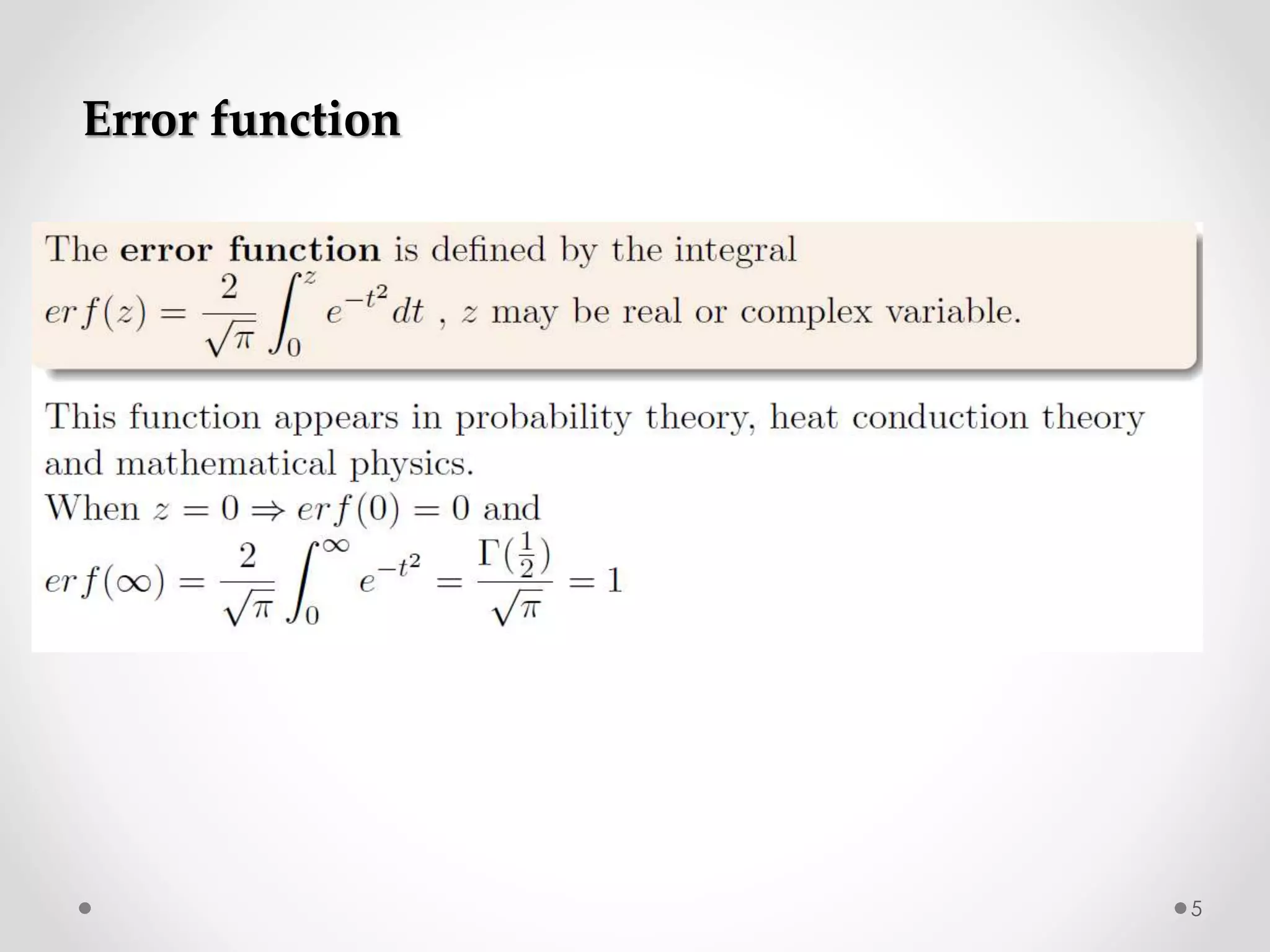
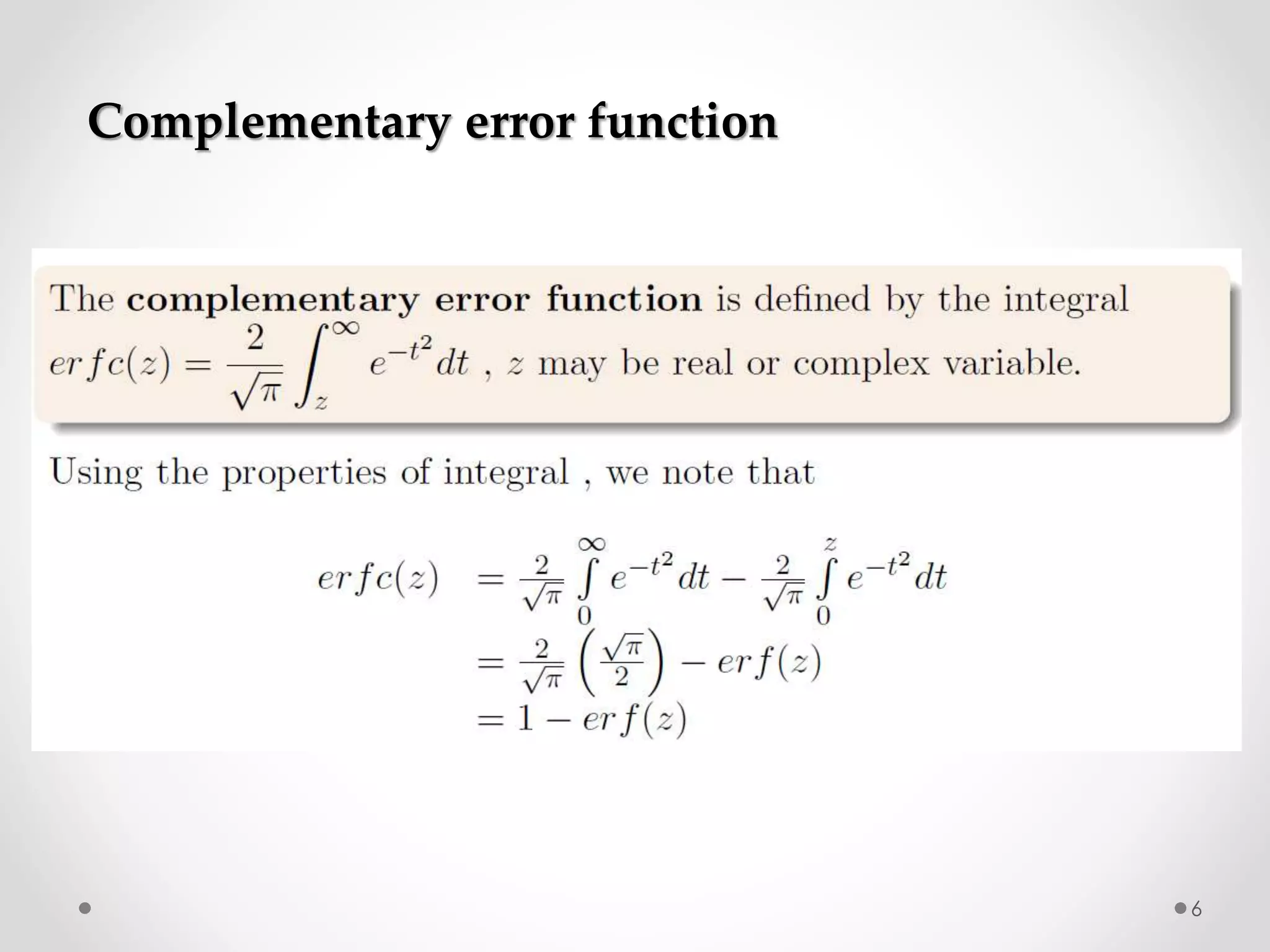
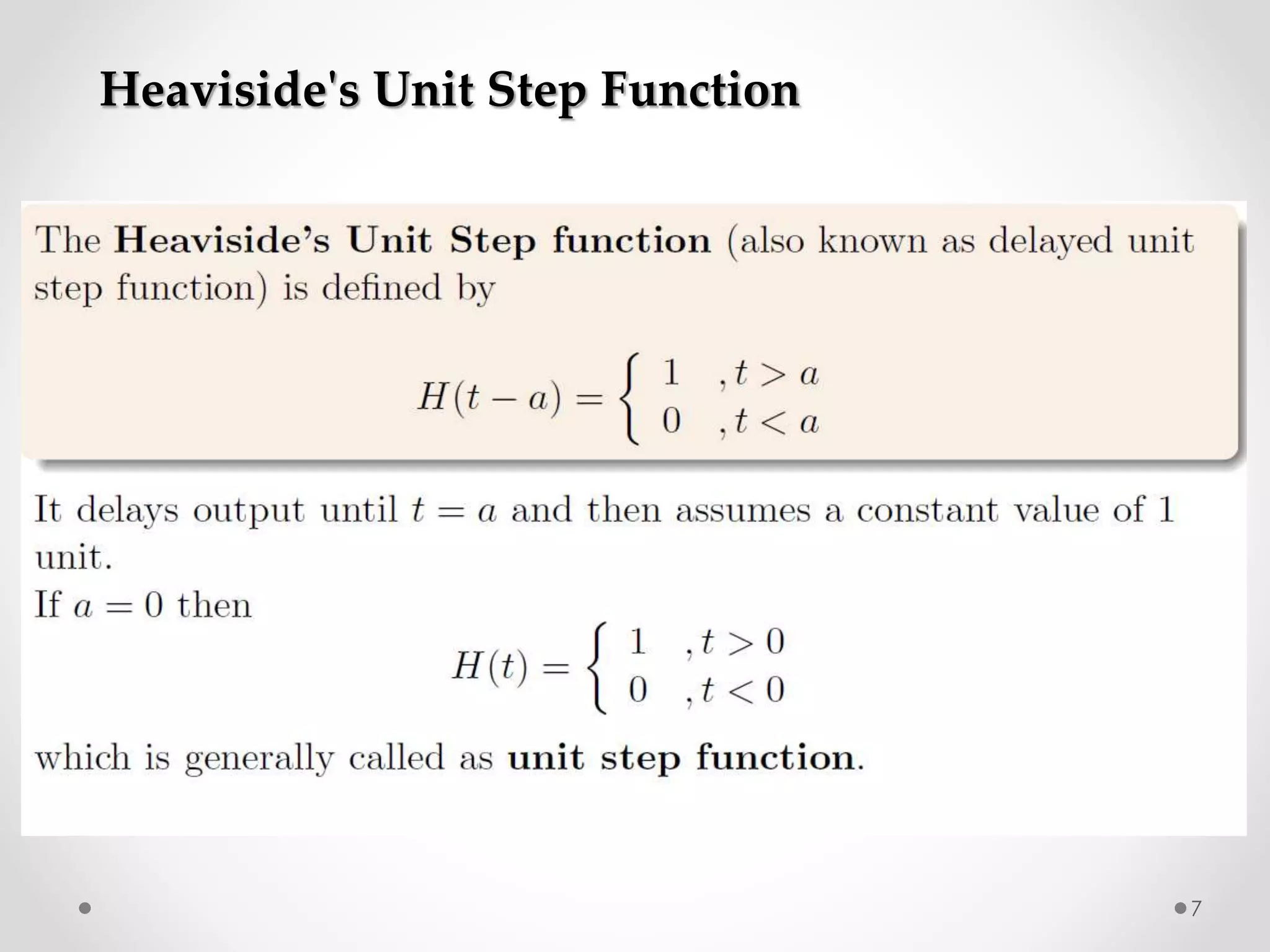
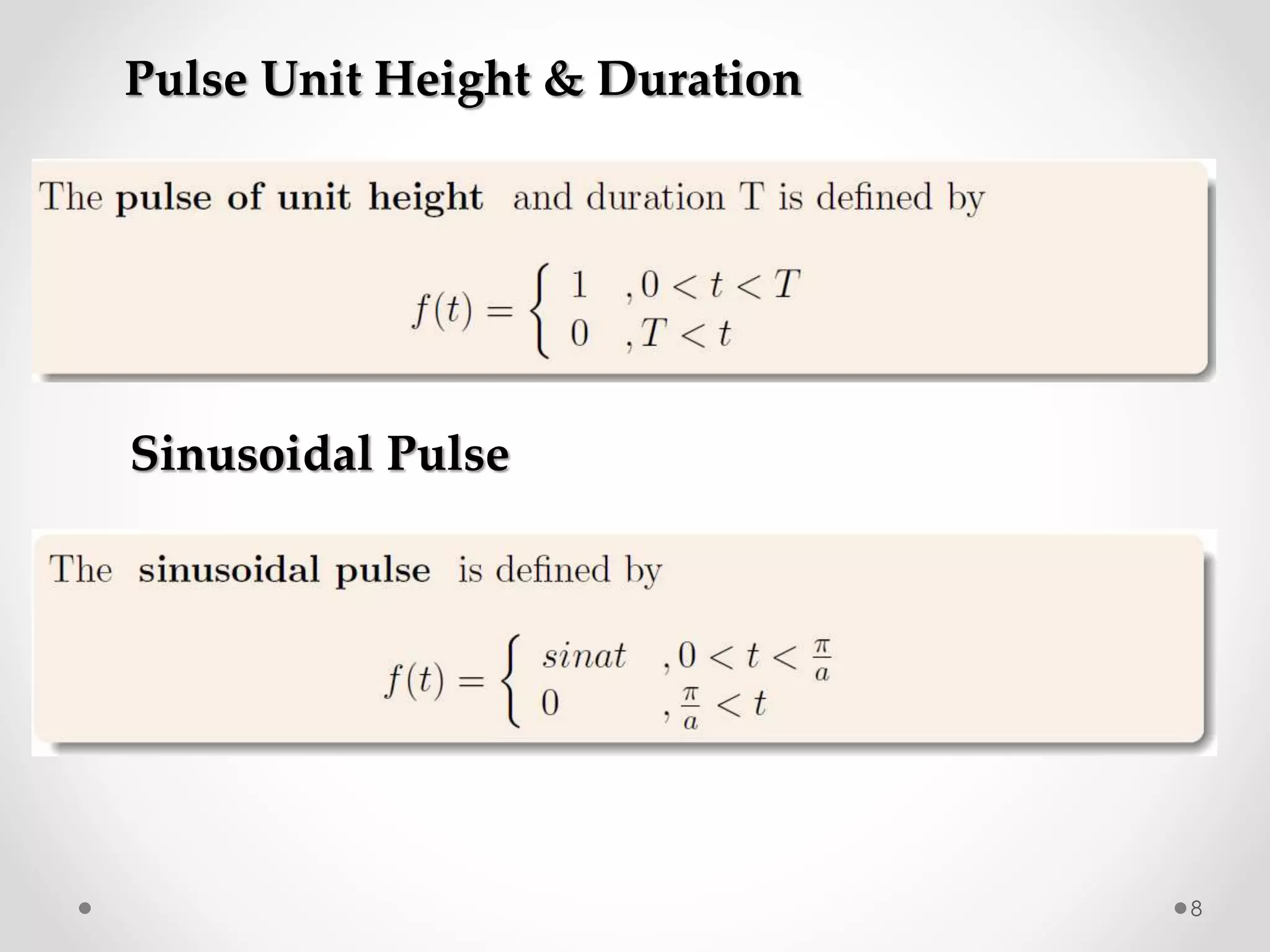
