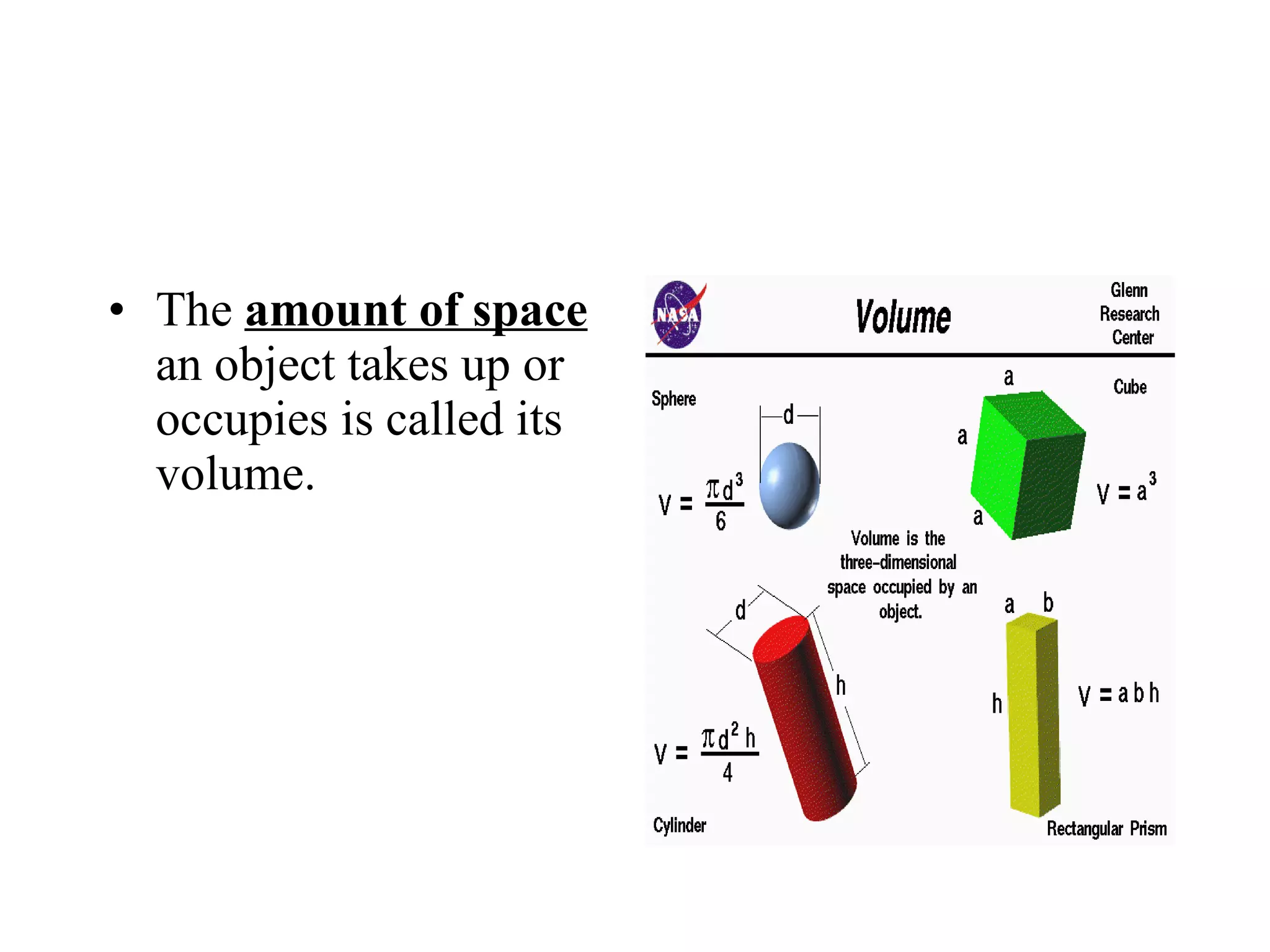
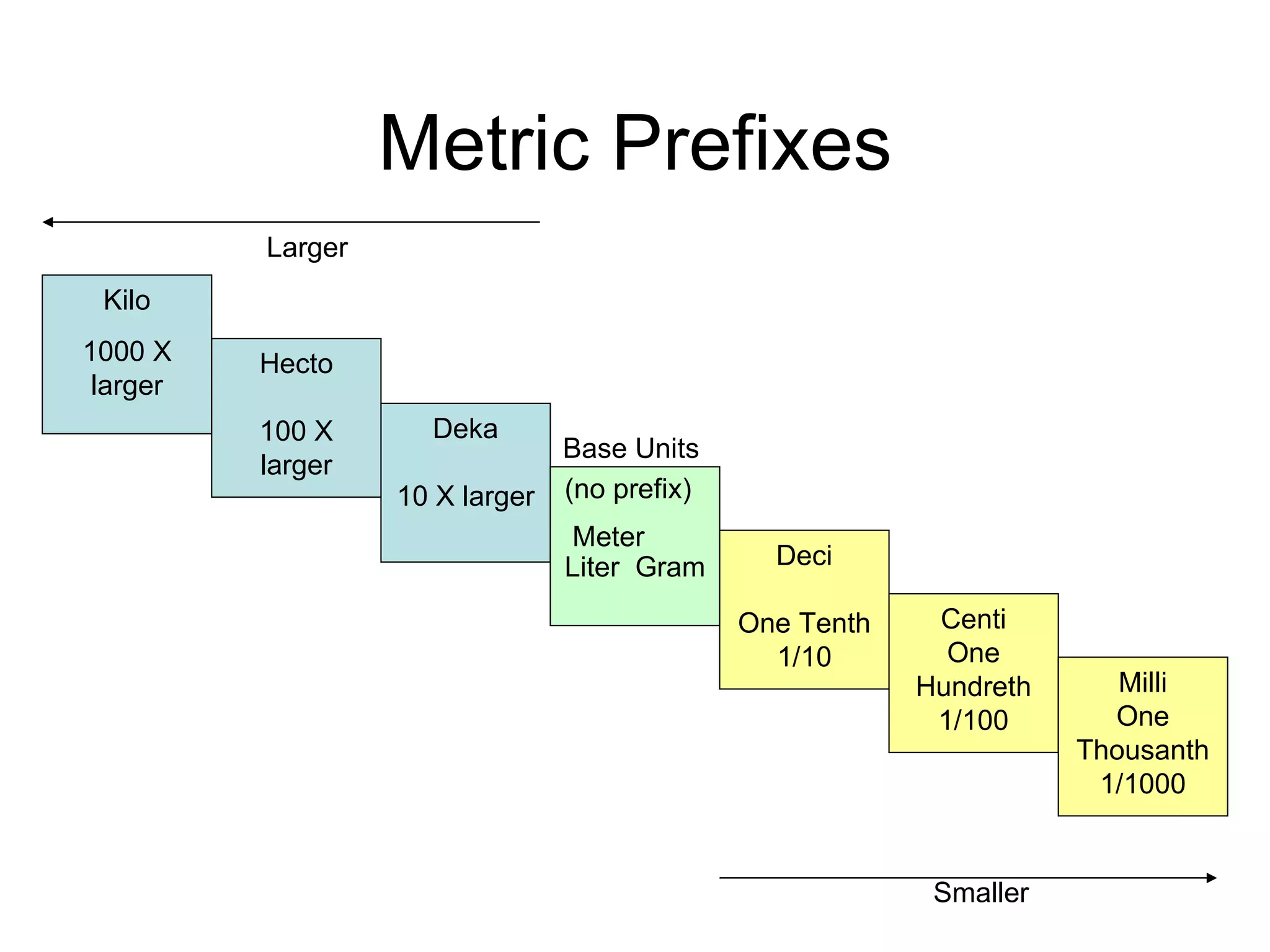
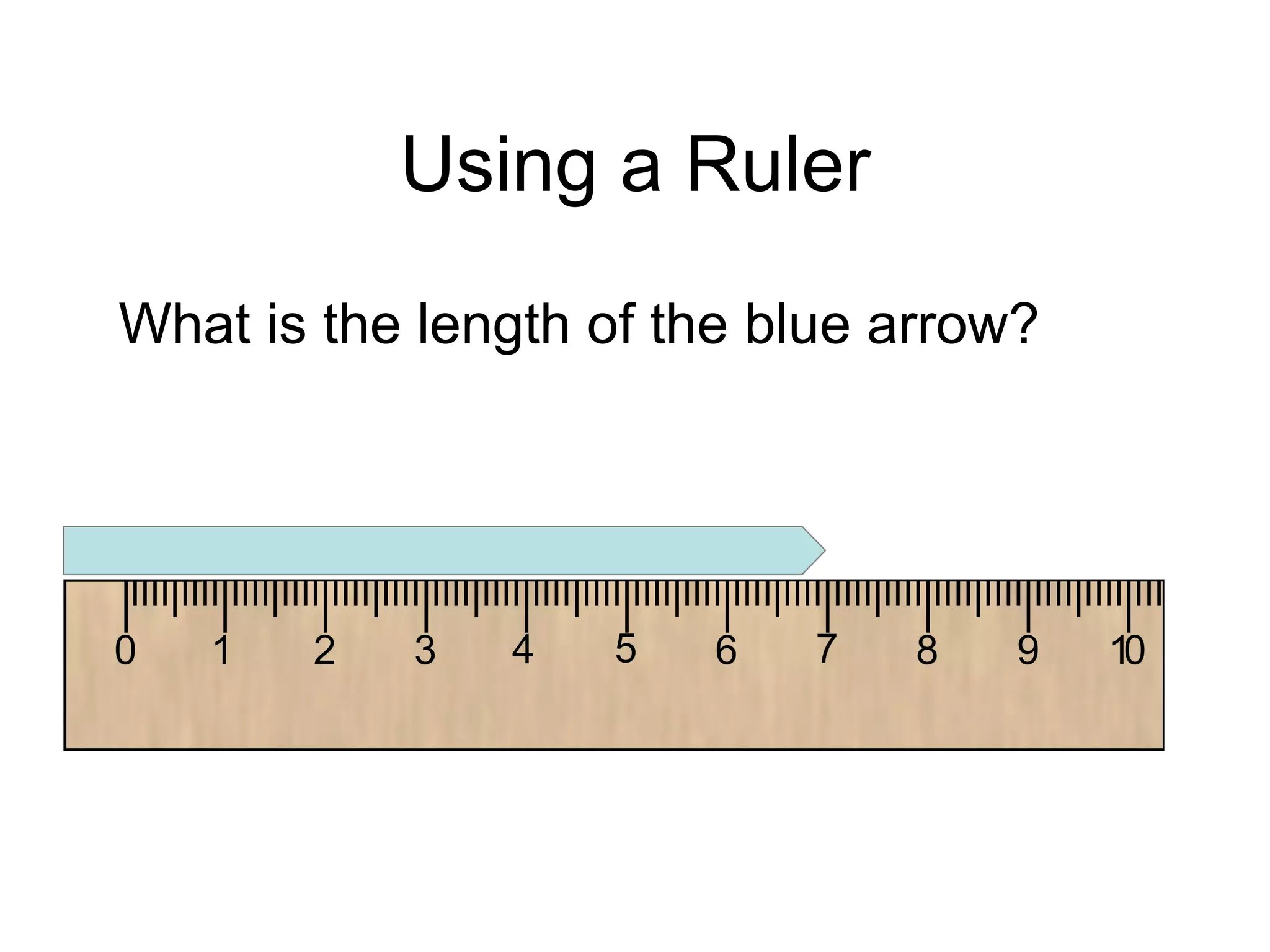
