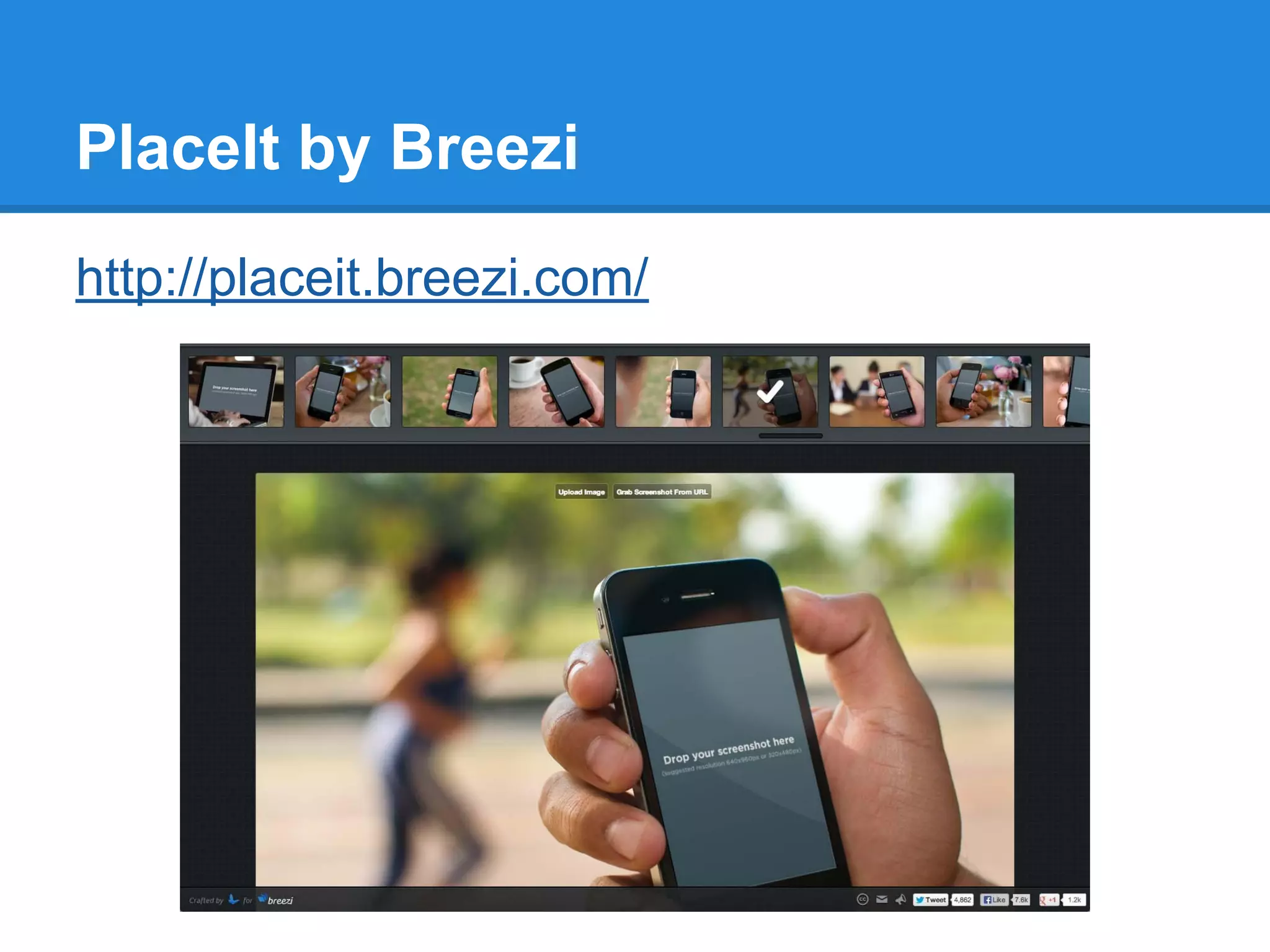
This document provides an introduction to Bootstrap, an open-source front-end framework for building responsive mobile-first websites and web applications. It discusses the basics of web development using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It then explains what Bootstrap is, how to add it to a website, and how to use its grid system, forms, buttons, and other common elements. Resources for using, customizing and finding additional components for Bootstrap are also provided.











