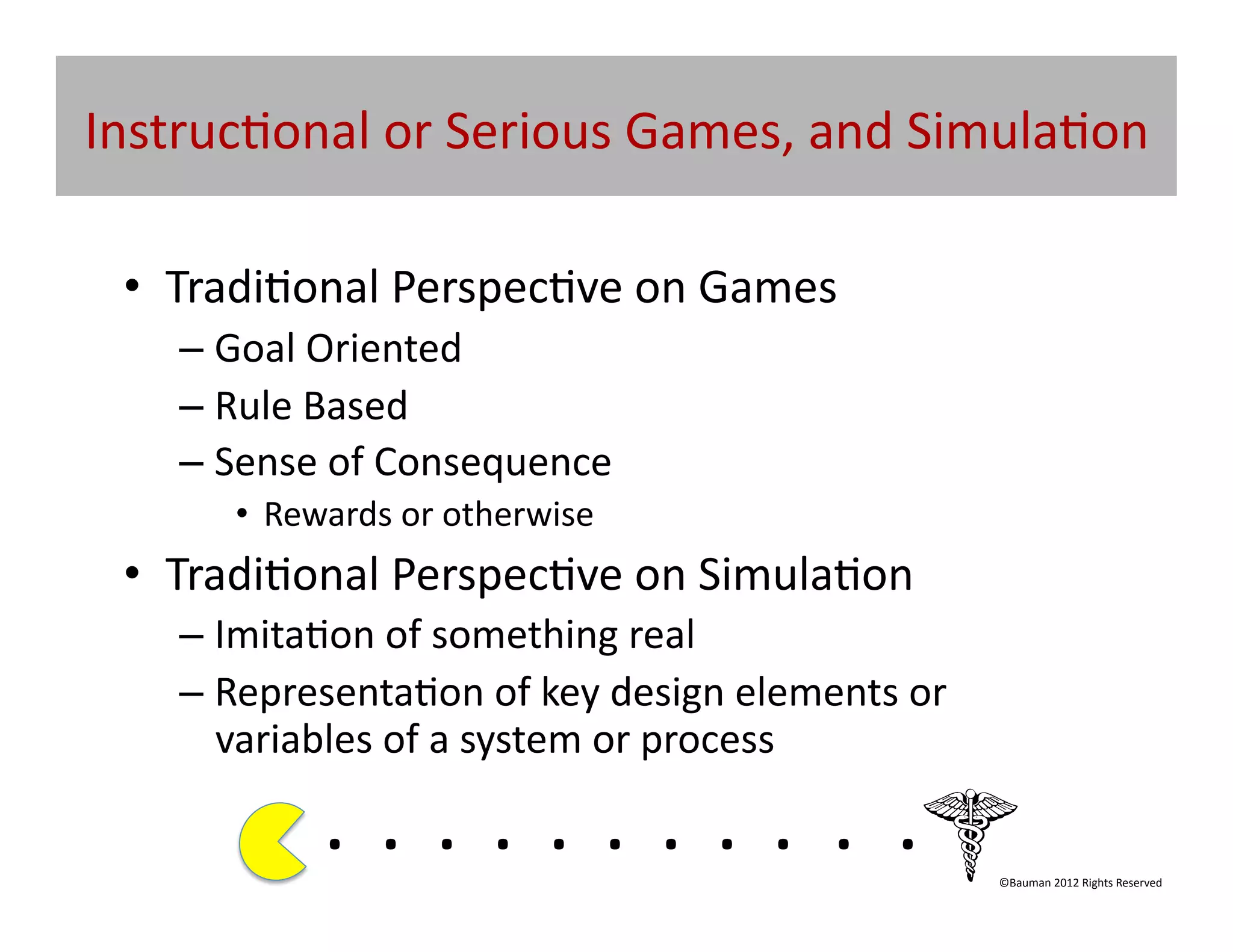
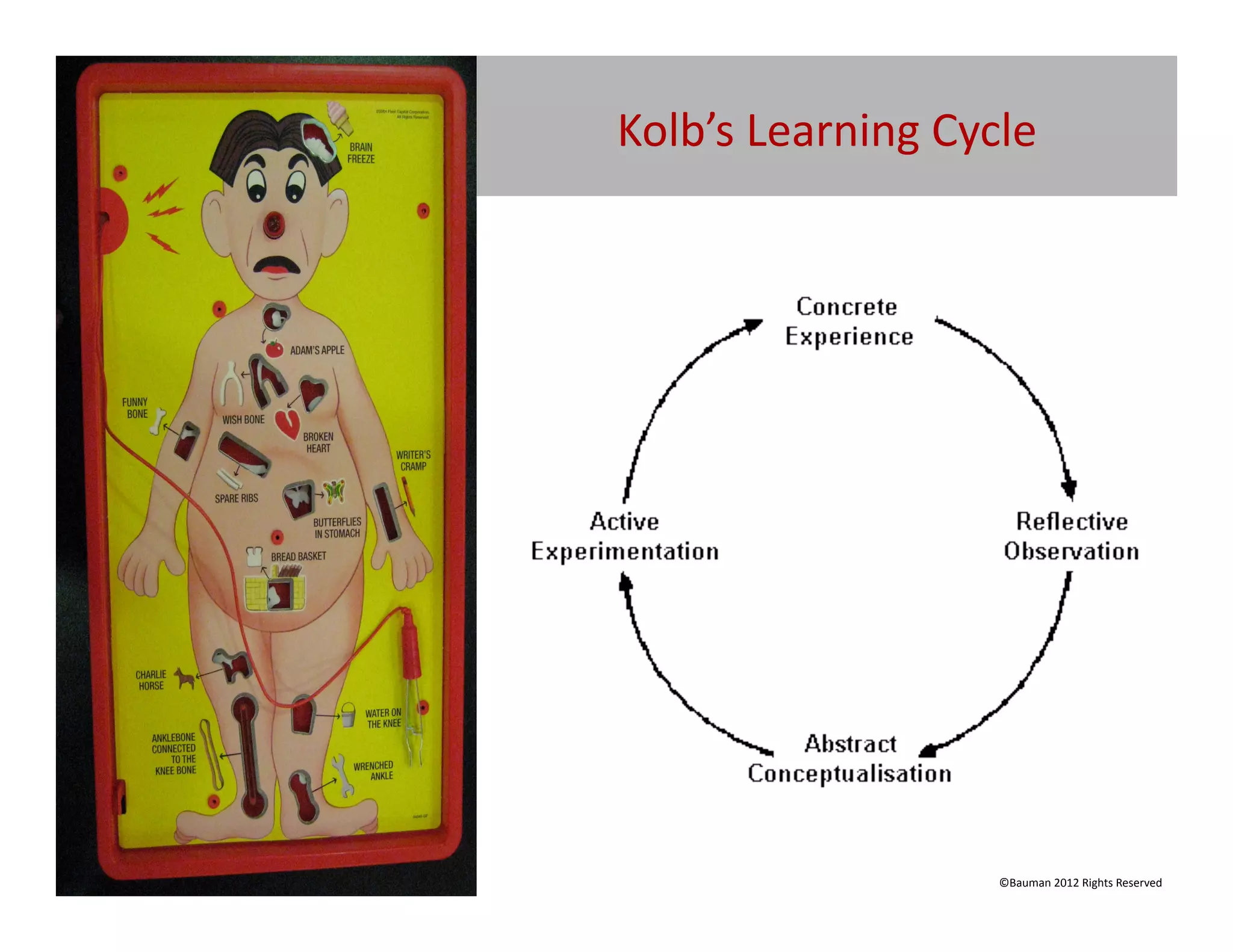
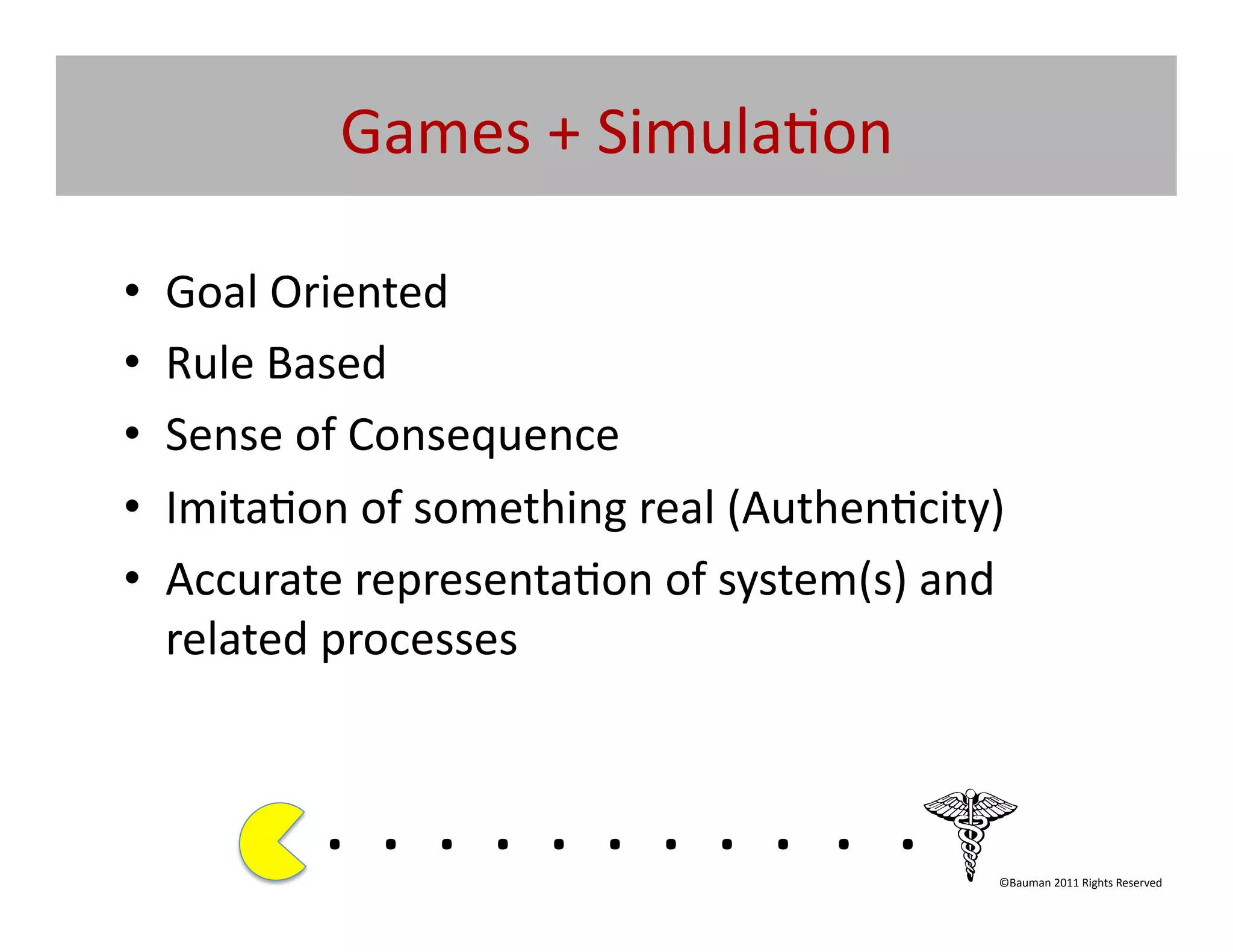
The document outlines the potential of game-based learning in education, emphasizing its integration into digital and media-rich environments to engage contemporary learners. It introduces concepts like ludology, gamification, and the importance of designing experiences that promote effective learning and retention. Participants are encouraged to explore and apply game-based learning techniques in their professional settings to enhance student engagement and educational outcomes.
















