The document discusses key aspects of procurement and order processing including:
1) Procurement refers to receiving, recording, filling, and assembling orders for shipment. It involves identifying suppliers, soliciting proposals, selecting suppliers, and reviewing supplier performance.
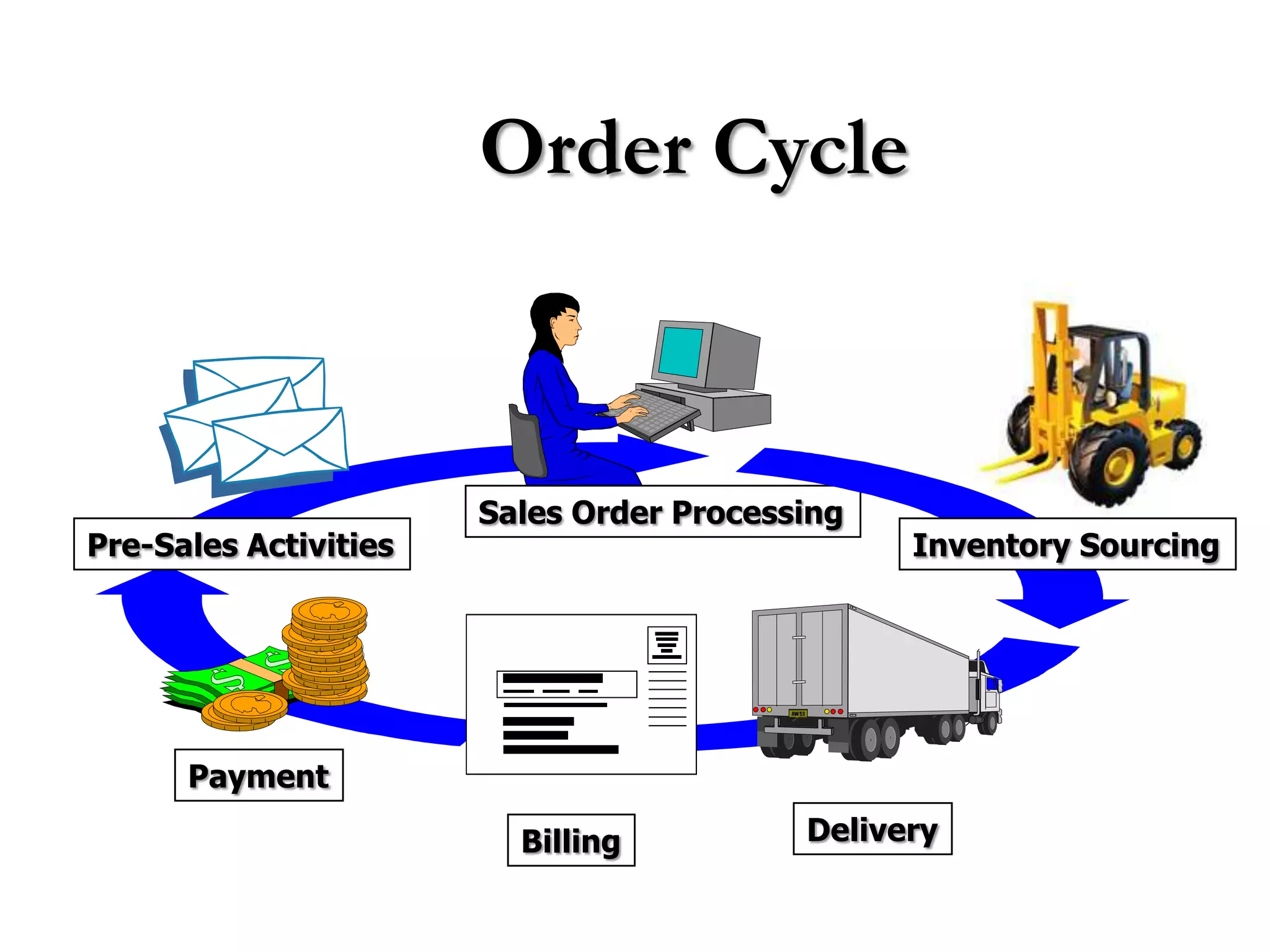
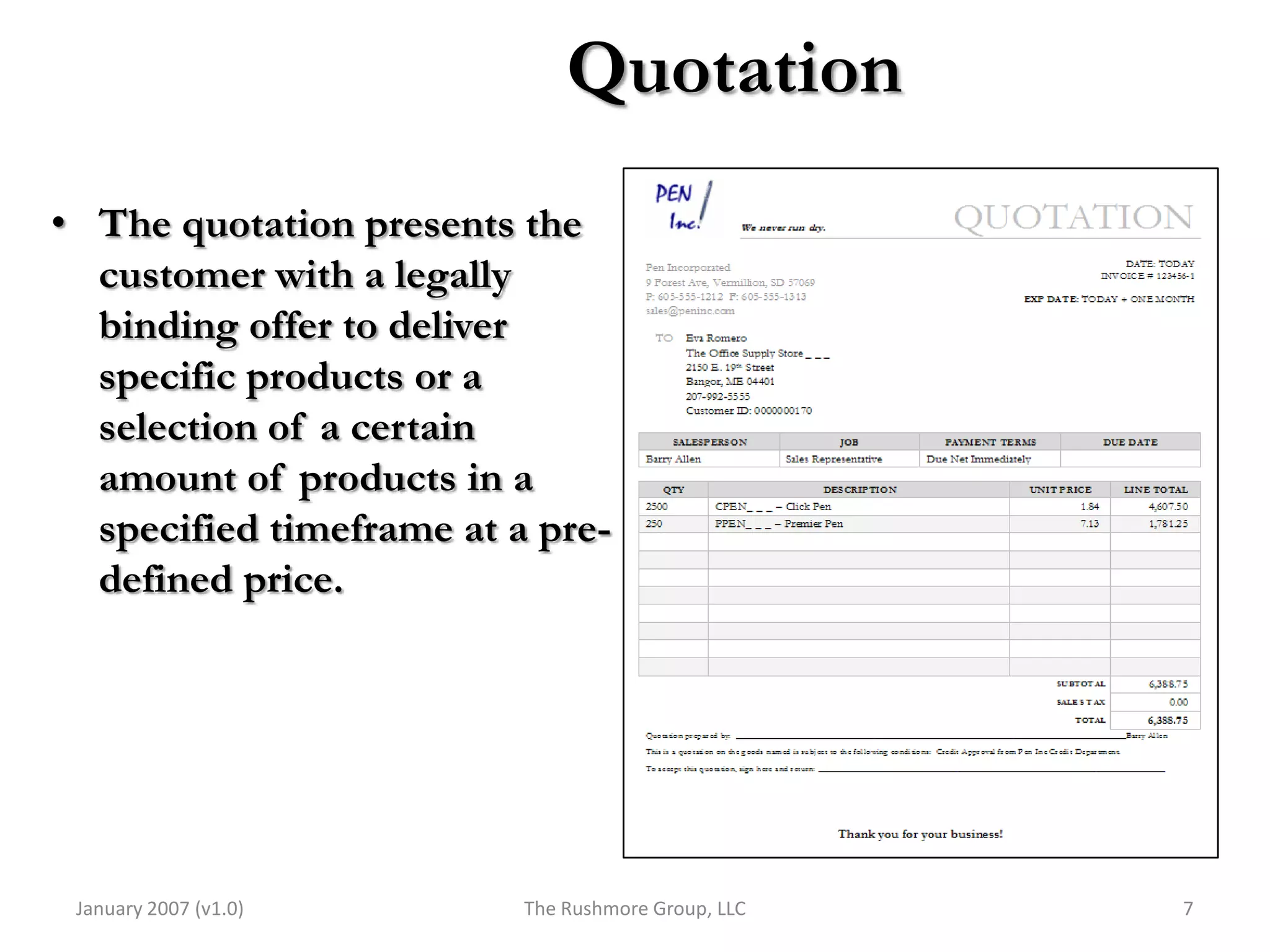
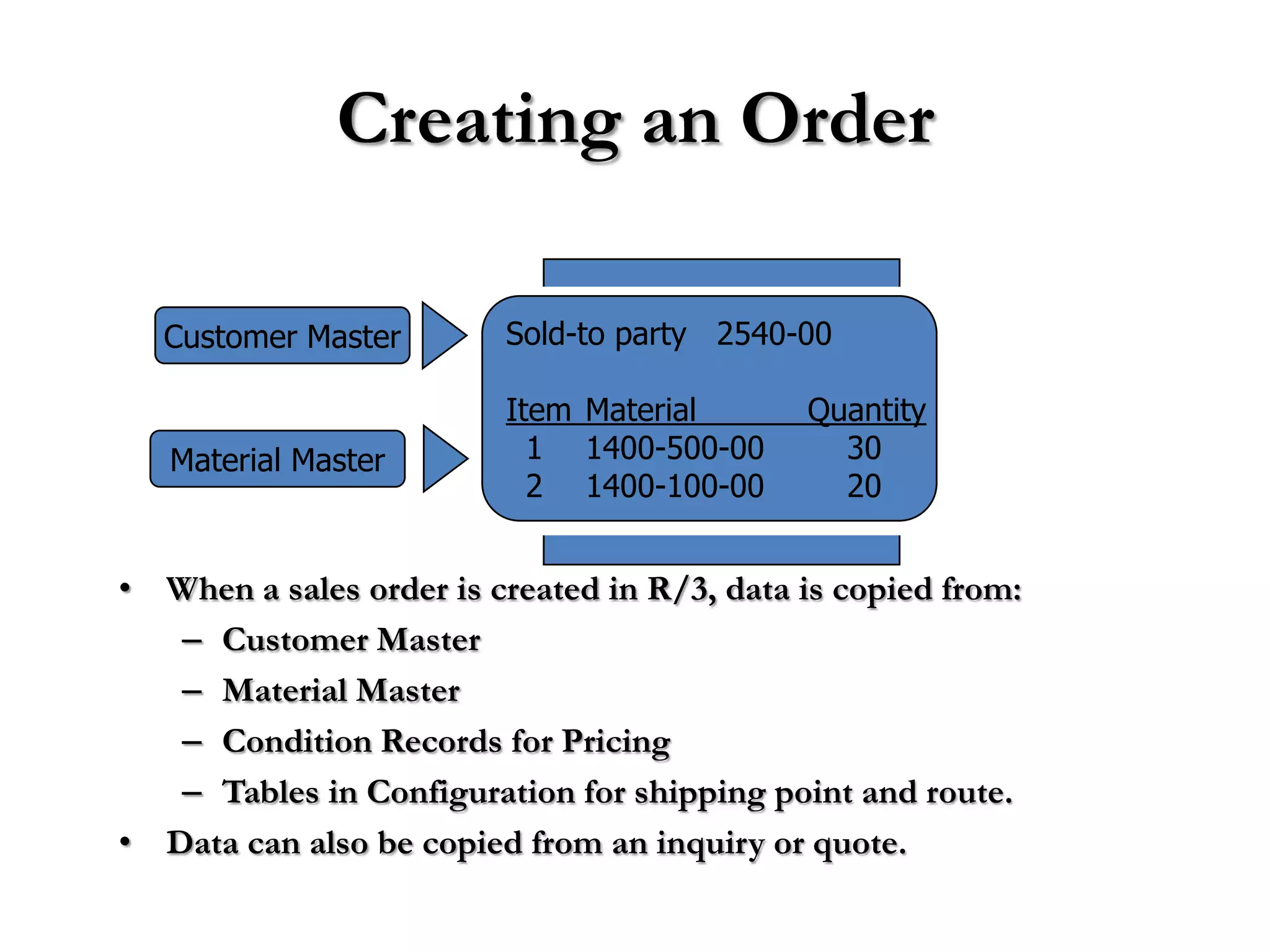