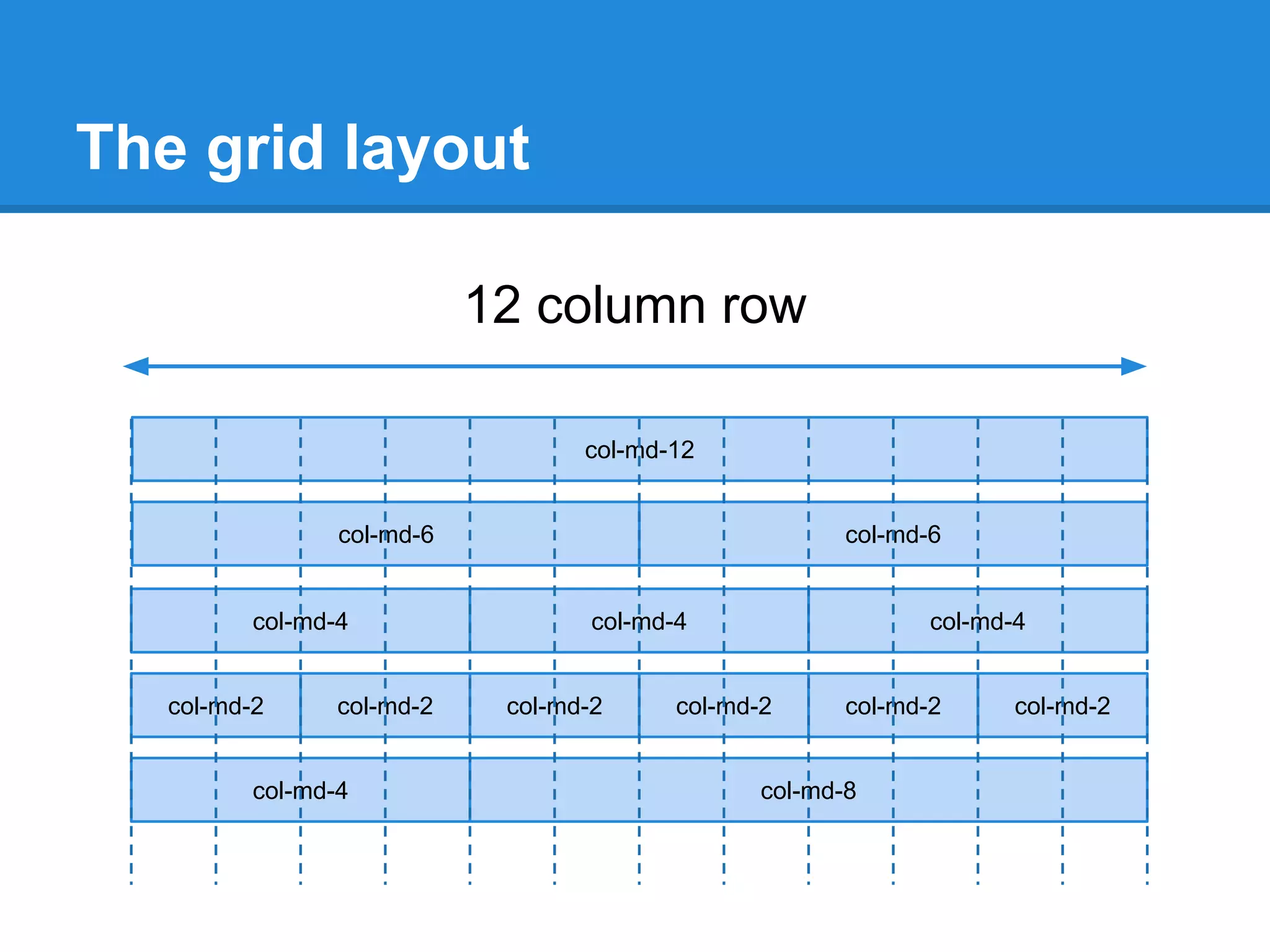

![The grid (cont.)
Bootstrap 3 features an always-responsive grid with a
maximum size:
1. col-xs-[num] grids have no maximum size (fluid)
2. col-sm-[num] grids resize up to 750px
3. col-md-[num] grids resize up to 970px
4. col-lg-[num] grids resize up to 1170px
You should choose col-md or col-lg for desktop sites.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bootstrap-130926104326-phpapp02/75/Introduction-to-Bootstrap-15-2048.jpg)