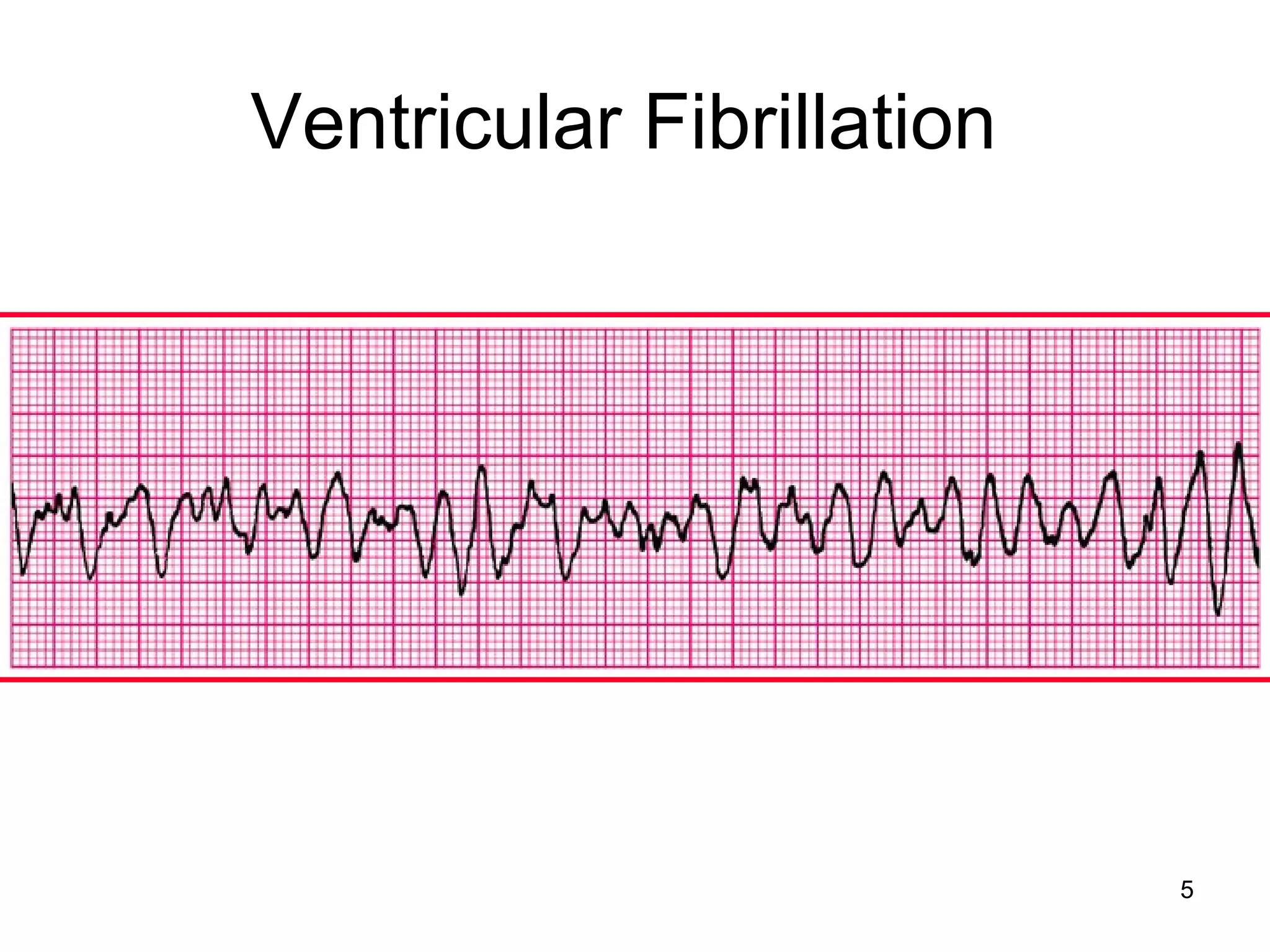