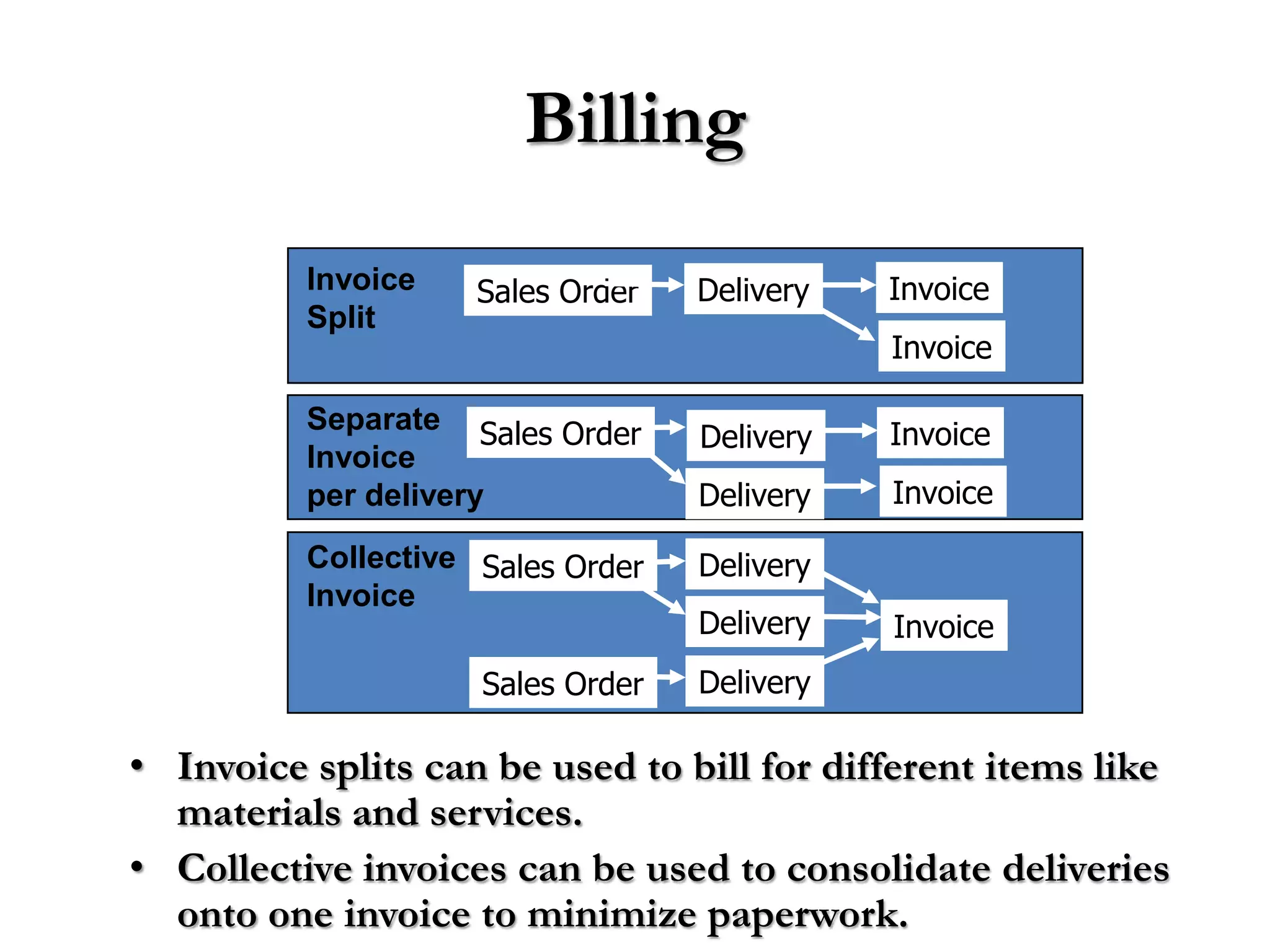
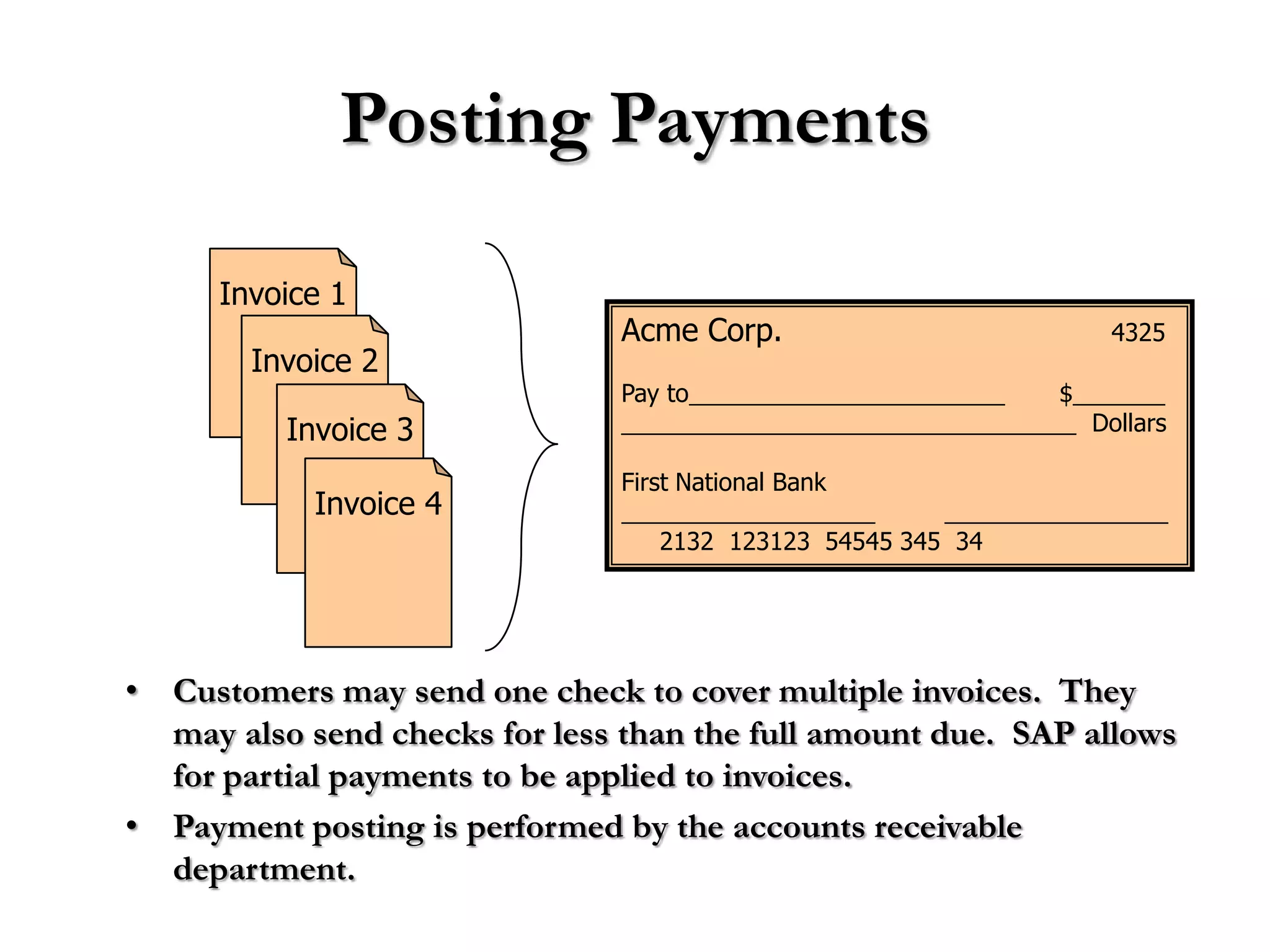
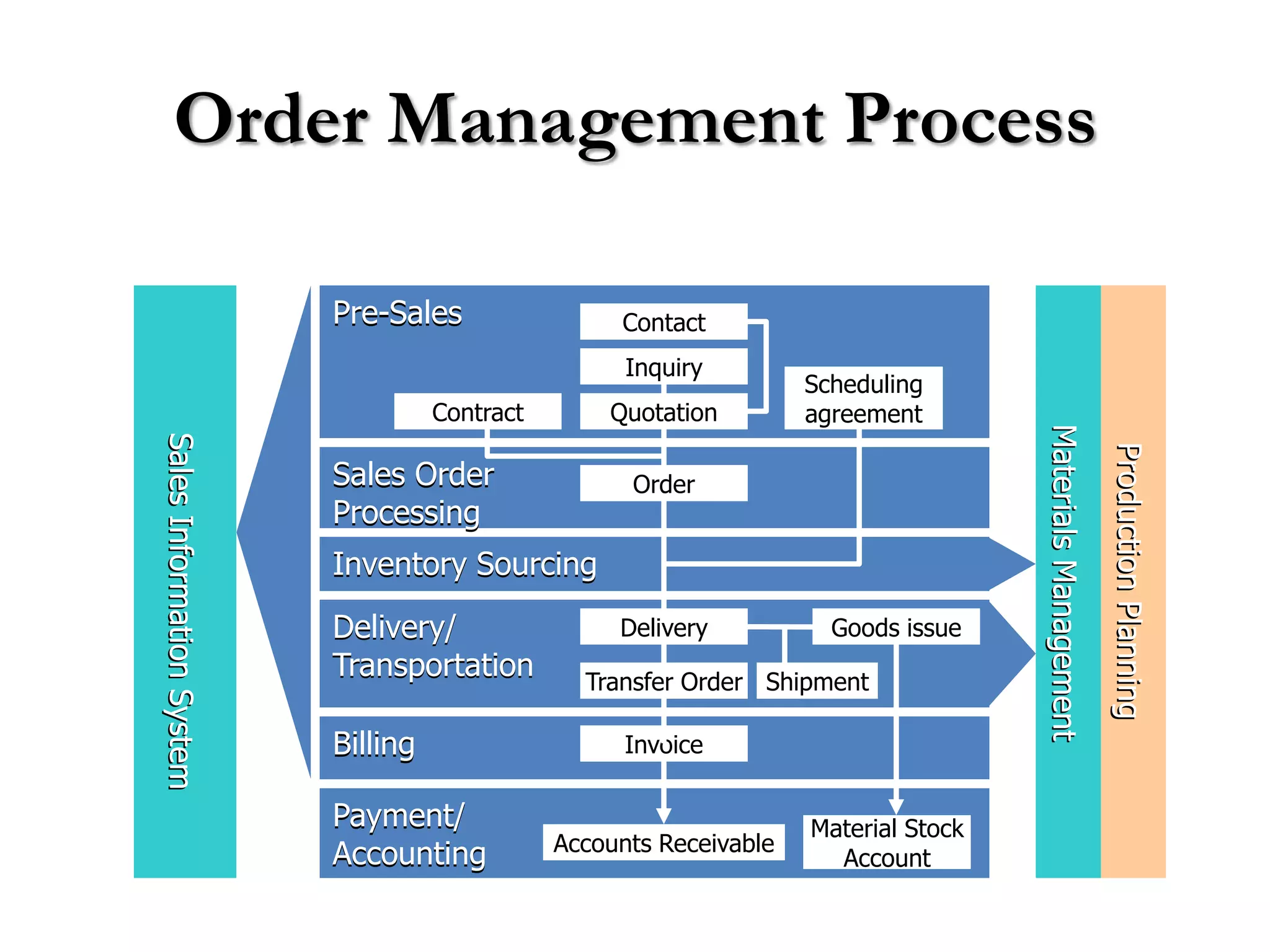
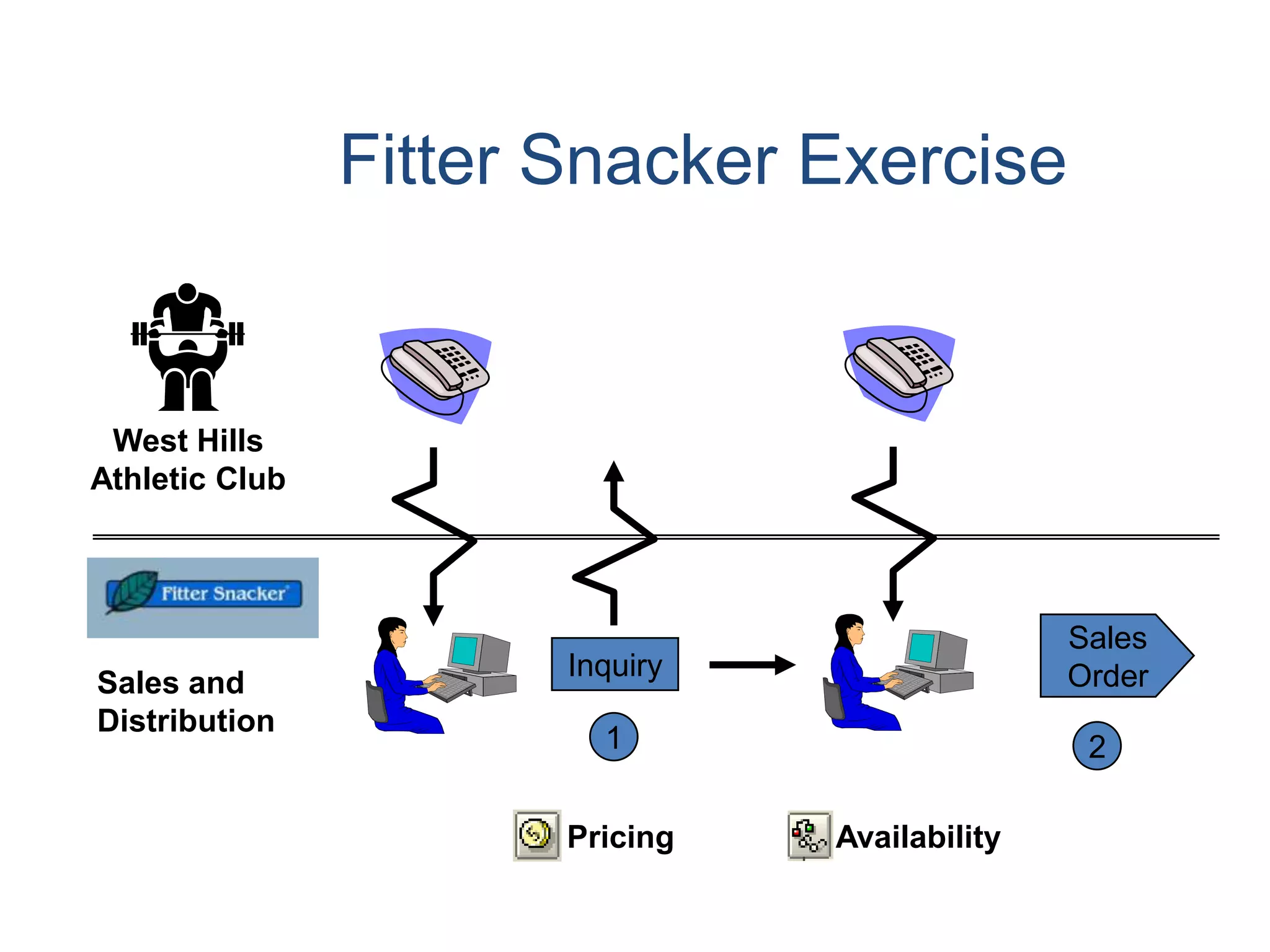
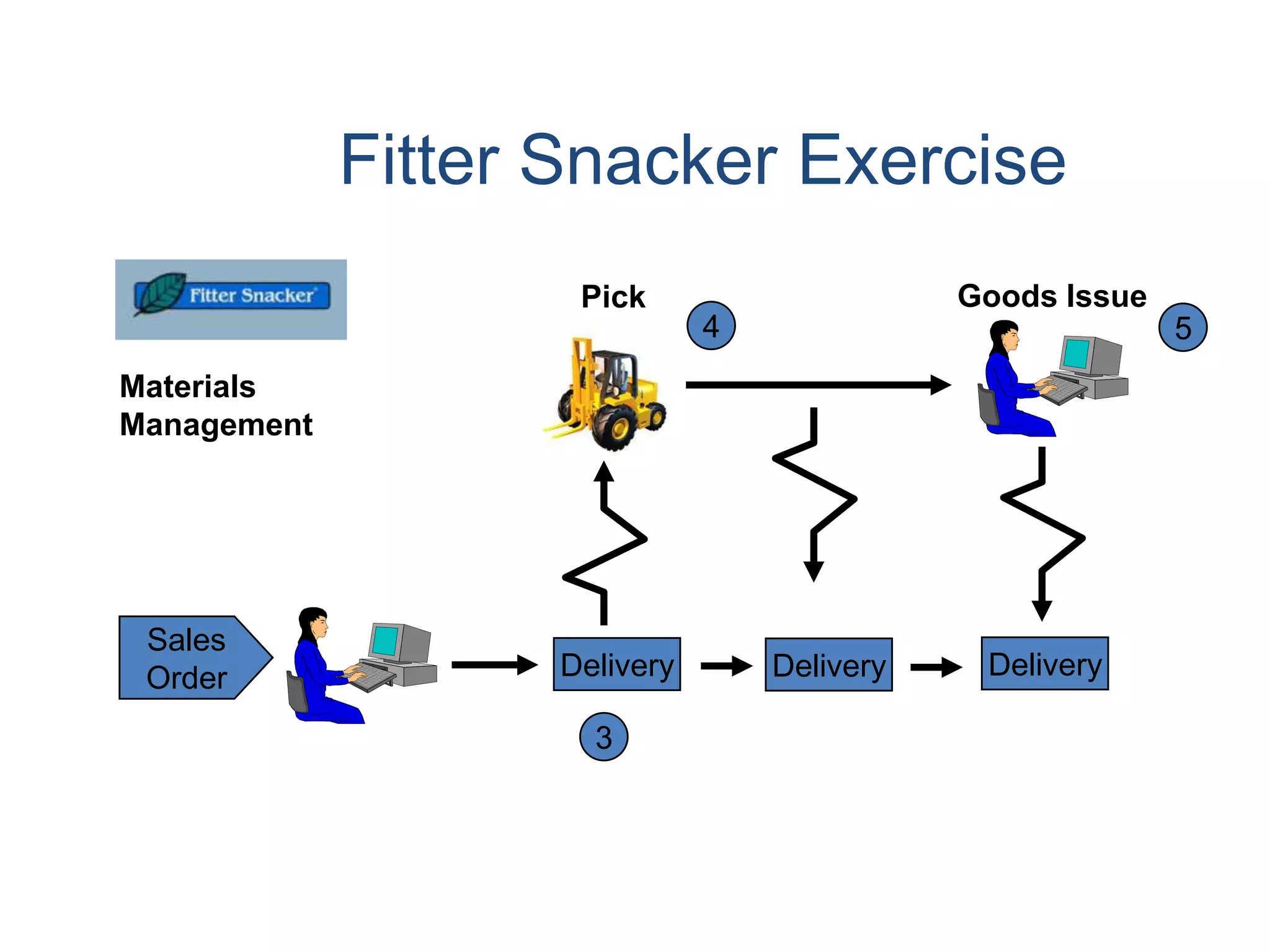