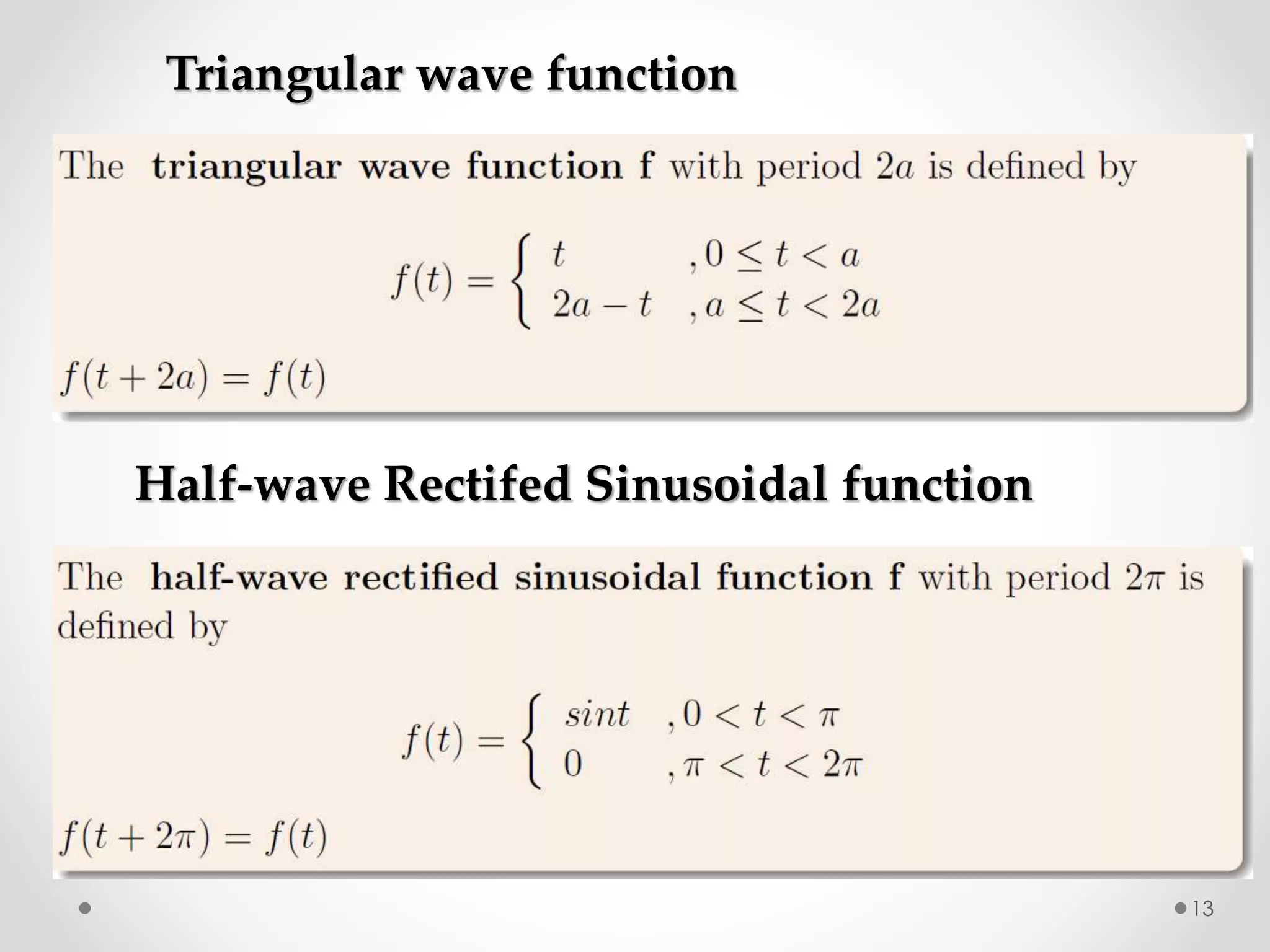
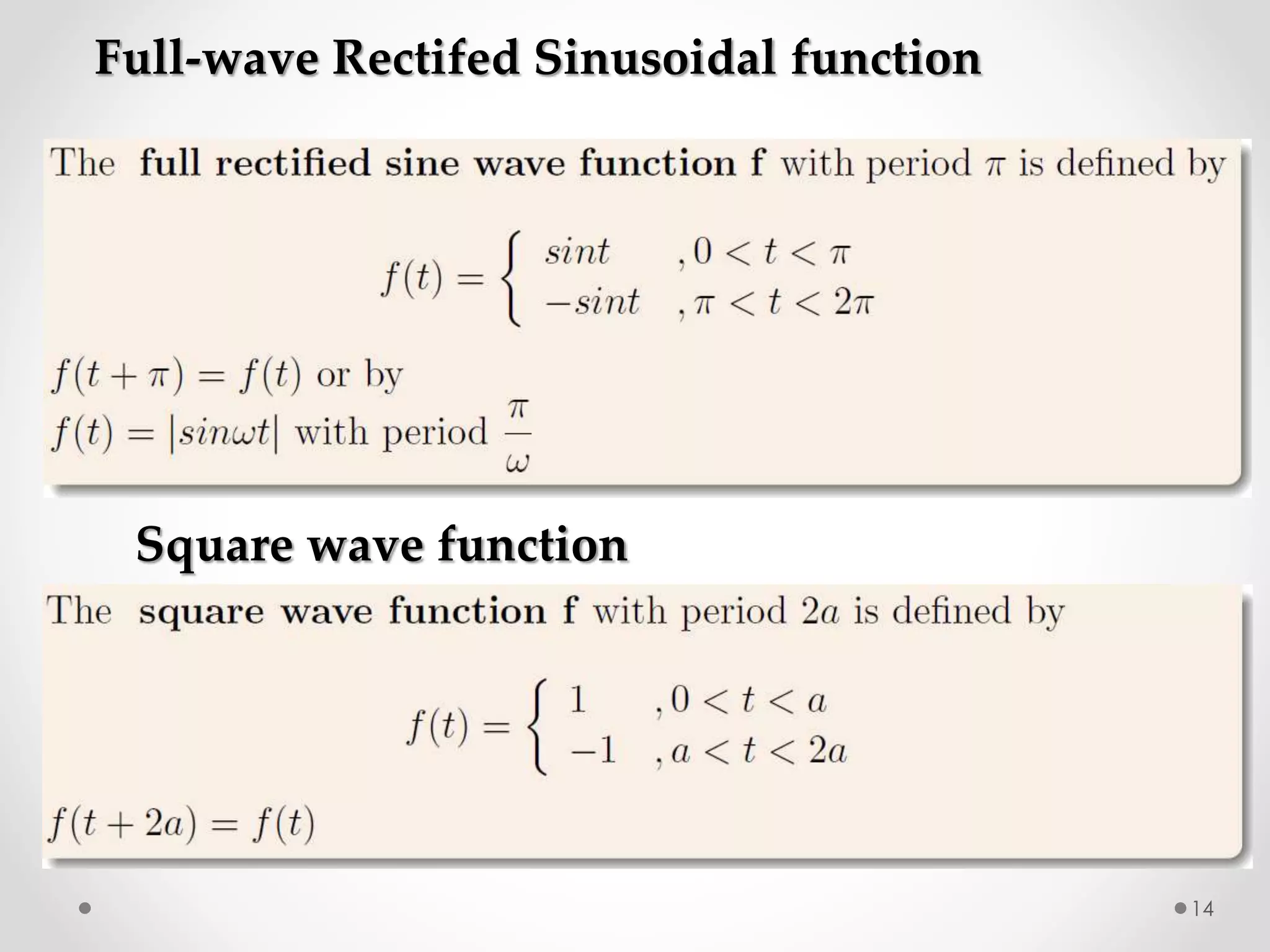
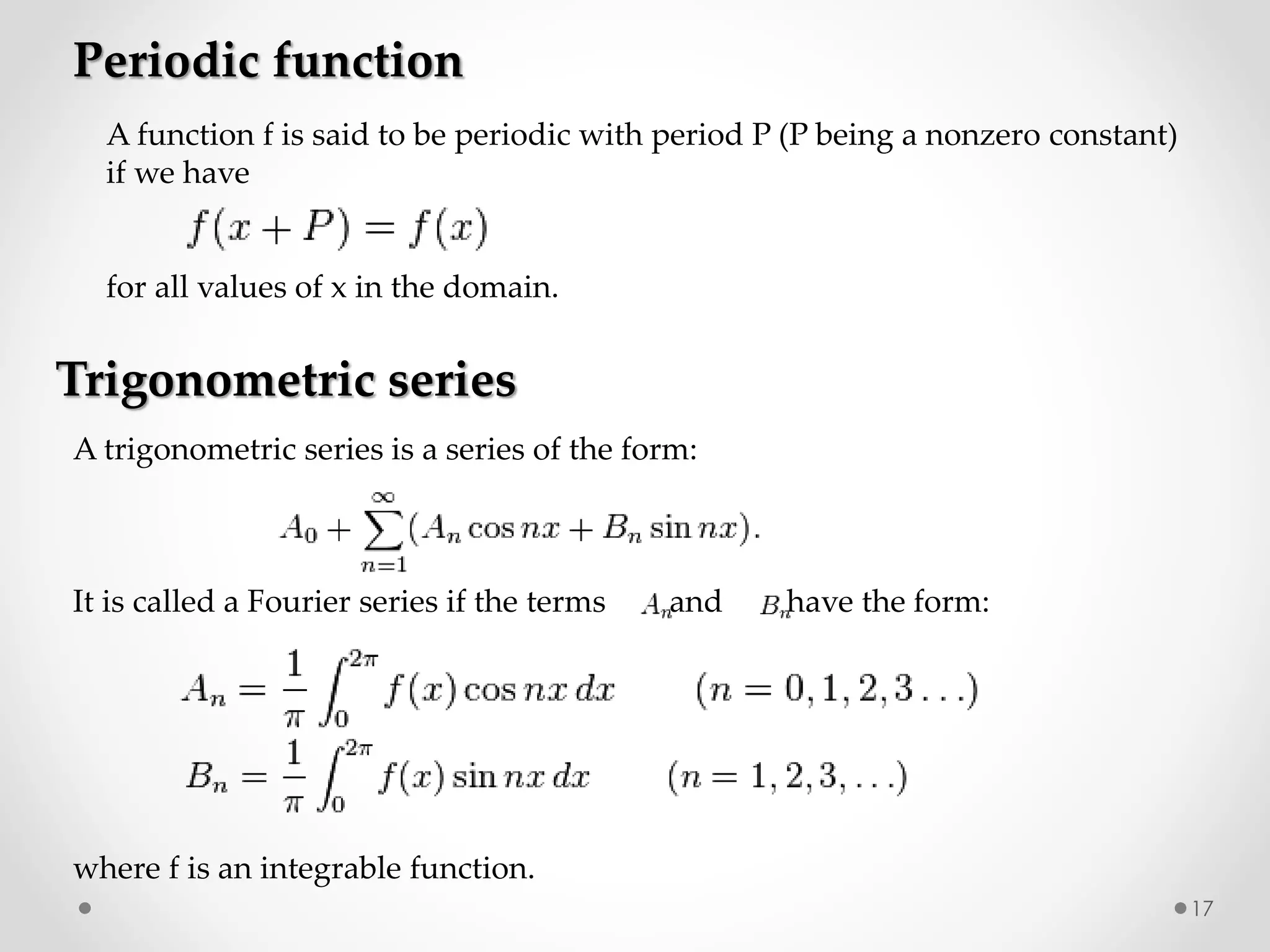