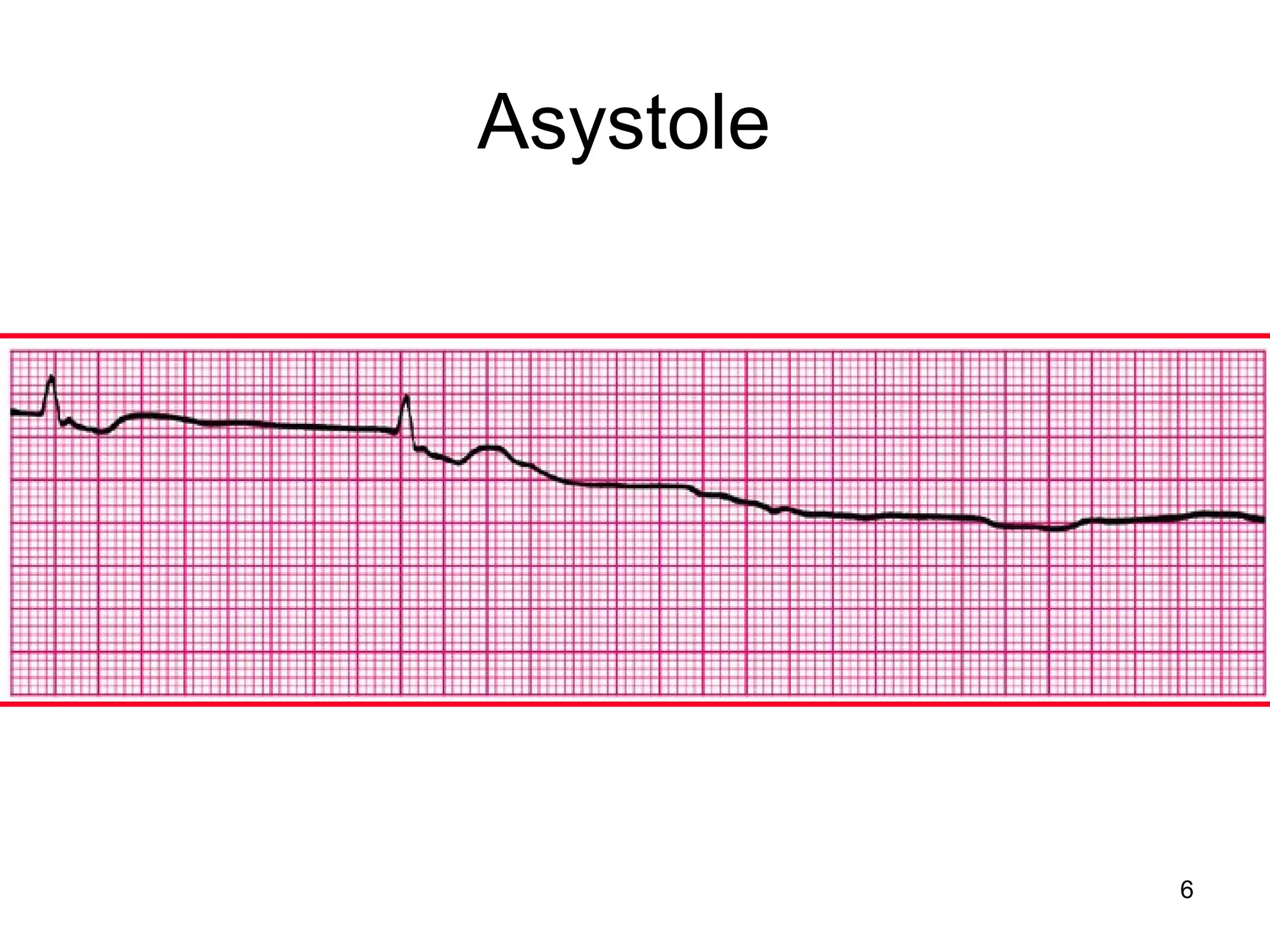
