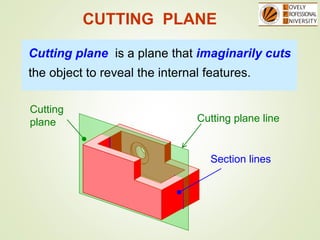
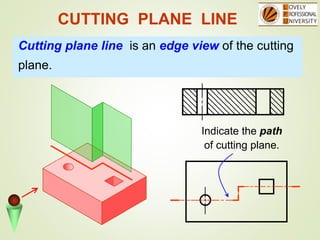
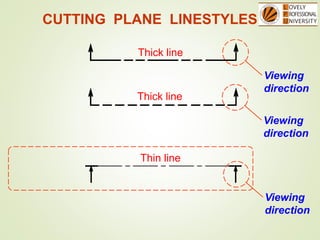
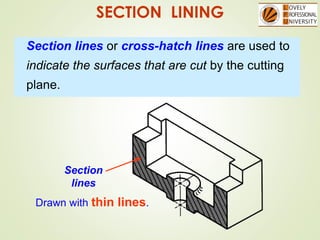
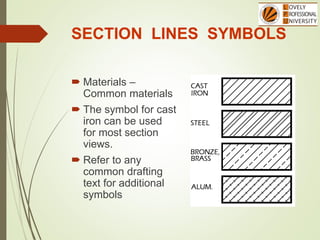
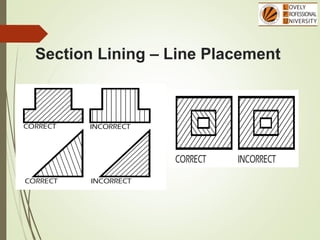
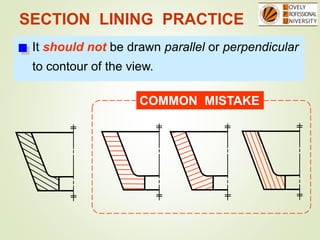
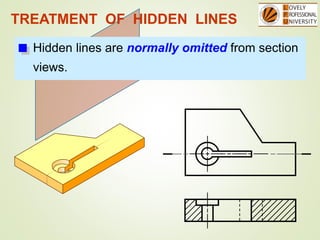
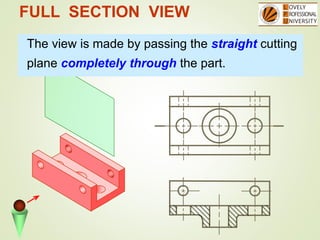
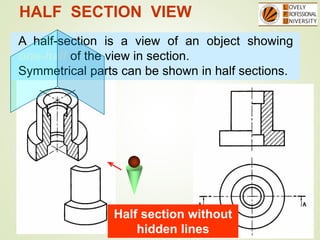
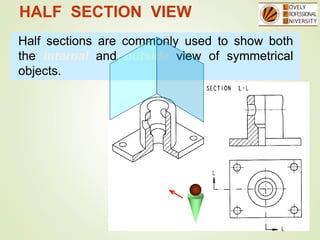
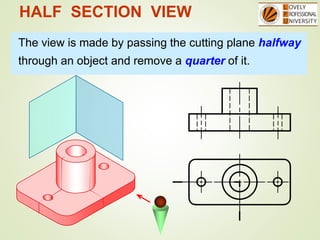
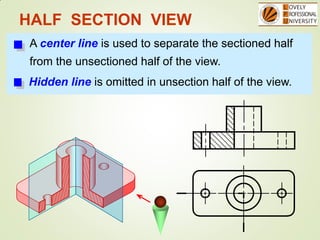
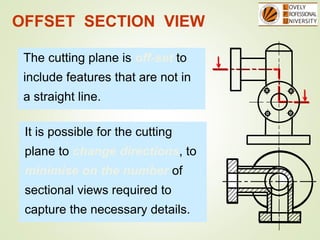
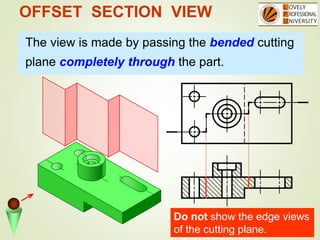
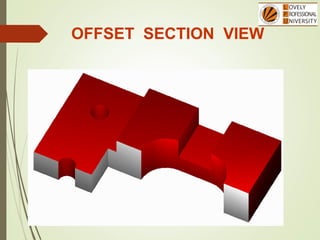
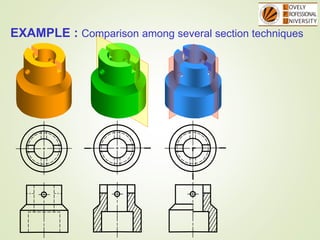
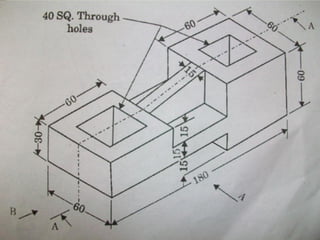
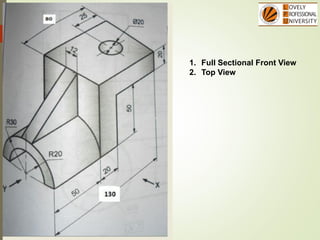
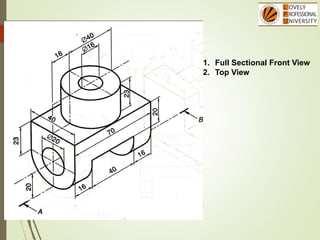
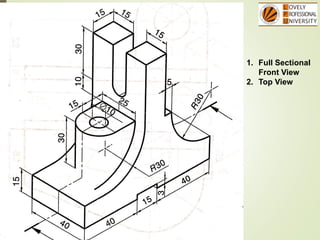
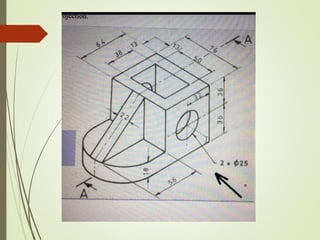
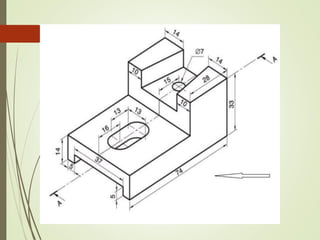
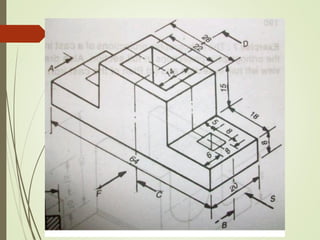
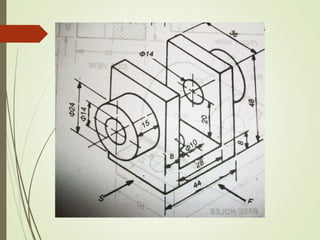
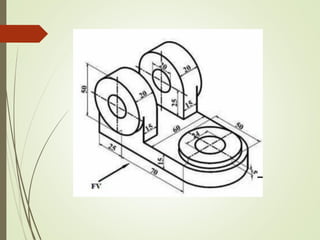
The document discusses sectional orthographic projections, focusing on their purpose to reveal internal shapes by reducing hidden lines and utilizing cutting planes. It describes various types of sections including full, half, and offset sections, along with guidelines for drawing section lines and symbols representing different materials. Common practices and mistakes in section lining are also highlighted to ensure clarity in depicting internal features of objects.