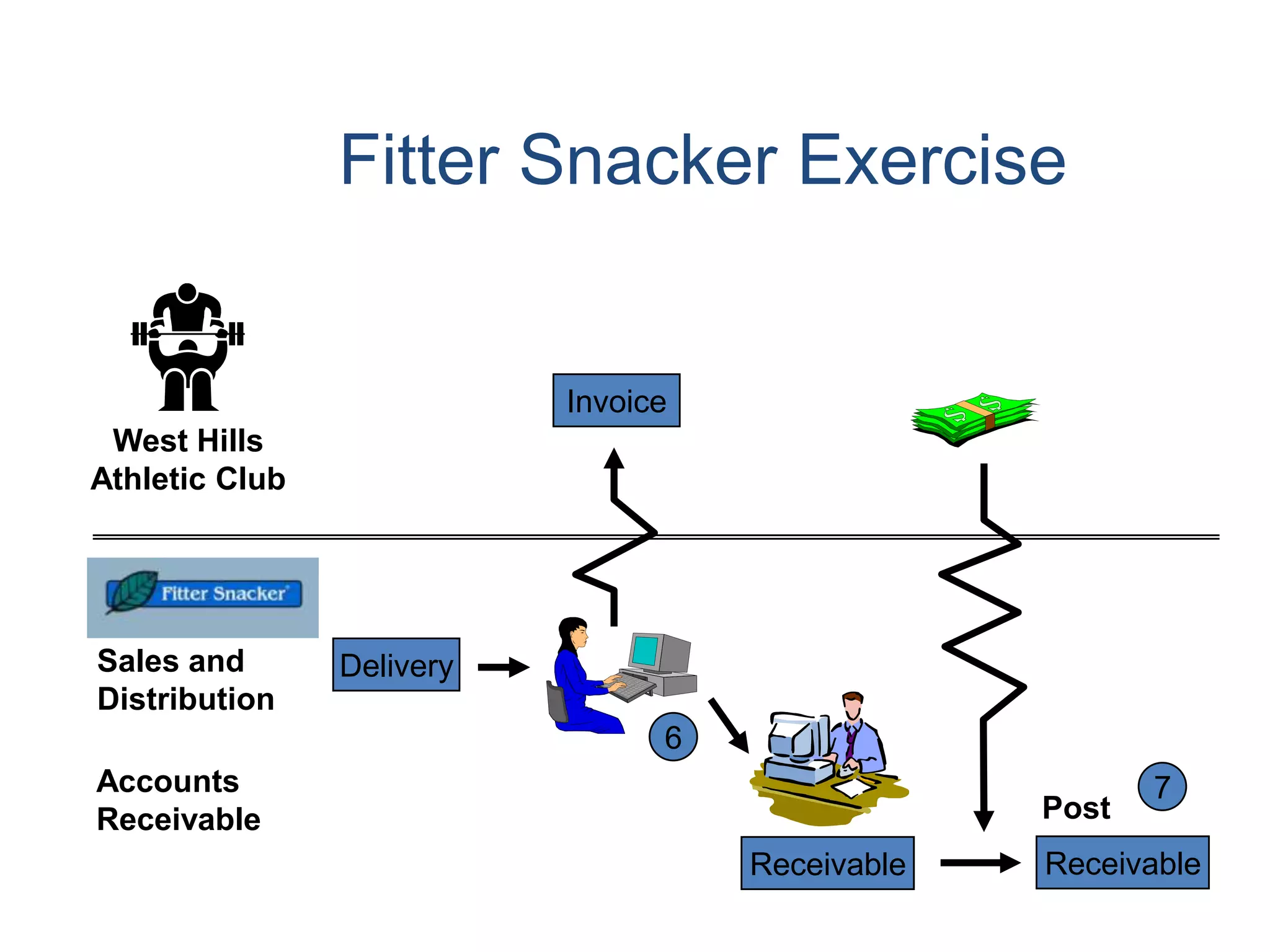
2) Order processing includes activities like creating sales orders, checking inventory availability, scheduling deliveries, generating billing documents, and tracking payments.