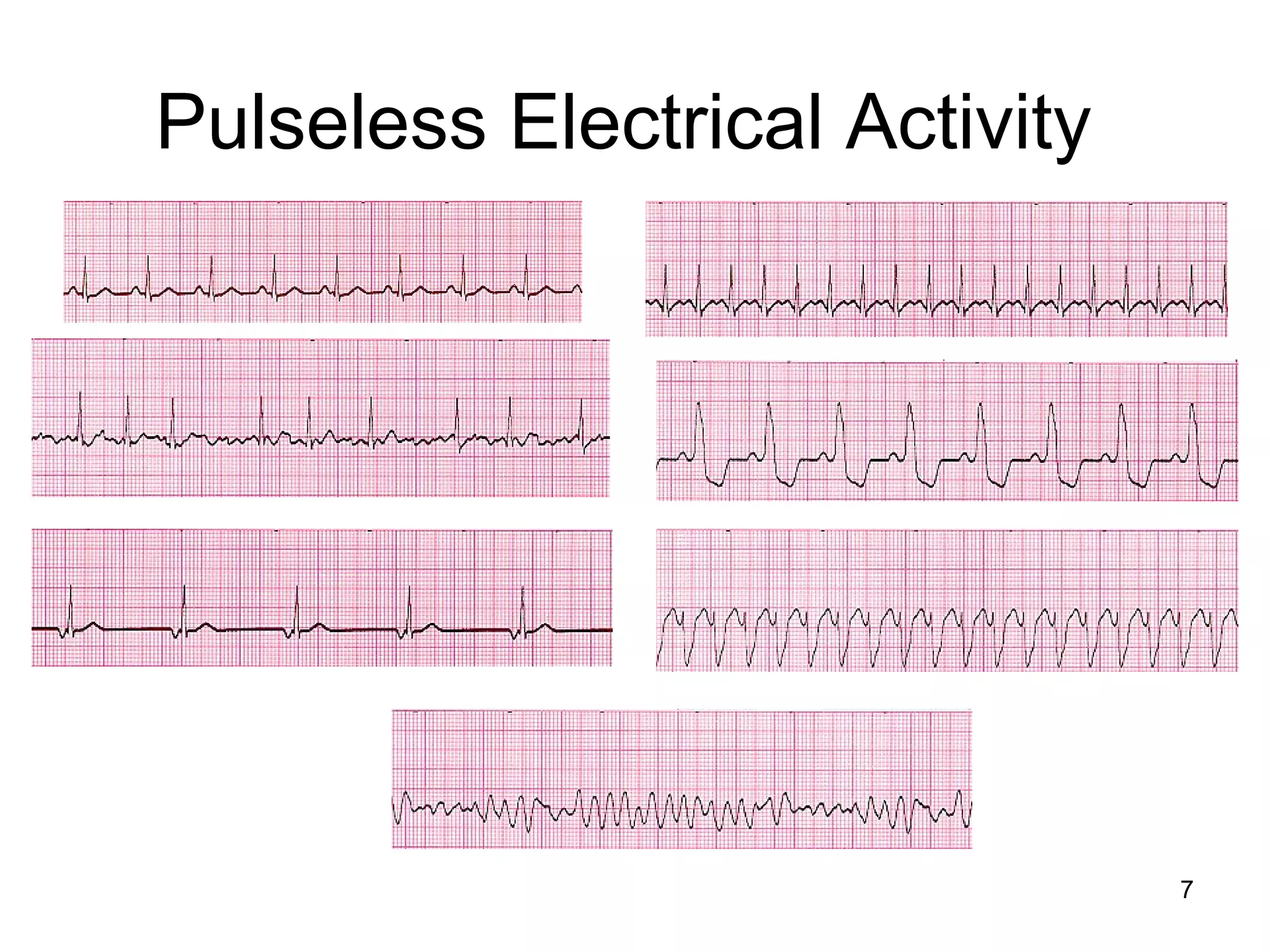
