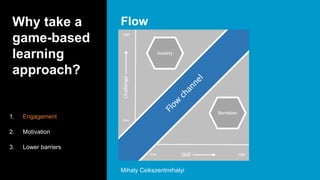
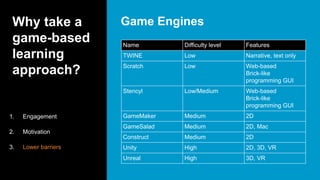
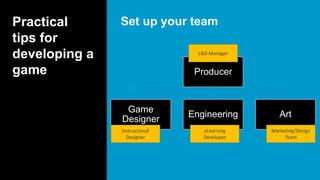
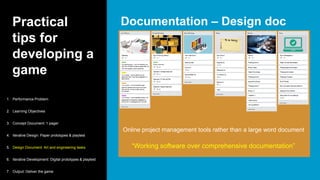
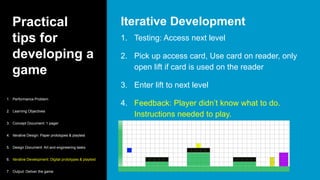
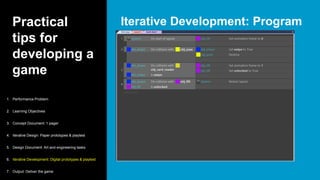
This document serves as a primer on game-based learning, detailing its definition, benefits, and implementation strategies. It highlights the importance of engagement and motivation in learning processes, as well as practical tips for developing effective game-based learning experiences. The content covers elements like gamification types, the development process, and the significance of playtesting in creating educational games.