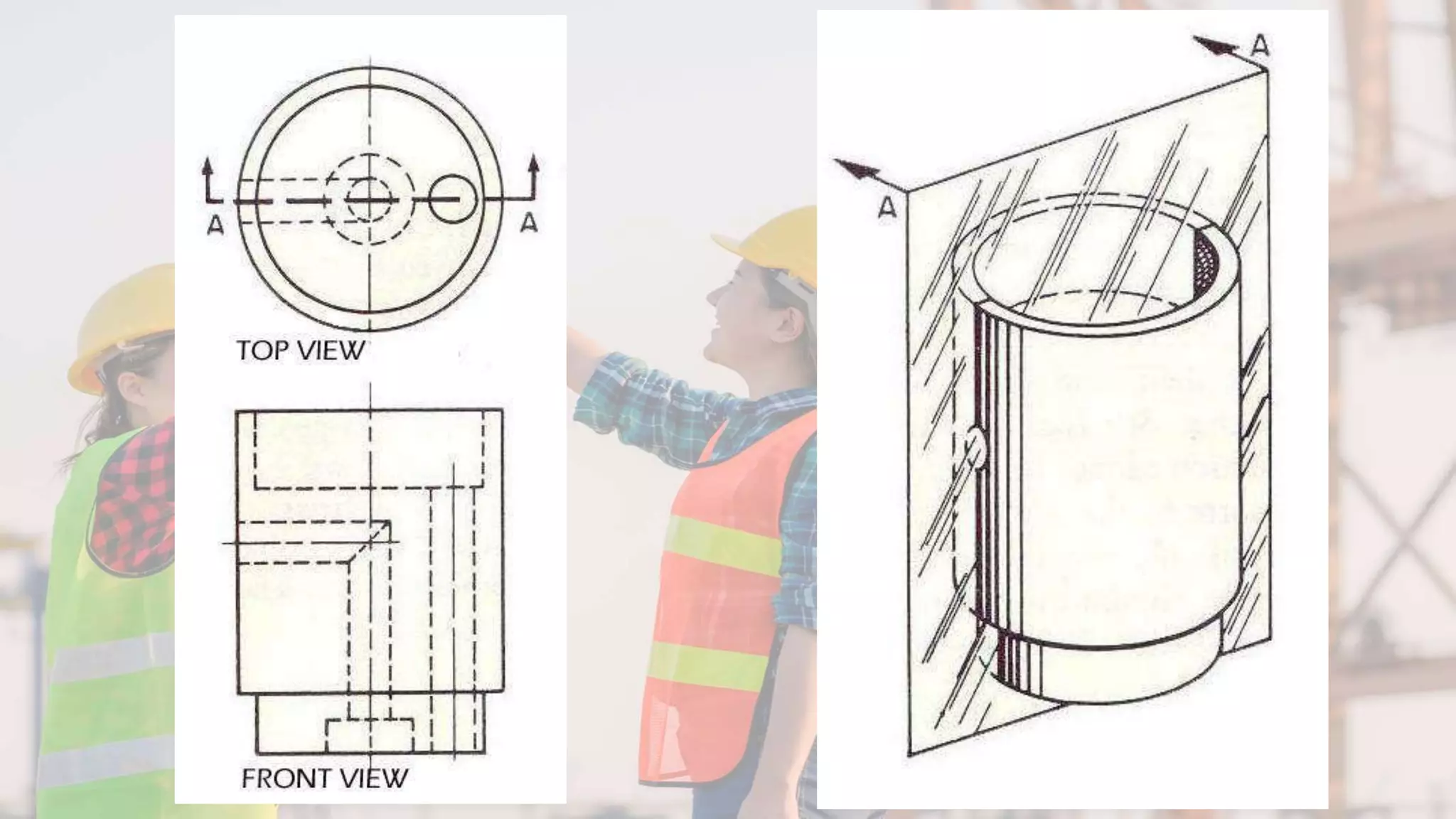
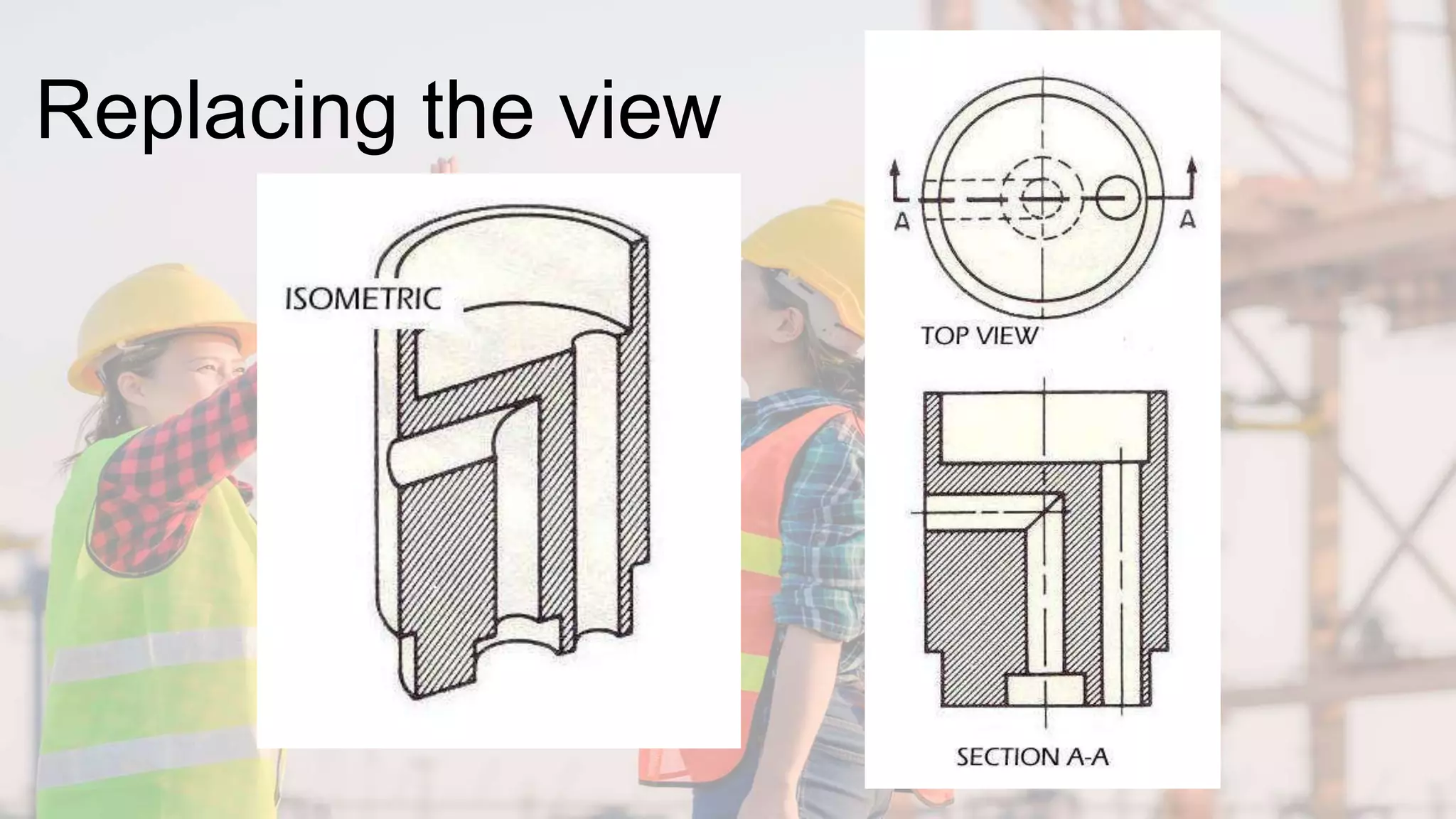
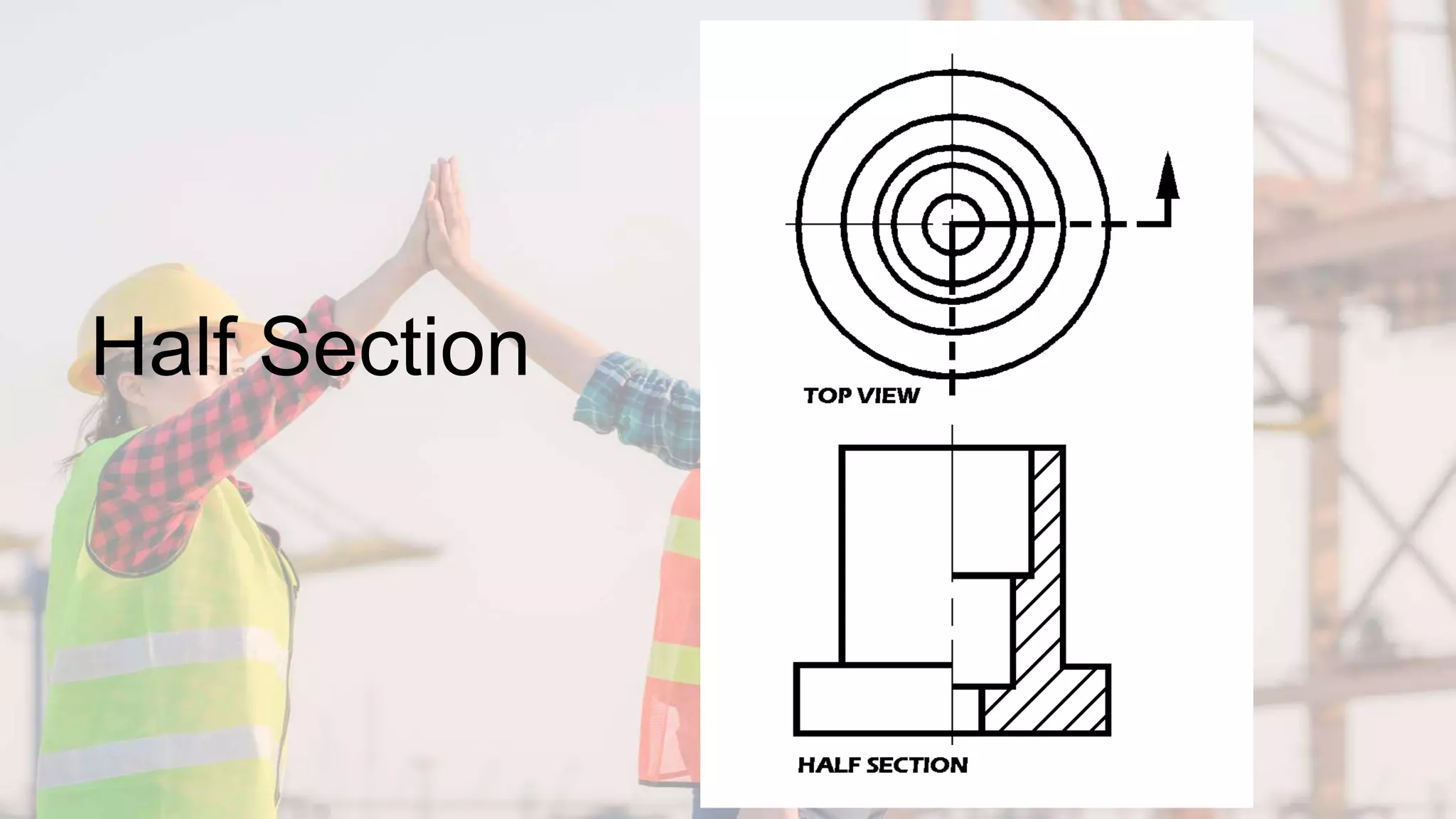