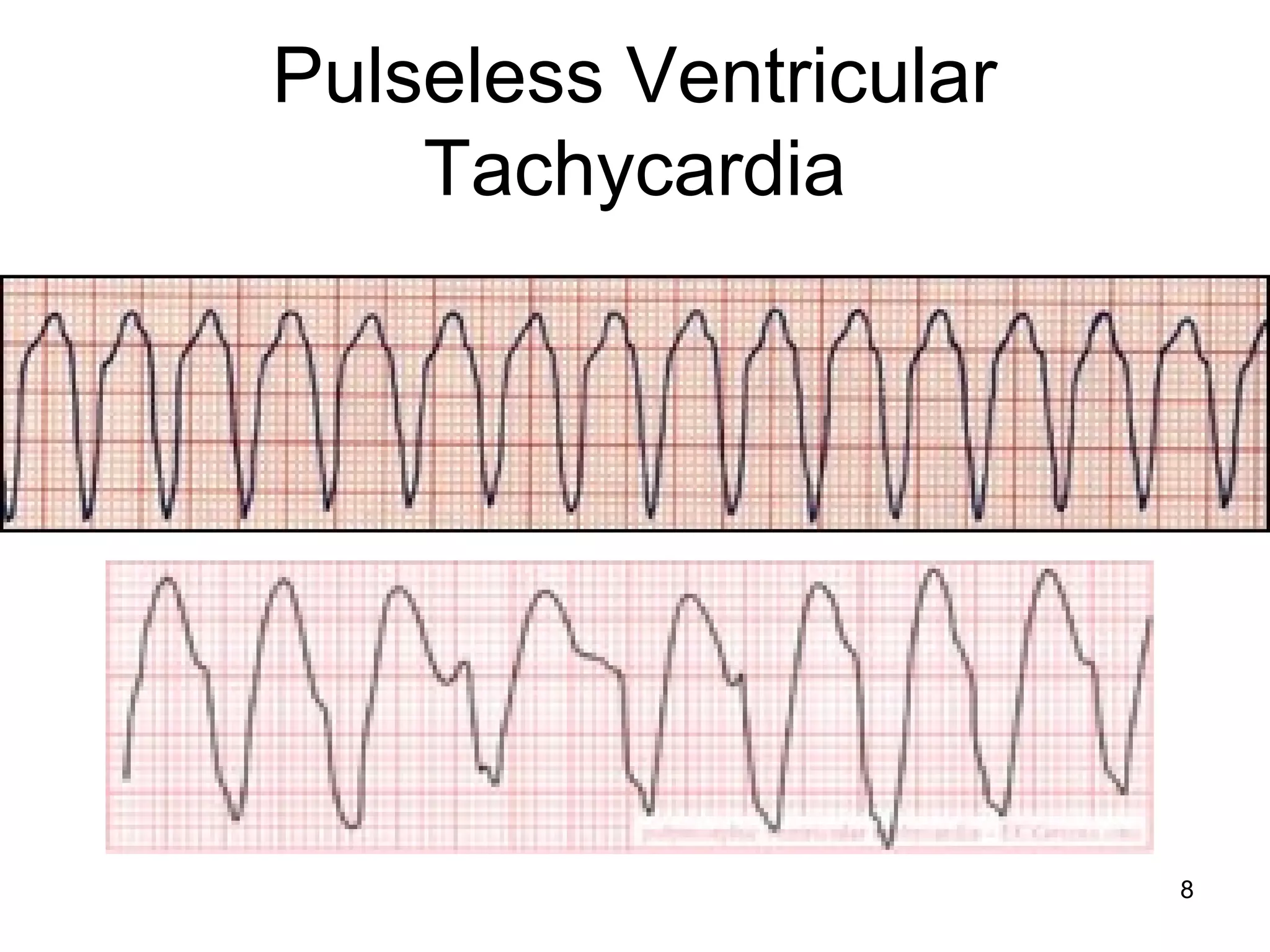
