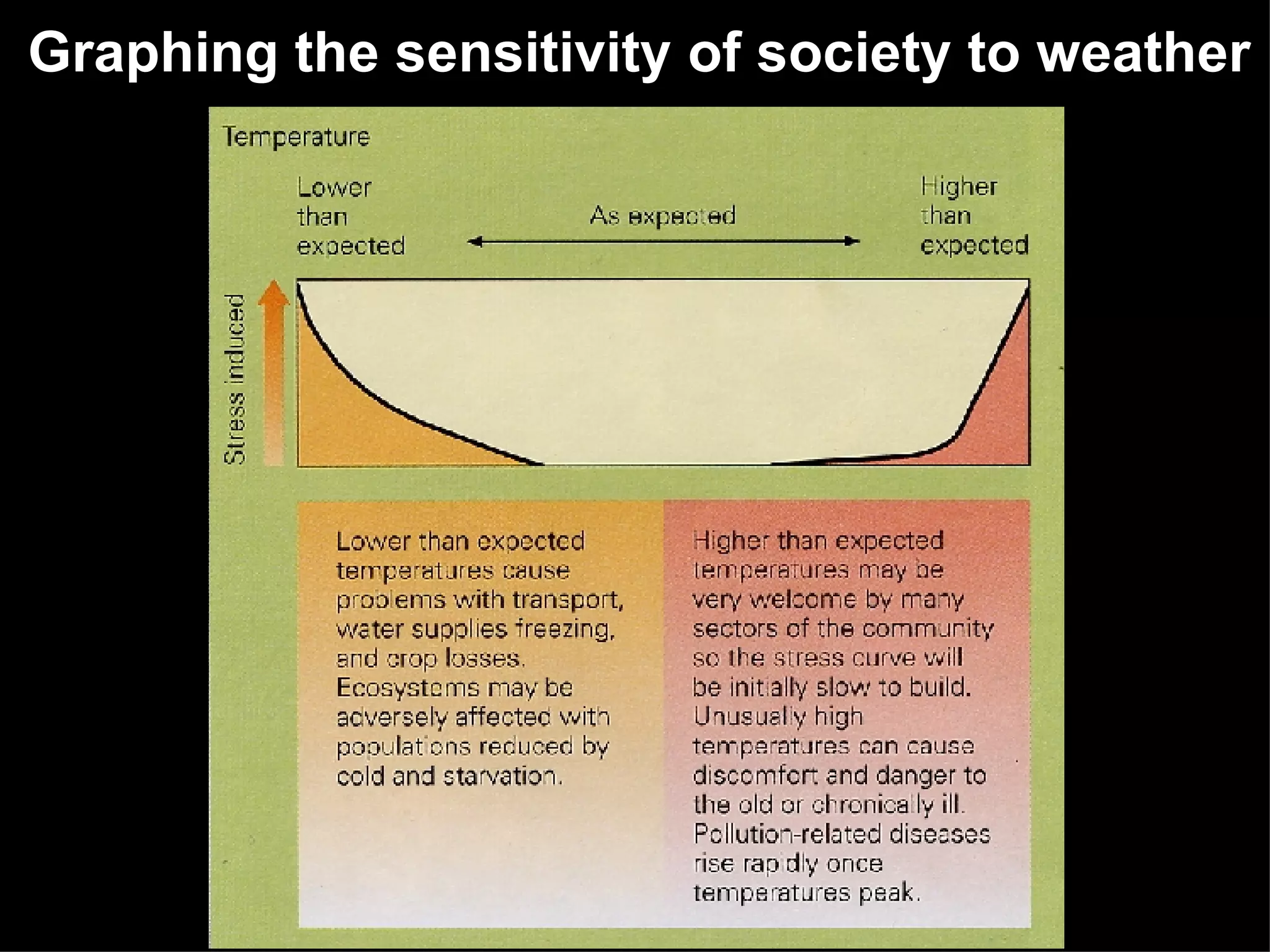
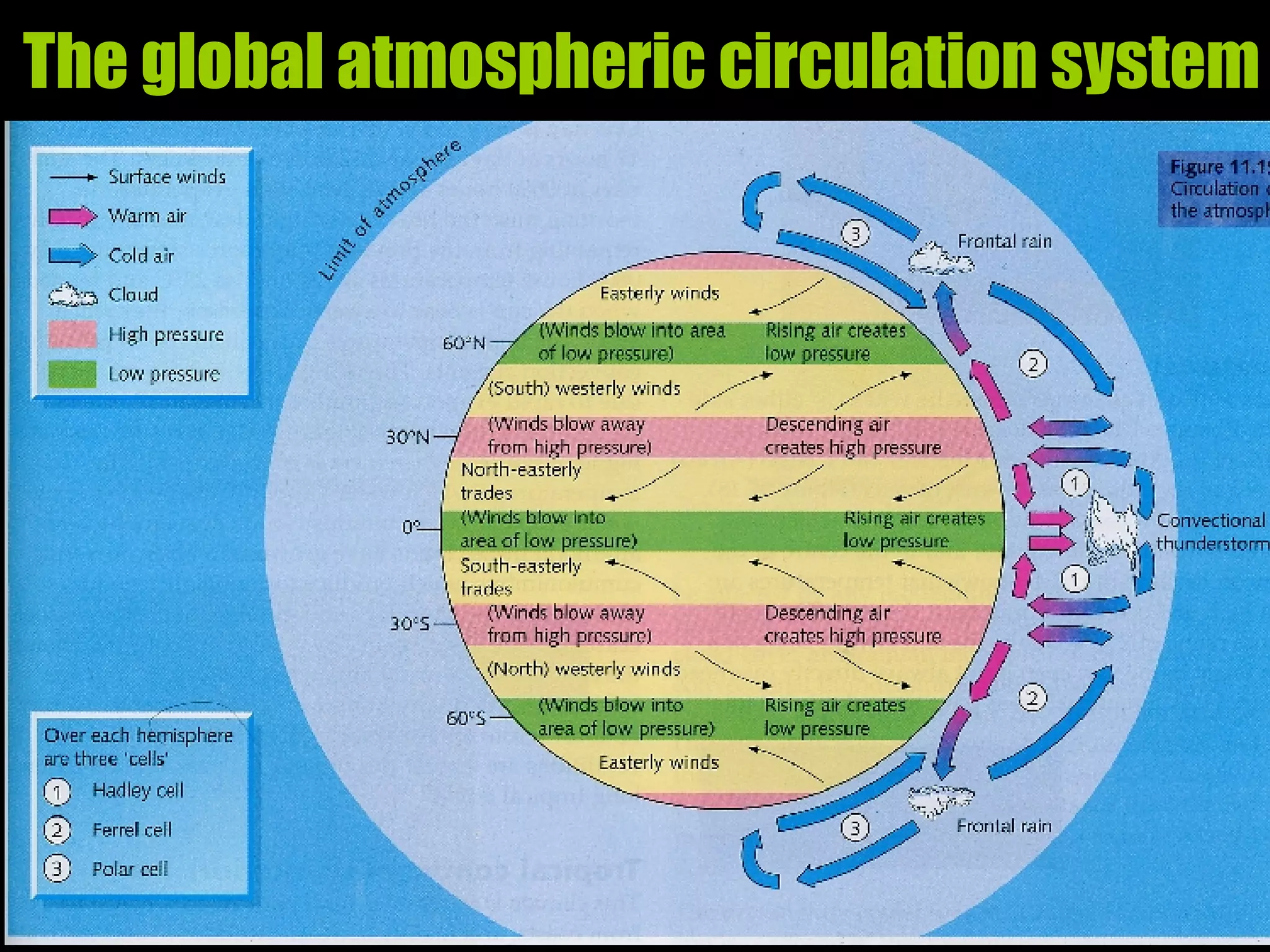
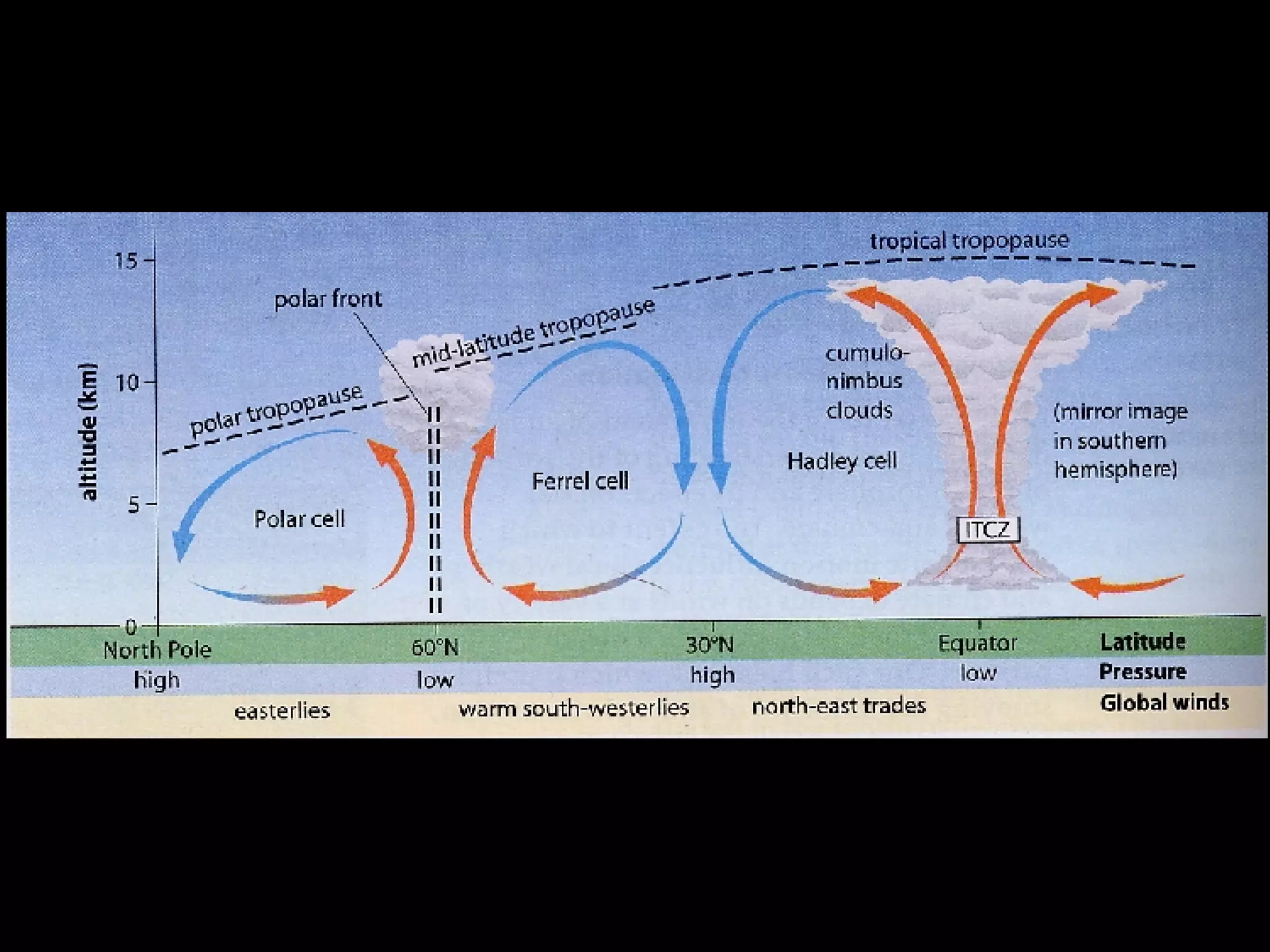
