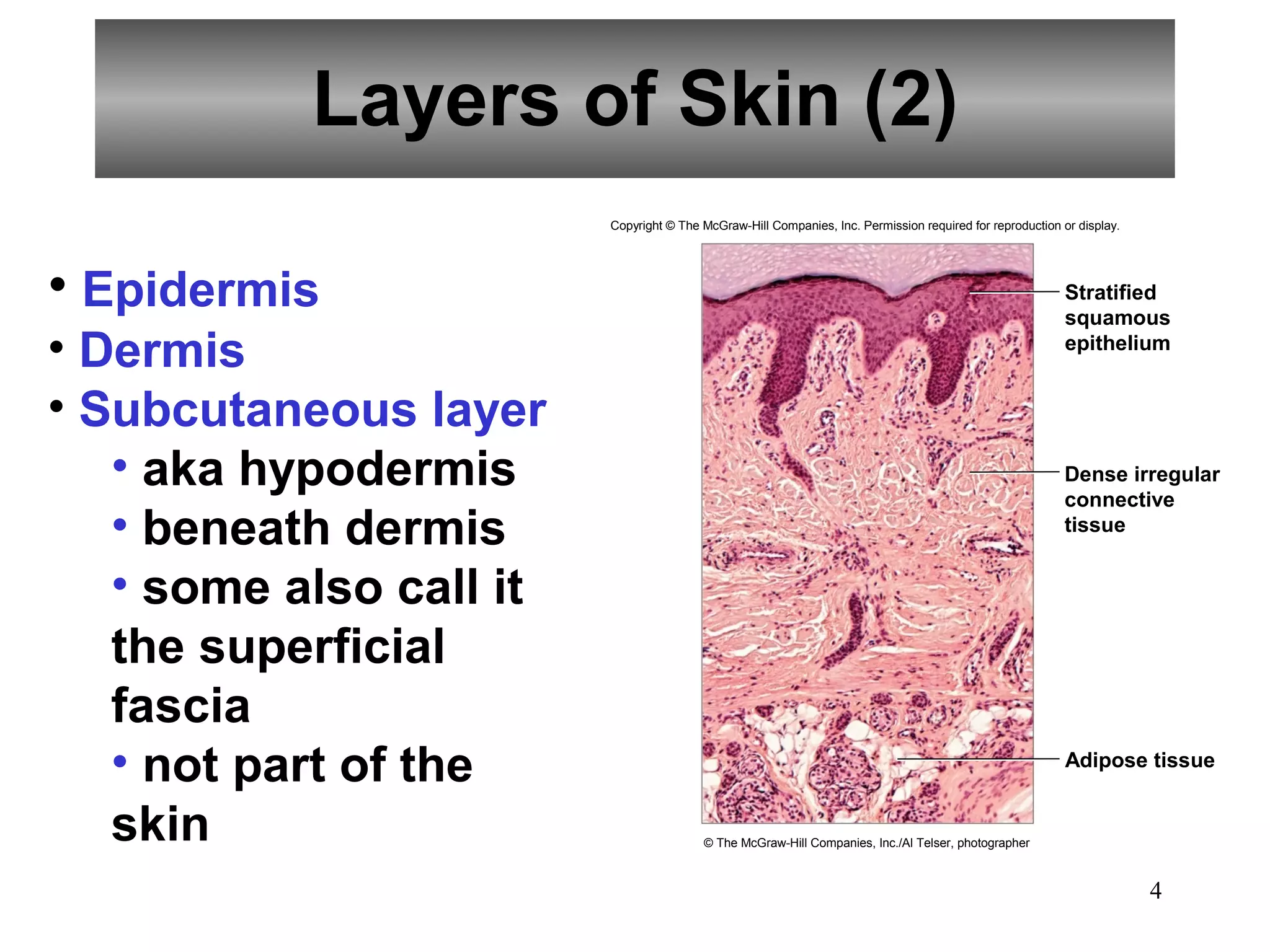
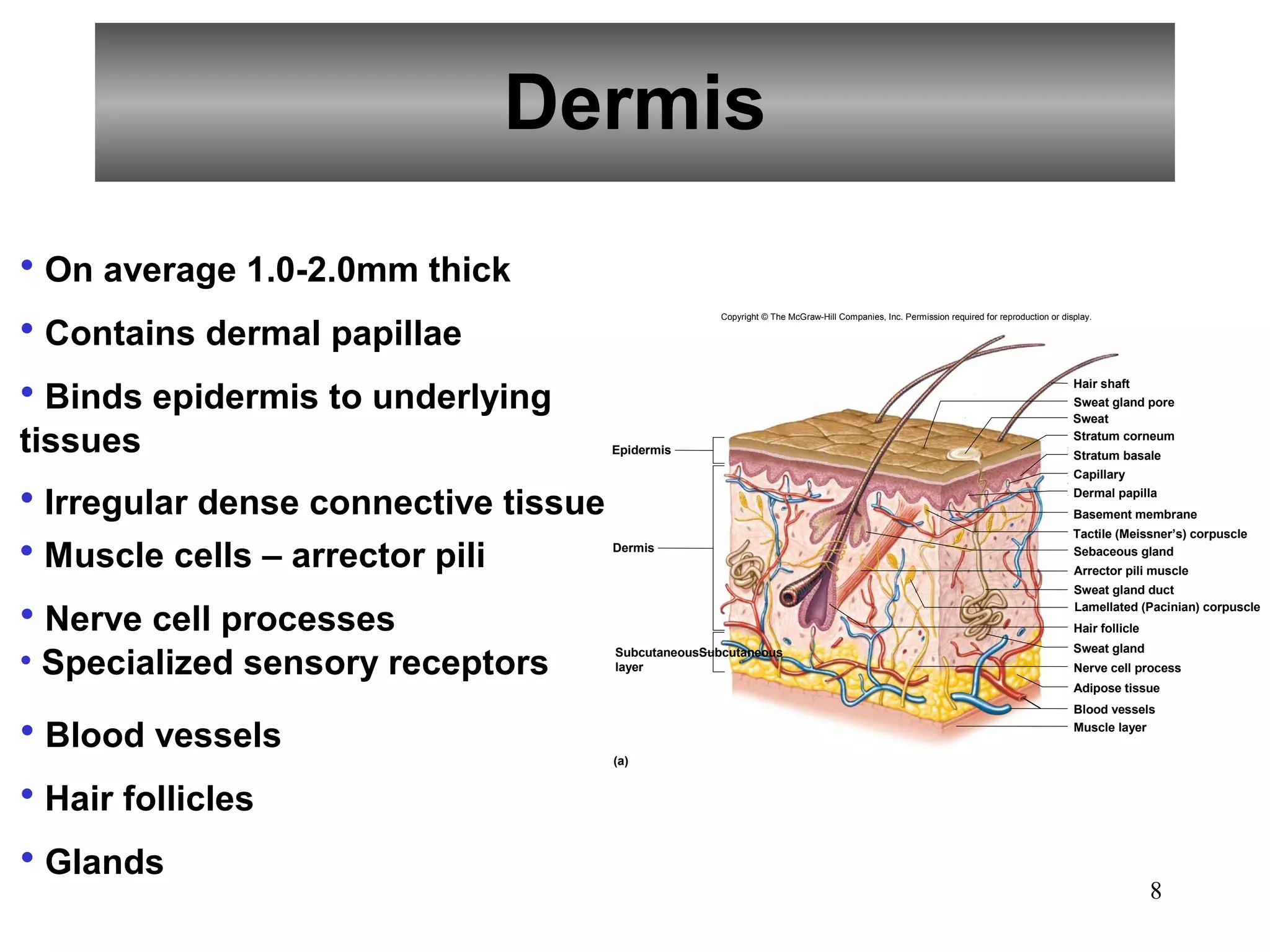
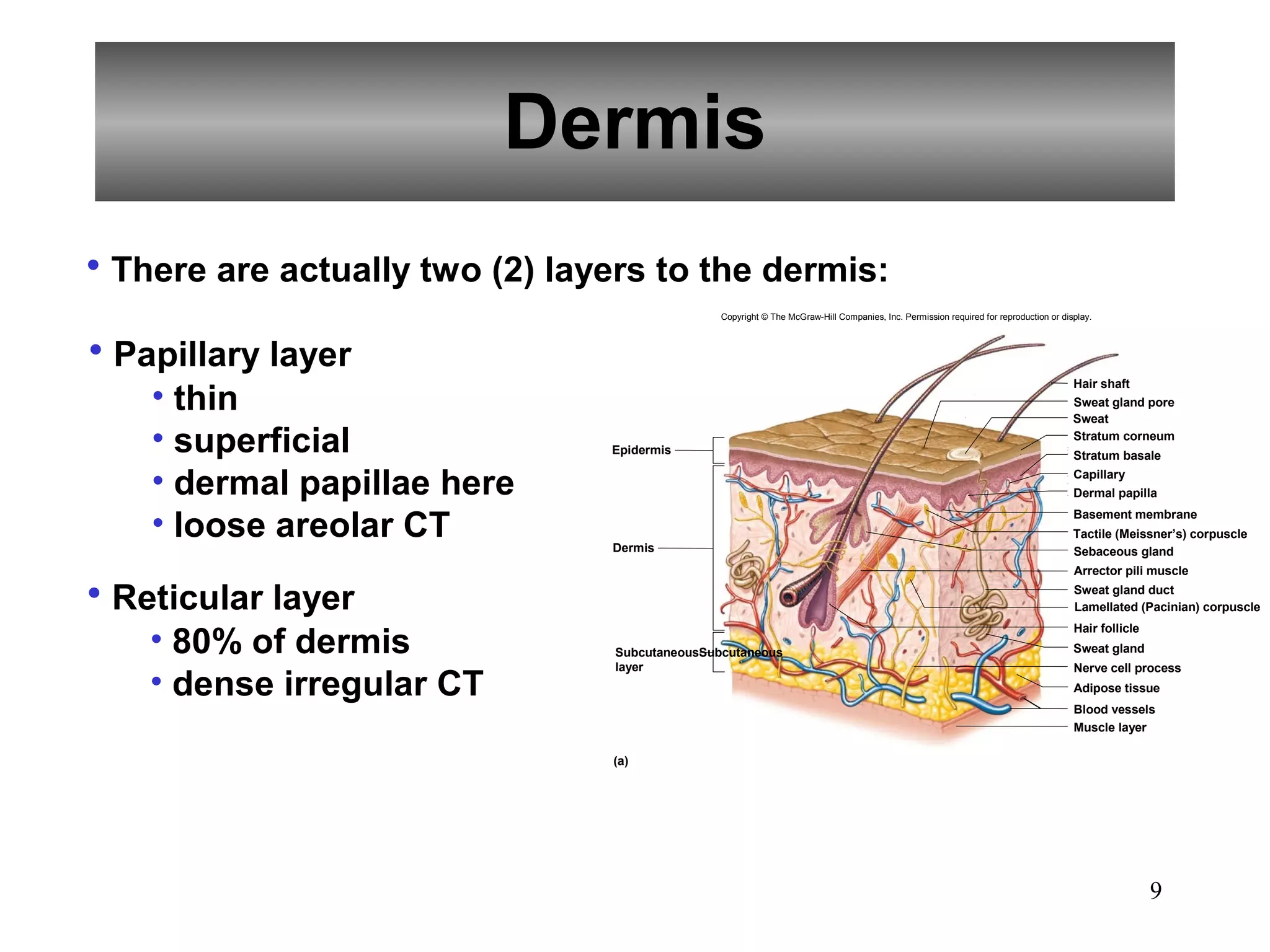
The integumentary system consists of the skin and its structures that protect the body from damage, regulate temperature and water balance, and synthesize vitamin D. The skin is composed of three main layers - the epidermis, dermis and subcutaneous layer. The epidermis contains keratinized stratified squamous epithelium and provides a protective barrier. The dermis contains blood vessels, hair follicles, and glands. The subcutaneous layer consists of connective tissue and adipose tissue. Accessory structures include hair, nails, sebaceous glands and sweat glands. The integumentary system helps regulate body temperature through vasodilation, sweating and shivering.