![Metagaming
It
is
the
use
of
out-‐of-‐game
[out
of
curriculum]
informa@on
or
resources
to
affect
one's
in-‐game
[prac@ce]
decisions…
Transcends
a
prescribed
rule
set
…uses
external
factors
to
affect
the
game
[prac@ce],
or
goes
beyond
the
supposed
limits
of
the
game
[prac@ce]
environment
h[p://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Metagaming
©Bauman
2012
Rights
Reserved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annharbor5-17-2012-120523221754-phpapp02/75/Game-Based-Learning-A-workshop-to-inform-educators-and-engage-contemporary-learners-20-2048.jpg)
![Ludic
Pedagogy
The
manner
through
which
games
teach
[learners]
players
to
play
[Learn]…
h[p://etd.lsu.edu/docs/available/etd-‐11092011-‐154402/unrestricted/jbroussard_disserta@on.pdf
The
ac@vity
of
play,
par@cularly
when
engaging
a
new
game
always
represents
a
learning
process
©Bauman
2012
Rights
Reserved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annharbor5-17-2012-120523221754-phpapp02/75/Game-Based-Learning-A-workshop-to-inform-educators-and-engage-contemporary-learners-21-2048.jpg)






![Who
Cares…
and
why
does
any
of
this
ma[er?