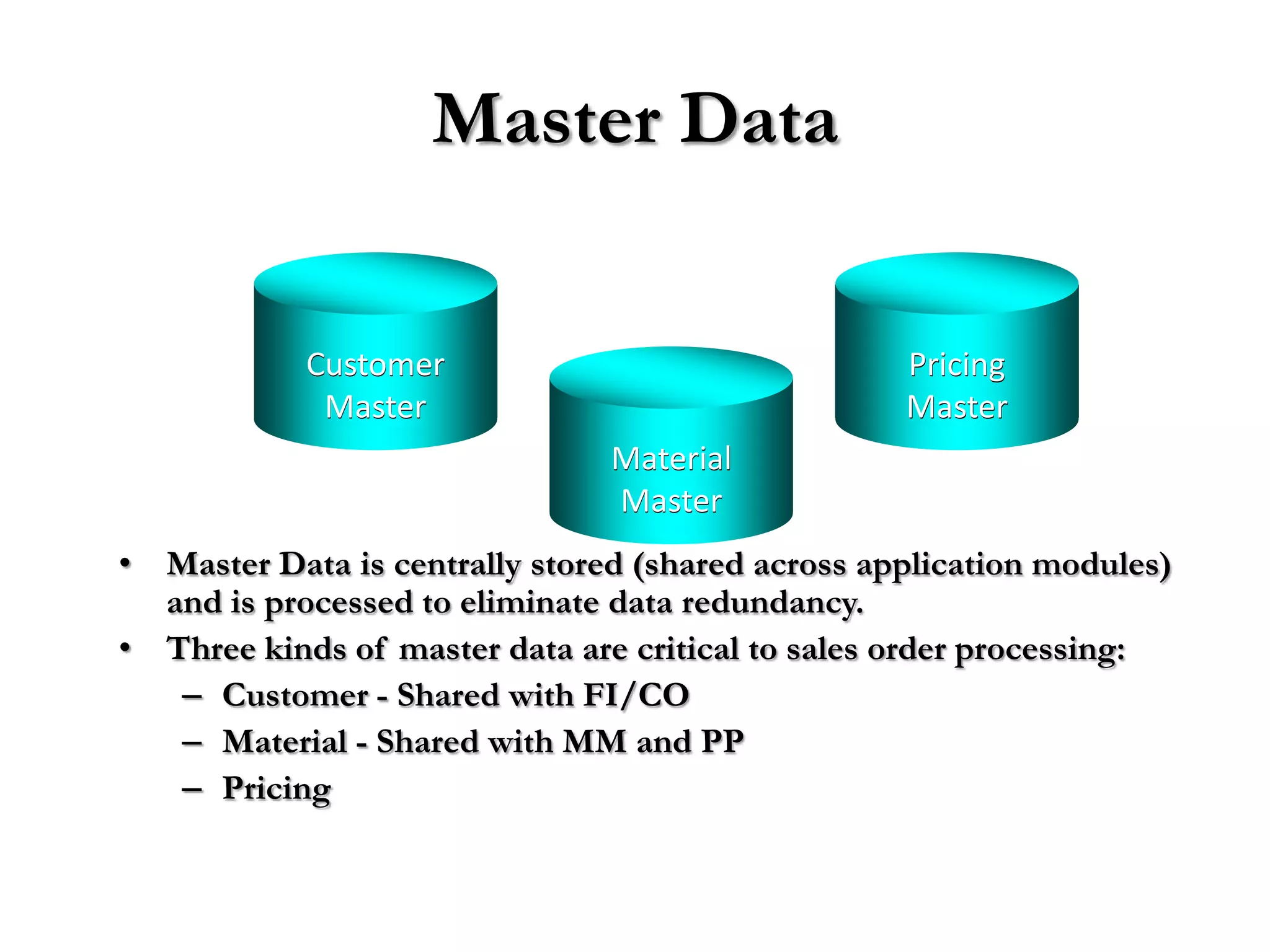
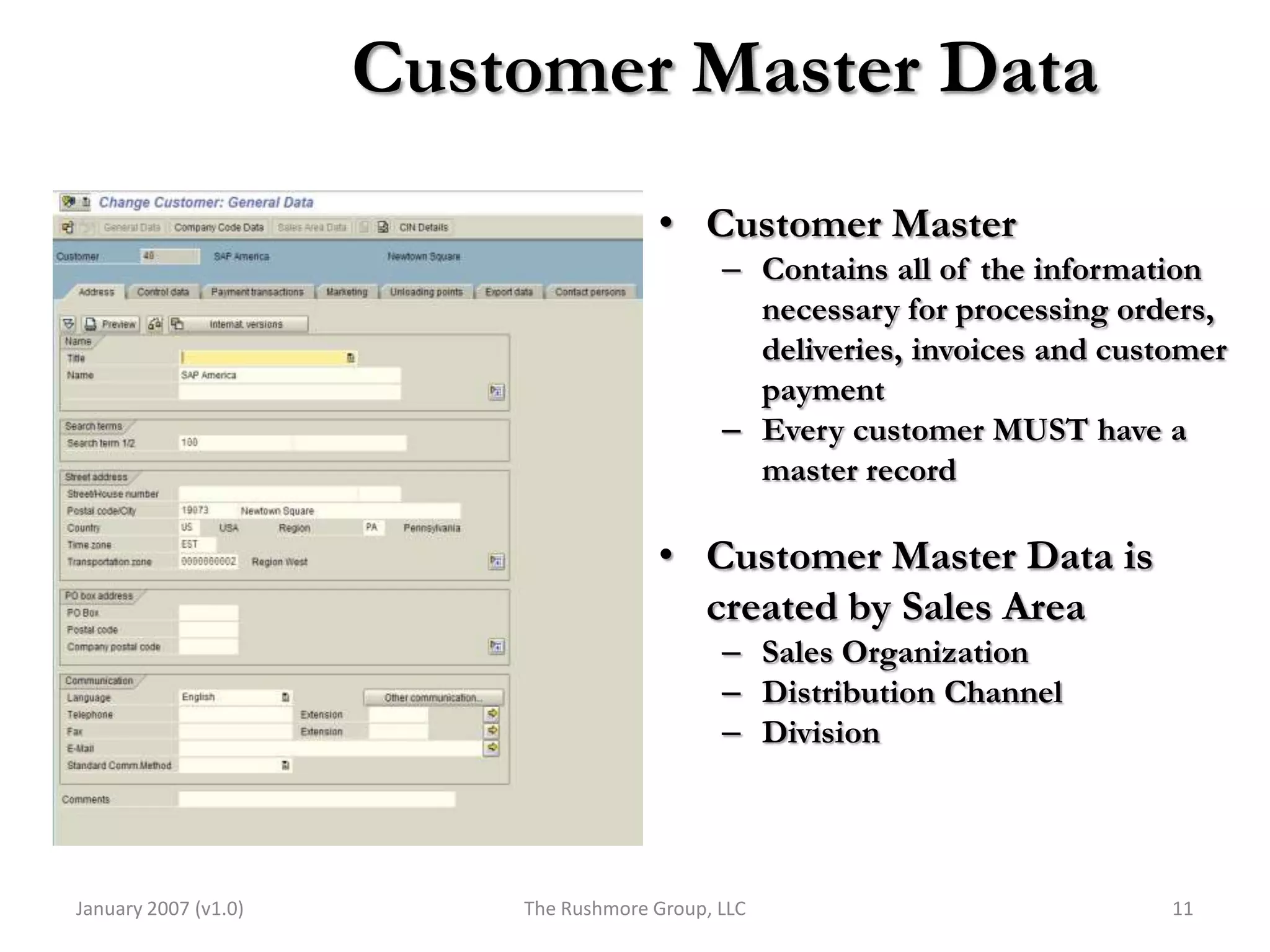
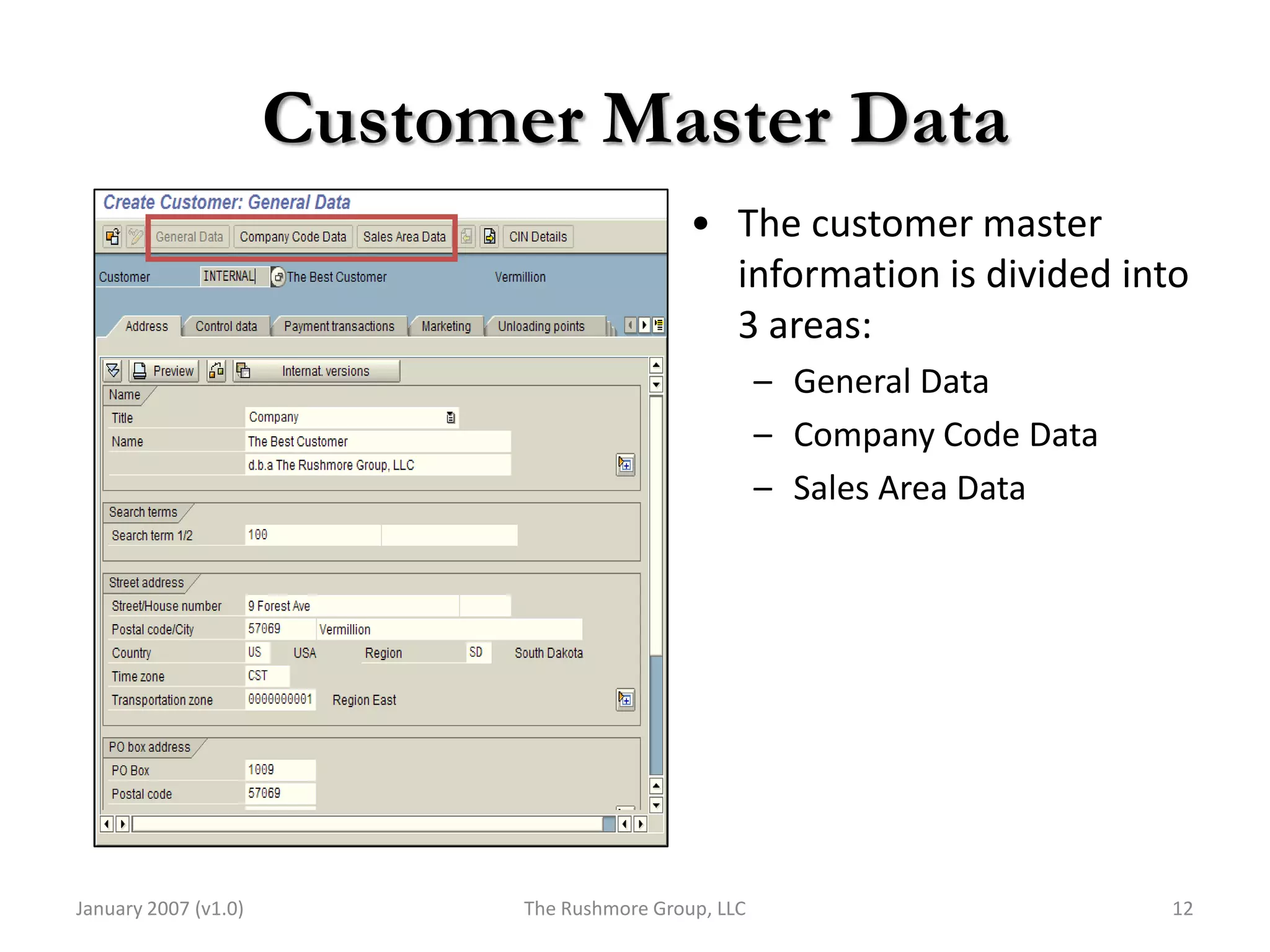
