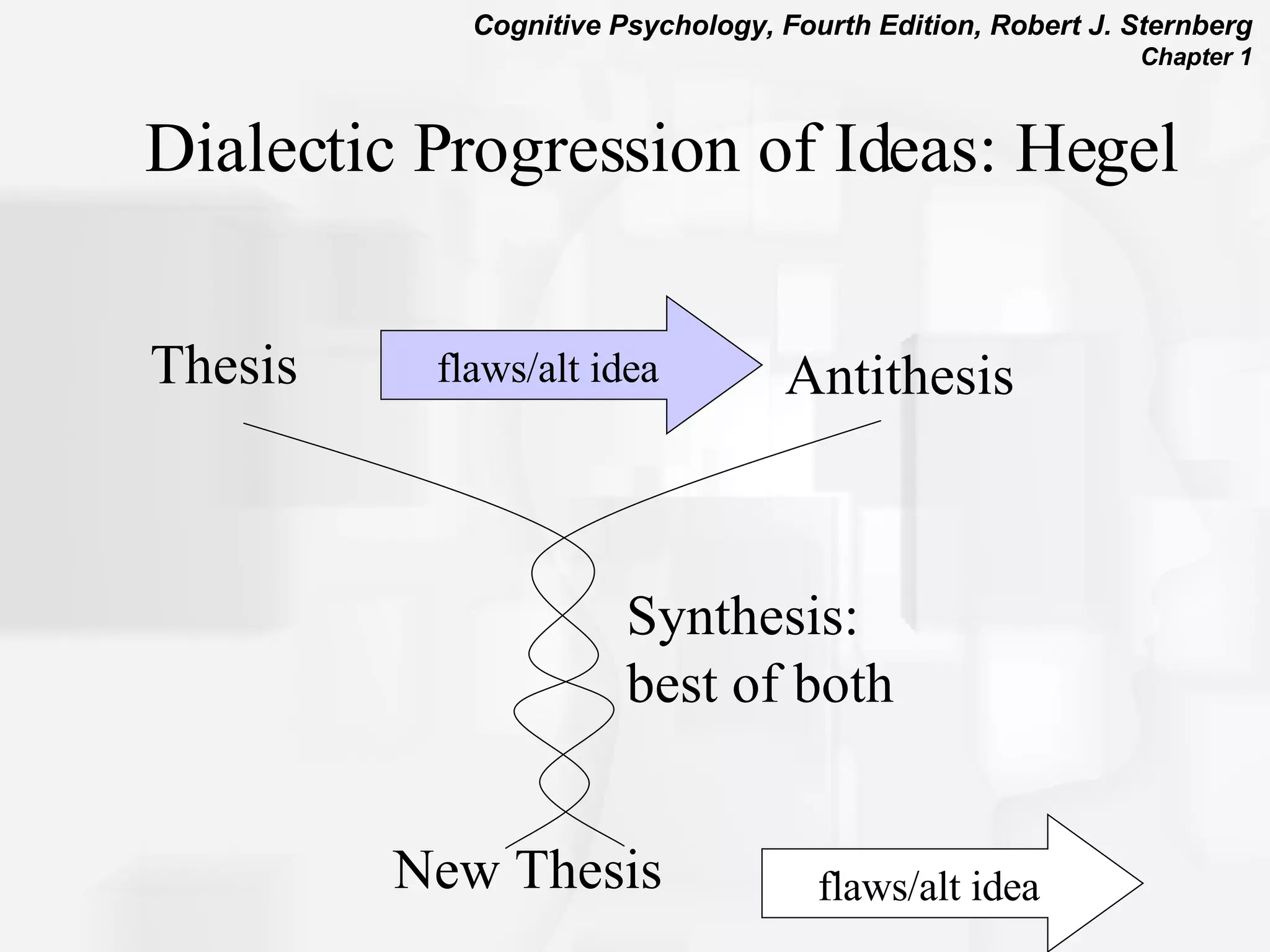
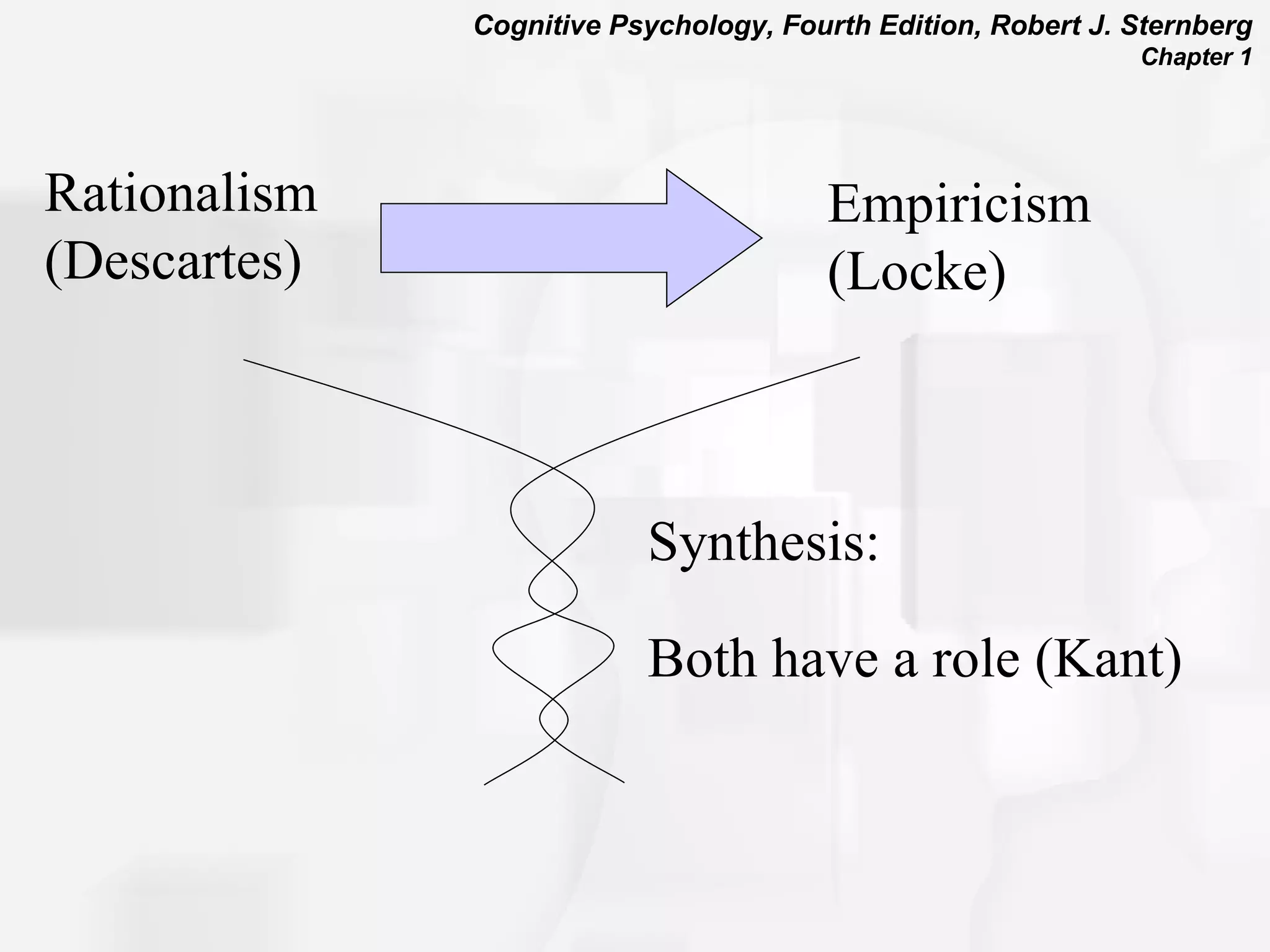
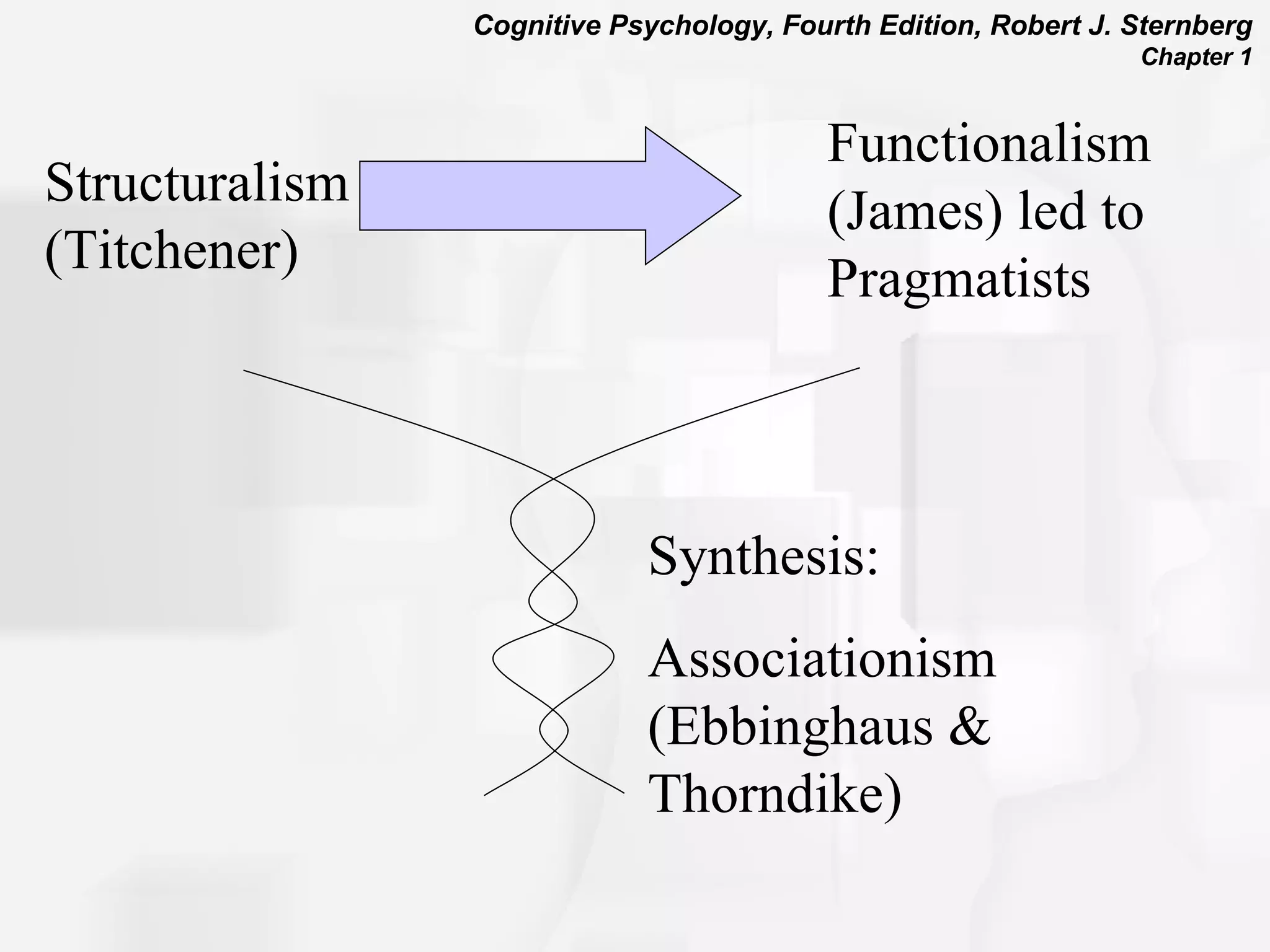