©Bauman
2012
Rights
Reserved
Because
the
best
and
brightest
learners
become:
Our
next
genera@on
of
scholars
Well
trained
and
excep@onally
educated
people
[clinicians,
teachers,
administrator,
etc..]
are
a
major
part
of
the
solu@on
to
the
healthcare
&
educa@on
crises
that
we
face
locally,
na@onally,
and
interna@onally](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annharbor5-17-2012-120523221754-phpapp02/75/Game-Based-Learning-A-workshop-to-inform-educators-and-engage-contemporary-learners-28-2048.jpg)



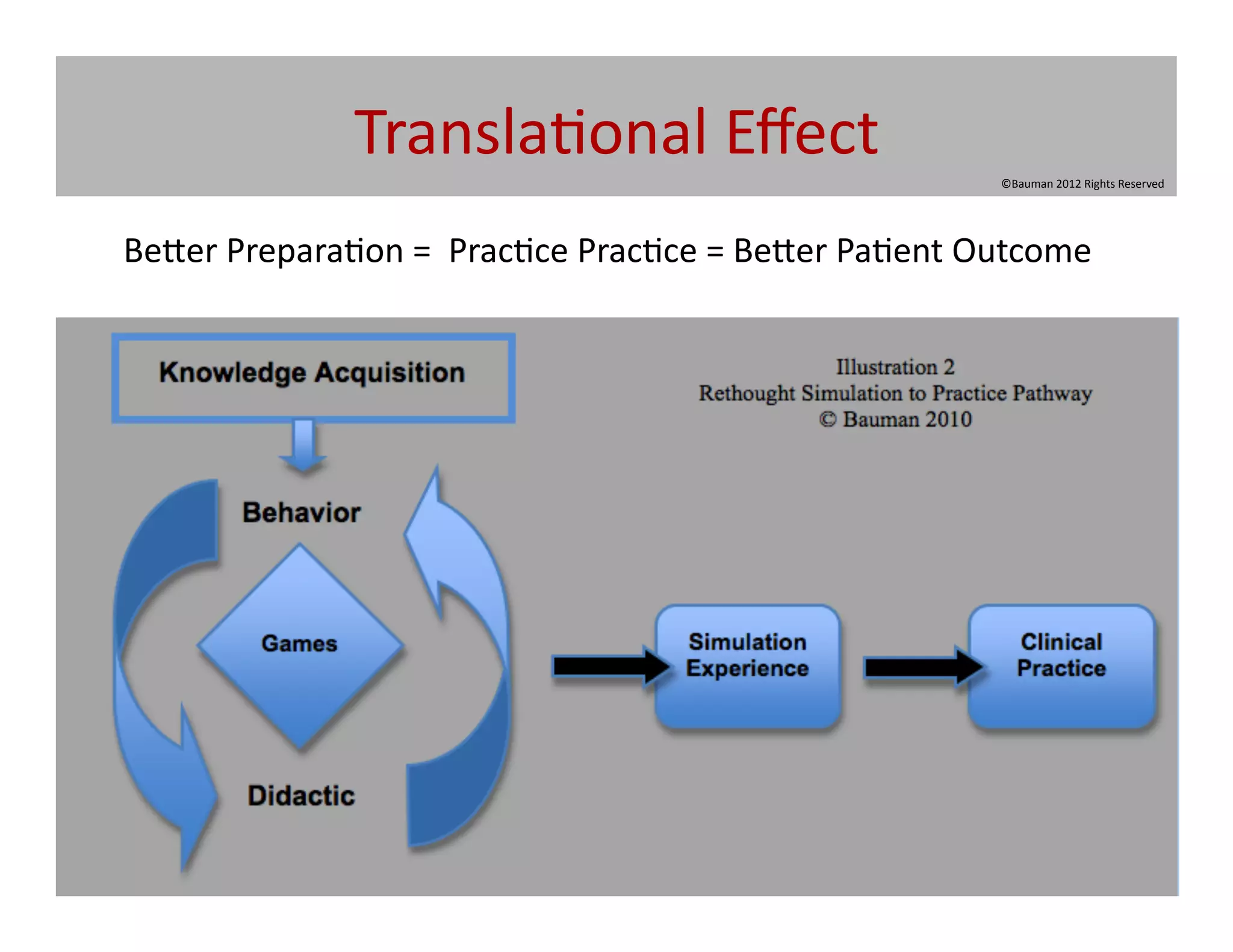
![Transla@onal
Effect
Serious
Games
[ludic
pedagogy]
leverage
created
environments
so
that
learning
takes
place
as
performance
though
carefully
designed
experiences
that
o|en
use
a
contextually
situated
narra5ve
to
promote
curriculum
objec@ves
©Bauman
2012
Rights
Reserved](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annharbor5-17-2012-120523221754-phpapp02/75/Game-Based-