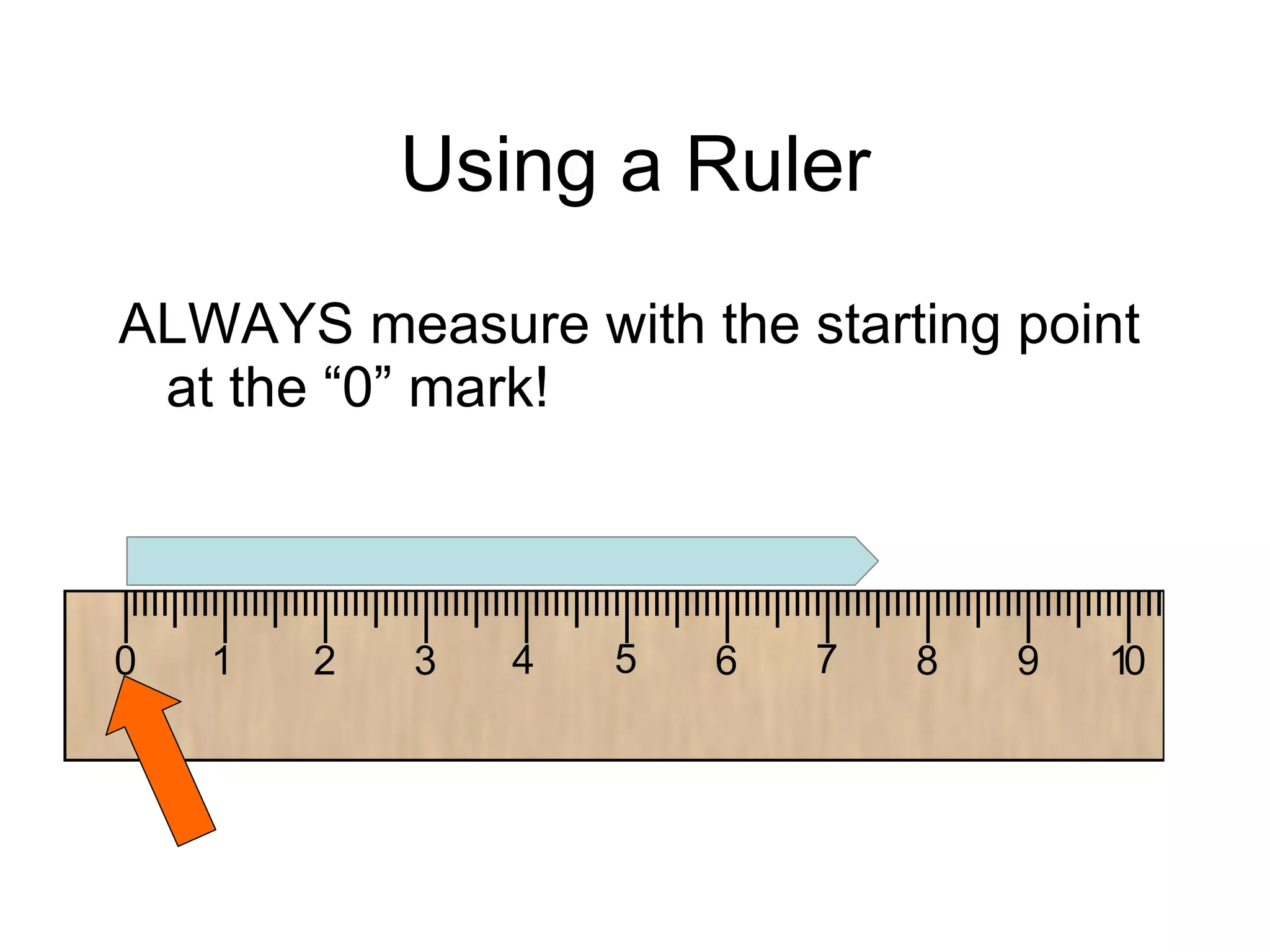
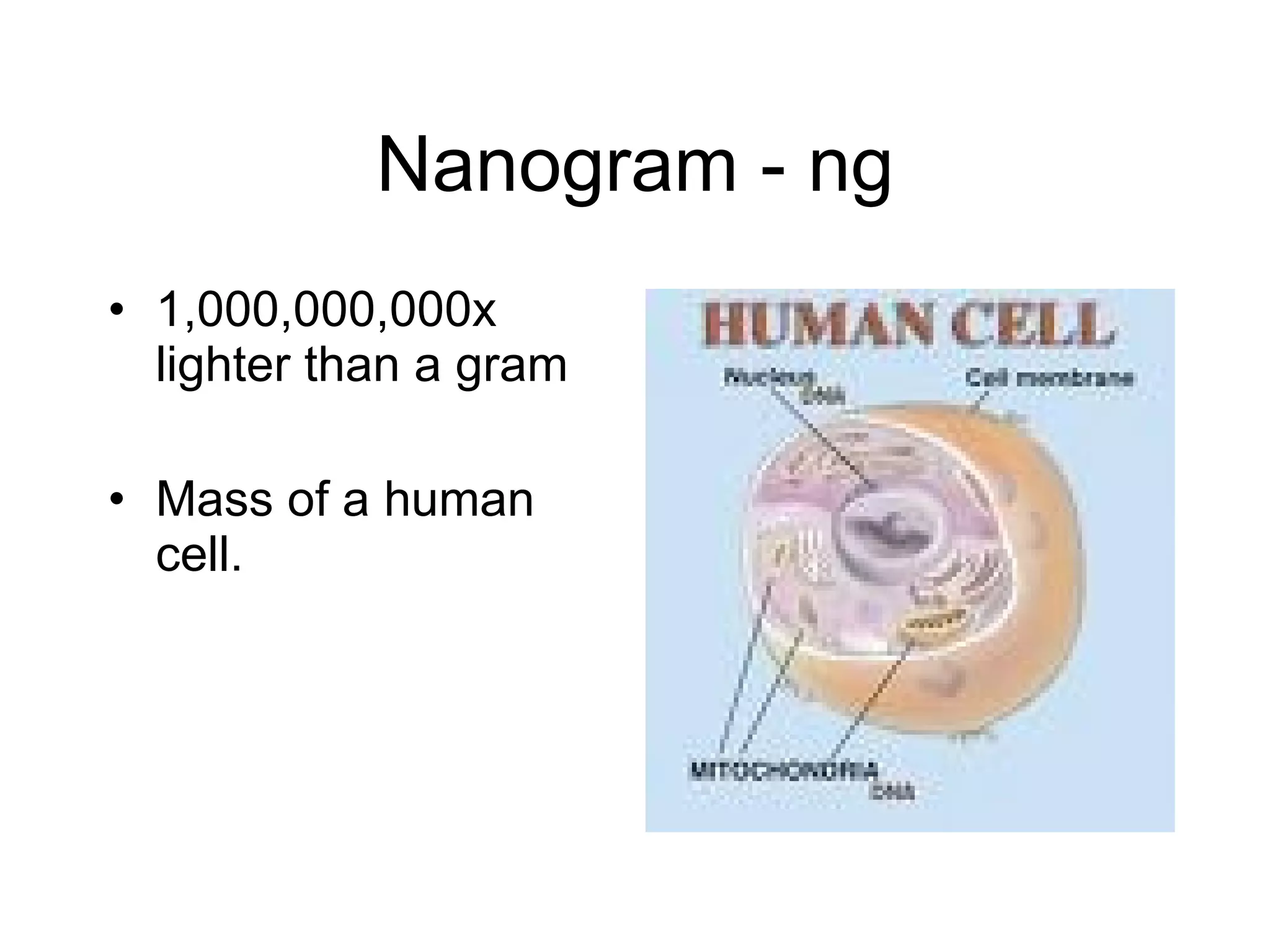
This document introduces matter and the metric system. It defines matter as anything that has mass and volume. The key properties of matter are then discussed as mass, weight, volume, and density. The metric system is introduced as being based on powers of 10 for consistent measurement units. The basic metric units of the meter, liter, and gram are covered along with common metric prefixes and their meaning in terms of powers of 10 when placed before a base unit.