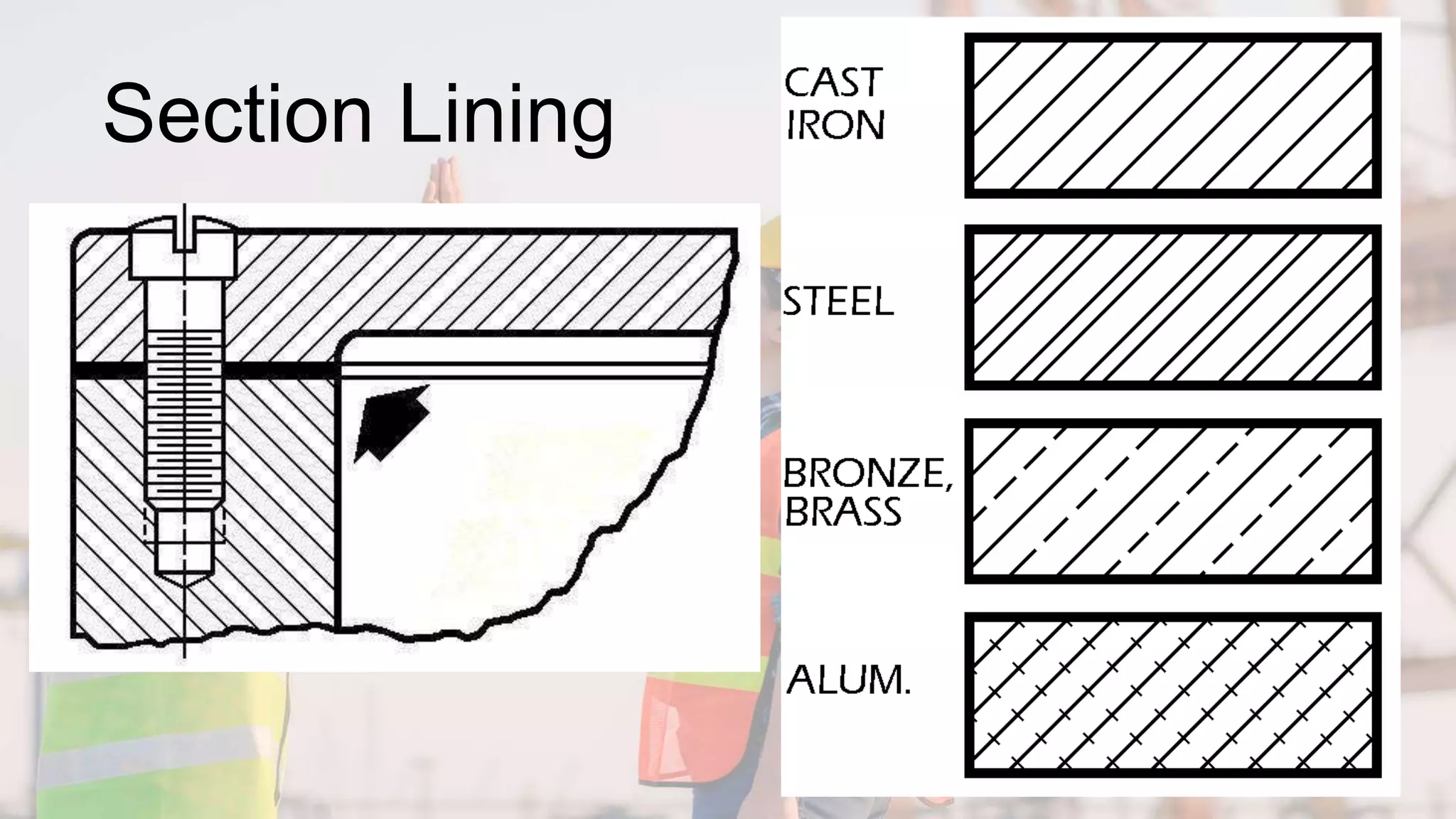
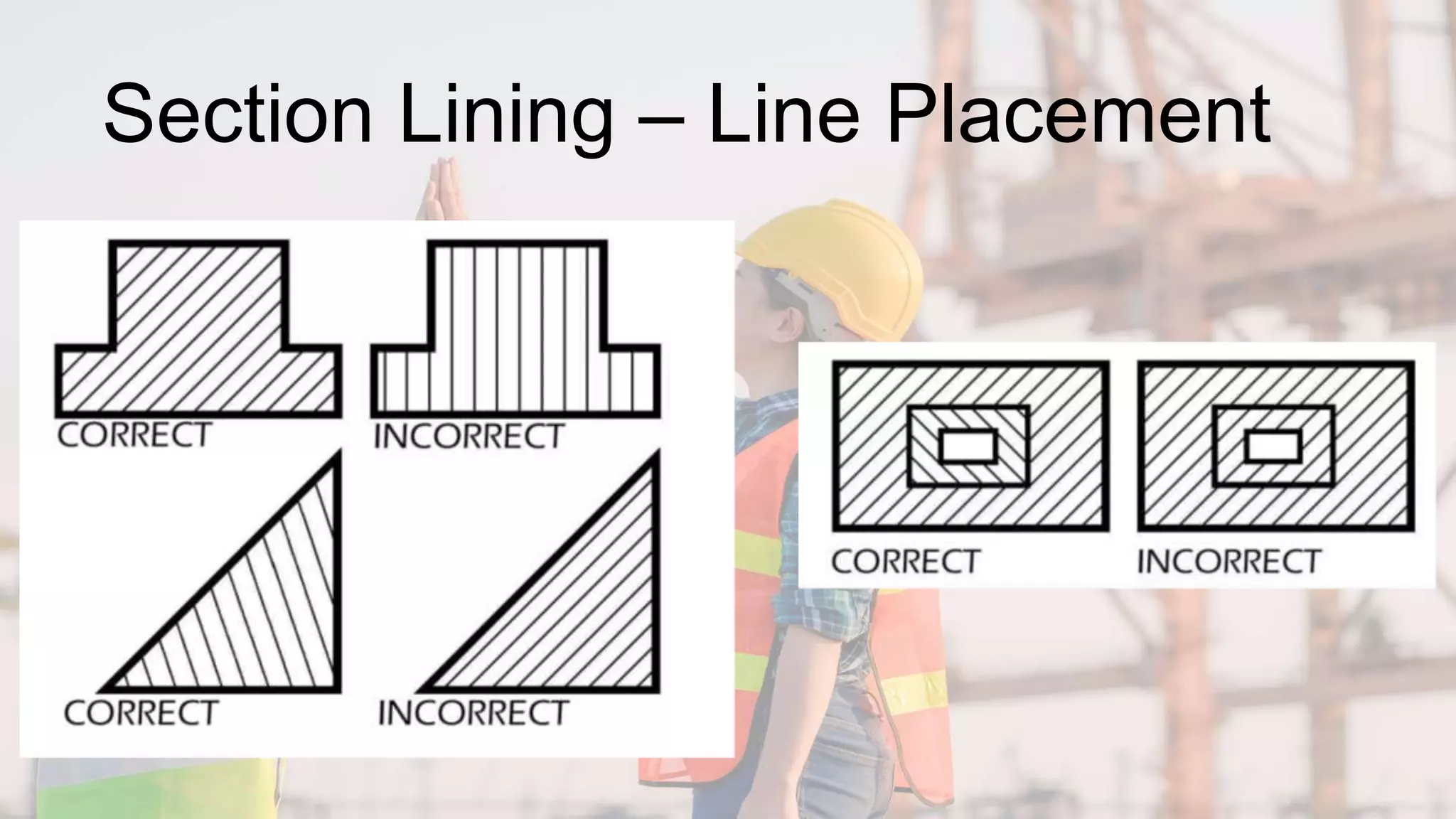
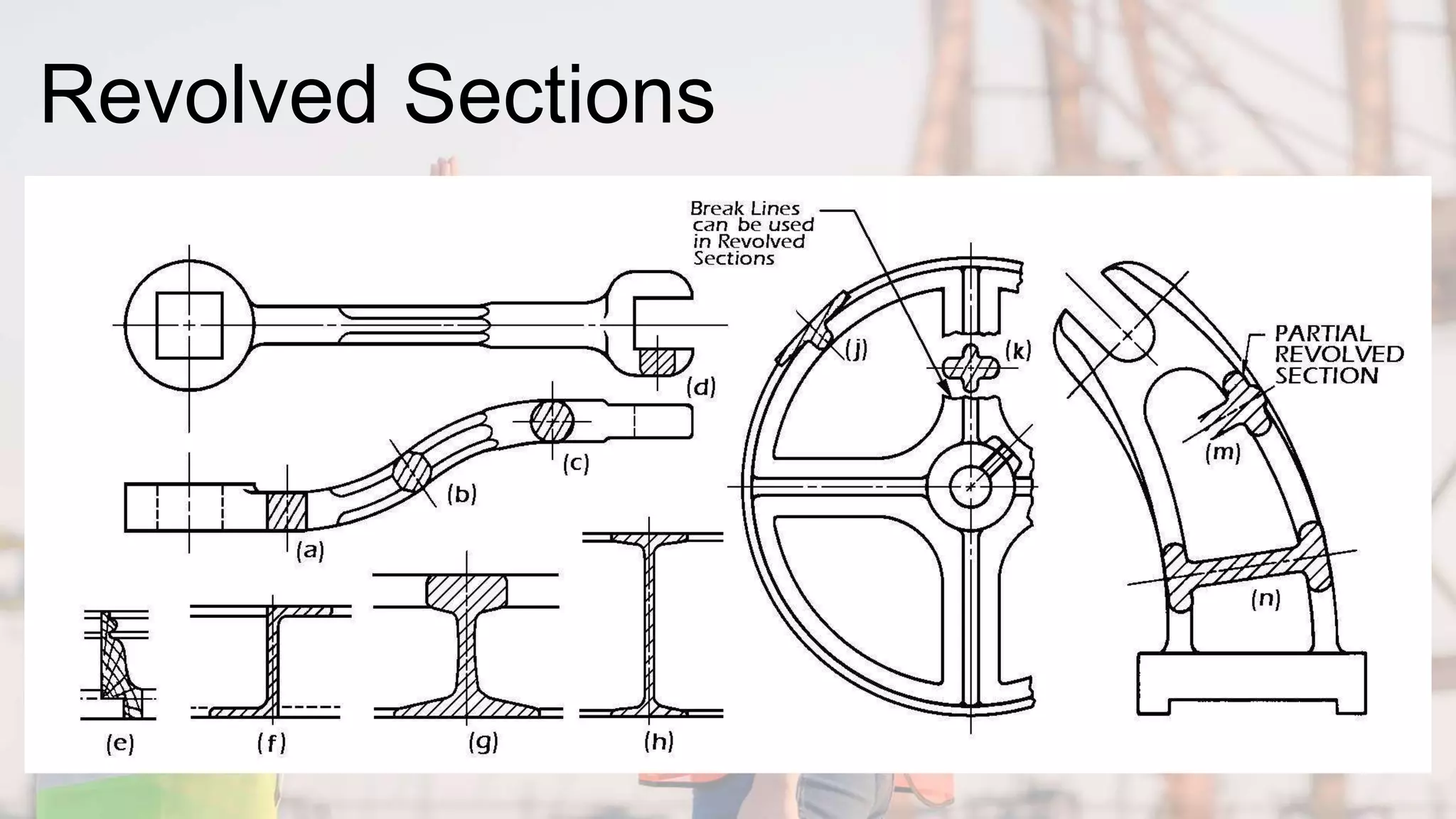
A section view shows hidden or internal parts of an object by imagining a cut through the object. There are several types of section views defined by the path of the cutting plane, including full sections where the cut fully passes through, half sections where the cut is halfway through, and offset sections where the cutting plane is not straight. Section lines are used in cut areas to indicate cut material and are placed at varying angles for clarity.