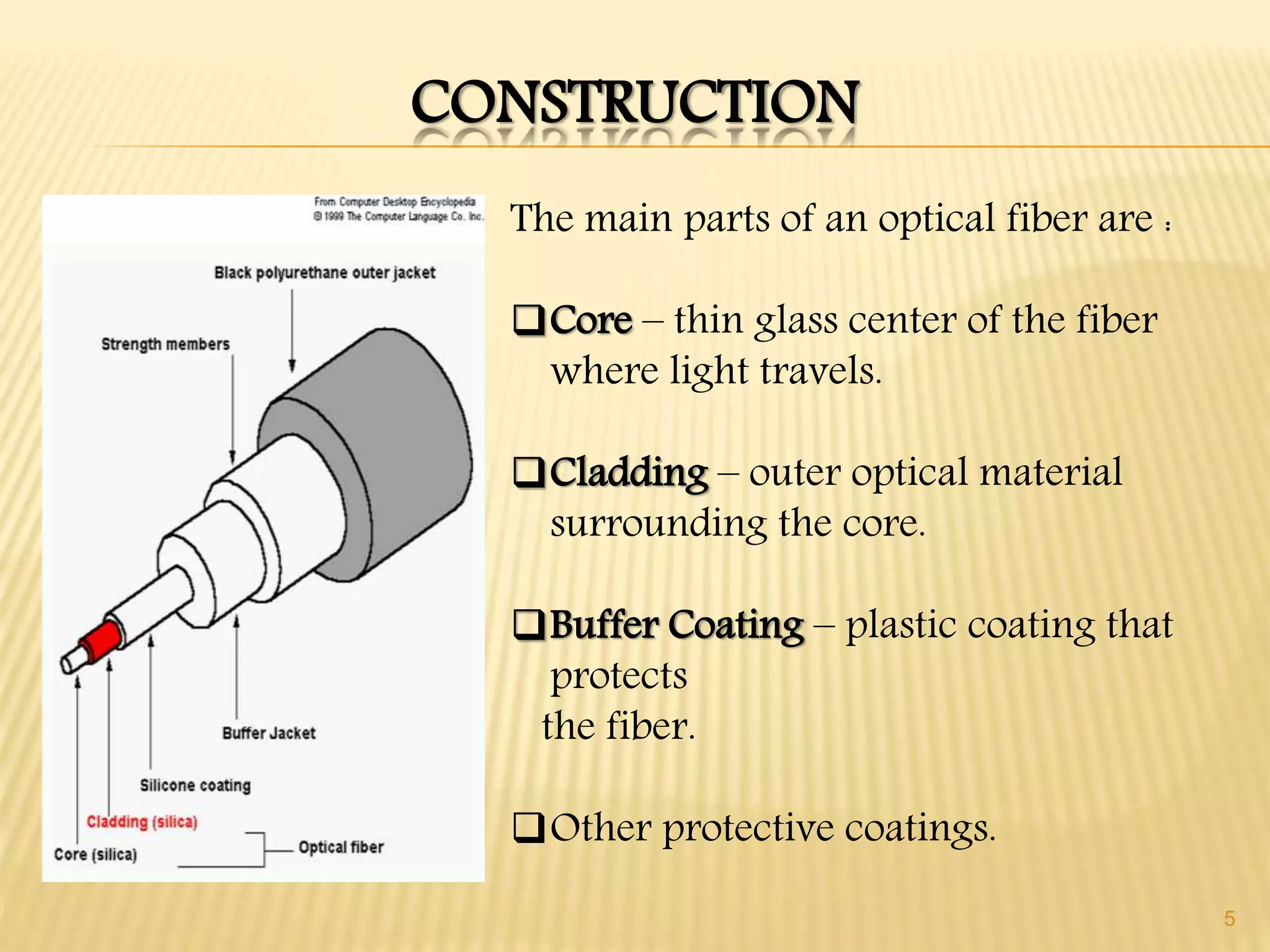
1. The document discusses optical fibers, including their construction, principle of total internal reflection, types based on material, mode of propagation and index profile, and configurations including singlemode step-index, multimode step-index, and multimode graded index fibers.