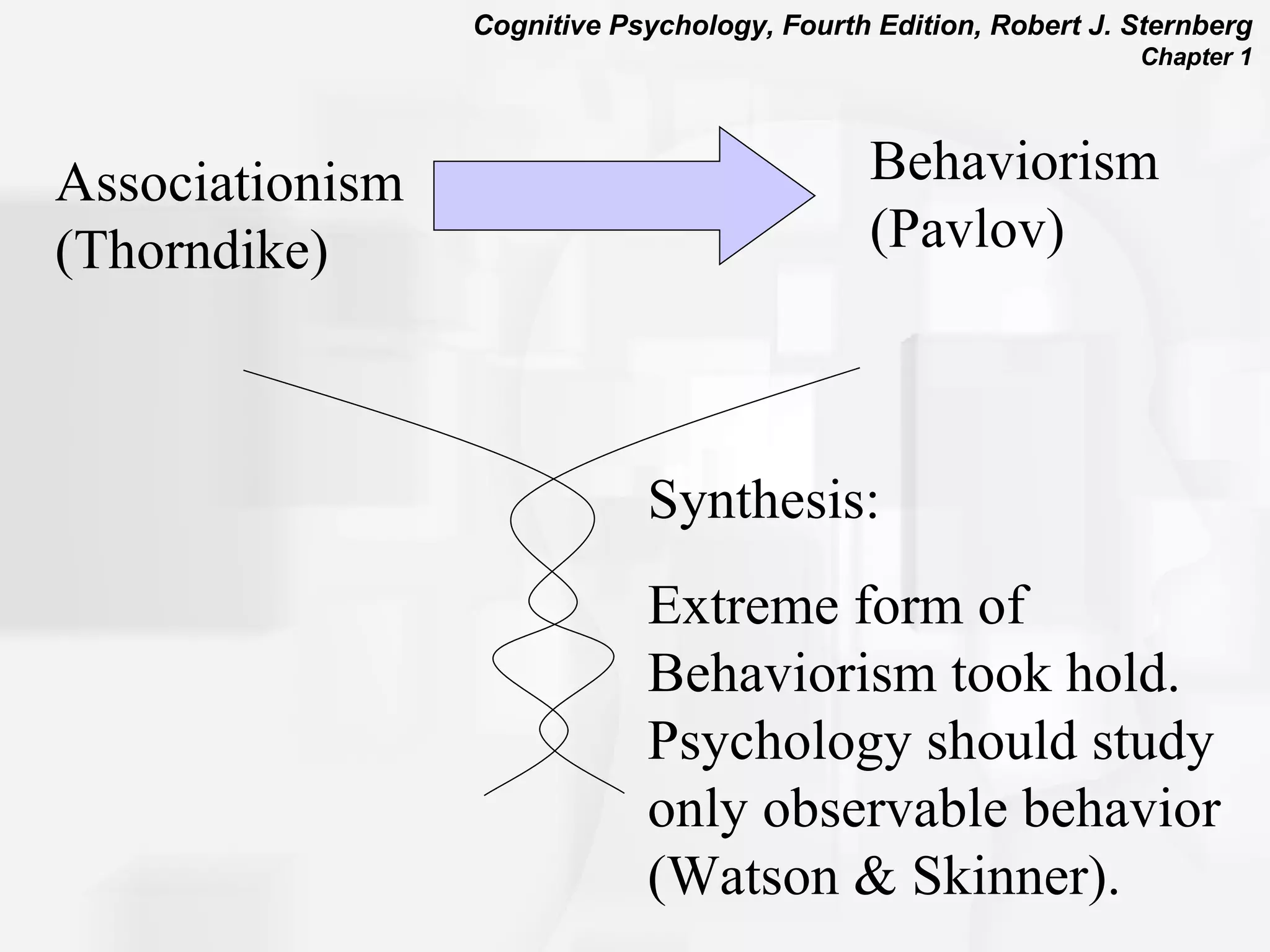
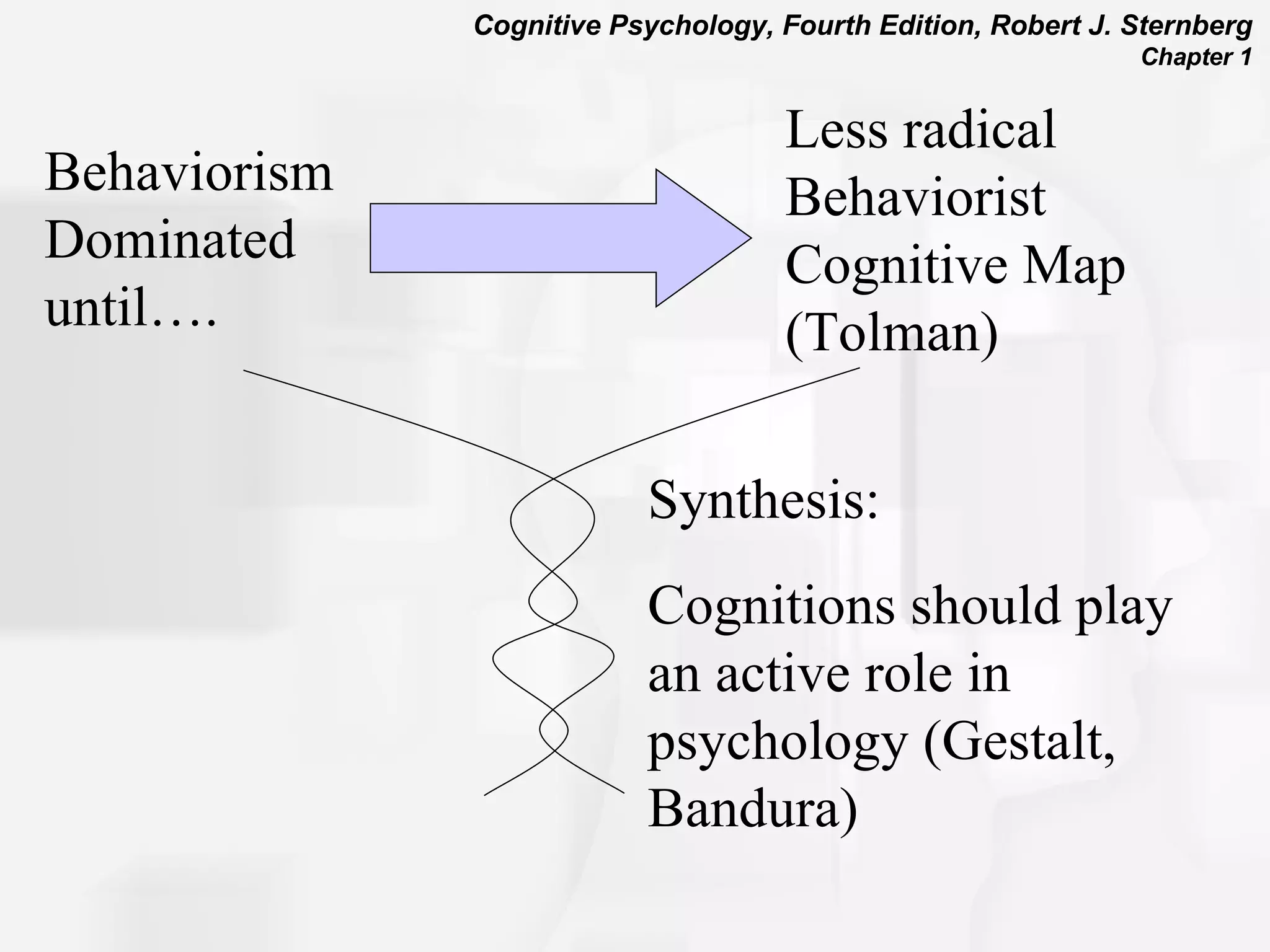
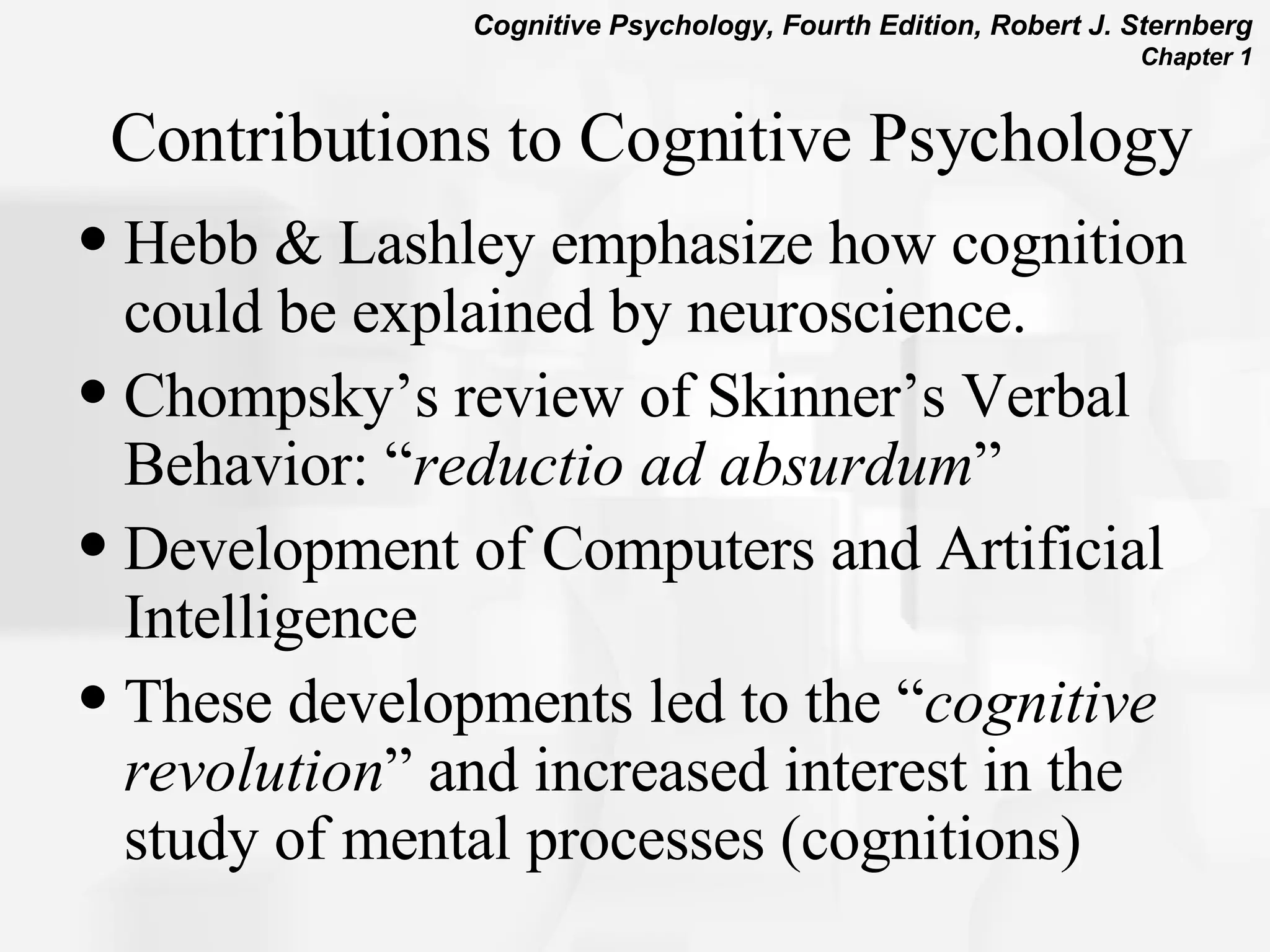
