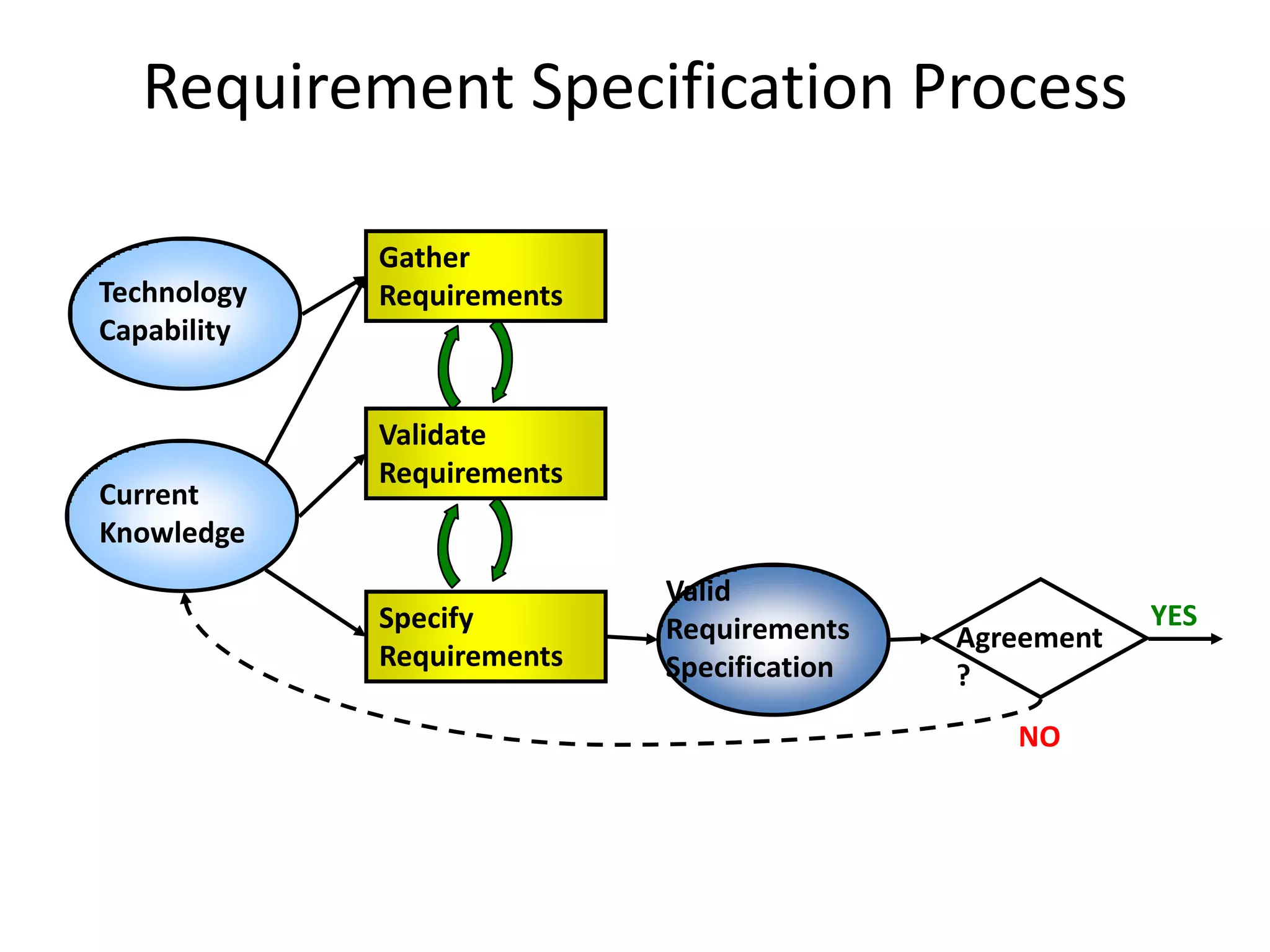
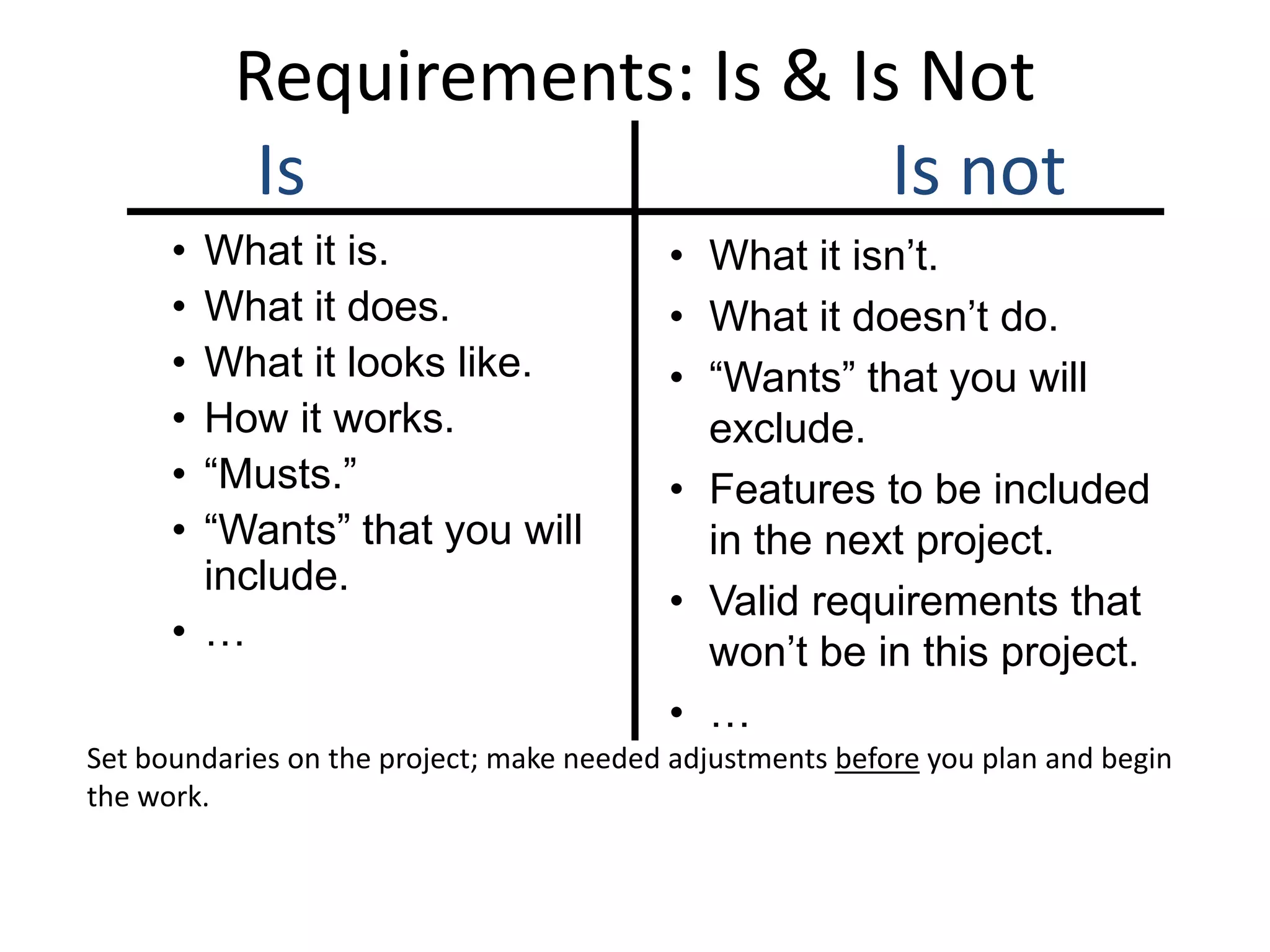
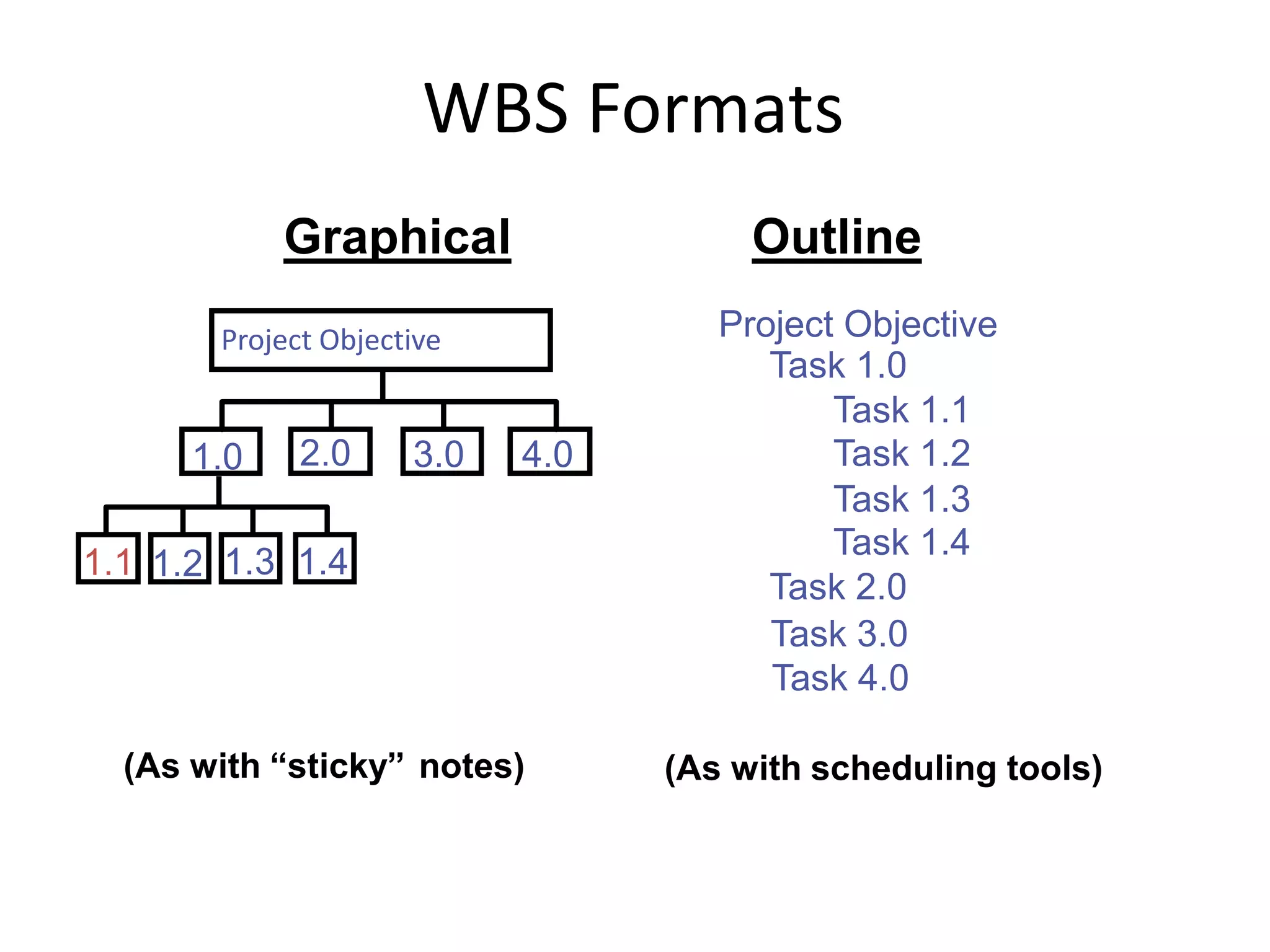
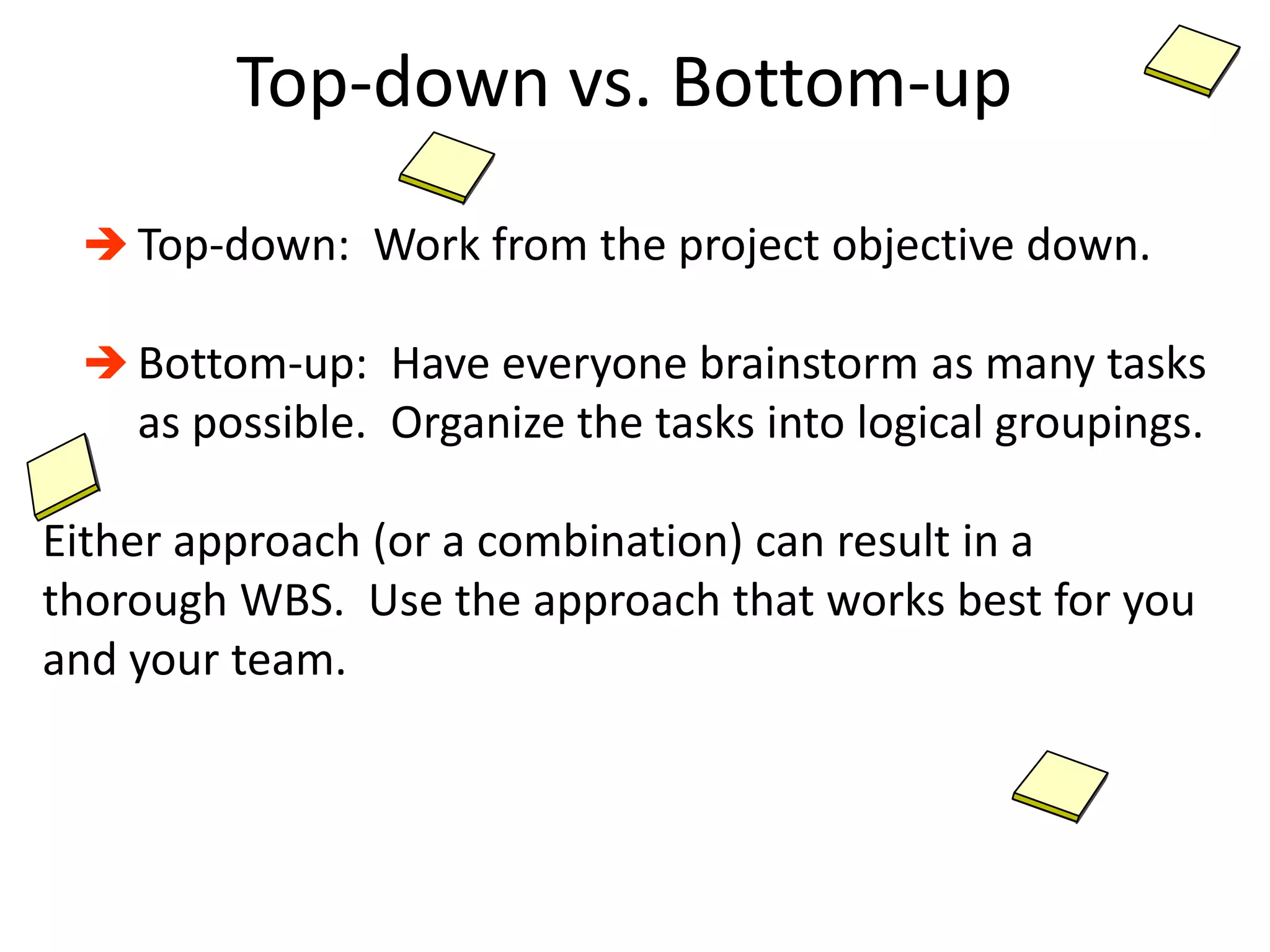
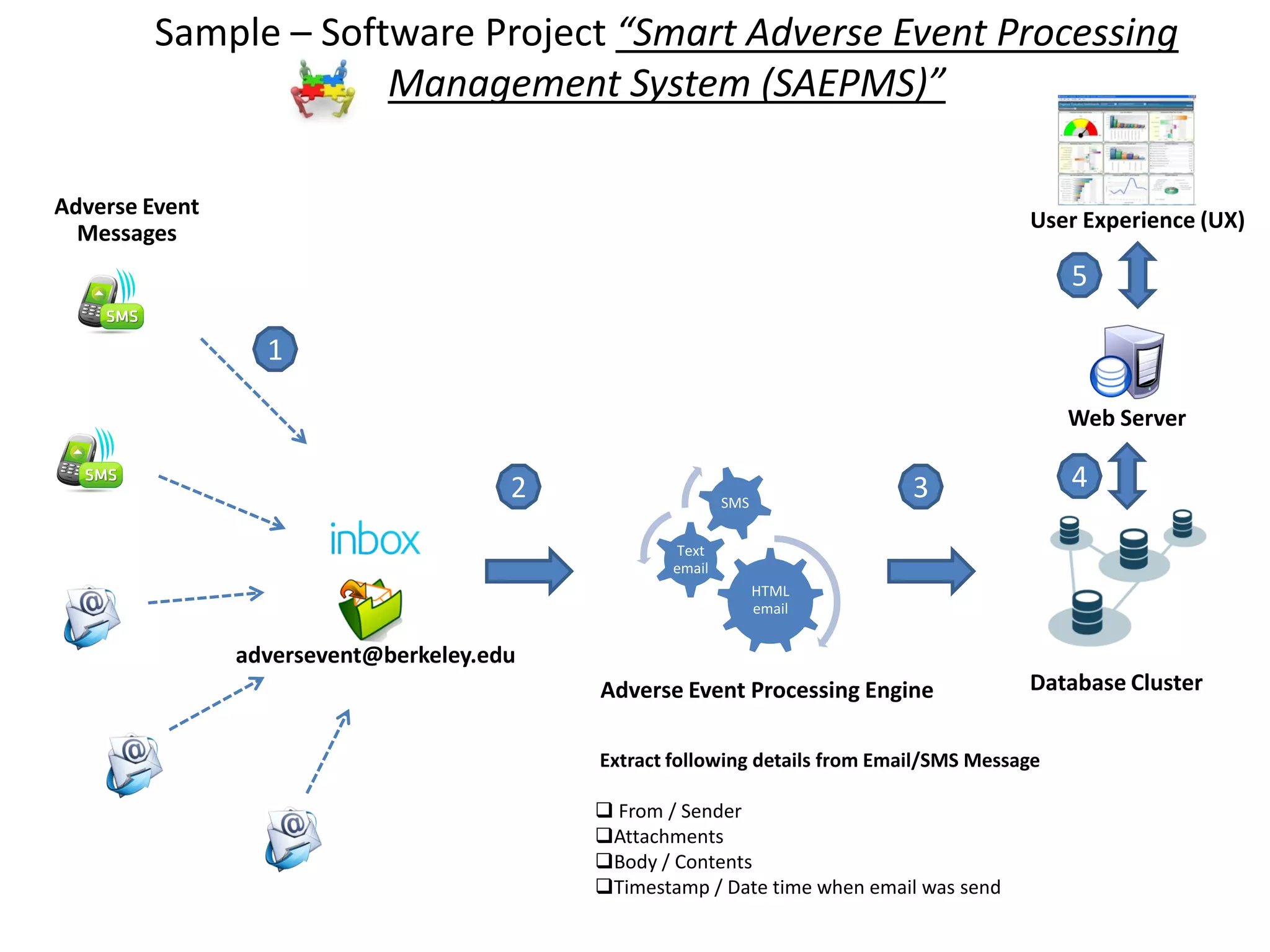
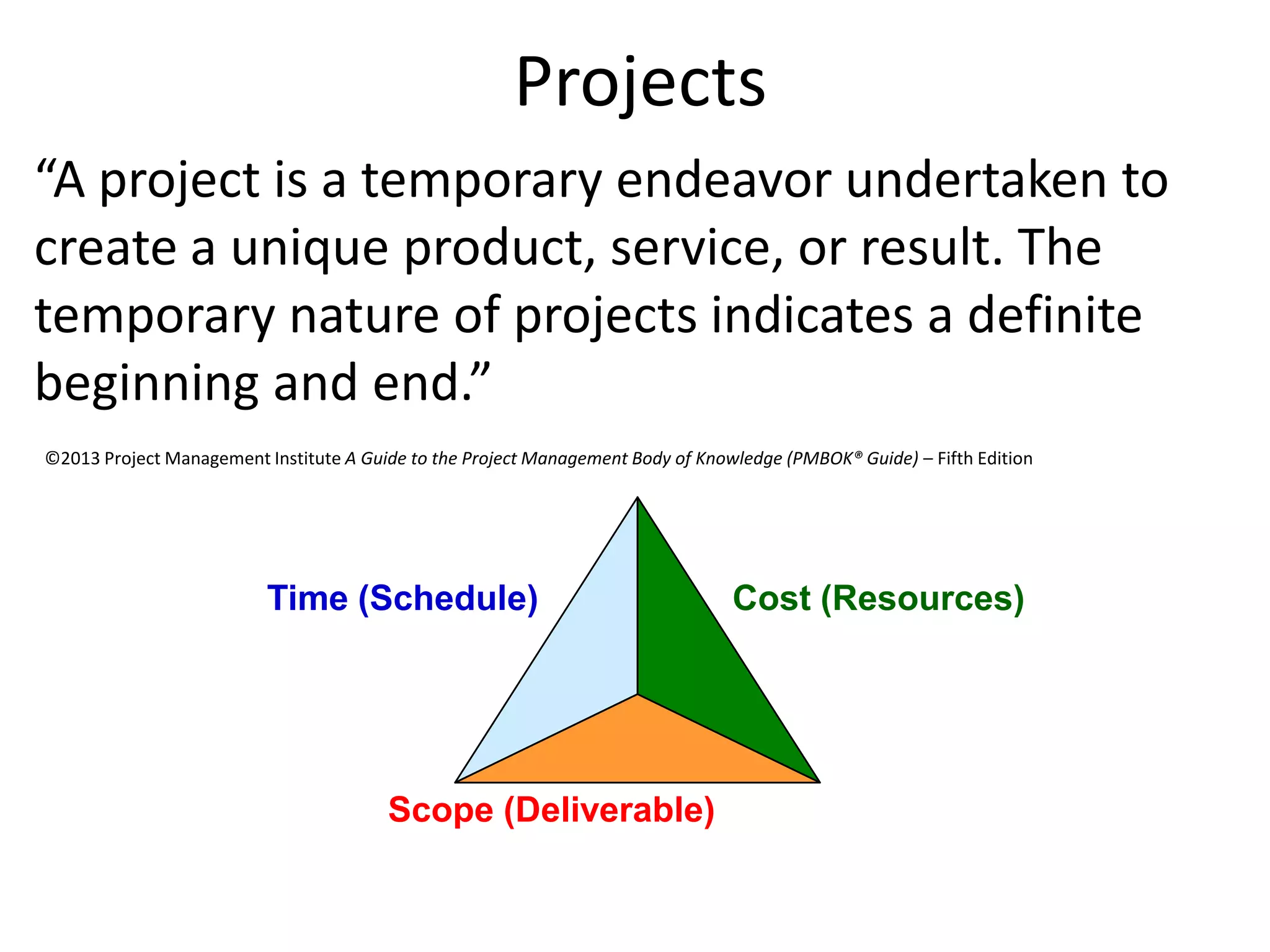