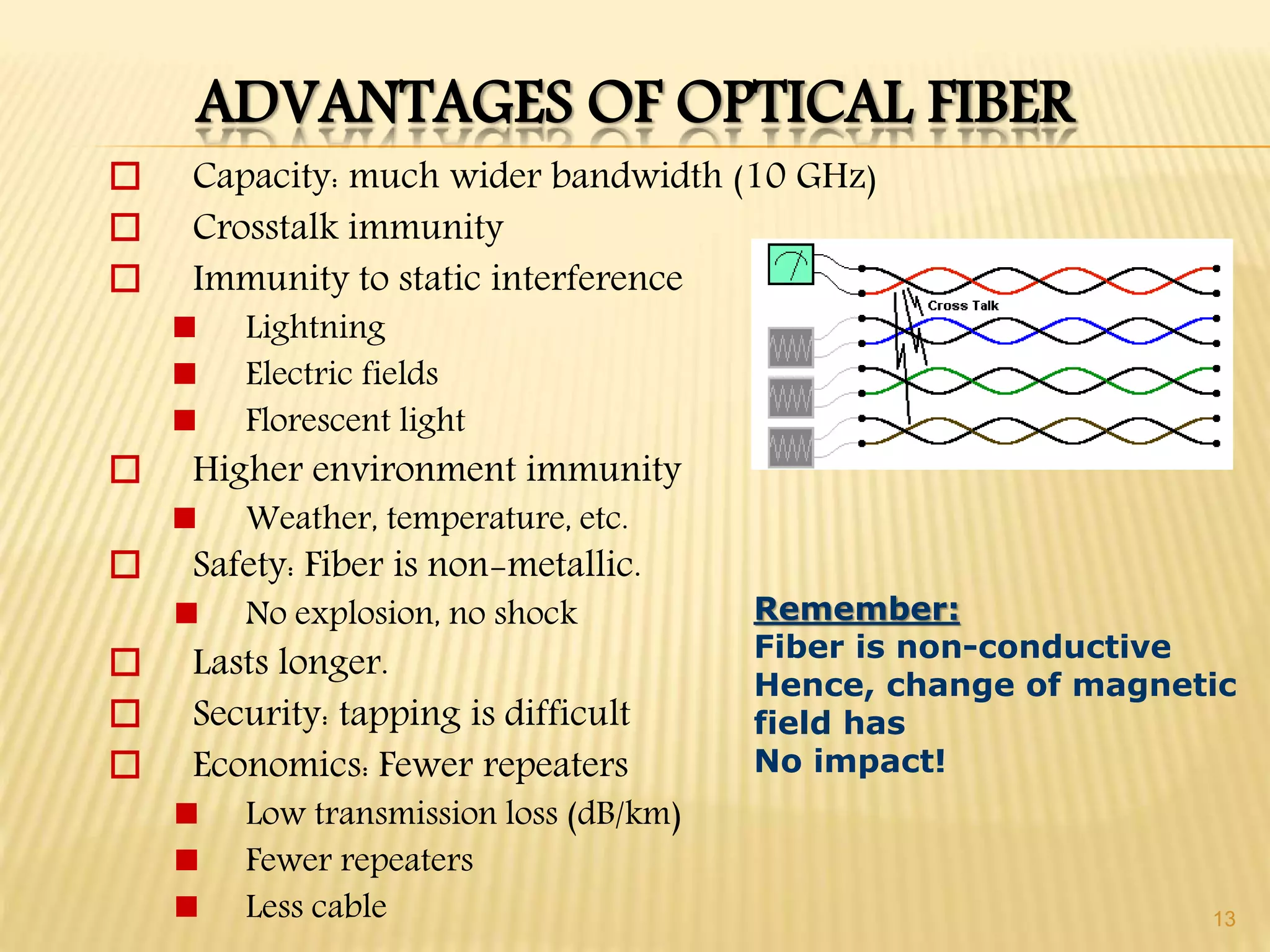
2. Optical fibers have advantages like high bandwidth, immunity to interference, safety, security and economics due to low loss, but also have disadvantages like higher initial installation cost and need for specialized repair tools.