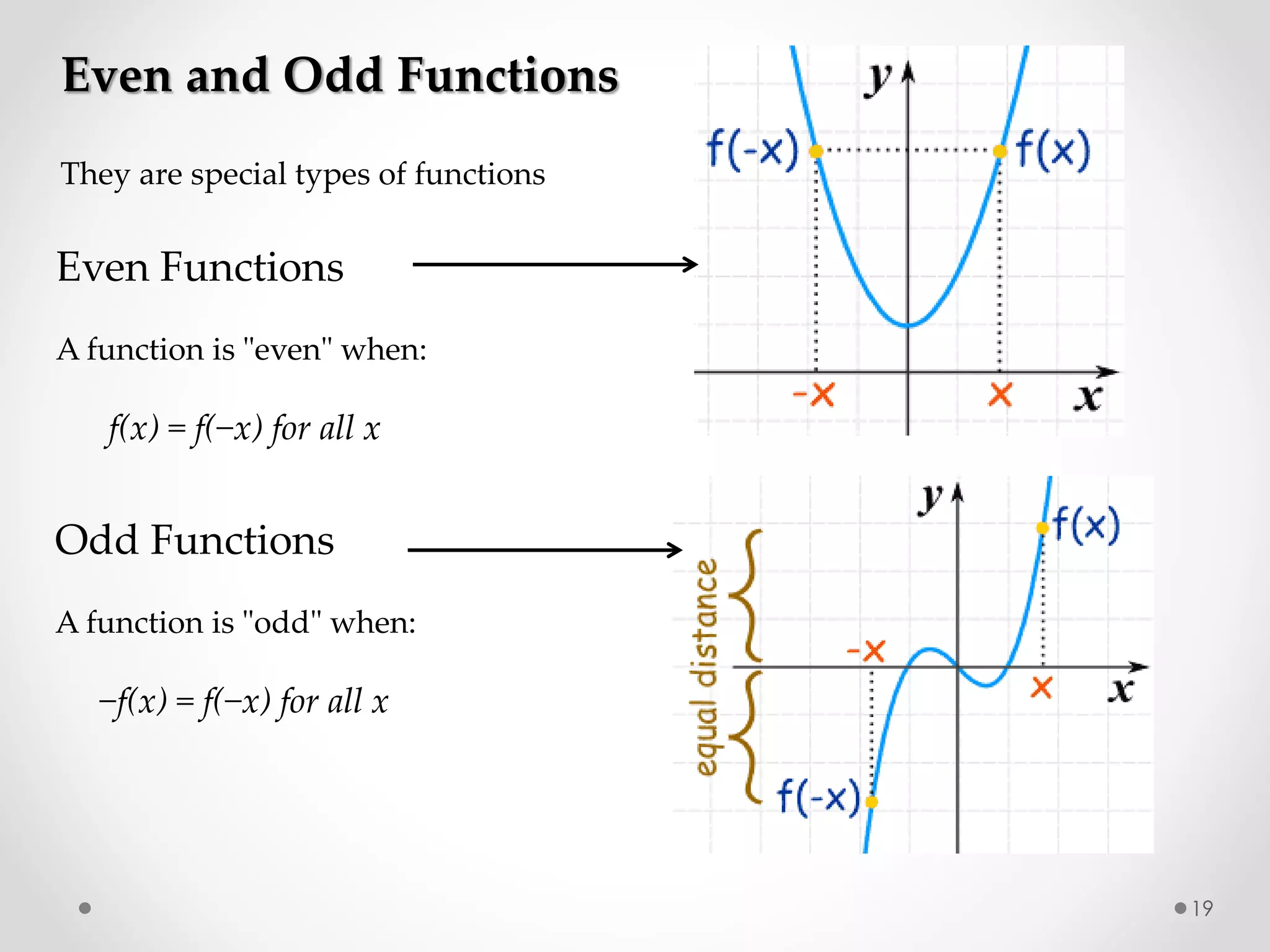
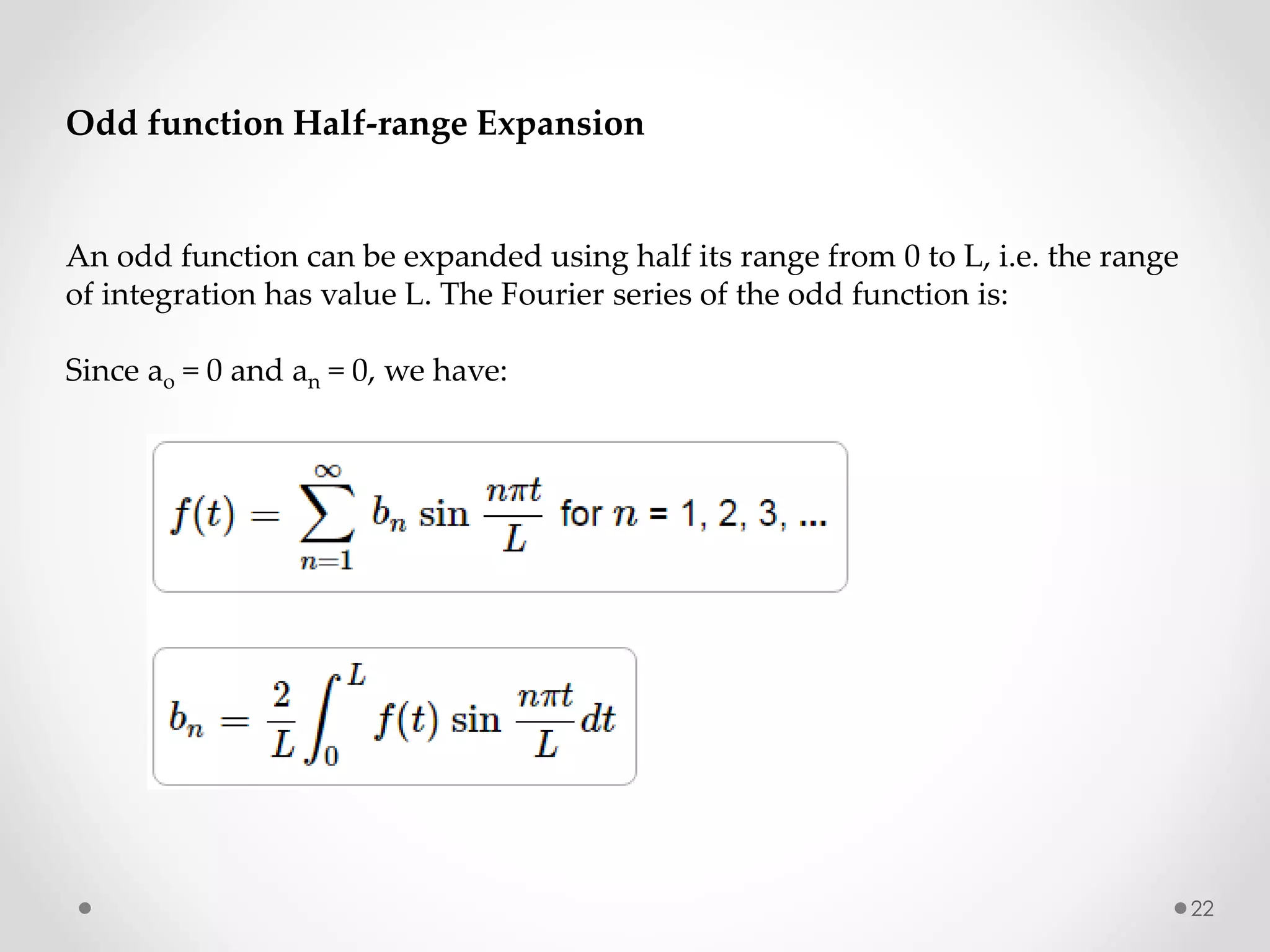
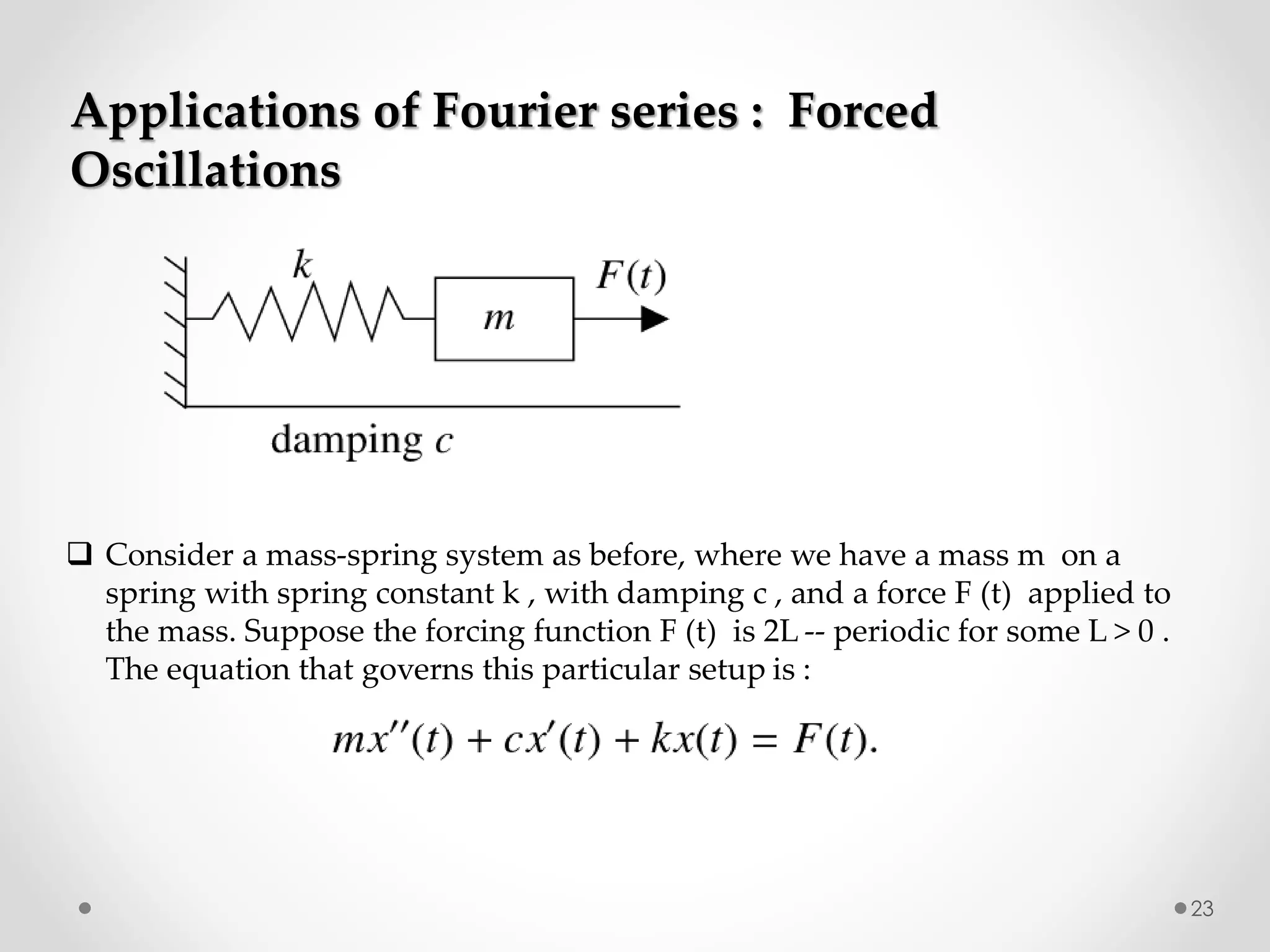
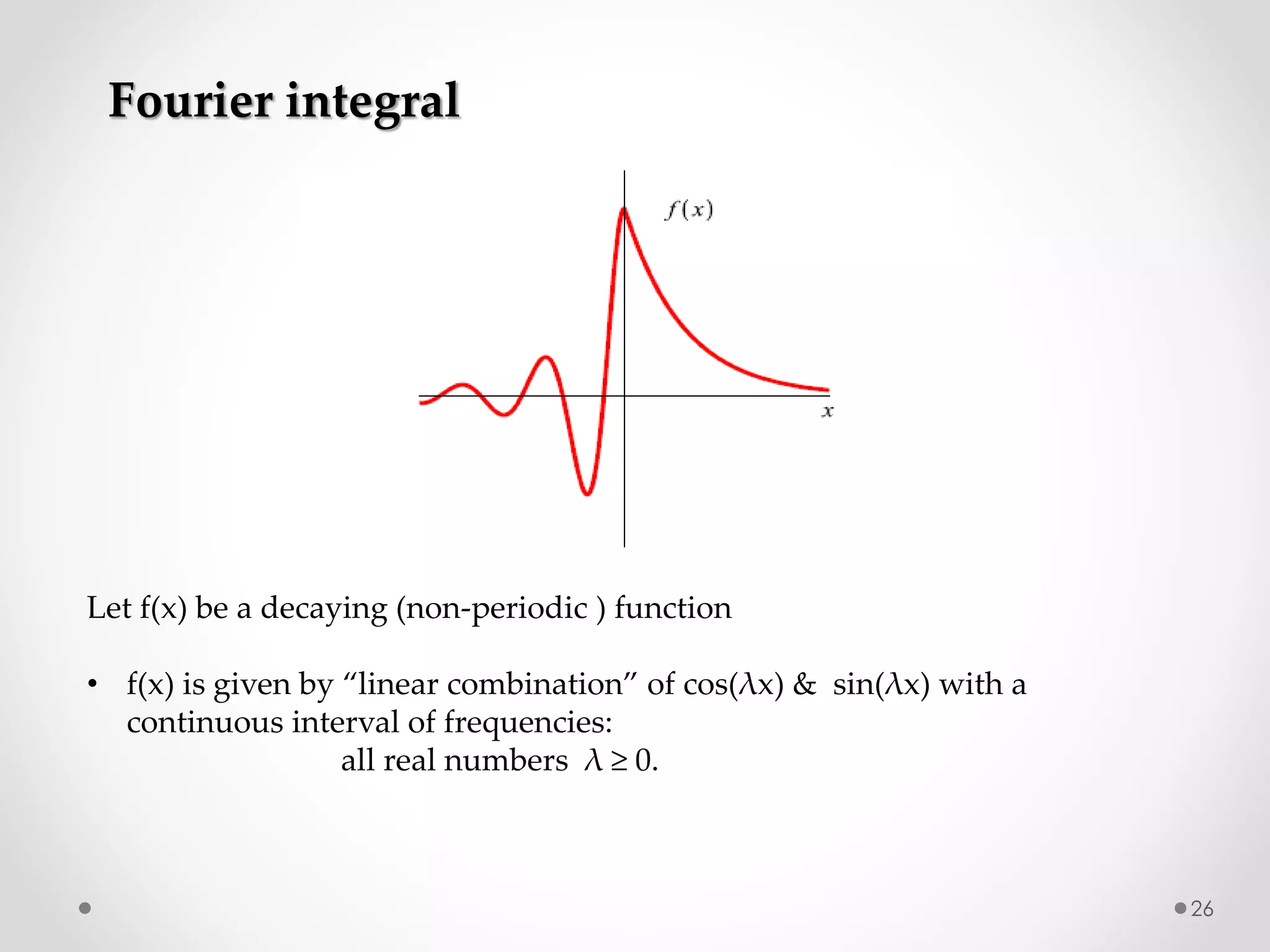
