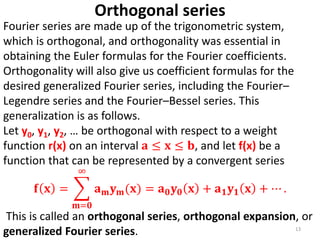
Fourier analysis uses Fourier series and Fourier integrals to represent functions. Fourier series represent periodic functions as the sum of sines and cosines, while Fourier integrals extend this to non-periodic functions using integrals of sines and cosines instead of series. Orthogonal function systems like sines and cosines allow determining the coefficients using formulas like the Euler formulas. Extensions include replacing sines and cosines with other orthogonal functions and applying Fourier methods to functions of any period by changing variables.