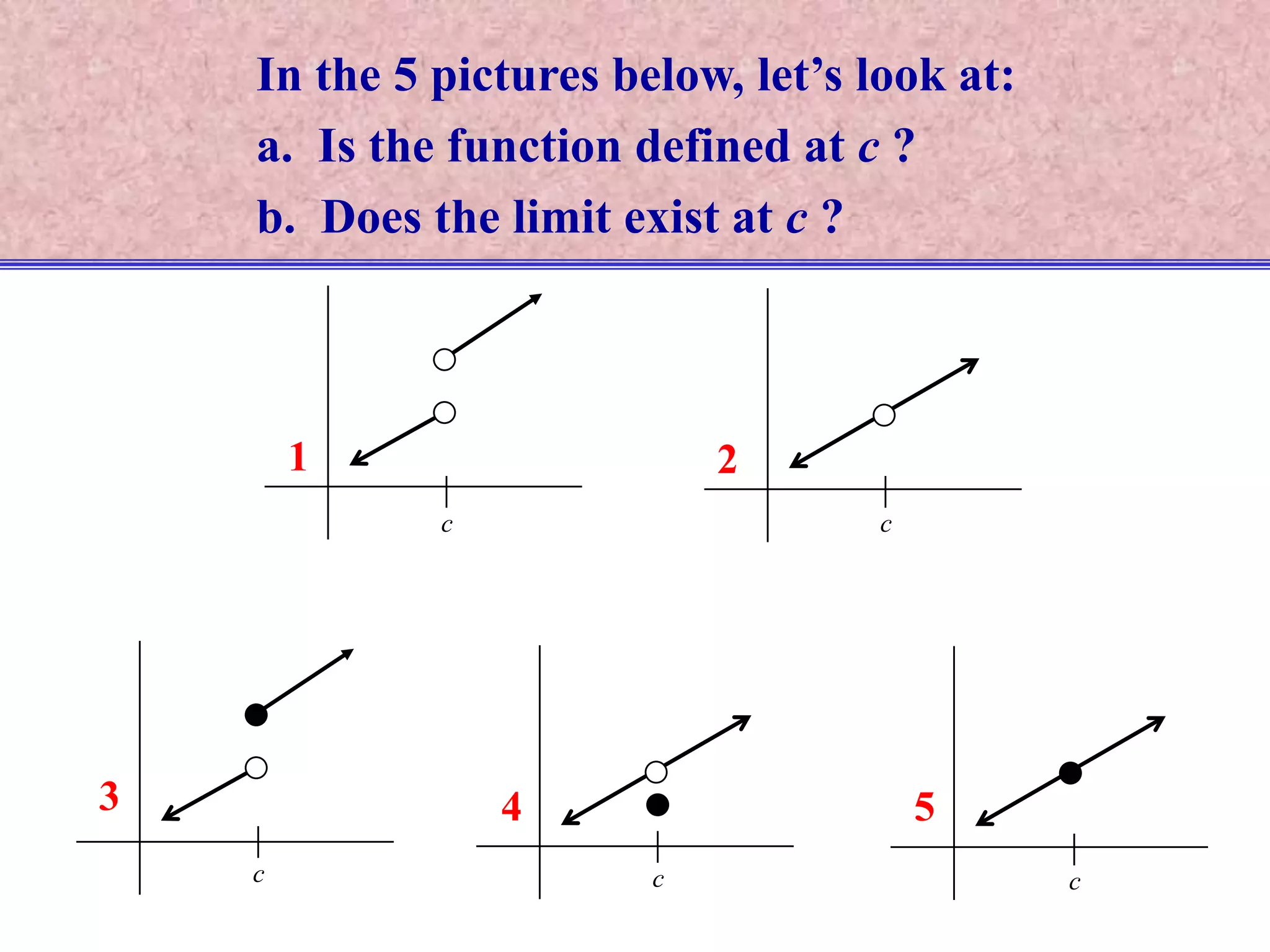
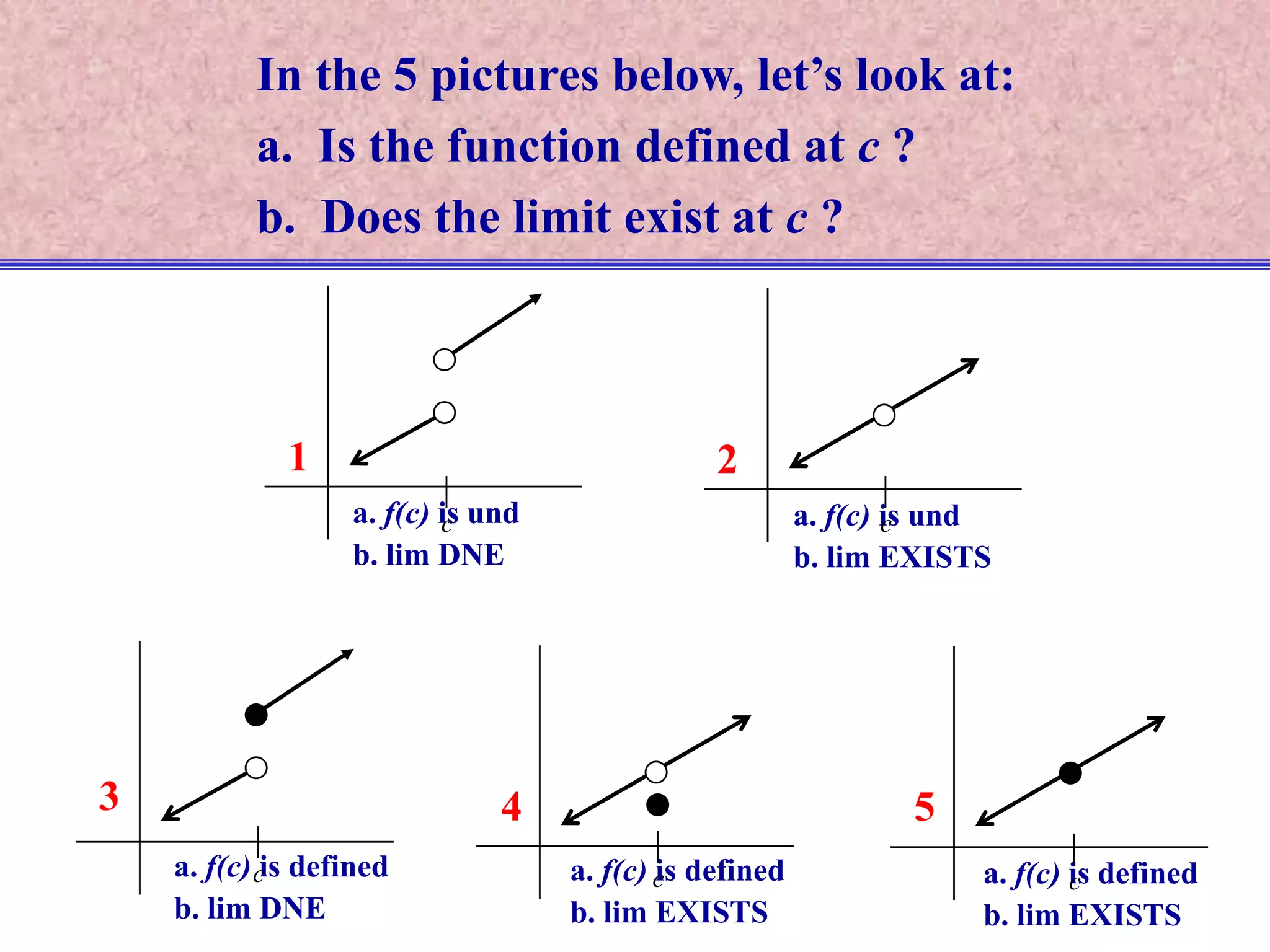
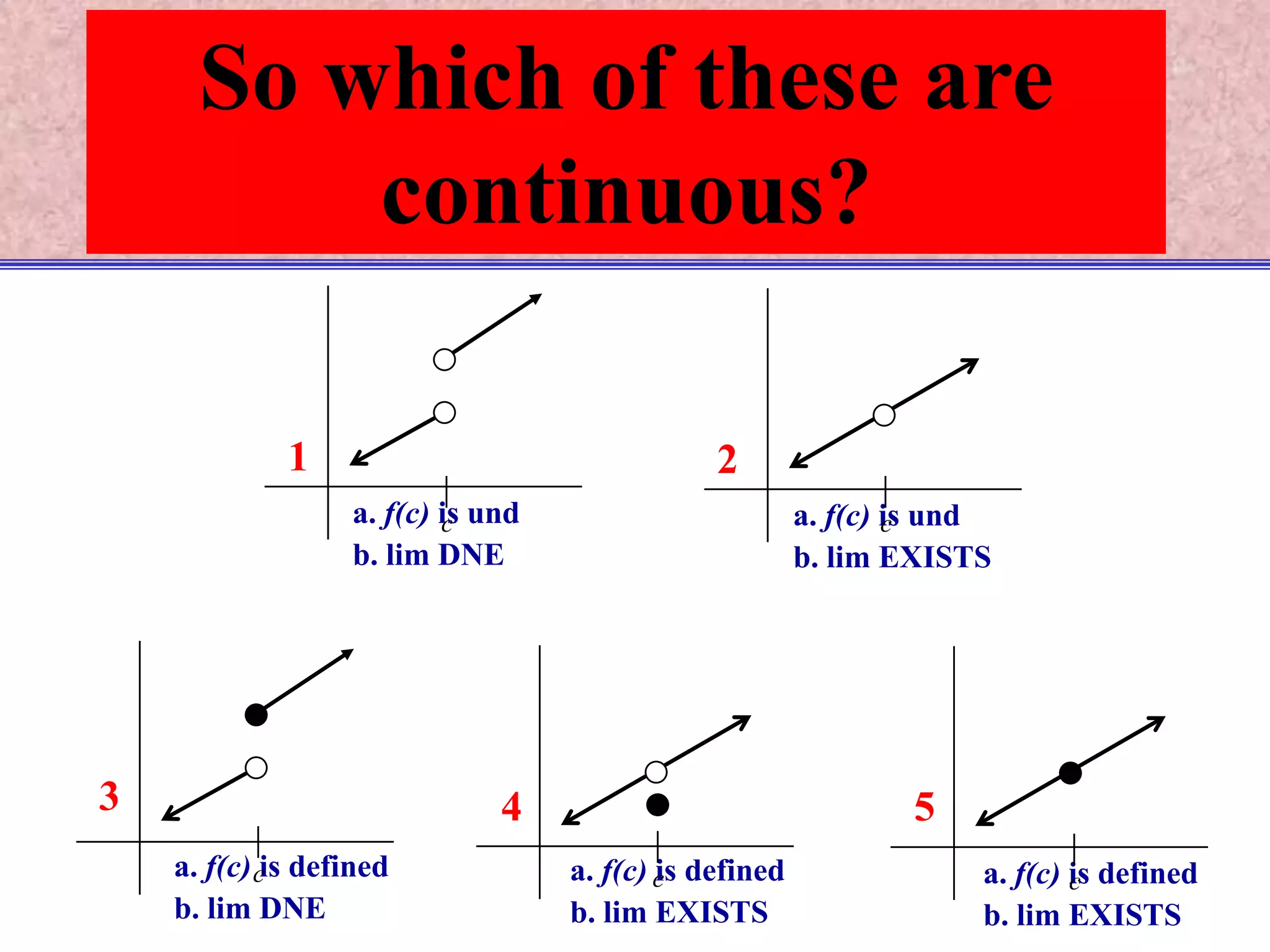
