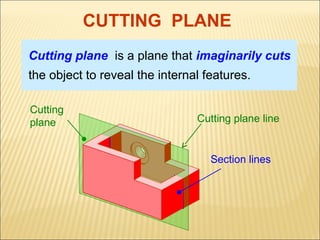
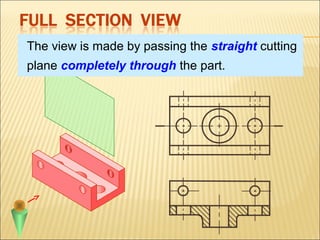
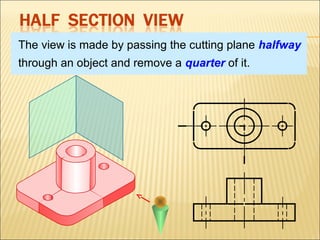
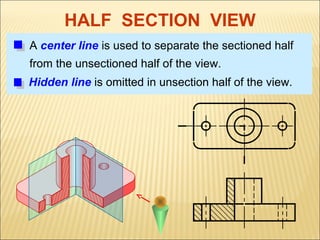
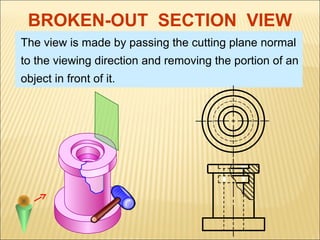
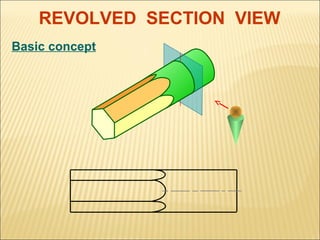
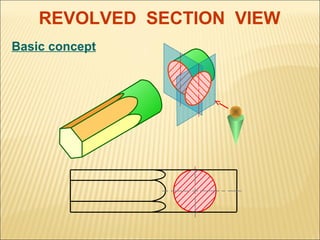
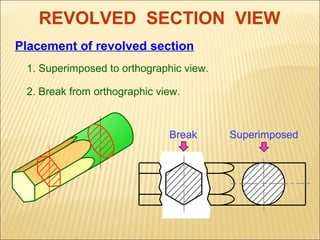
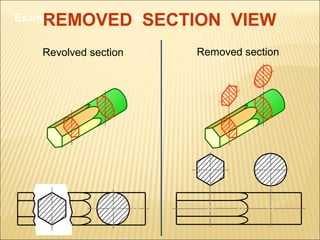
Sections are used to show interior details of objects clearly. A cutting plane line indicates where the object was cut to create the section view, and cross hatching shows cut surfaces. There are different types of section views like full, offset, half, broken-out, revolved, and removed sections. Revolved sections rotate a cross section to show features that vary, while removed sections separate the section view from the main view when space is limited.