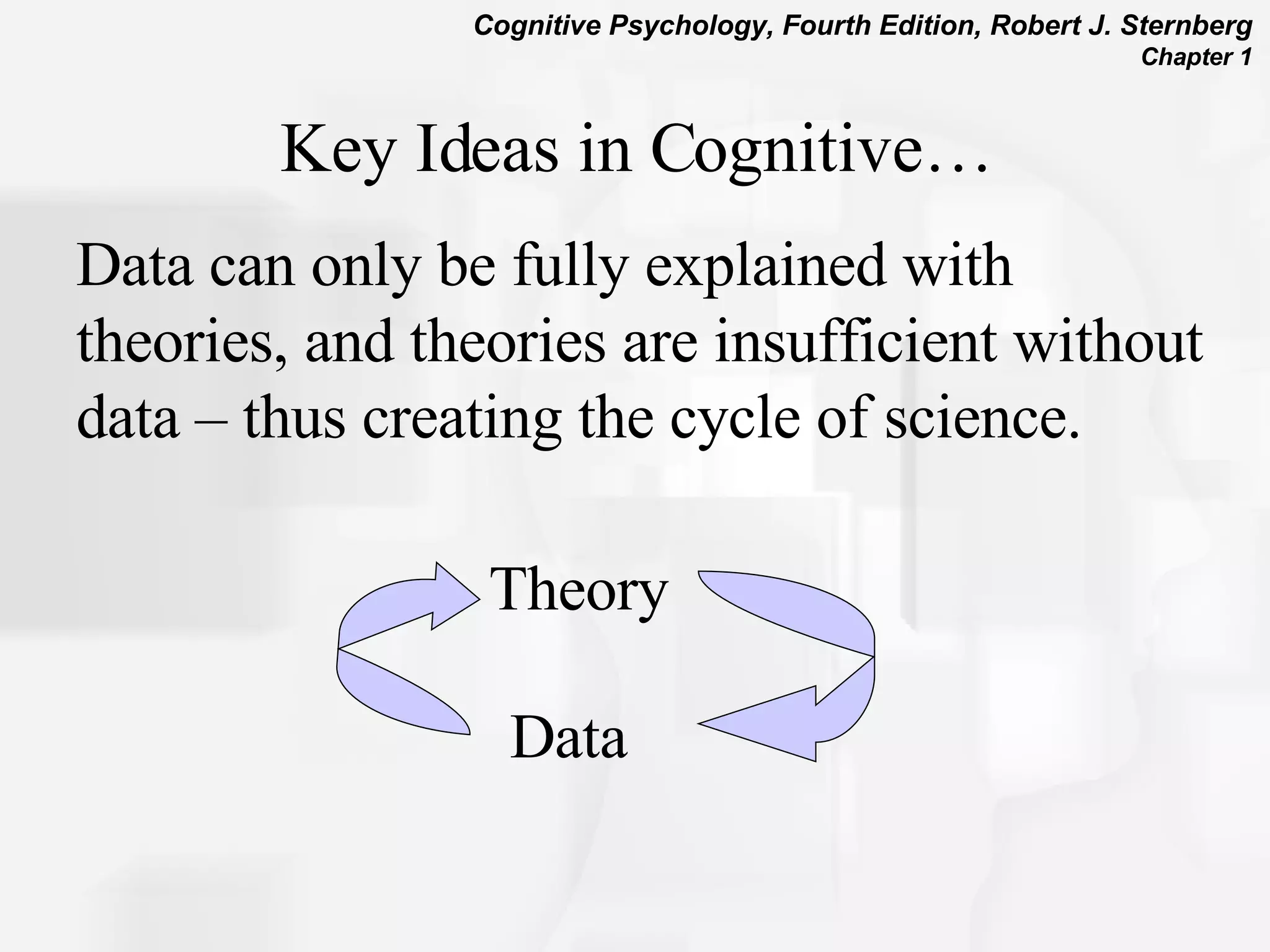
Cognitive psychology is the study of how people perceive, learn, remember, and think. It has roots in rationalism, empiricism, and their synthesis. Early approaches included structuralism, functionalism, and behaviorism. The cognitive revolution incorporated cognitions and mental processes, influenced by developments in computer science. Cognitive psychology uses experimental methods, psychobiological studies, self-reports, case studies, and computer simulations to understand phenomena like attention, problem solving, memory, decision making, language, and reading.