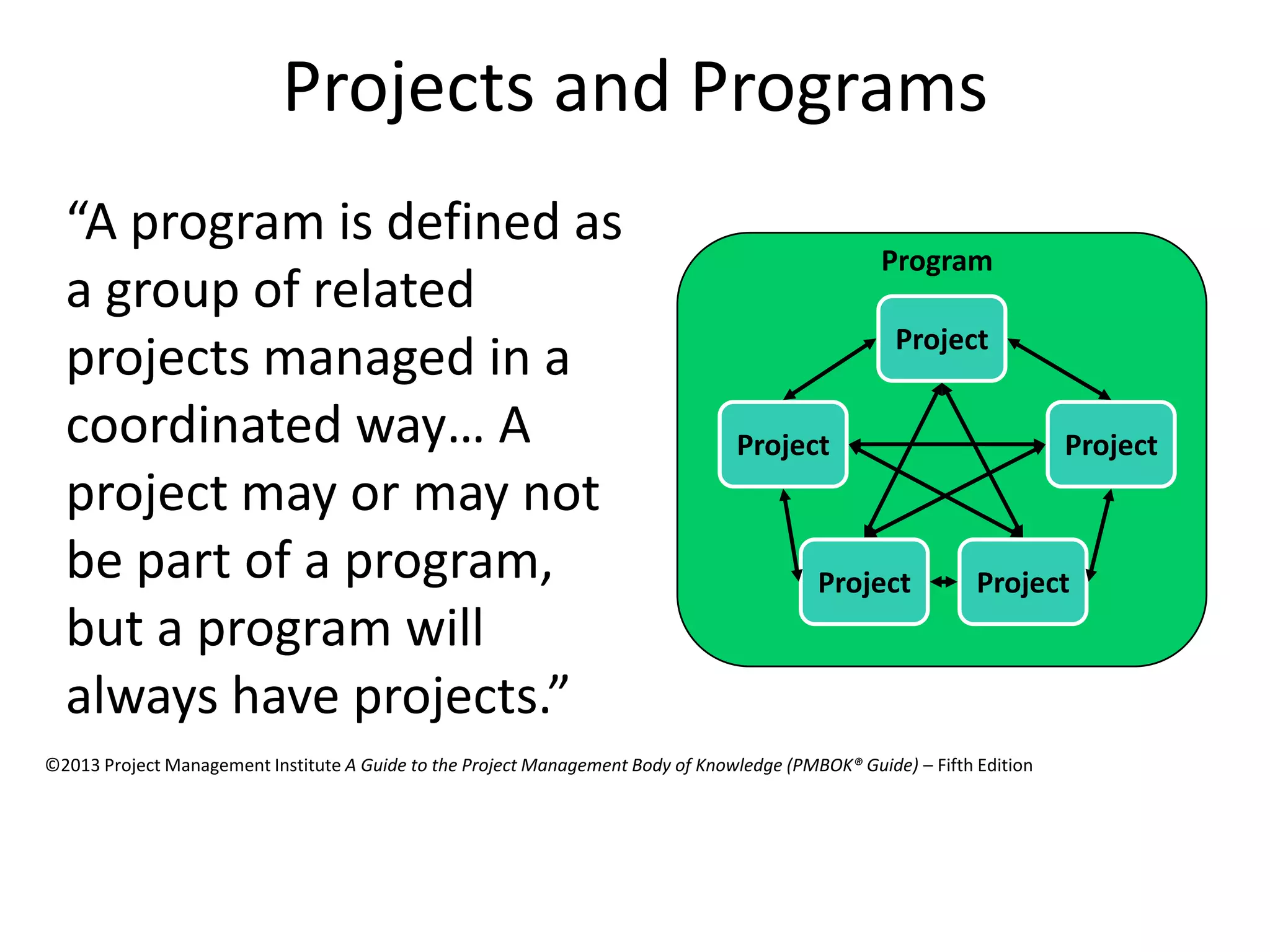
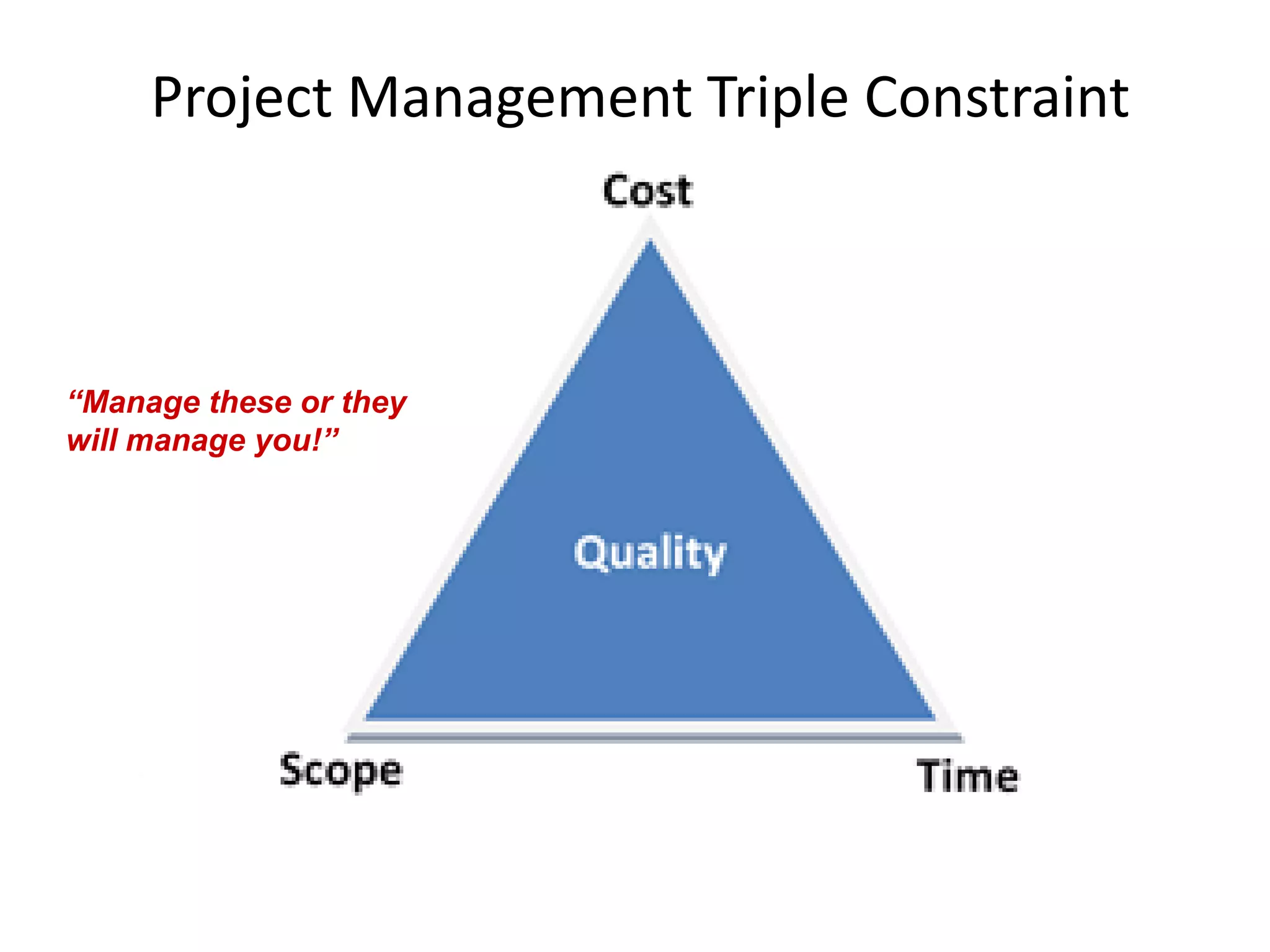
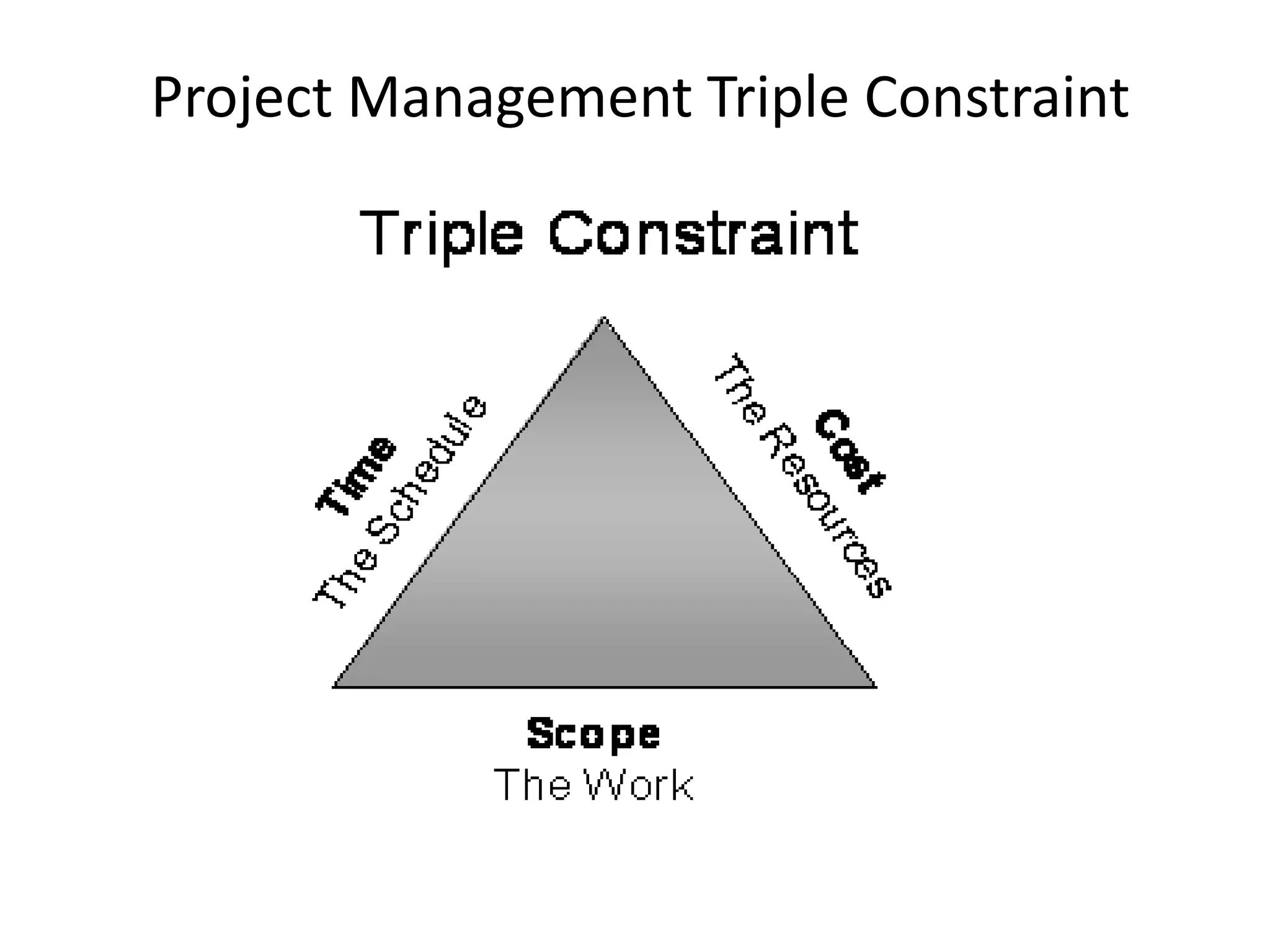
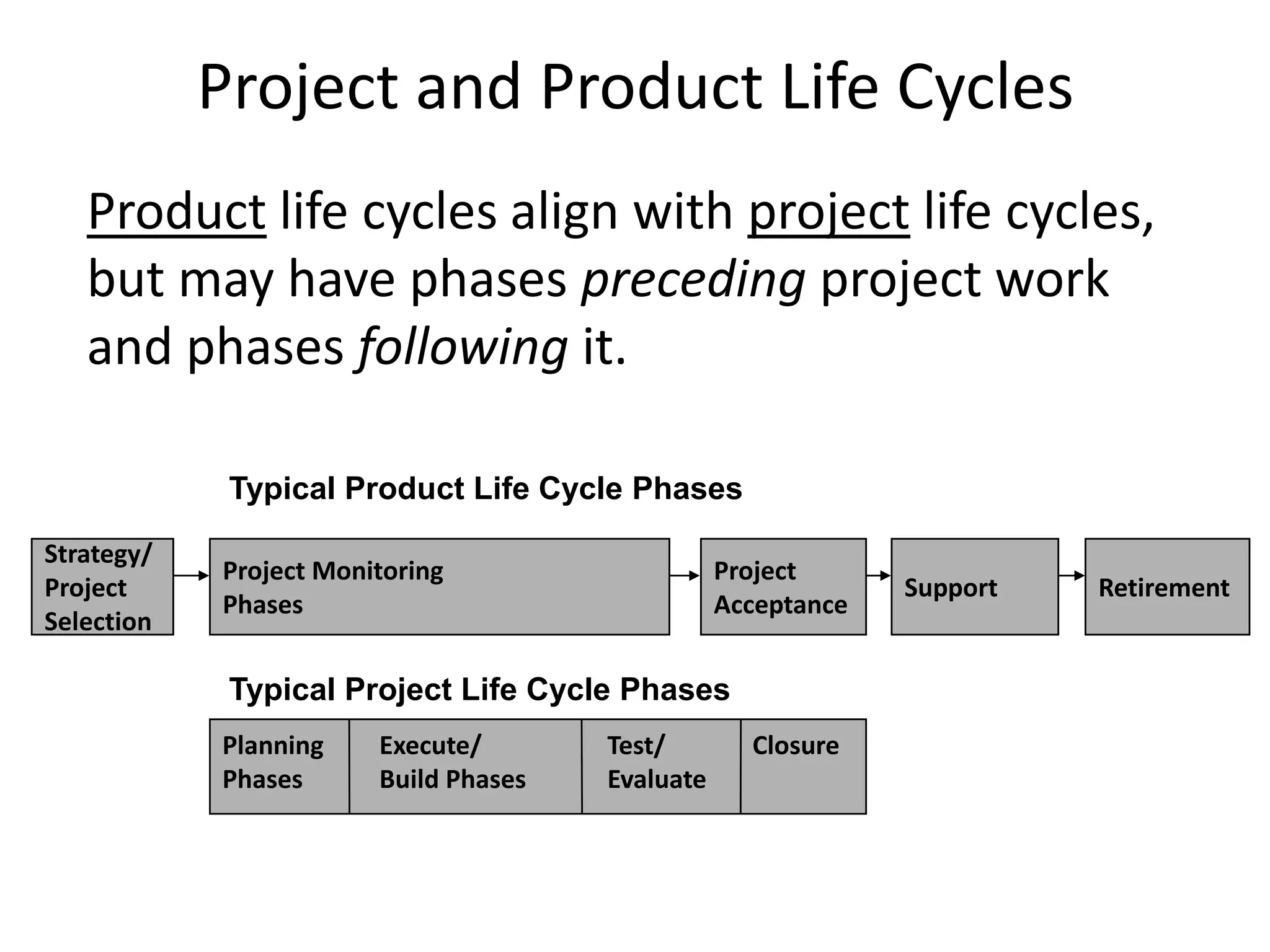
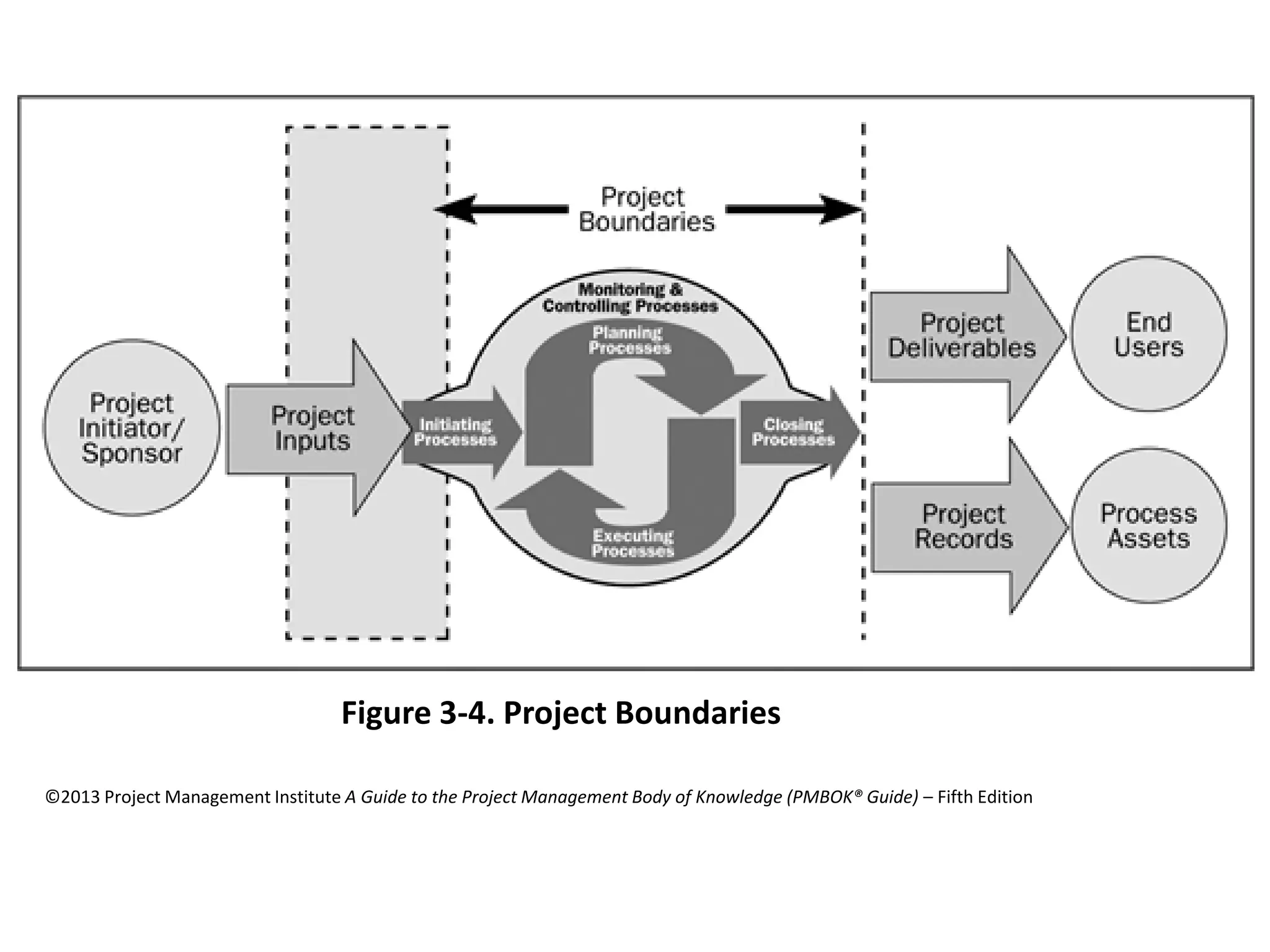
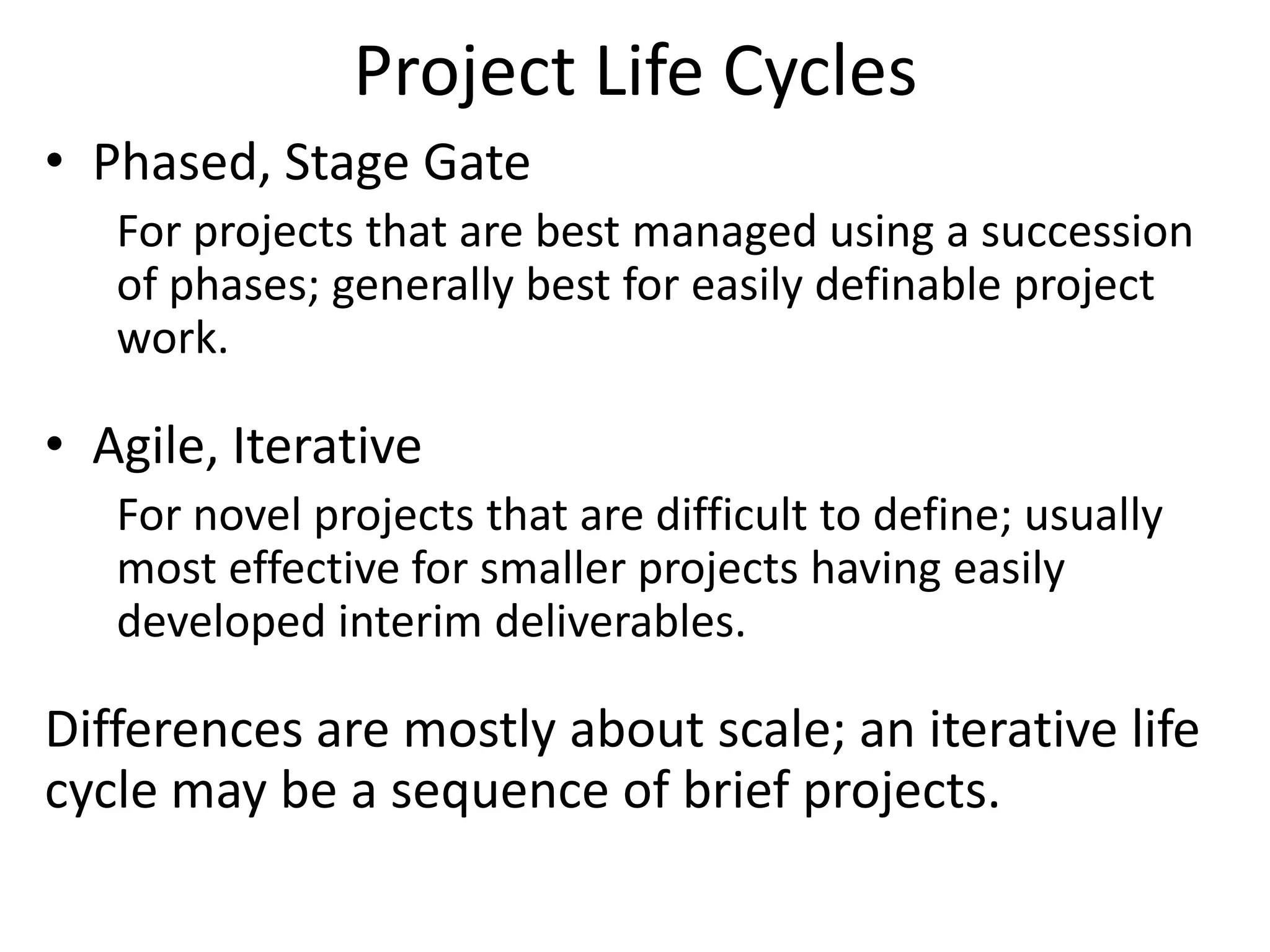