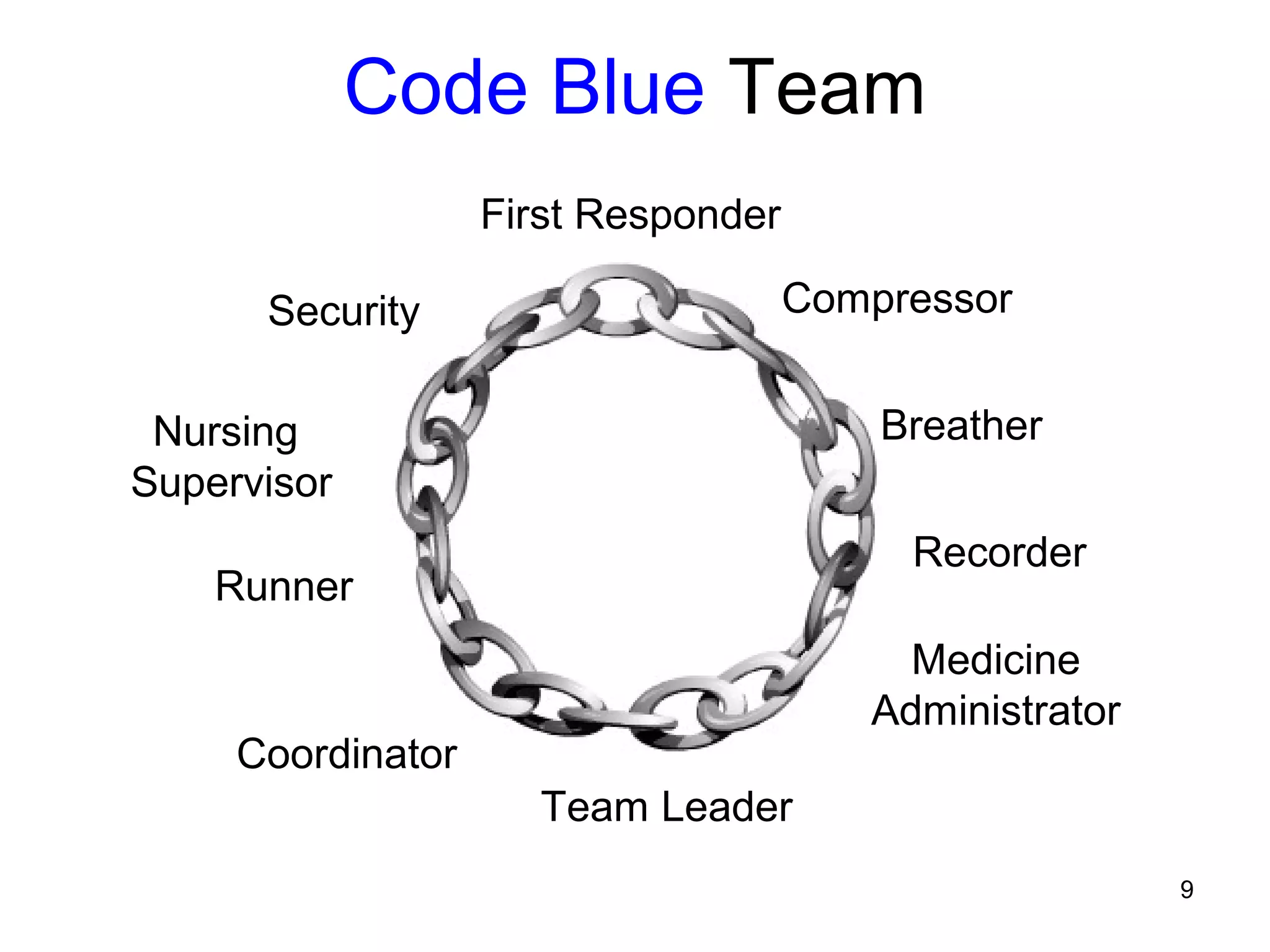