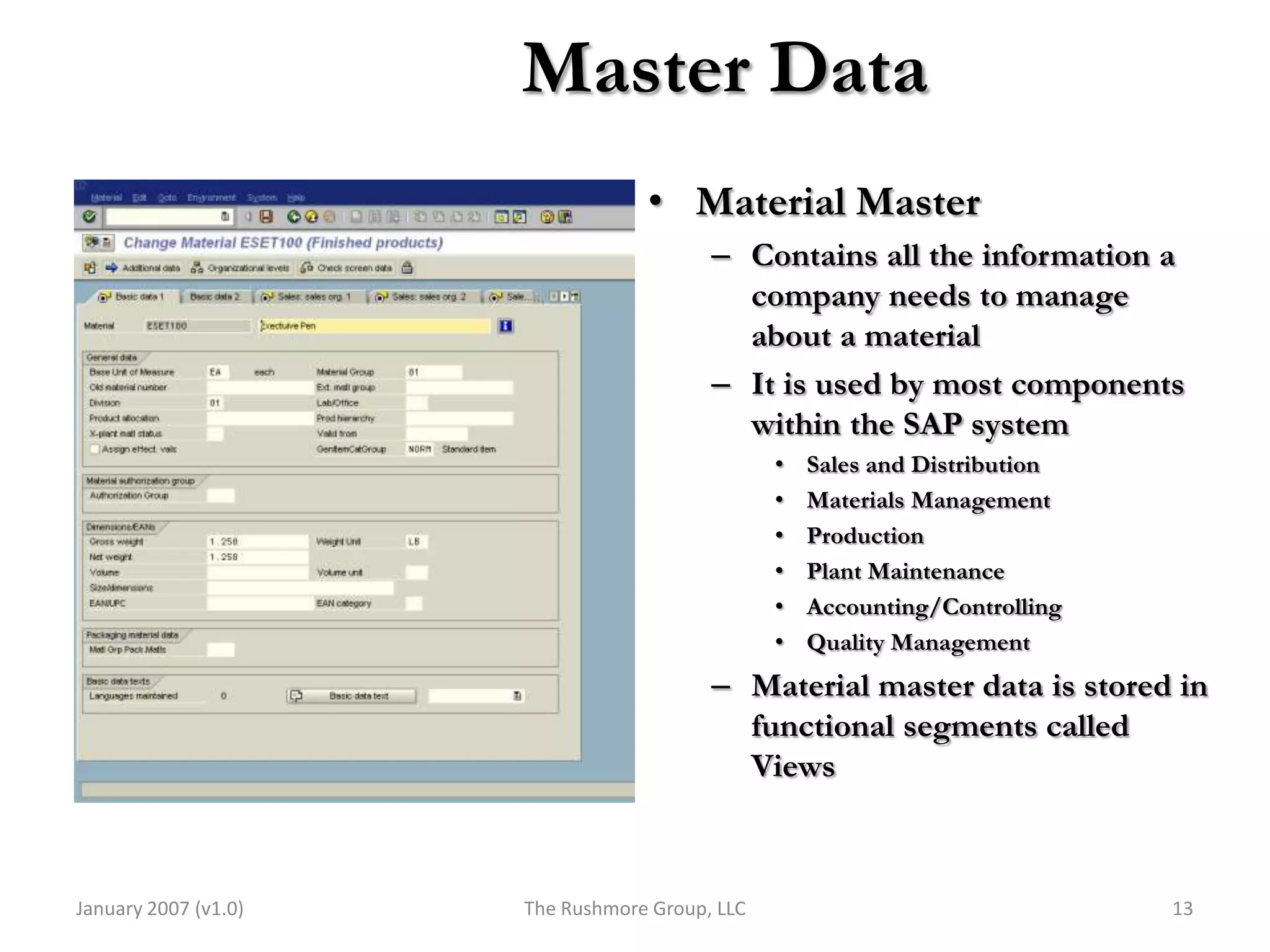
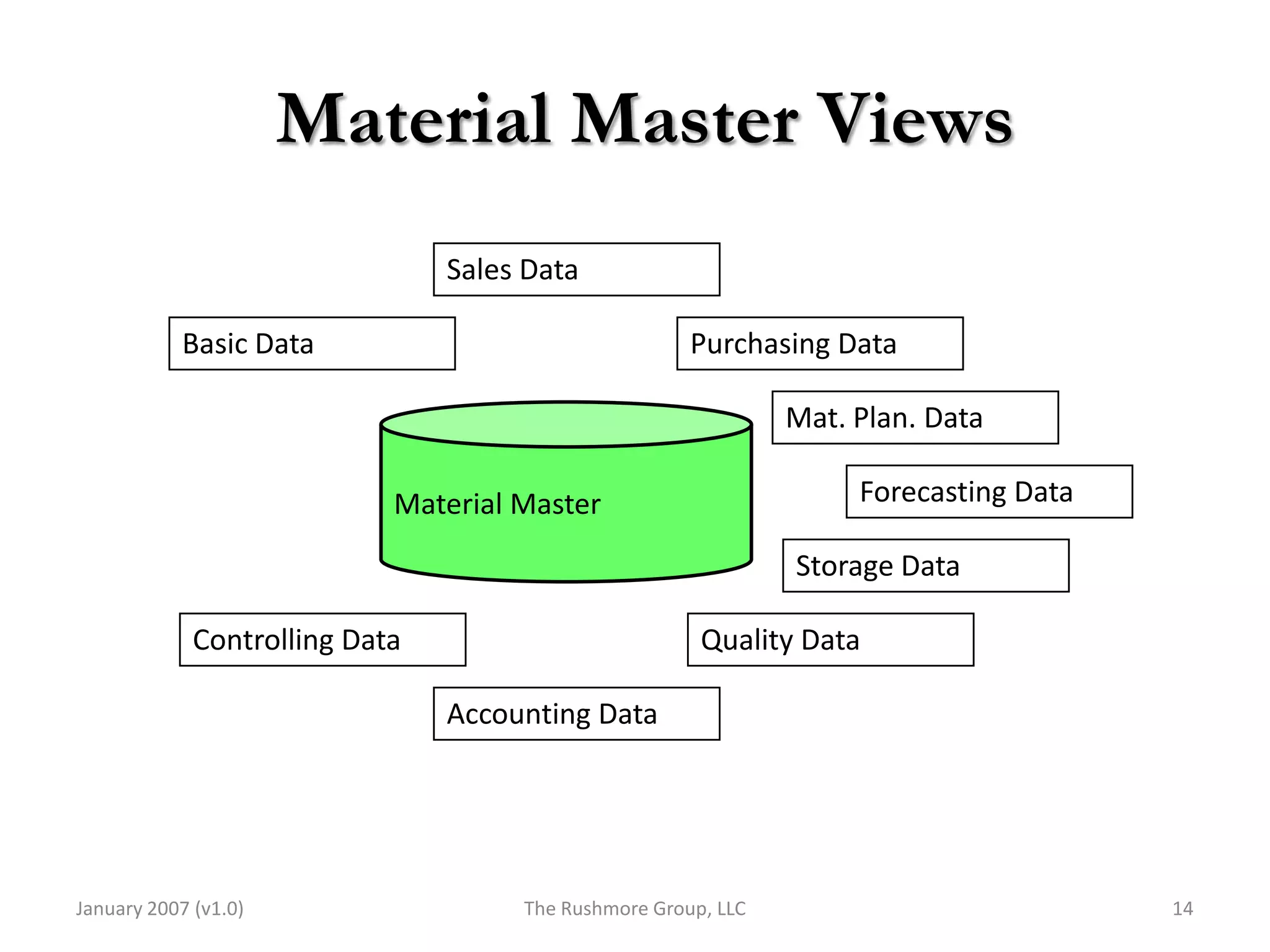