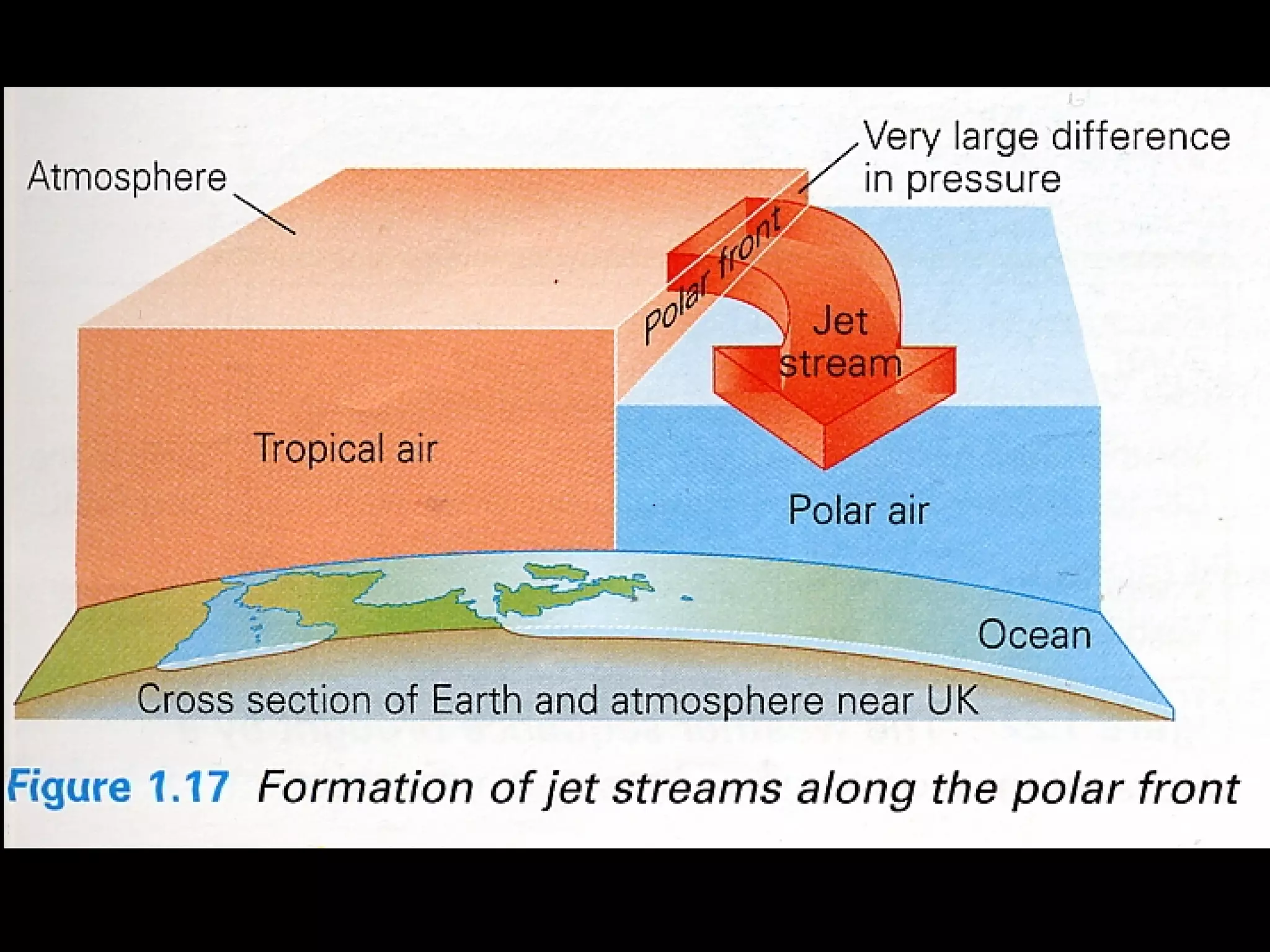
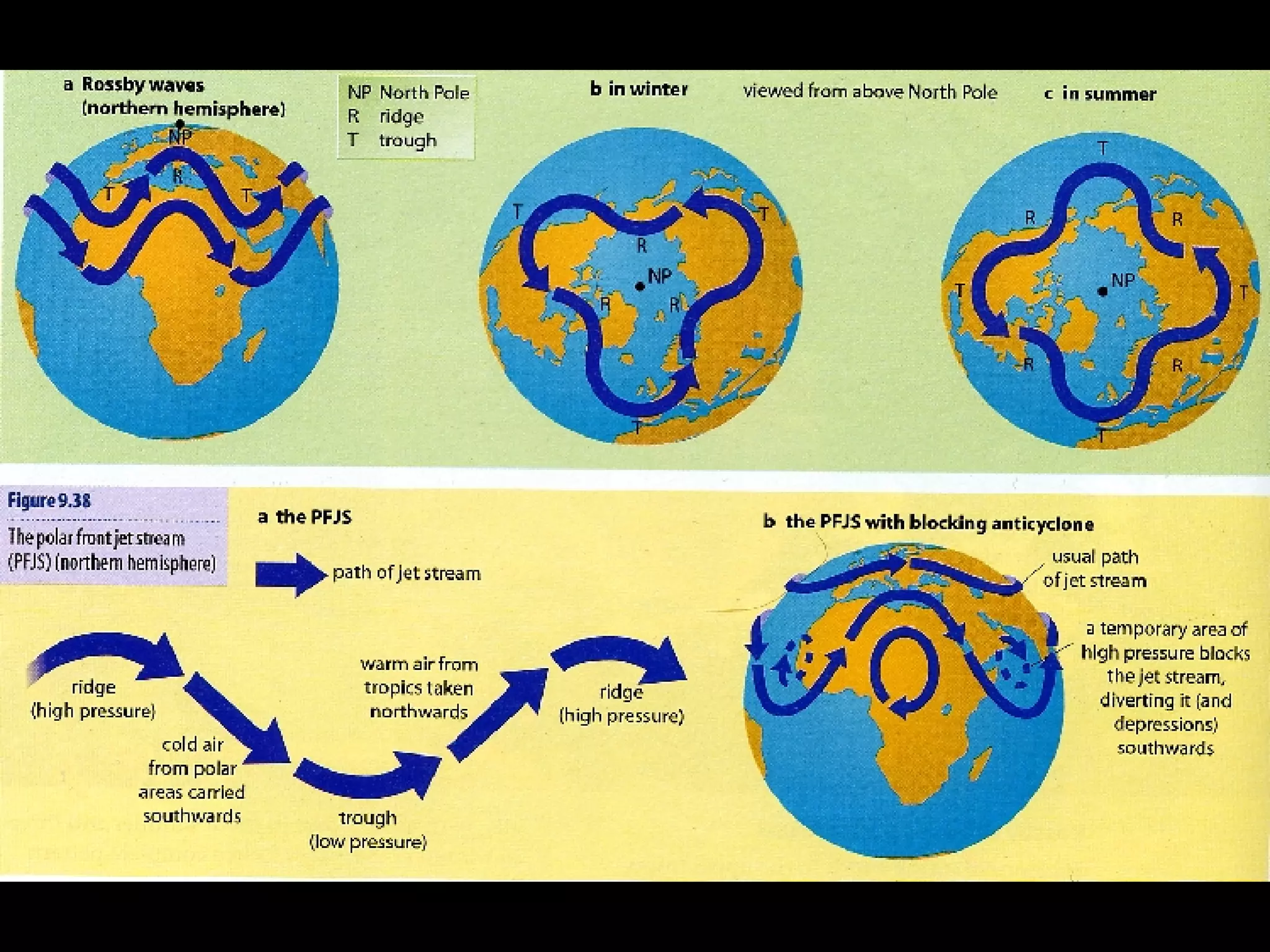
