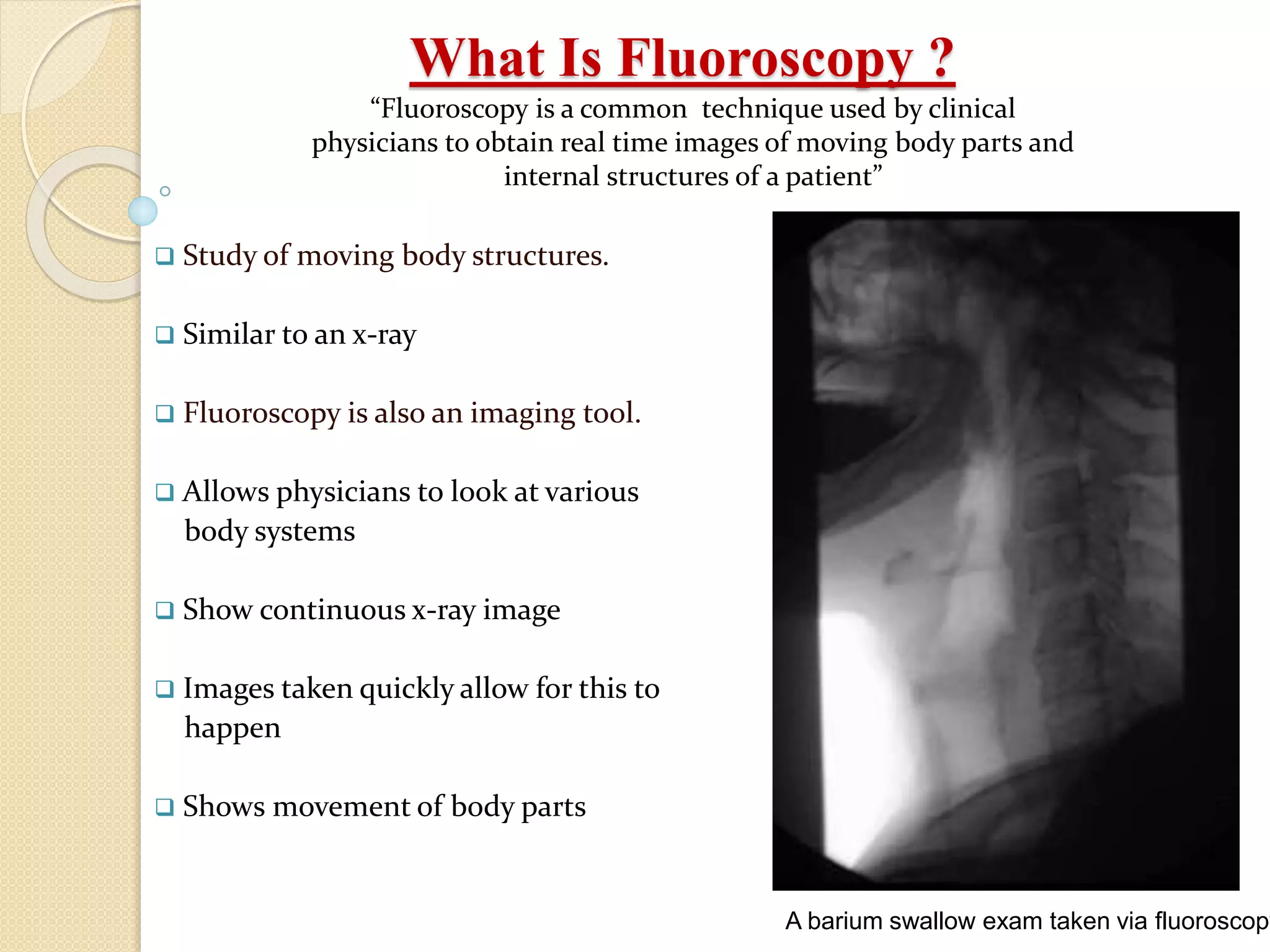
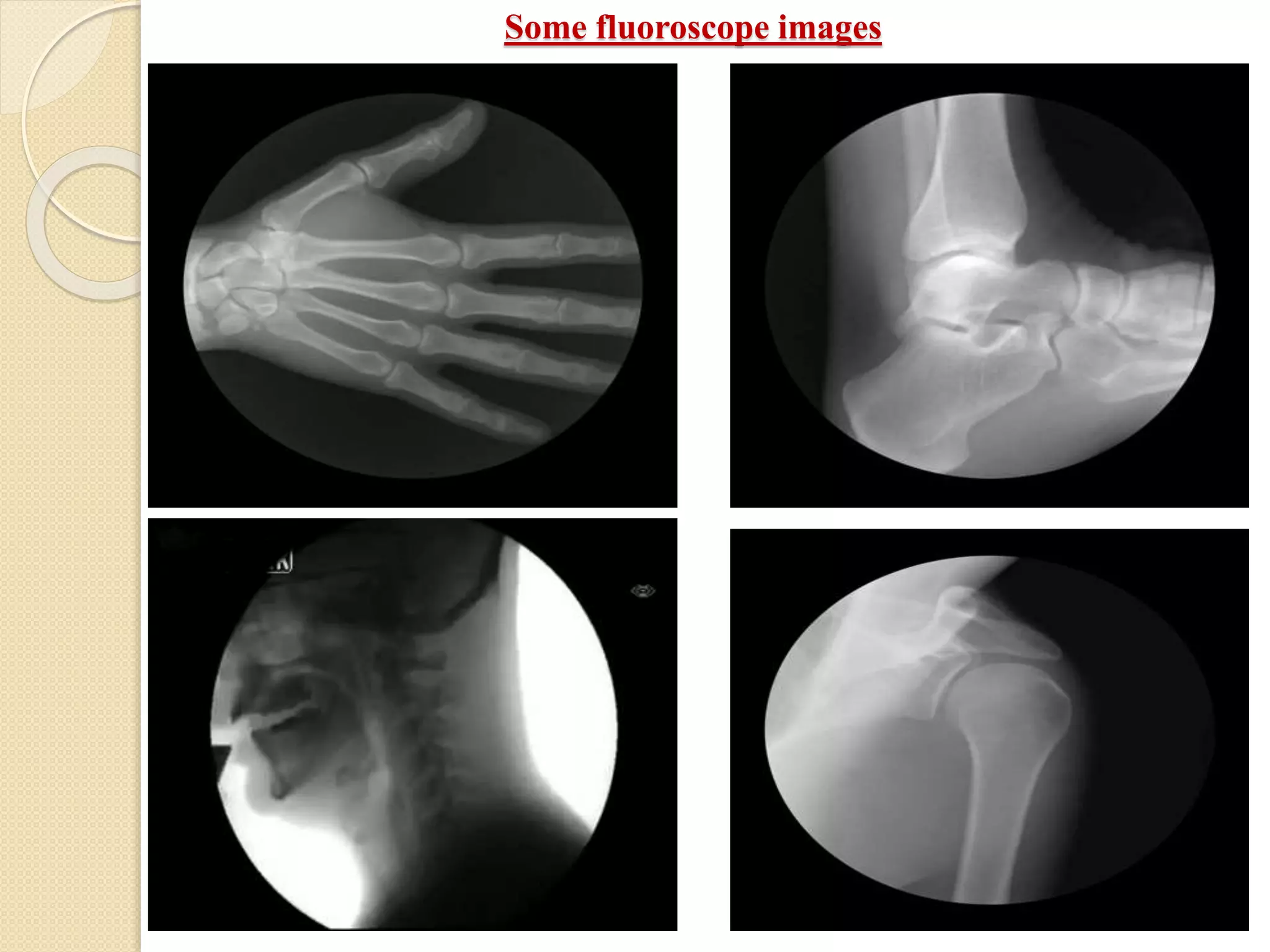
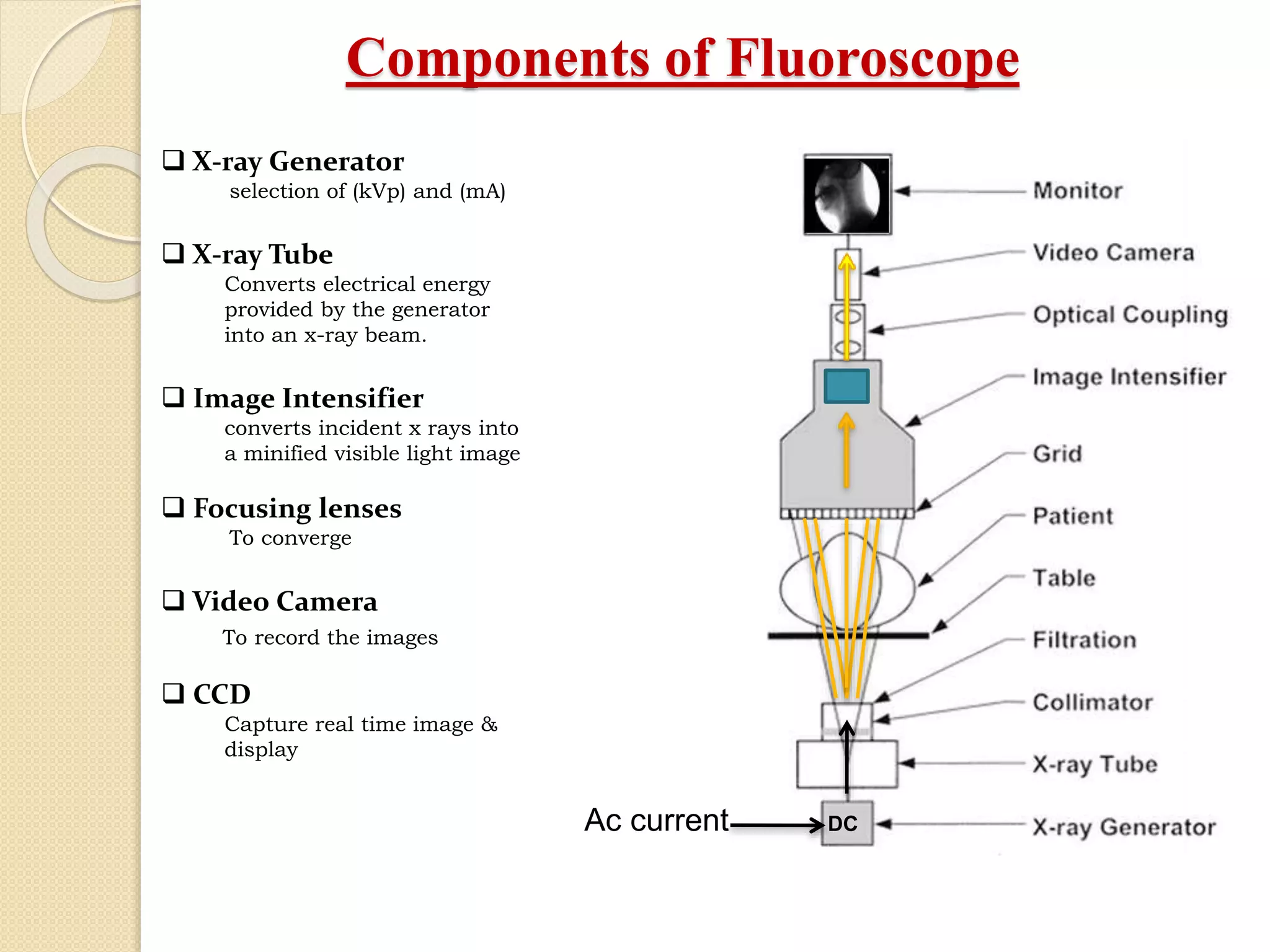
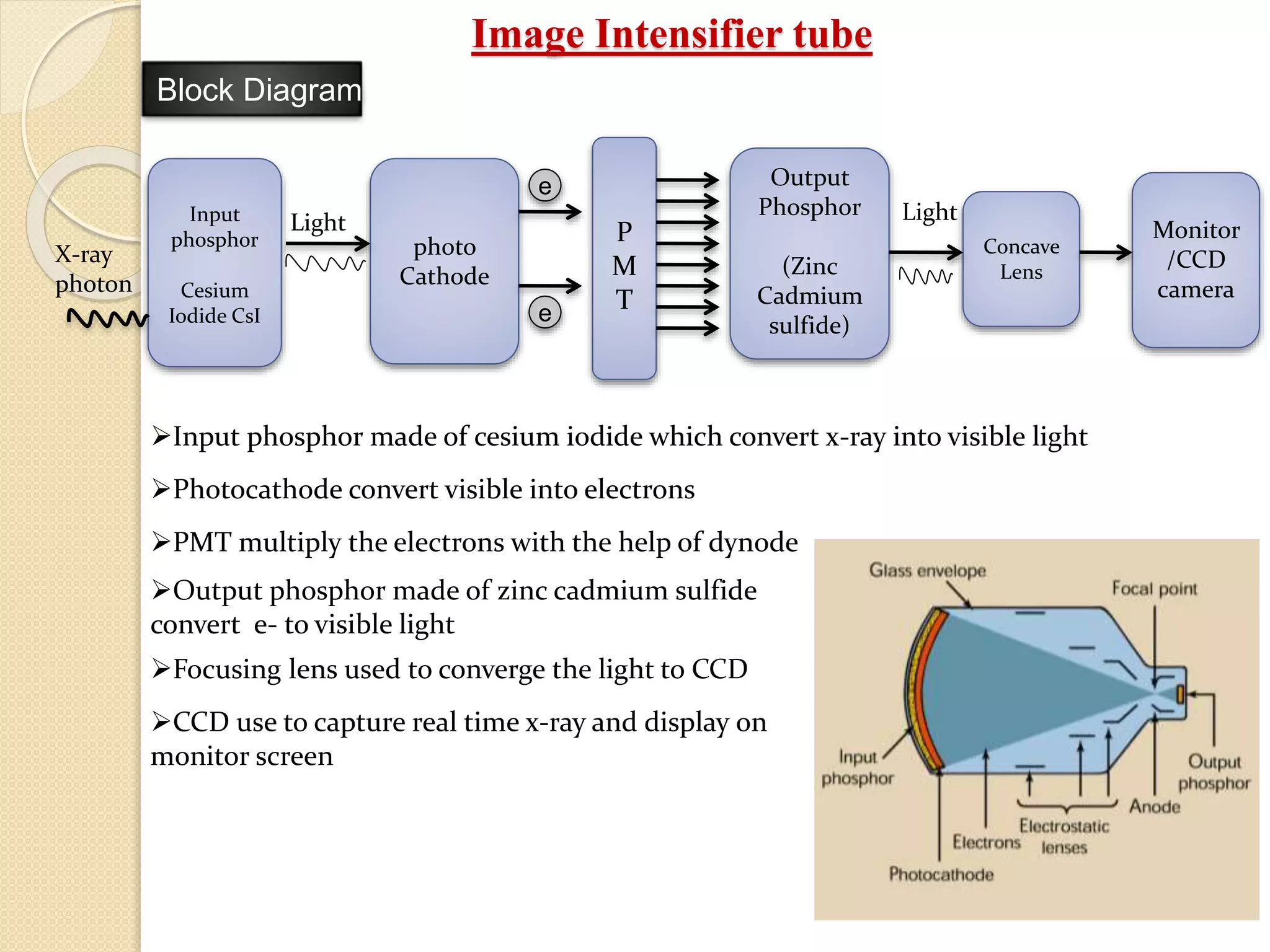