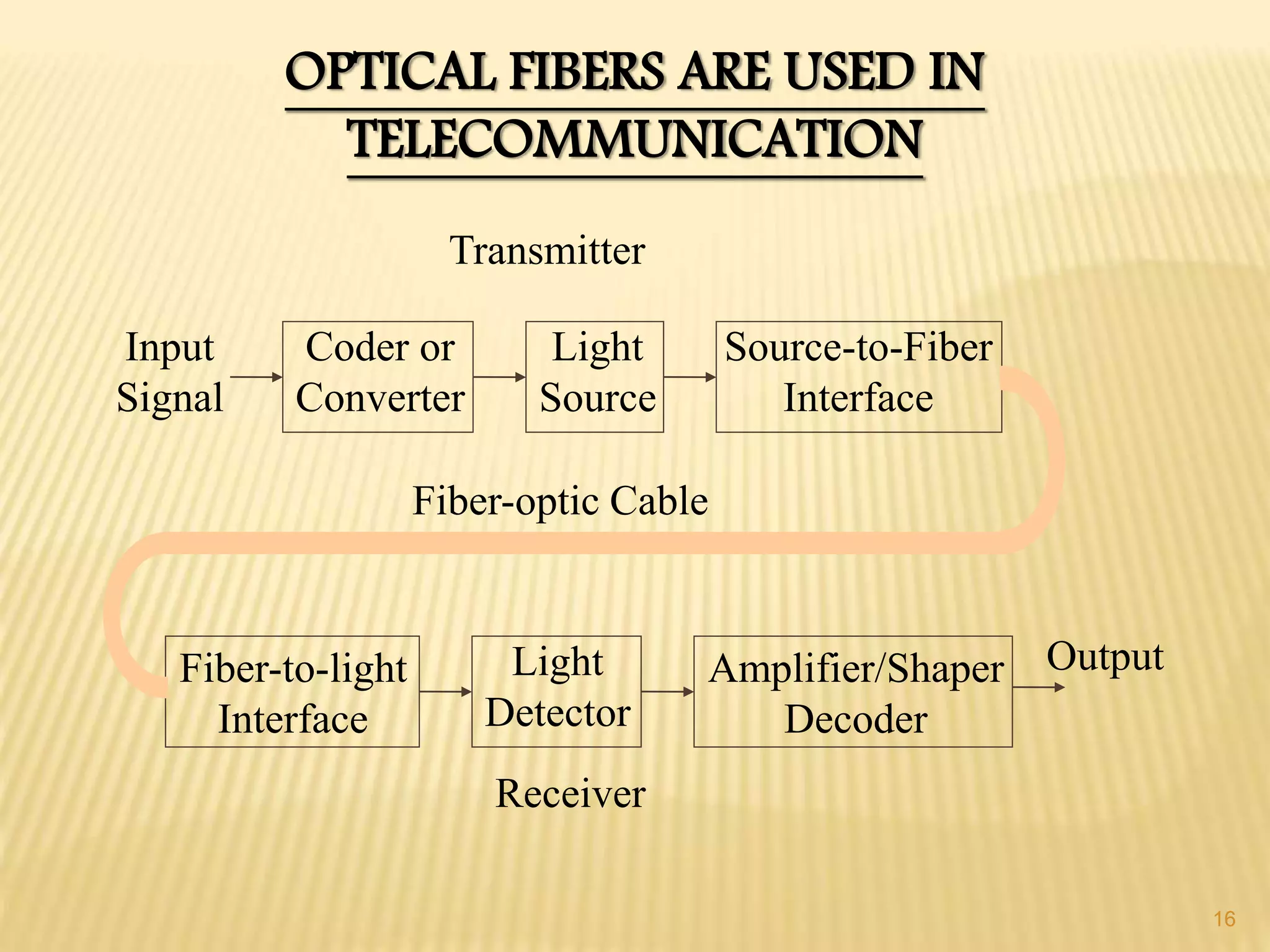
3. Applications of optical fibers include telecommunications, local area networks, cable TV, sensors, endoscopy, and decoration. Optical fibers are used to transmit data in telecommunications systems and endoscopic surgery.