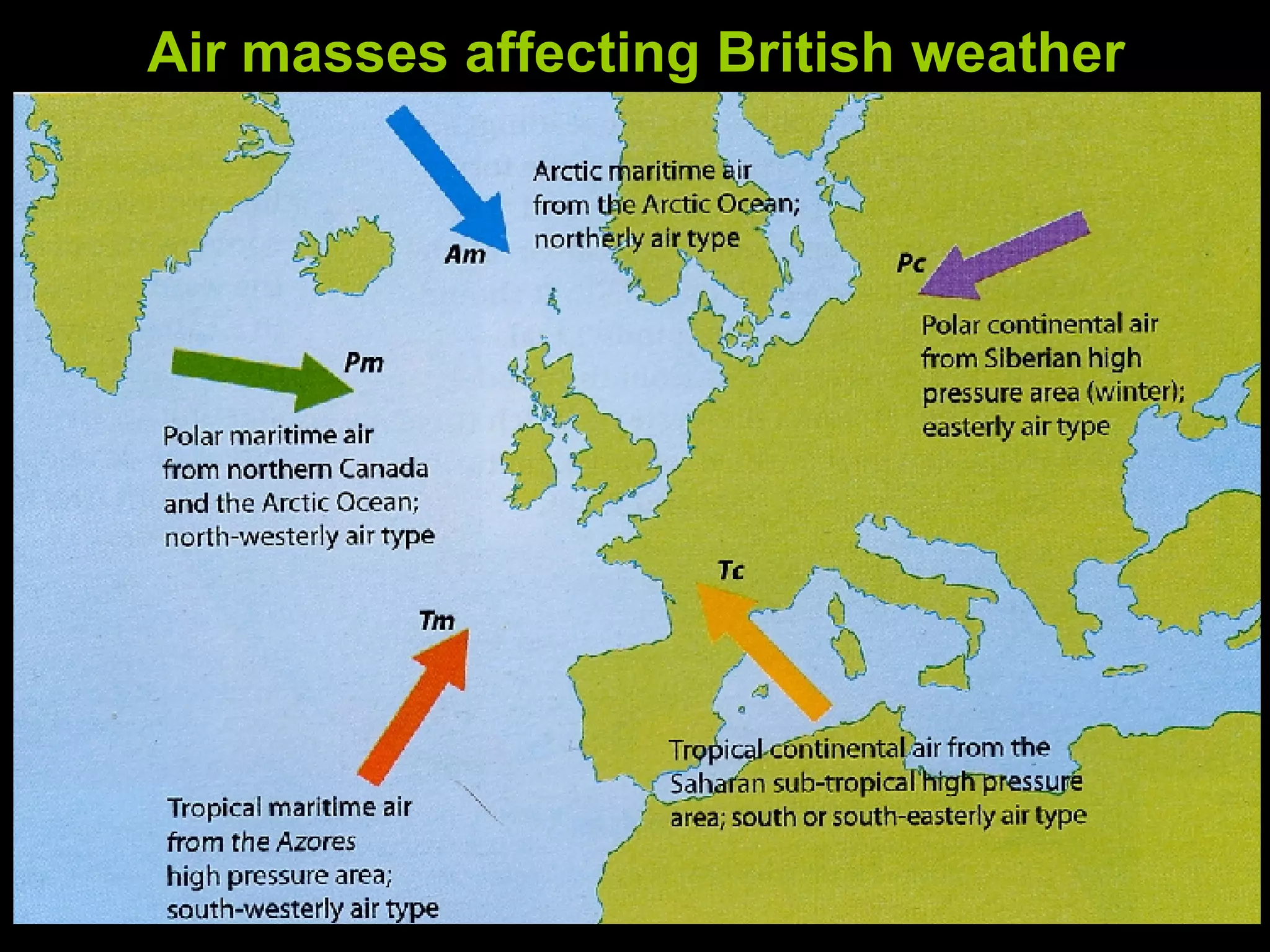
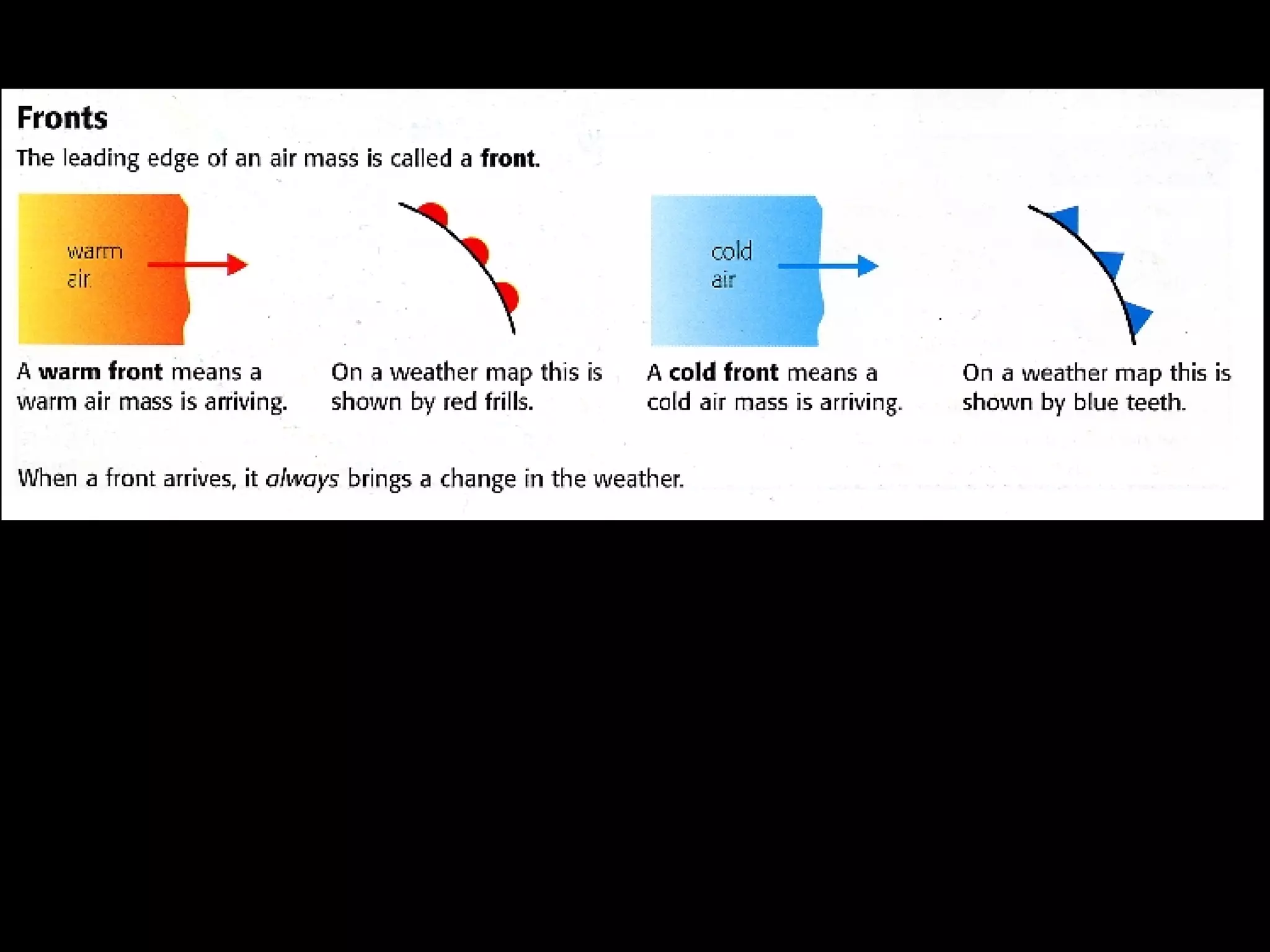
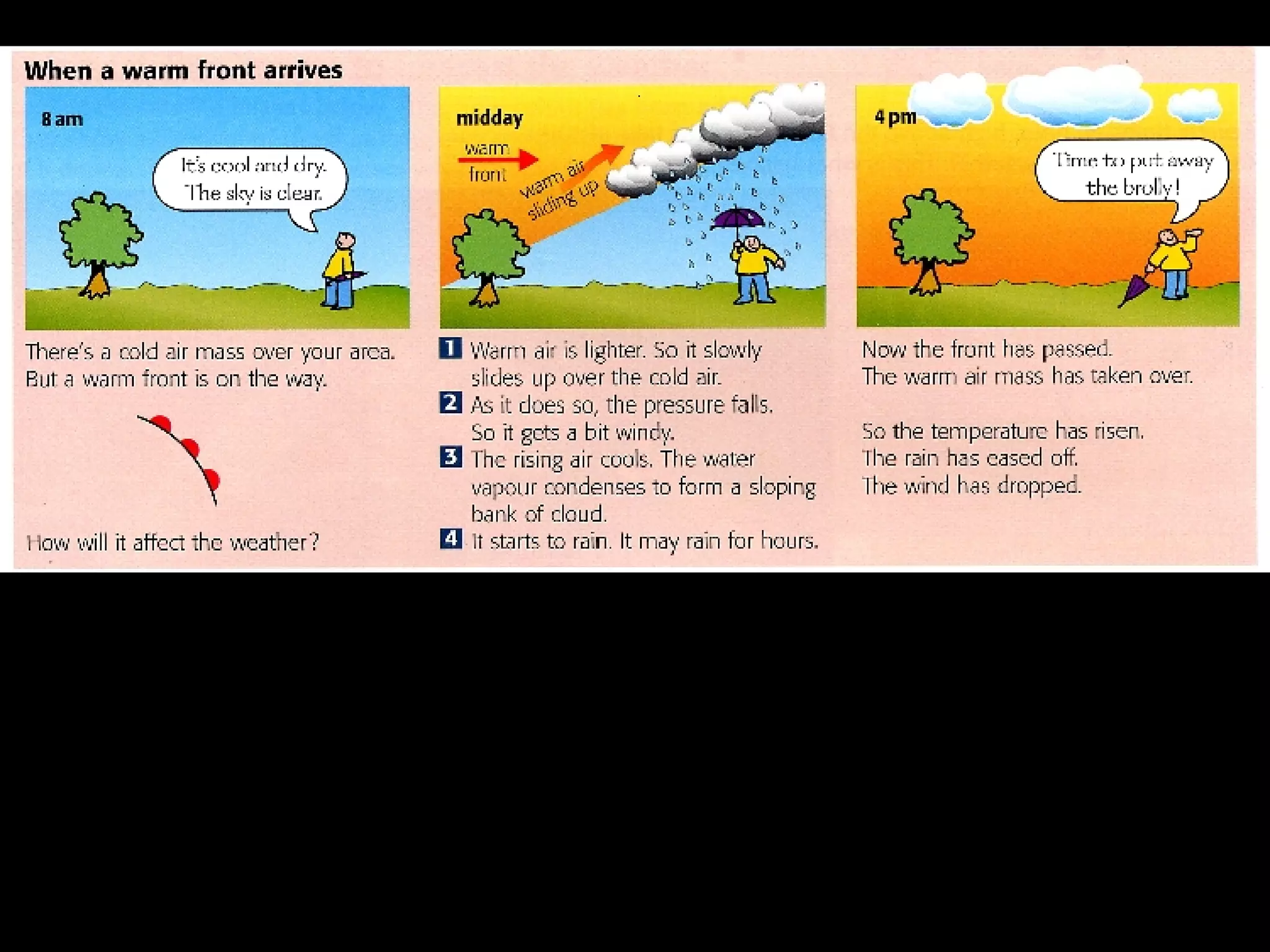