Learning-A-workshop-to-inform-educators-and-engage-contemporary-learners-33-2048.jpg)






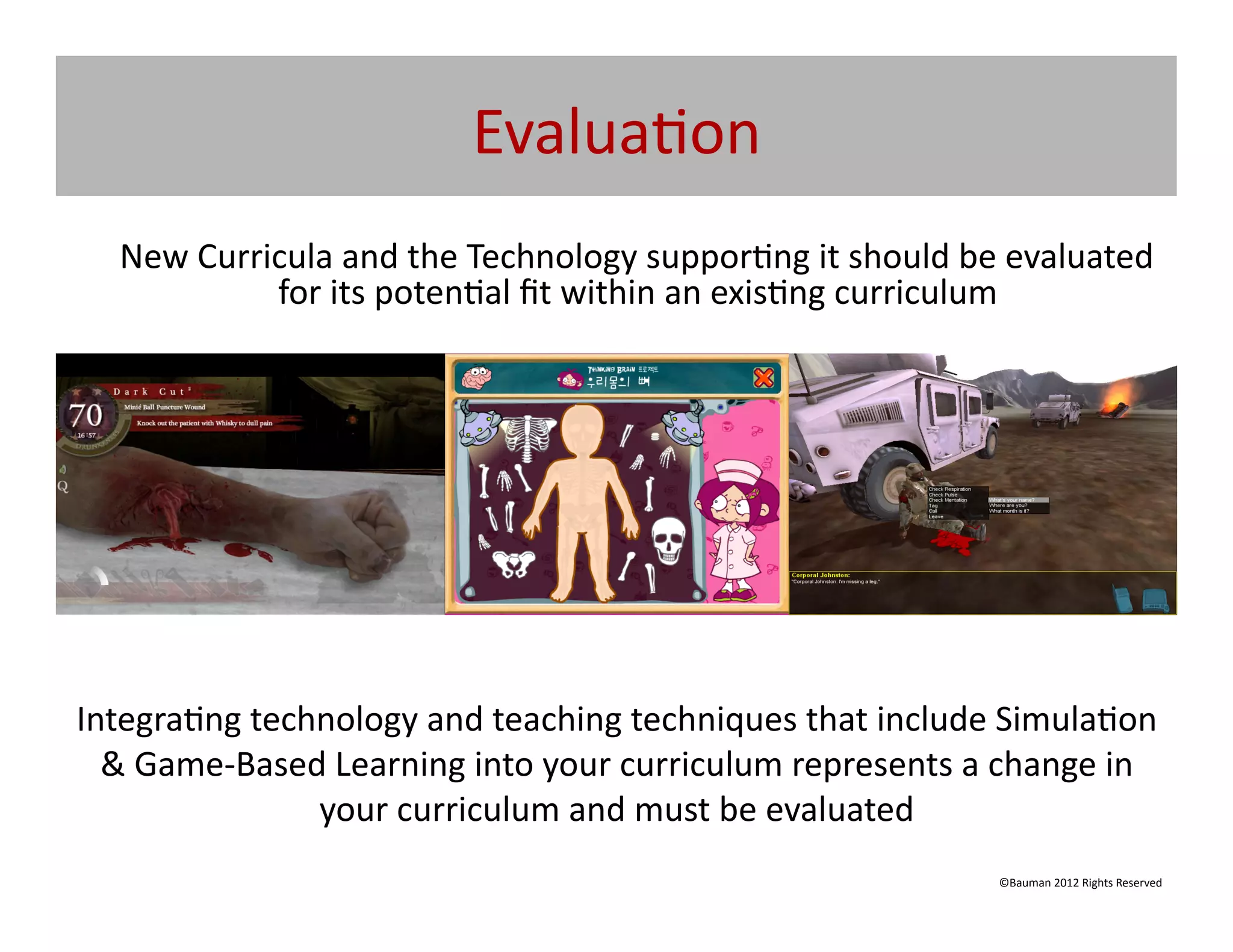









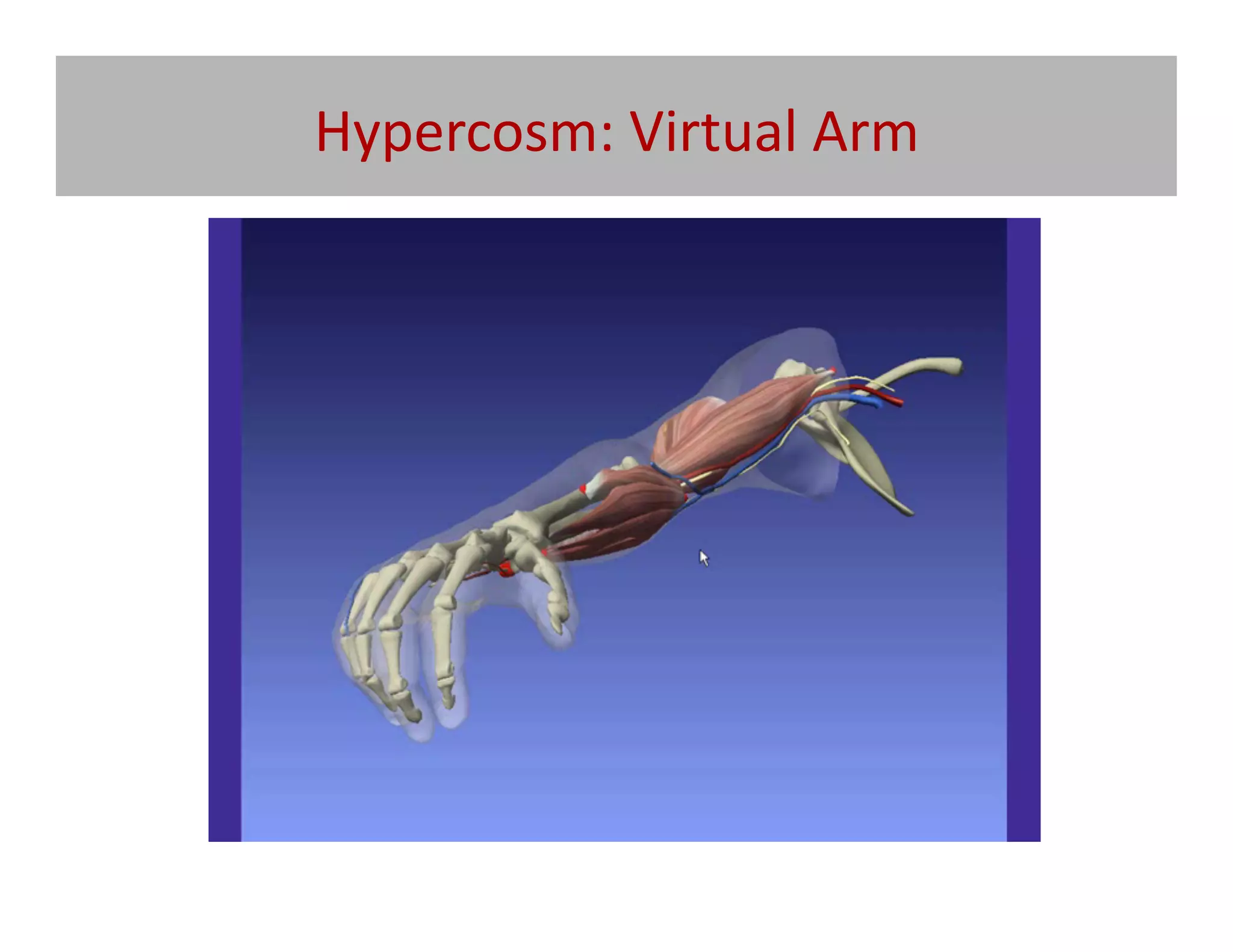
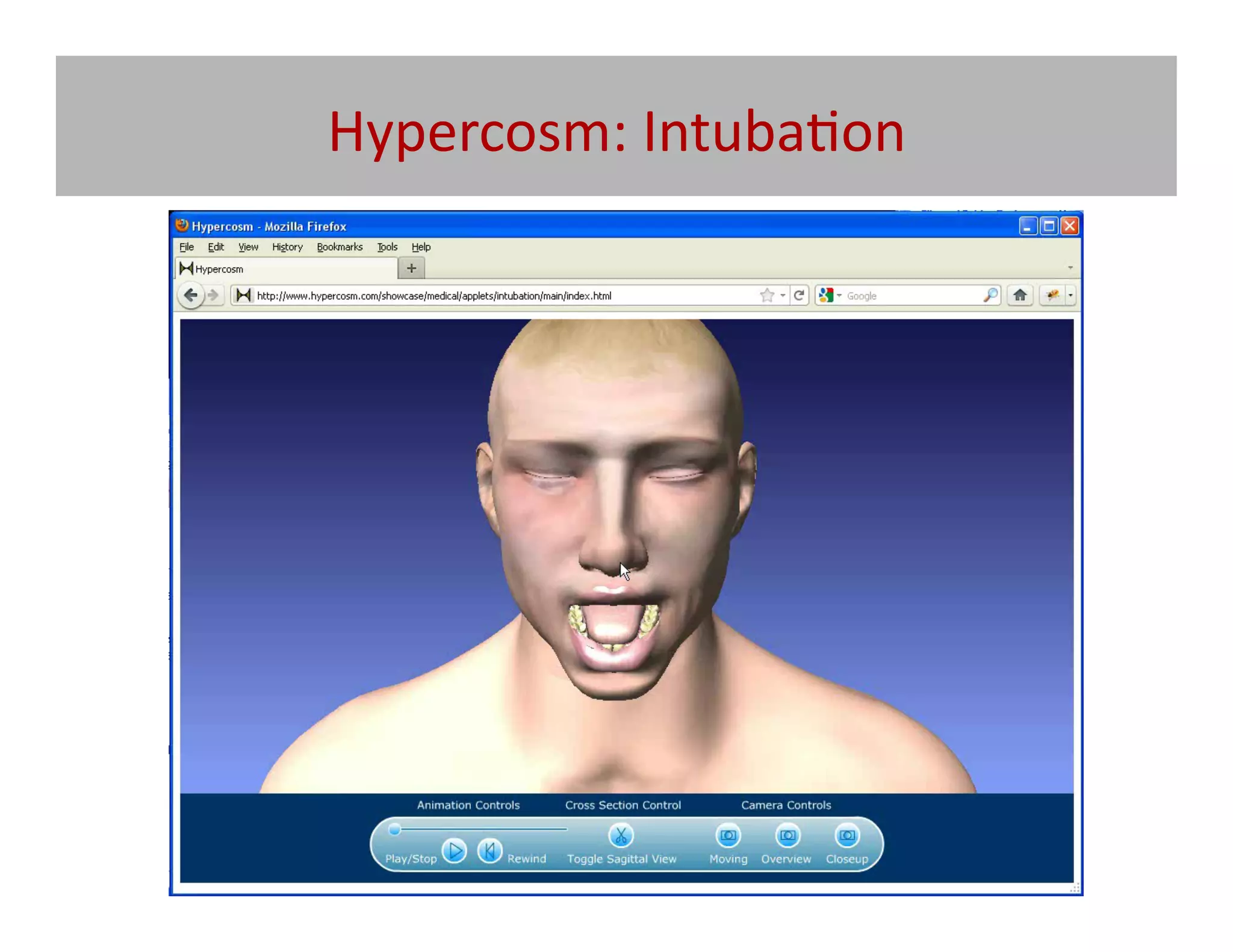
![What
sorts
of
Games
&
Environments
are
out
there…
©Bauman
2012
Rights
Reserved
MMOG’s
–
Massively
Mul@-‐player
online
Games
[Repurposing
Commercial
Games
and
exis@ng
mul@-‐media]
Starcra|
II
–
4.5
Million
Copies,
14
Languages,
5
Con@nents
World
of
WarCra|
Quest
Atlan@s
(K12
Audience)
50K
Children,
6
Con@nents
Second
Life
(+/-‐)
These
environments
provide
online
virtual
worlds
that
can
promote
many
of
the
objec@ves
we
find
valuable
to
clinical
disciplines
Teamwork
Cri@cal
Thinking
Problem
Solving
Pa[ern
Recogni@on](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/annharbor5-17-2012-120523221754-phpapp02/75/Game-Based-Learning-A-workshop-to-inform-educators-and-engage-contemporary-learners-52-2048.jpg)