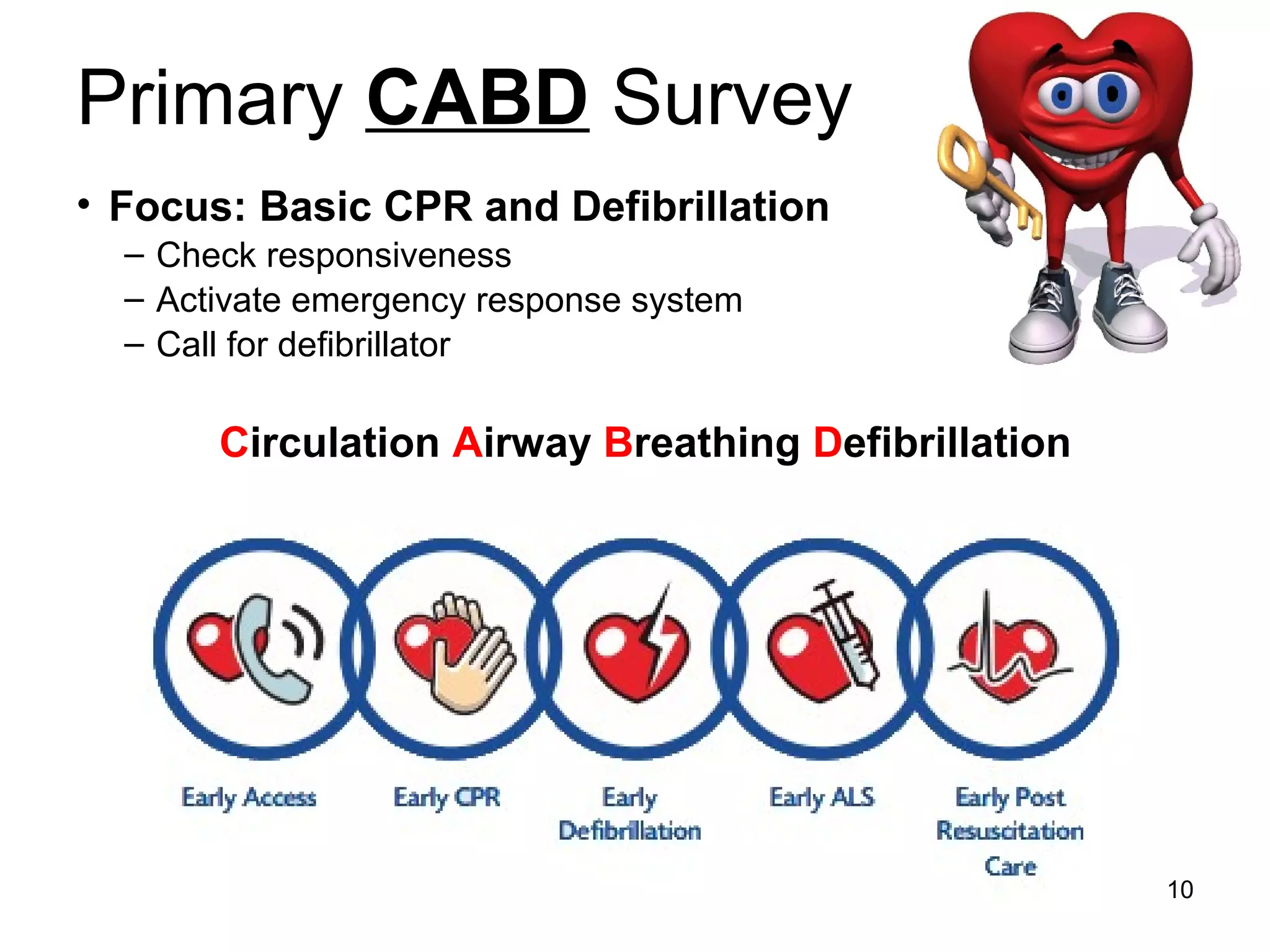