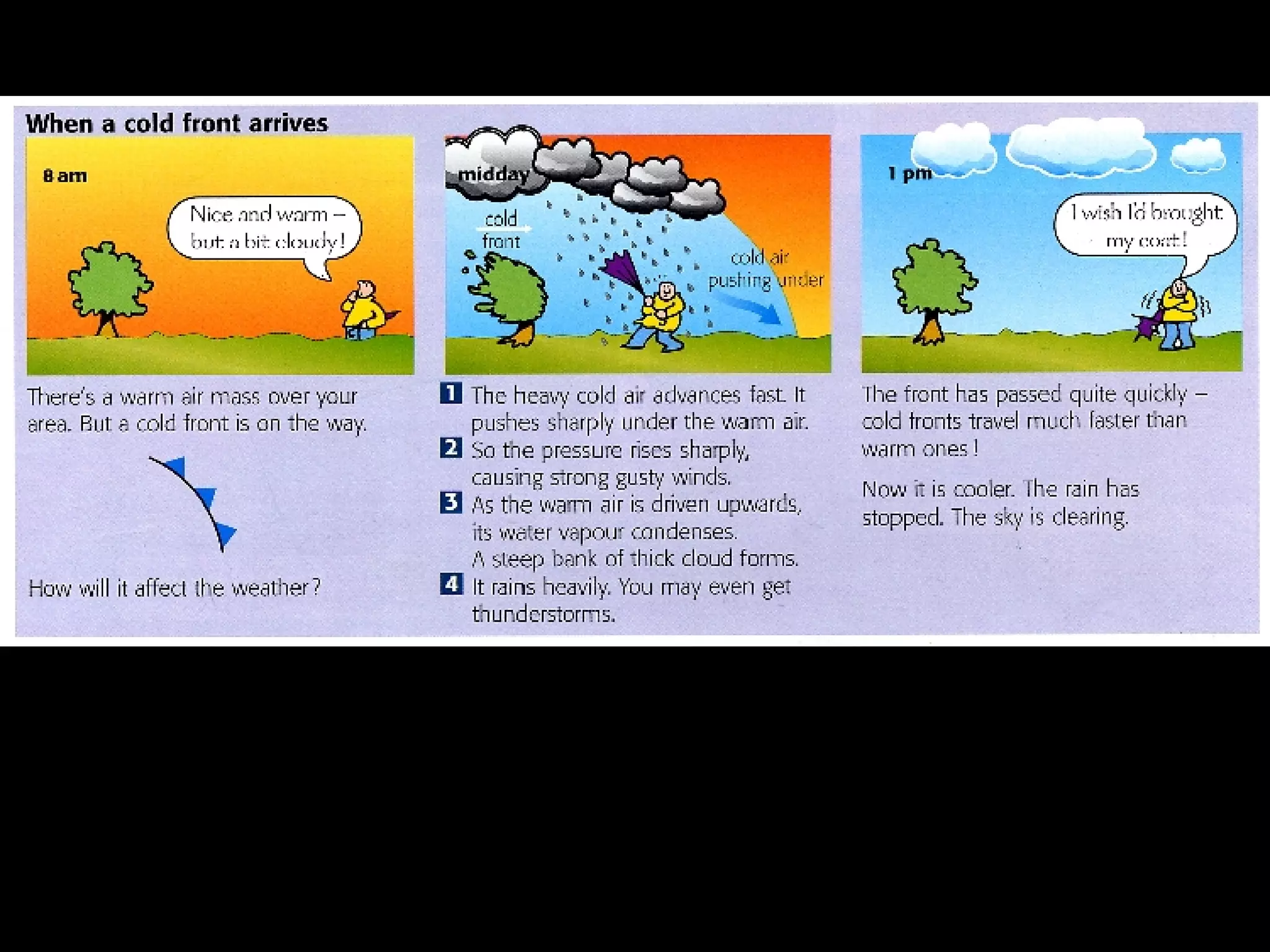
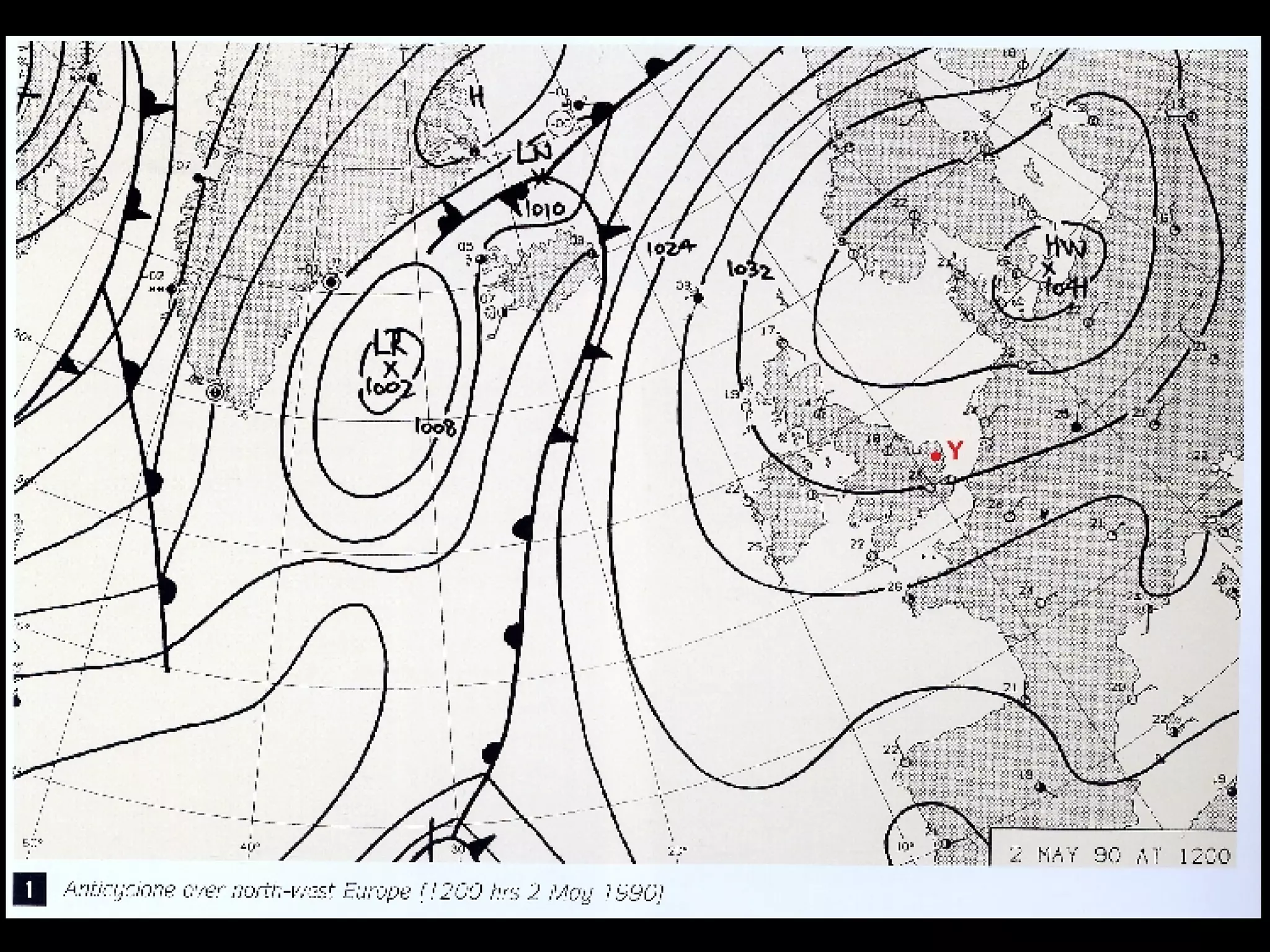
The document outlines key concepts about weather, climate, and the global atmospheric circulation system. It discusses weather forecasting, global wind patterns like depressions and anticyclones, extreme weather events, seasonal climate variations, phenomena like El Niño and La Niña, and climate change. It also contains review questions about weather systems and definitions of terms like isobars, jet streams, fronts, and air masses.