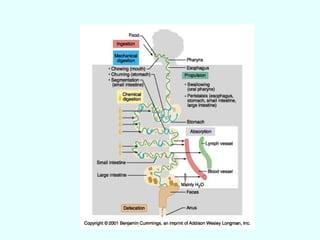
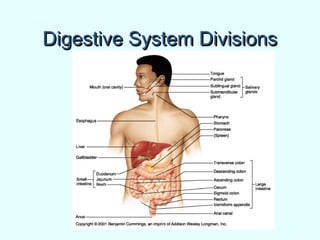
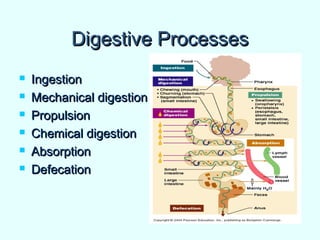
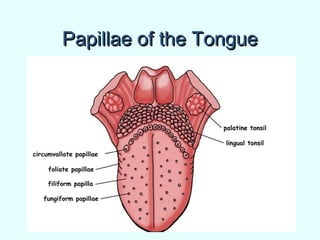
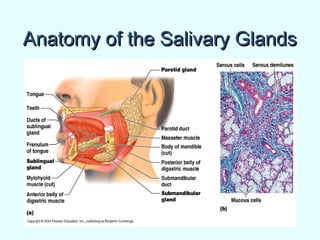
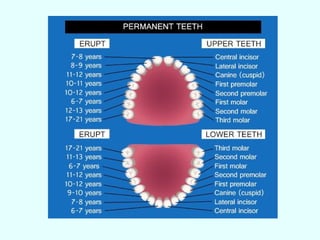
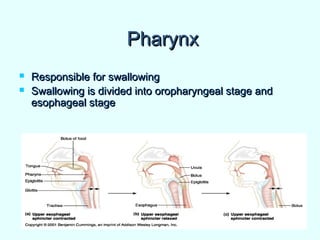
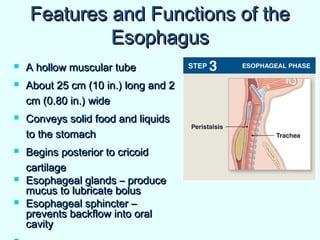
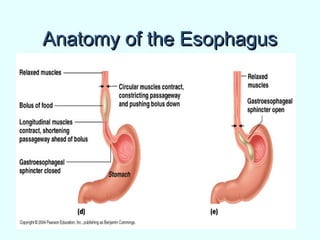
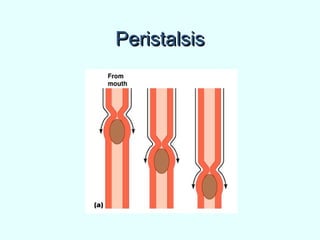
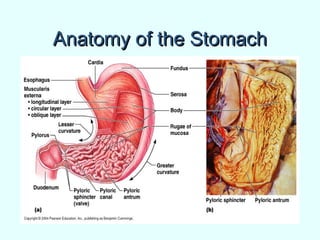
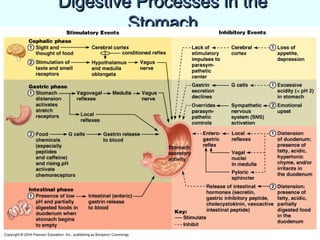
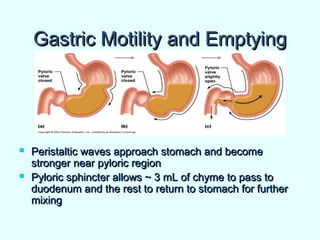
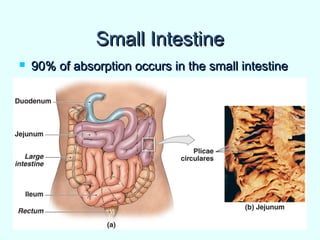
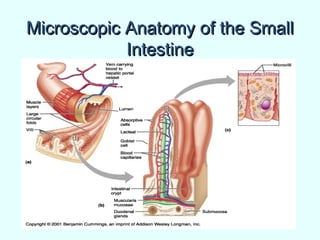
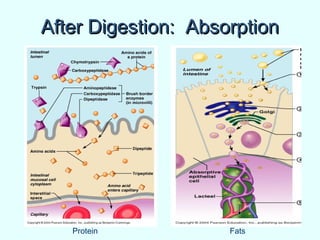
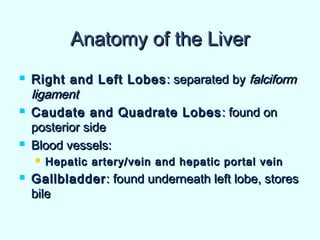
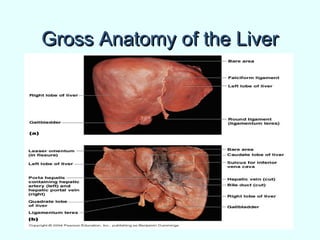
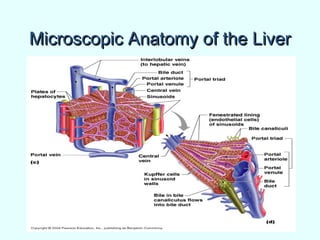
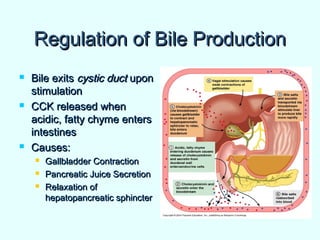
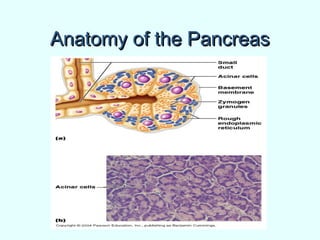
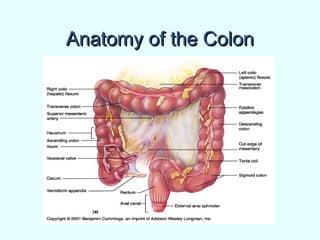
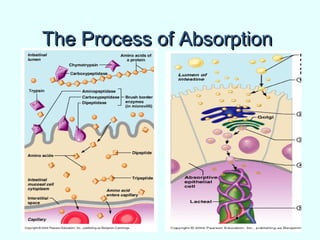
The document discusses the structure and functions of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract or digestive system. It describes the main divisions and organs of the GI tract including the mouth, esophagus, stomach, and intestines. It explains the key processes of digestion such as ingestion, mechanical and chemical breakdown of food, absorption of nutrients, and excretion of waste. It provides details on the anatomy and roles of specific organs like the salivary glands, teeth, esophagus, and stomach in the digestion process.