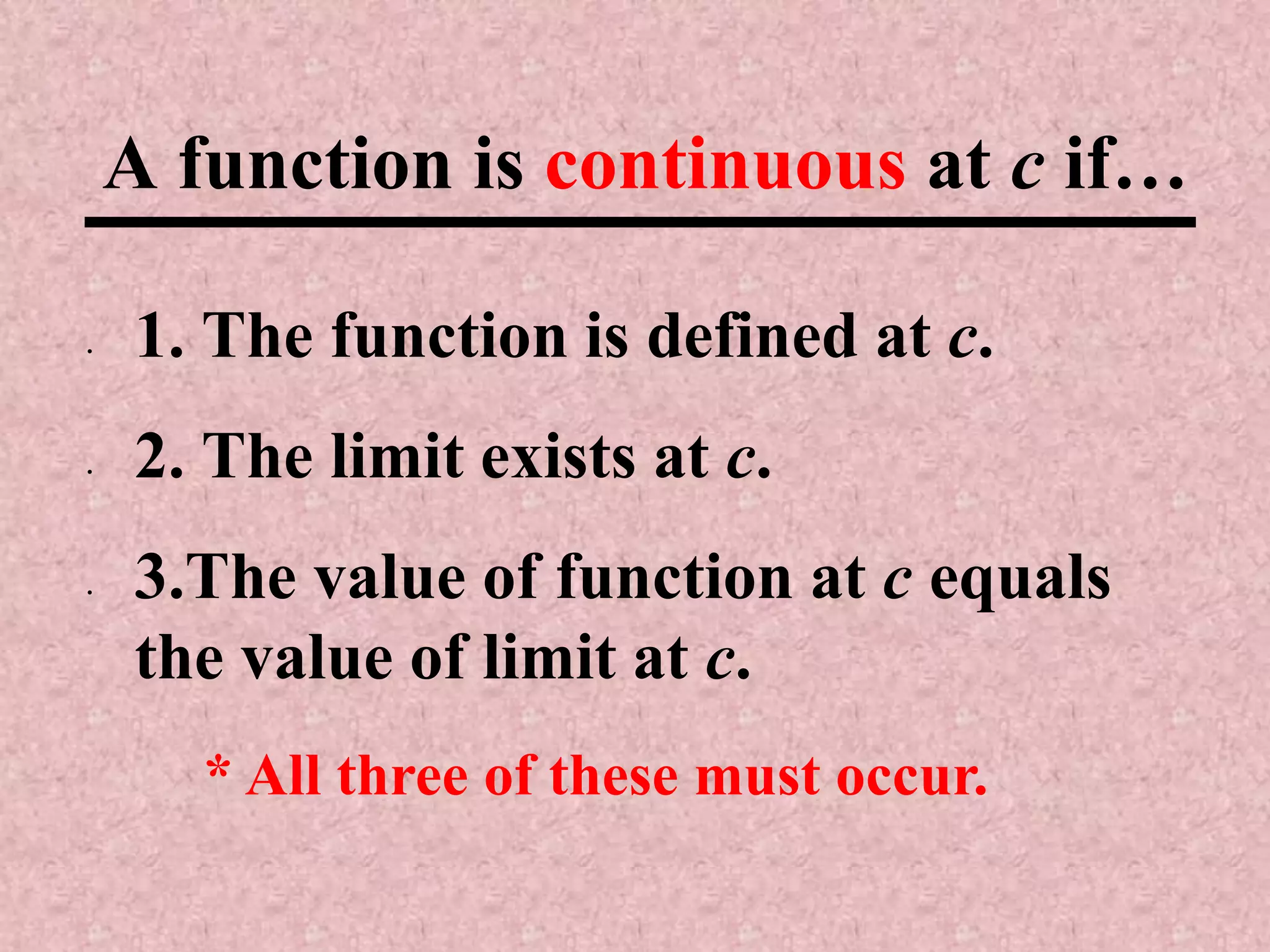
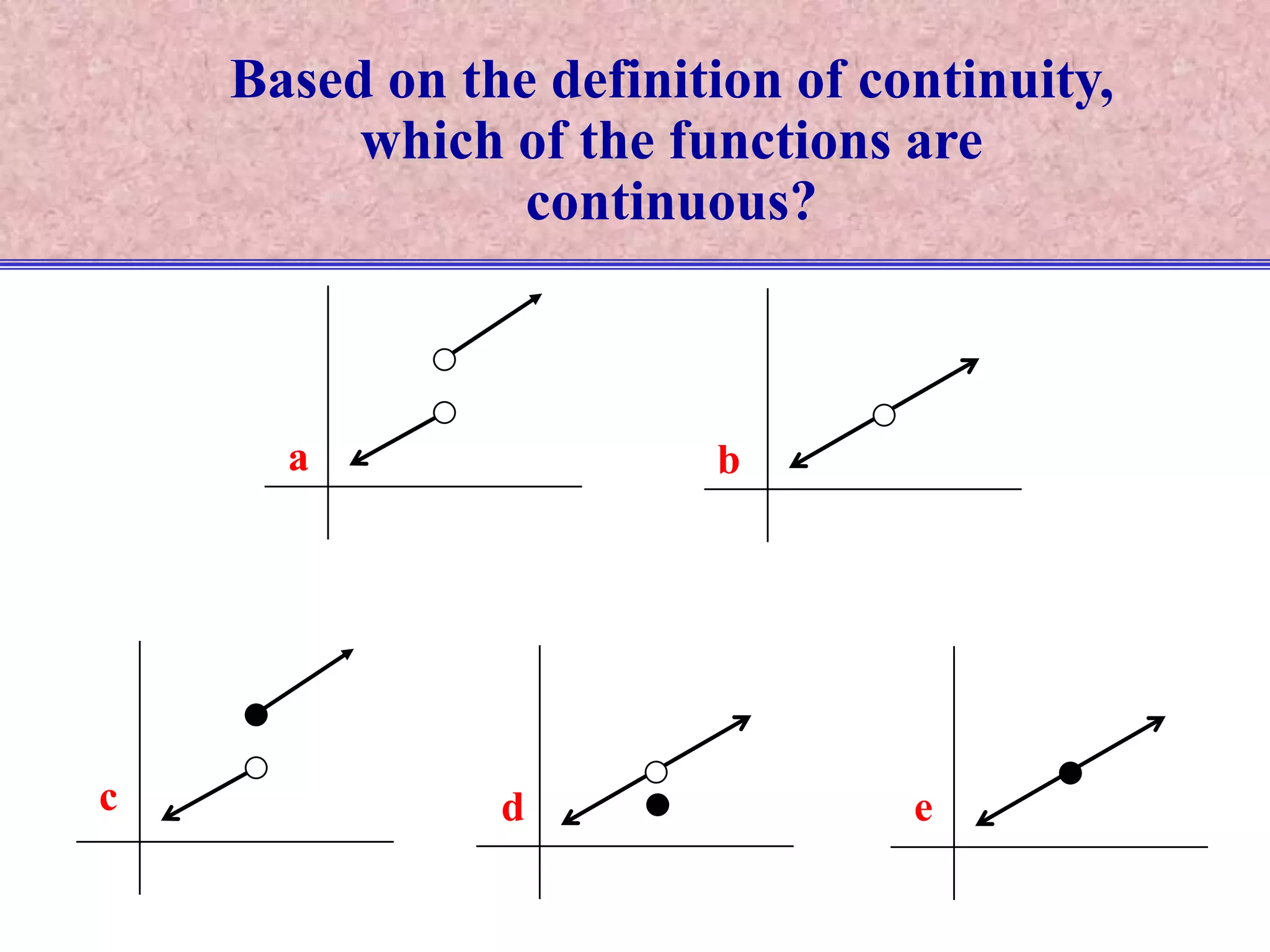