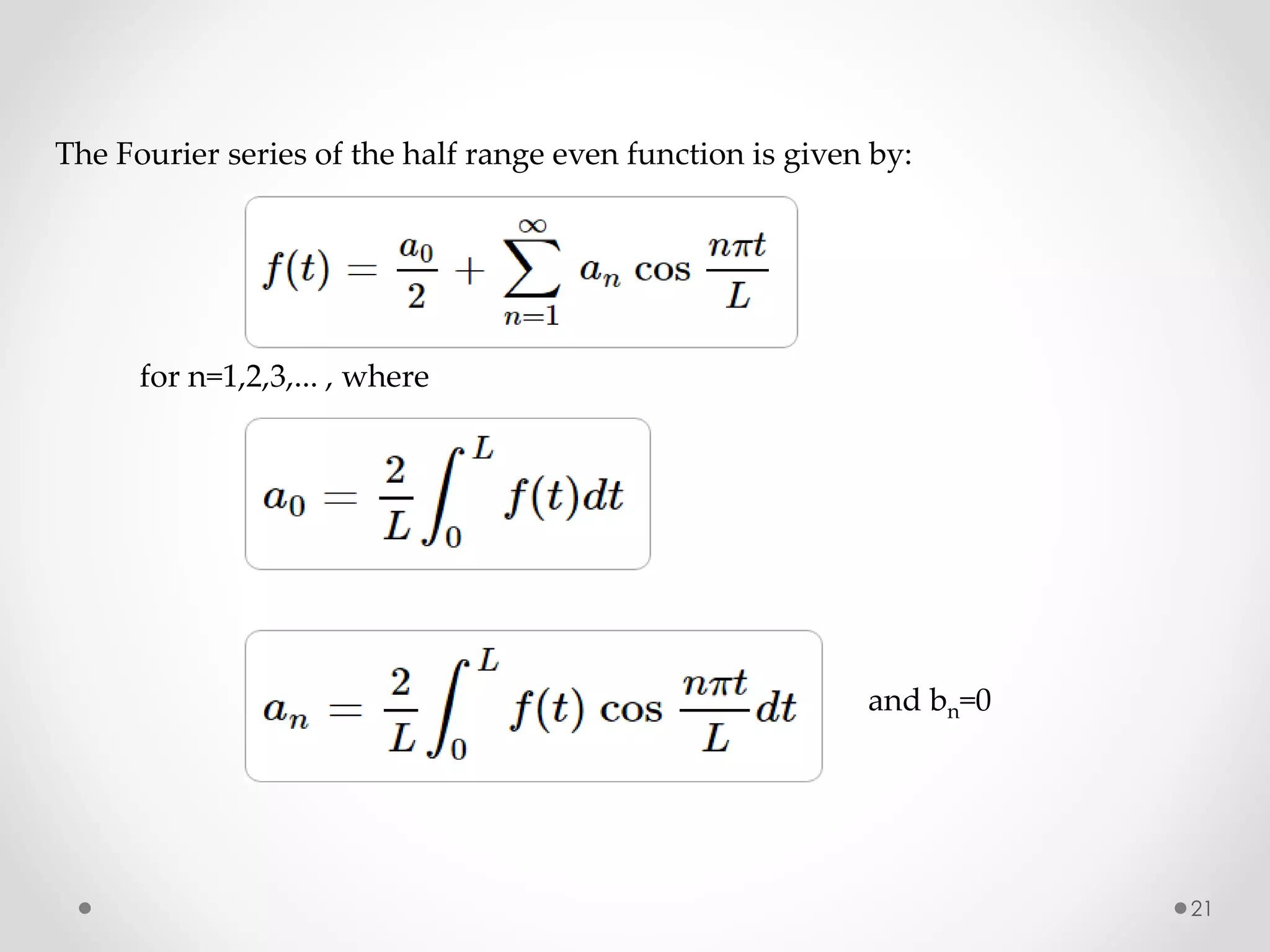The document discusses various special functions used in engineering and mathematics. It begins with an introduction to beta and gamma functions, Bessel functions, error functions, Heaviside's unit step function, pulse functions, sinusoidal pulses, and other periodic functions. It then explains Fourier series and their applications for representing periodic functions as infinite sums of sines and cosines. Specifically, it discusses even and odd functions, half-range expansions, and using Fourier series to model forced oscillations. Finally, the document briefly introduces the Fourier integral as representing a function as a continuous range of frequencies.