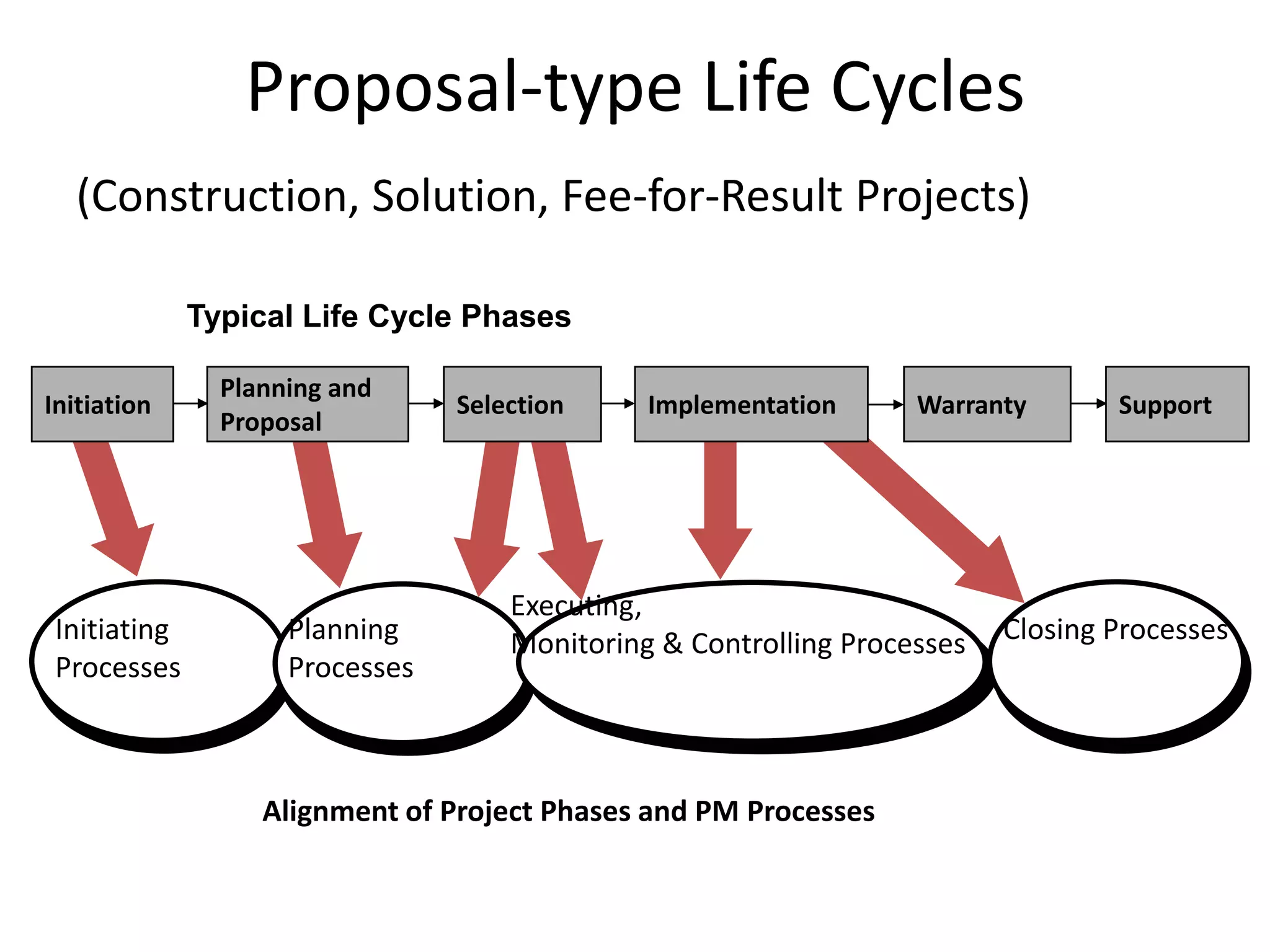
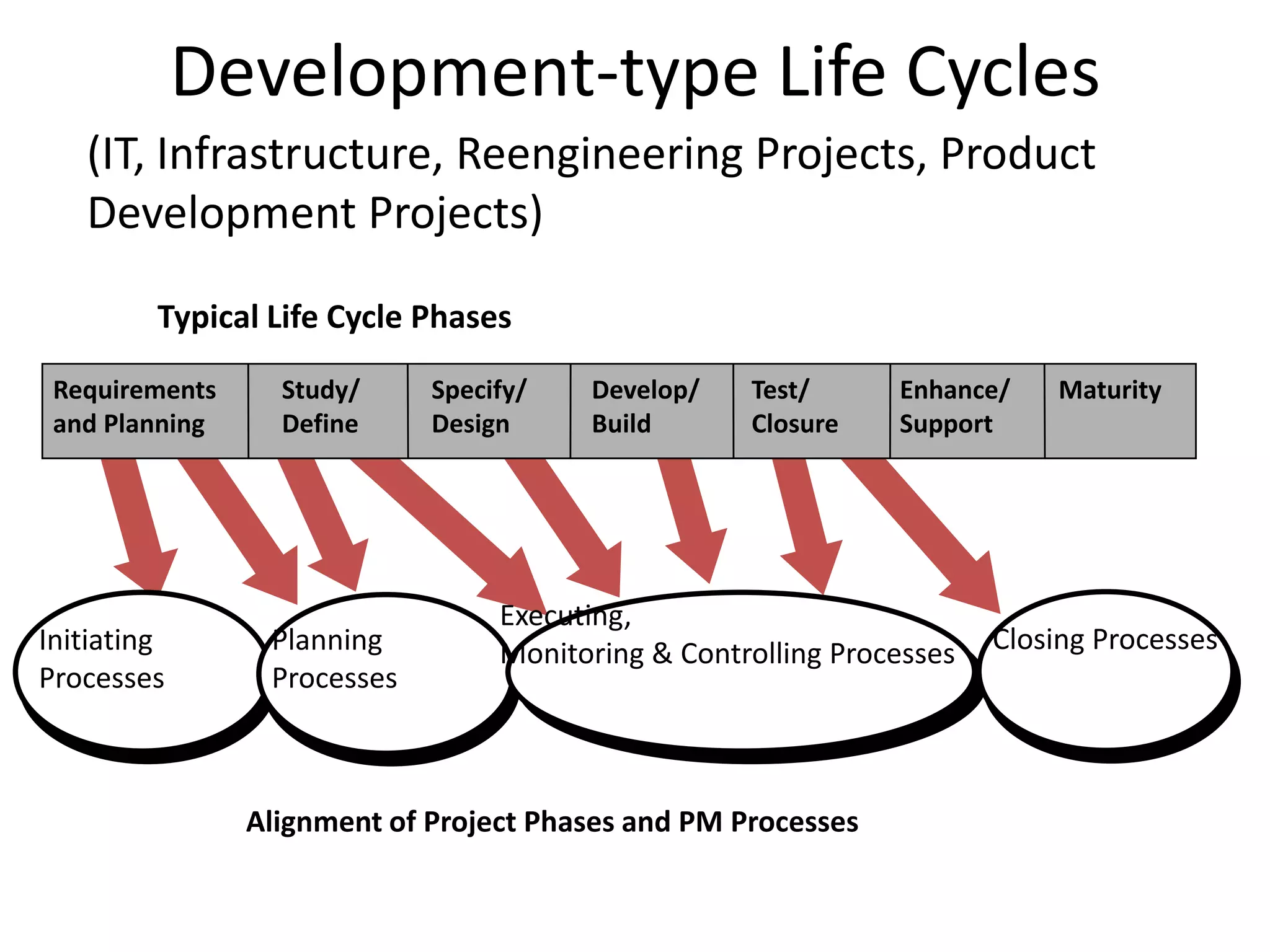
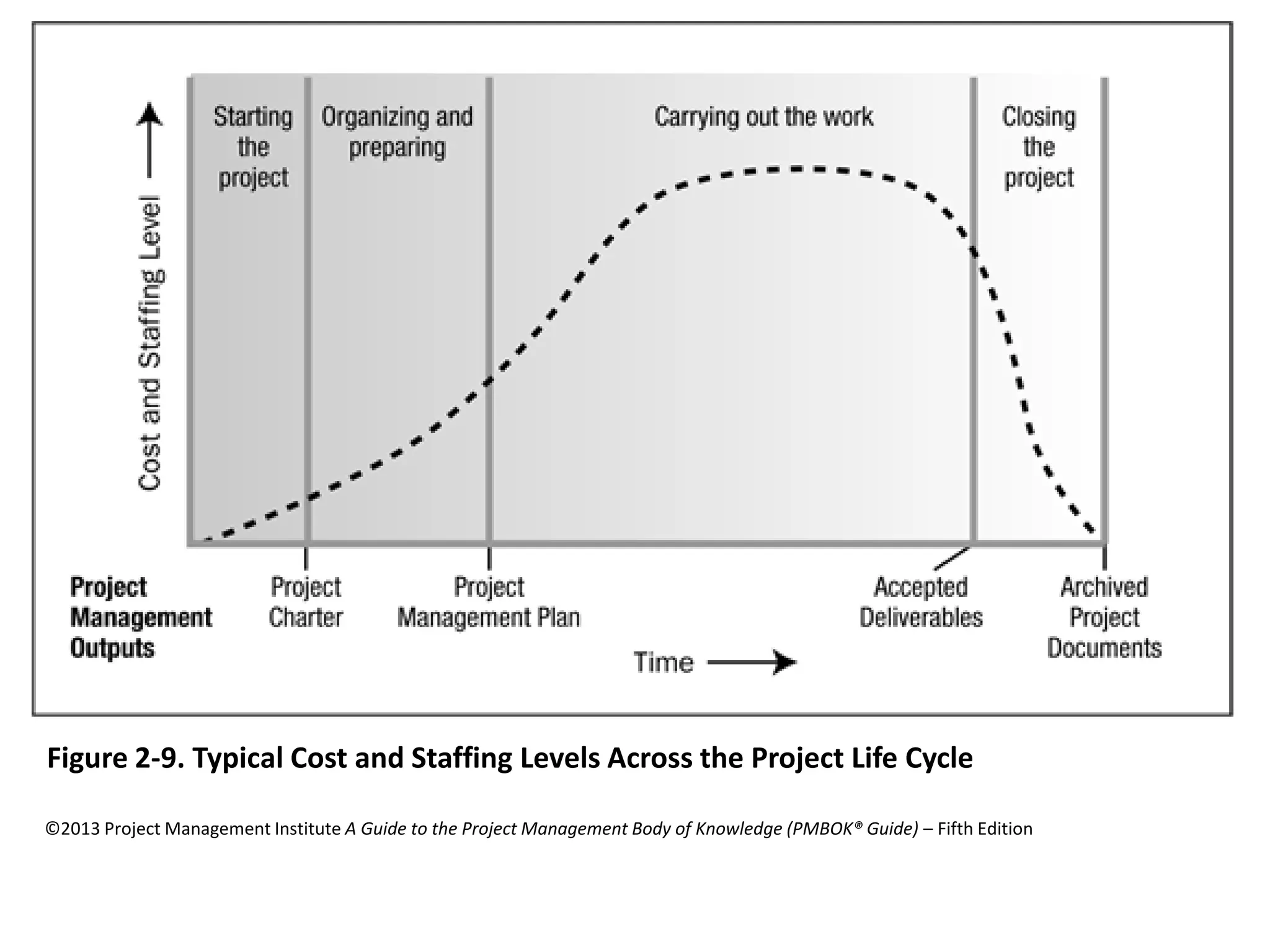
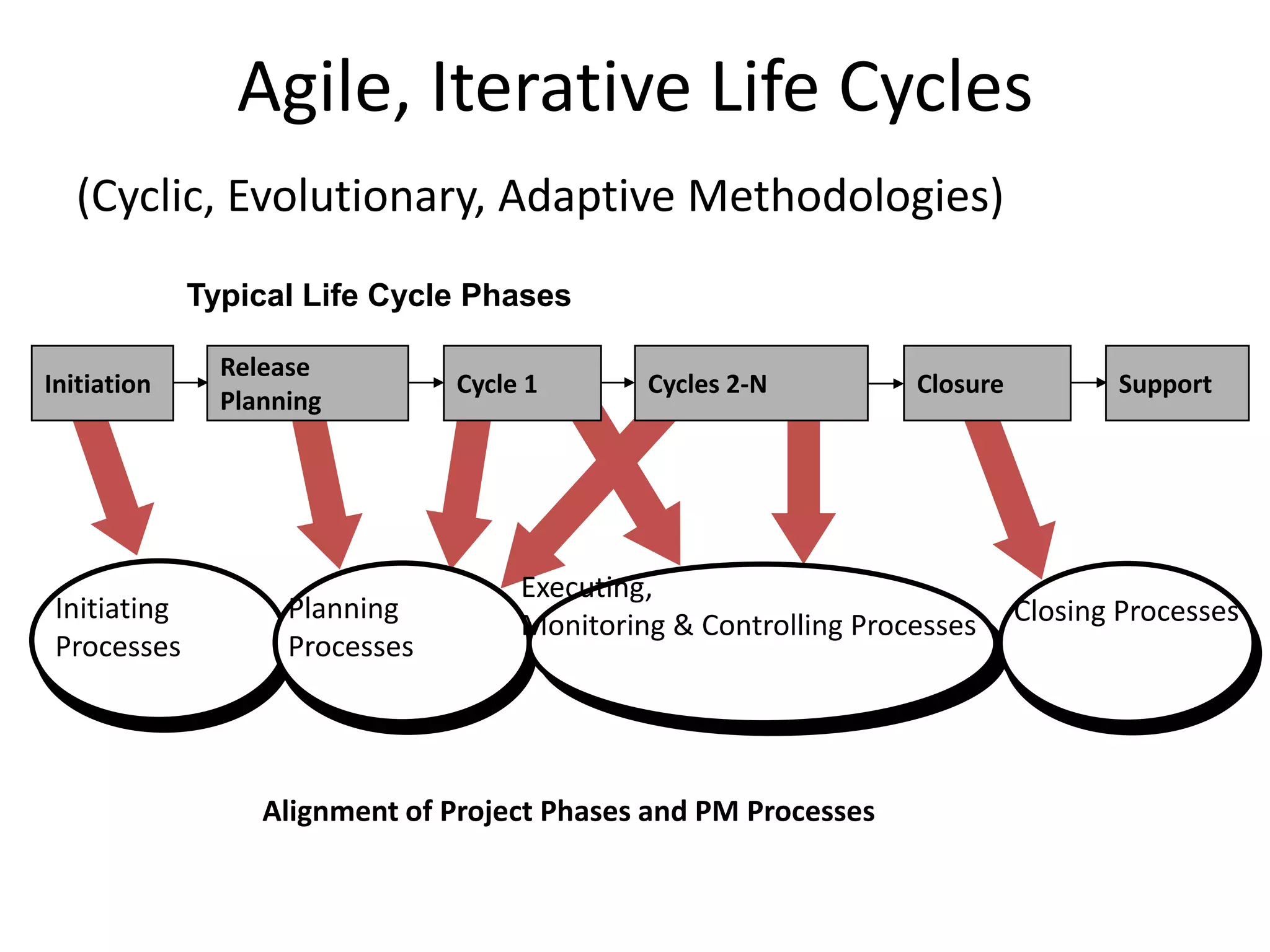
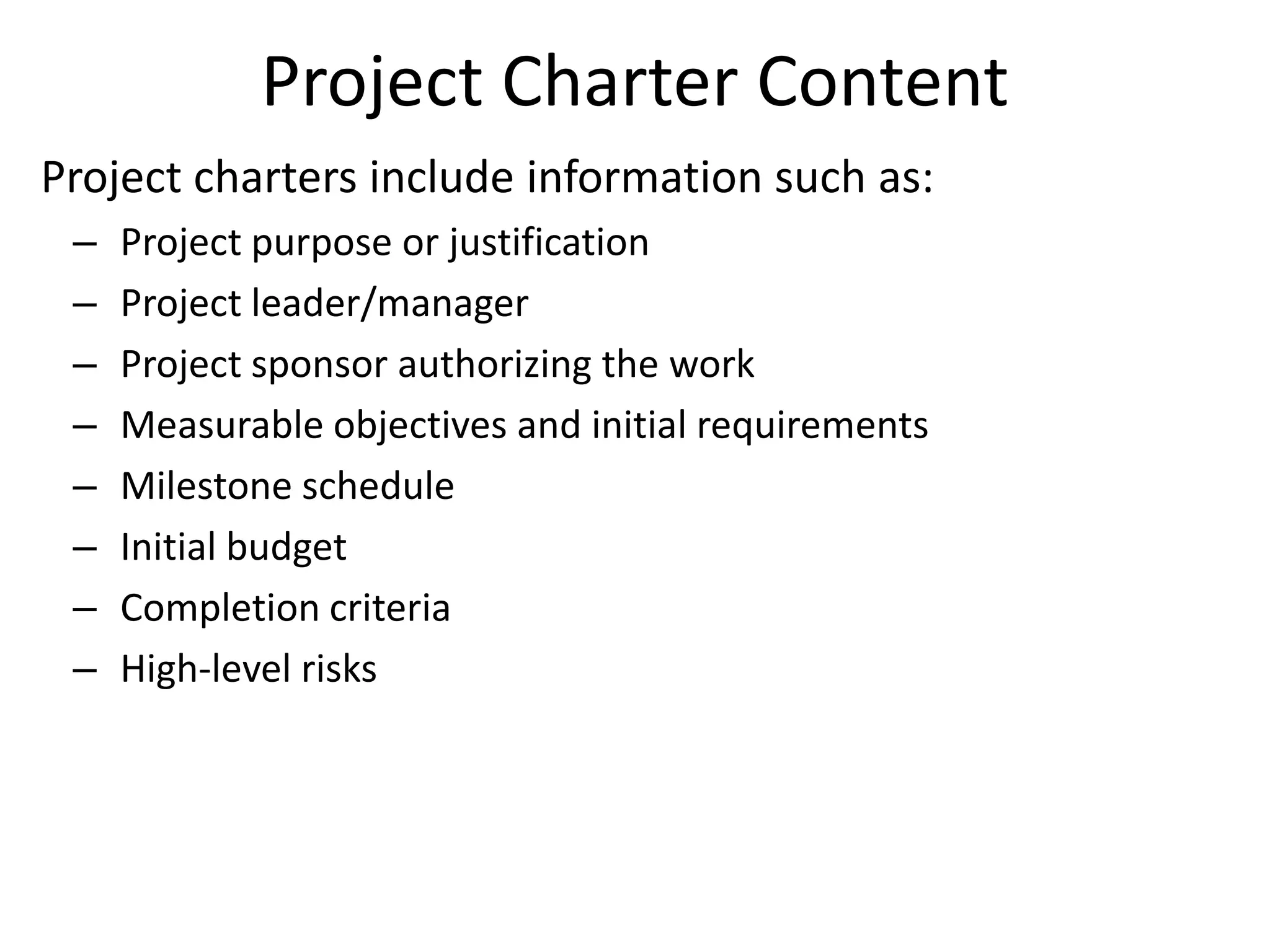
The document provides an overview of project management concepts and processes. It discusses the typical phases of project initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure. It also describes key planning steps such as developing a project charter, identifying stakeholders, acquiring a project team, defining objectives and requirements, creating a work breakdown structure, and developing a project management plan. The document emphasizes the importance of thorough planning and defines some common challenges that can arise in projects.













![Define a Project Vision
Vision is about why your project matters.
– Describes how the world will be better or different when the
project is successfully completed.
– Answers: “What’s in it for me?”
– Can motivate the project team.
“[We will create] a motor car for the great multitude. It will be so
low in price that no man making a good salary will be unable to own
one. The automobile will be taken for granted ... [and we will] give a
large number of men employment at good wages.”
- Henry Ford](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projectmanagementpart1-160418193202/75/Project-management-part-1-36-2048.jpg)