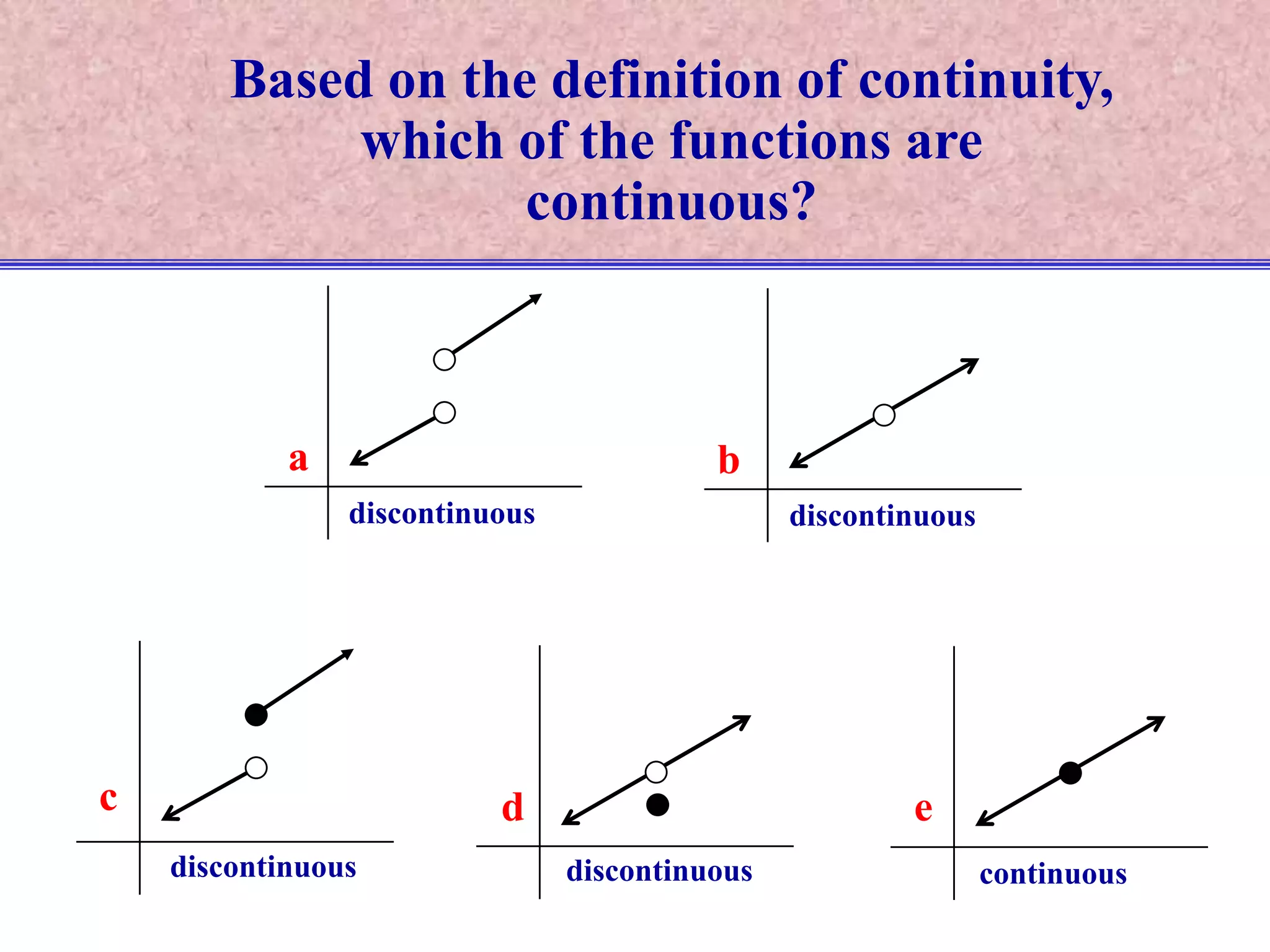
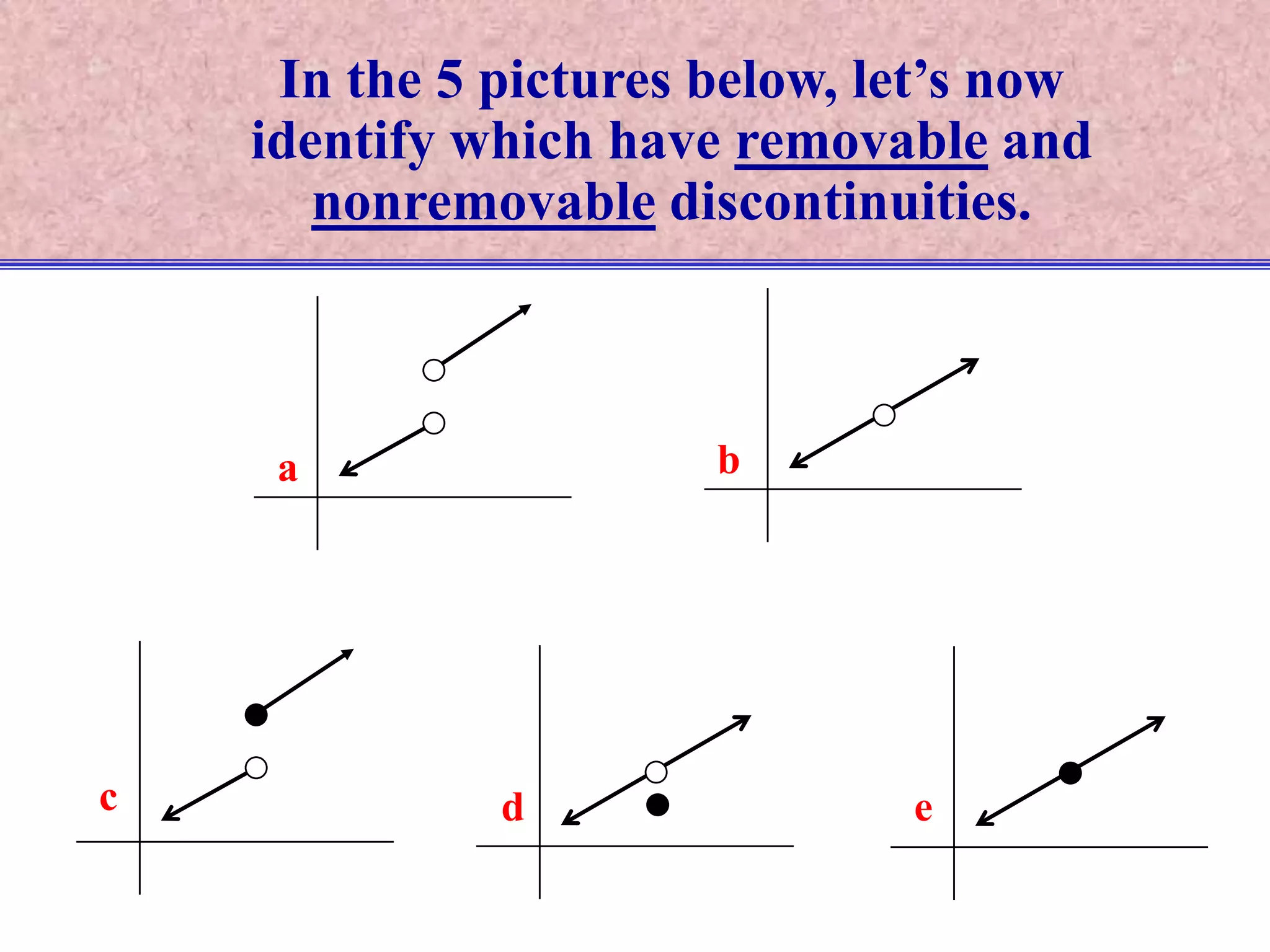
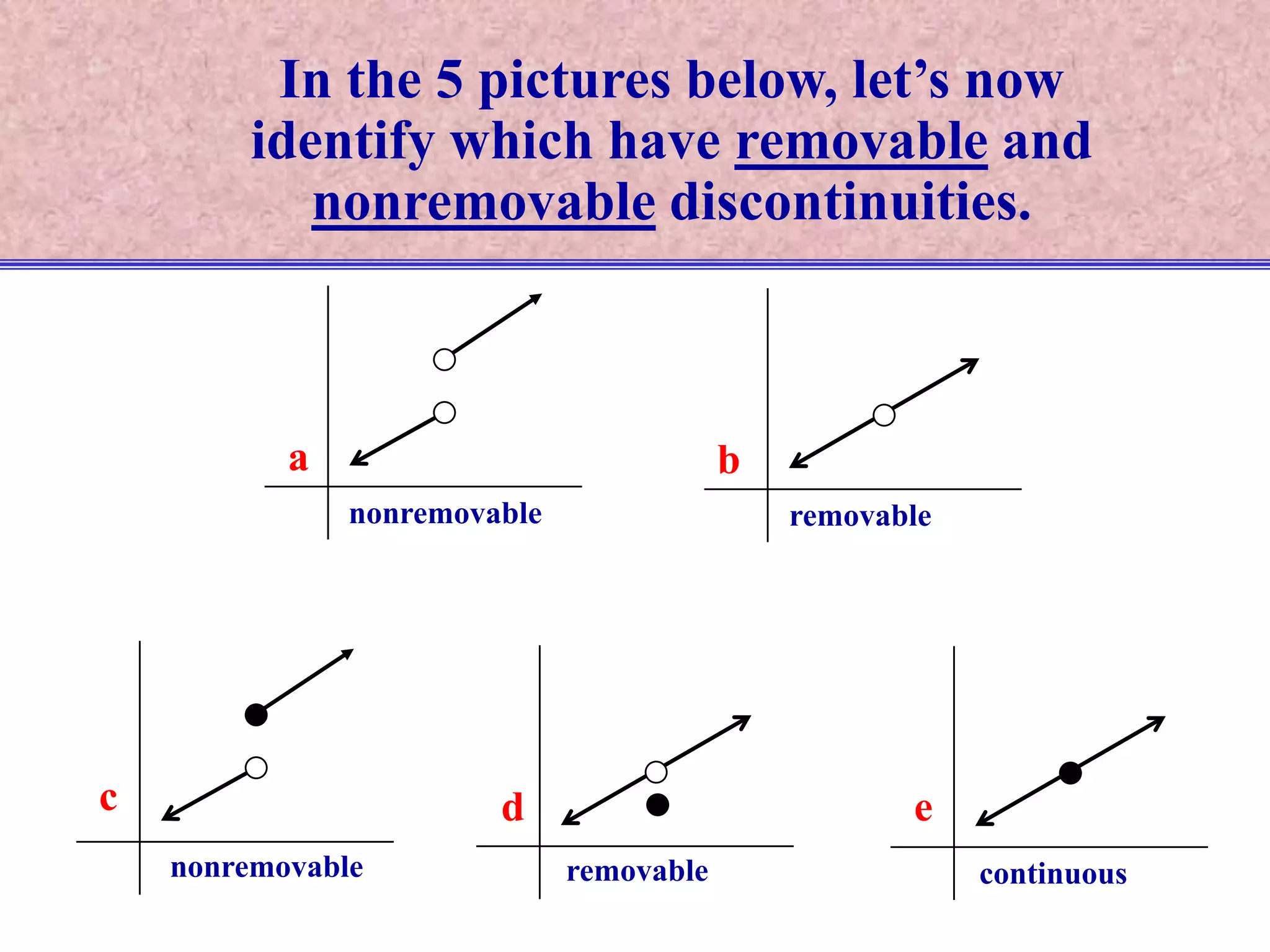
The document discusses continuity of functions at a point c. It defines a function as continuous at c if the function is defined at c, the limit exists at c, and the function value equals the limit value. Only functions meeting all three criteria are continuous. Discontinuities can be removable if defining the function value makes it continuous, or nonremovable if no definition works. The document analyzes five functions in pictures to identify which are continuous, discontinuous with removable or nonremovable discontinuities.