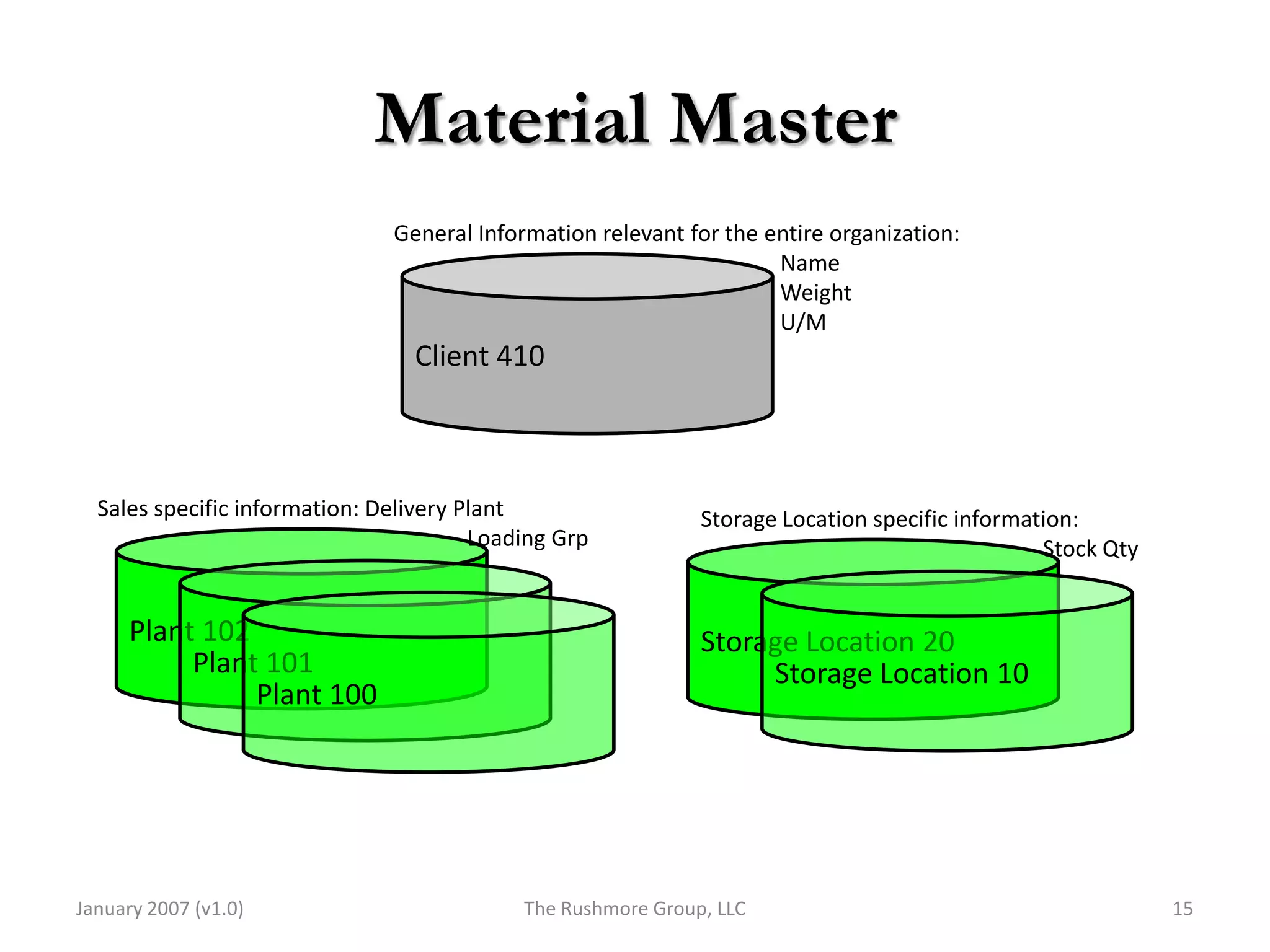
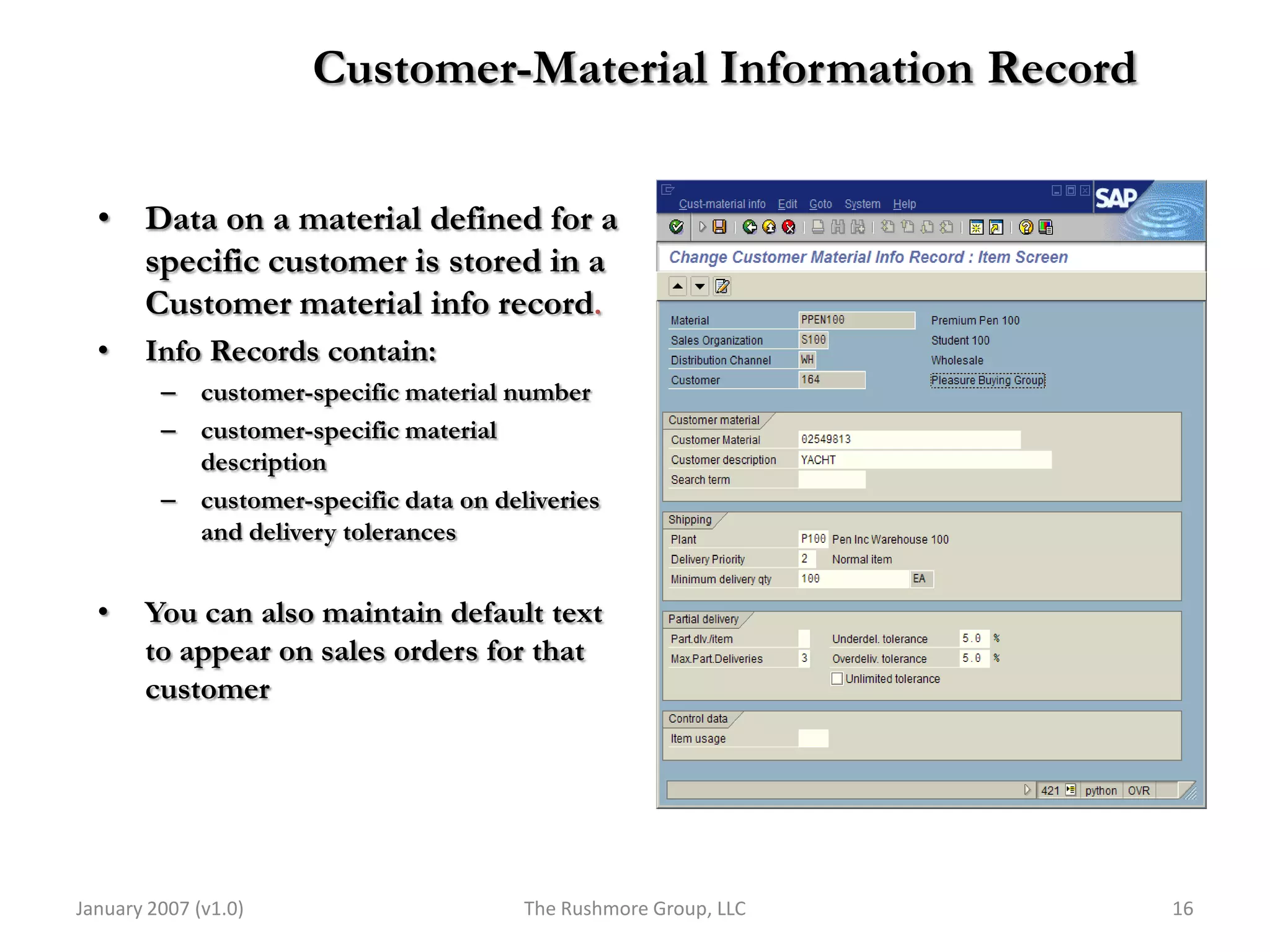
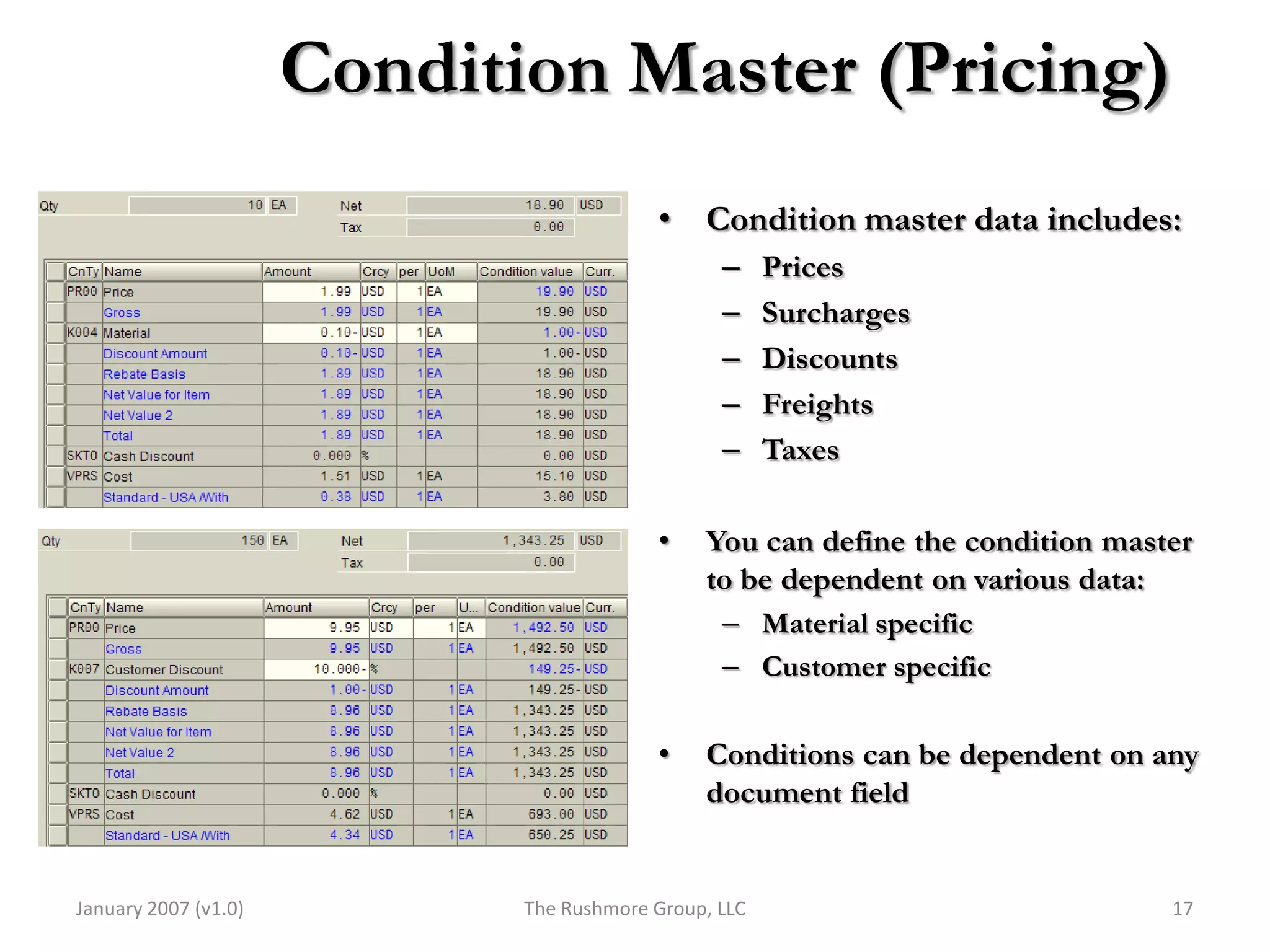
3) Master data like customer, material, and pricing information is critical for minimizing errors during order processing.