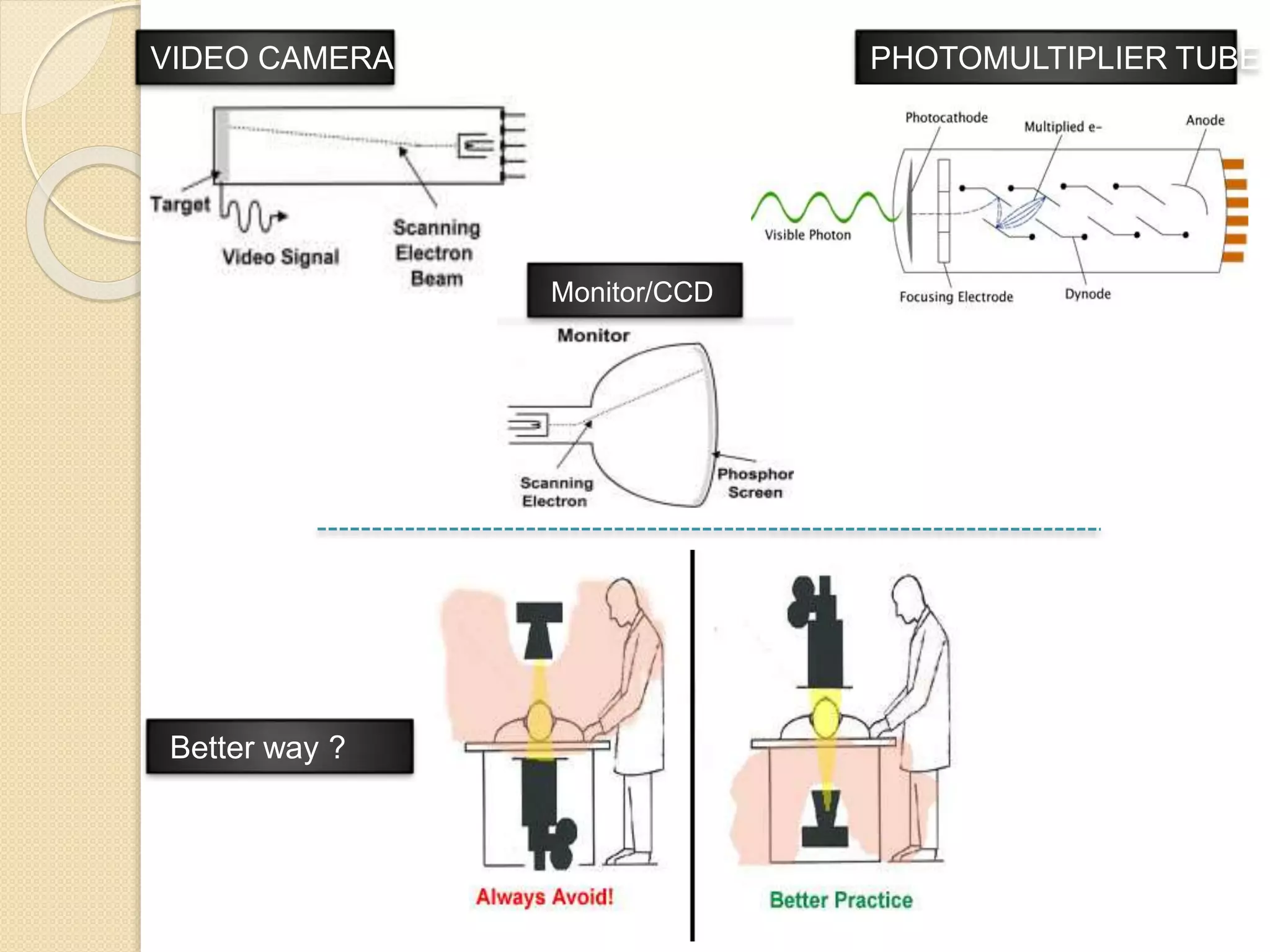
Fluoroscopy is a medical imaging technique that uses x-rays and an image intensifier to obtain real-time moving images of the internal structures of the body. It allows physicians to see the movement of internal body parts and is commonly used for procedures like barium swallow exams. The key components of a fluoroscope system include an x-ray generator, x-ray tube, image intensifier tube, focusing lenses, video camera, and CCD. The image intensifier tube converts x-rays into a visible light image using a photocathode, phosphor, and PMT to multiply electrons and allow real-time x-ray images to be captured by the video camera and displayed on a monitor.