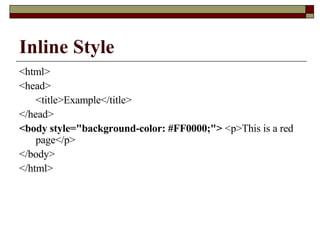
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a style sheet language used to describe the presentation of structured documents written in HTML. CSS controls the layout of multiple documents from a single style sheet and allows for more precise control over layouts and different styles for different media like screens and print. CSS syntax uses selectors to apply styles denoted by properties and values to HTML elements. Styles can be applied inline, internally in the <style> tag, or externally in a separate .css file linked via the <link> tag.