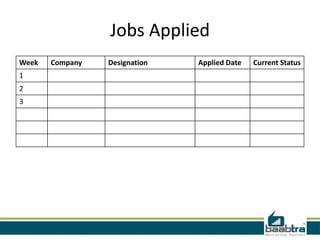
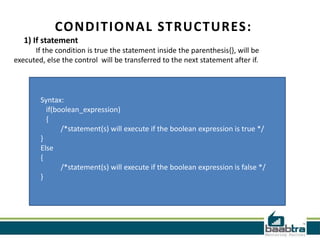
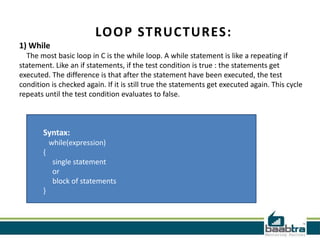
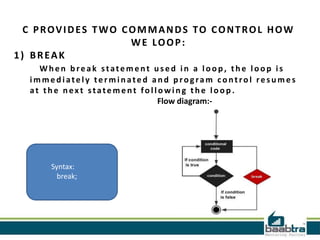
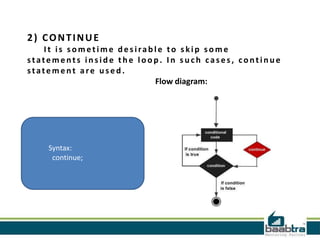
This document provides an overview of different types of control structures in C programming language. It discusses conditional structures like if, else if, and switch statements. It also covers loop structures like while, do while, and for loops. Finally, it mentions the break and continue commands used to control loops. The document was prepared by trainees of Baabtra as part of a mentoring program and is not an official Baabtra document. It includes contact details for Baabtra offices in Kerala, India.