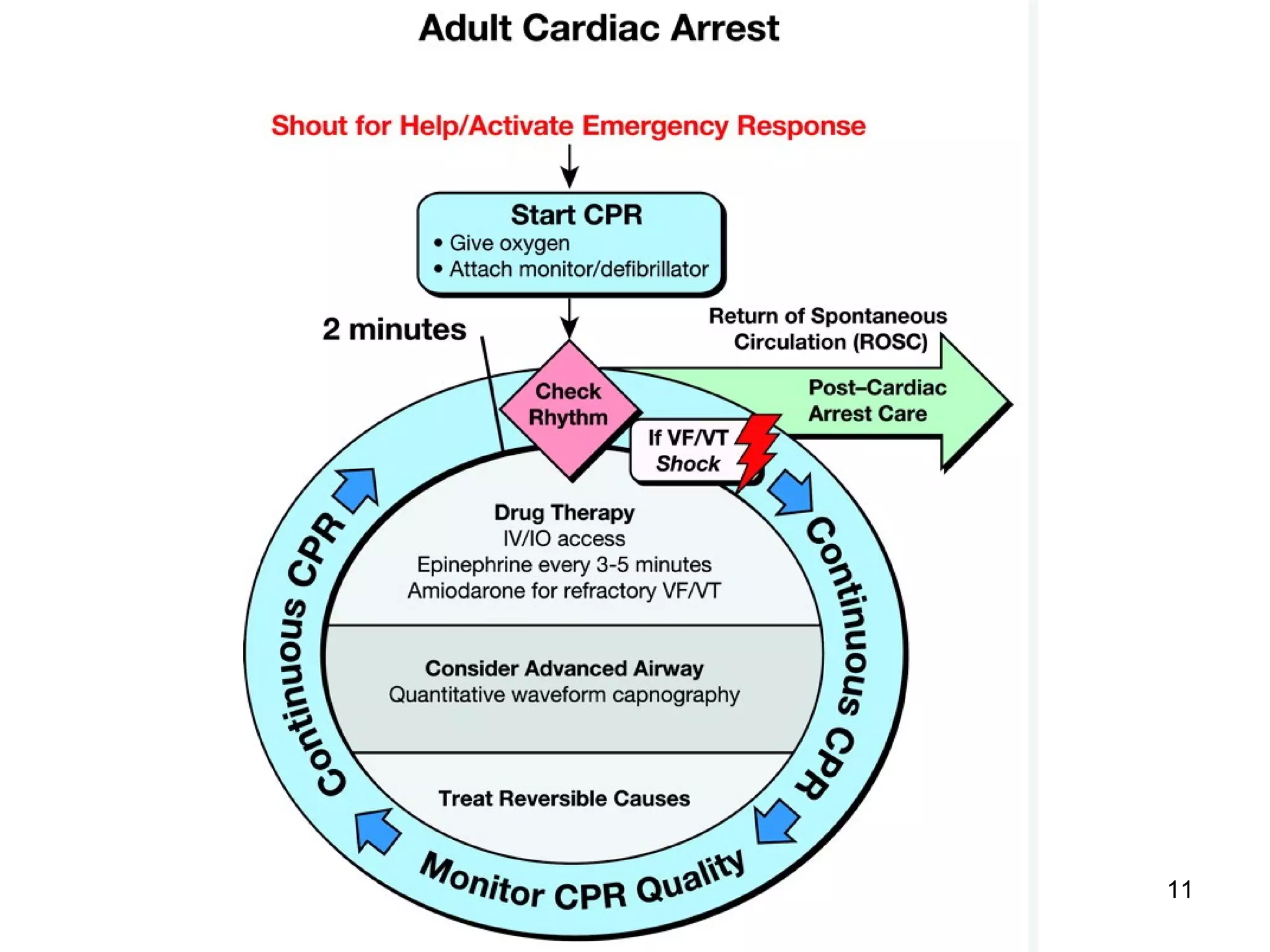
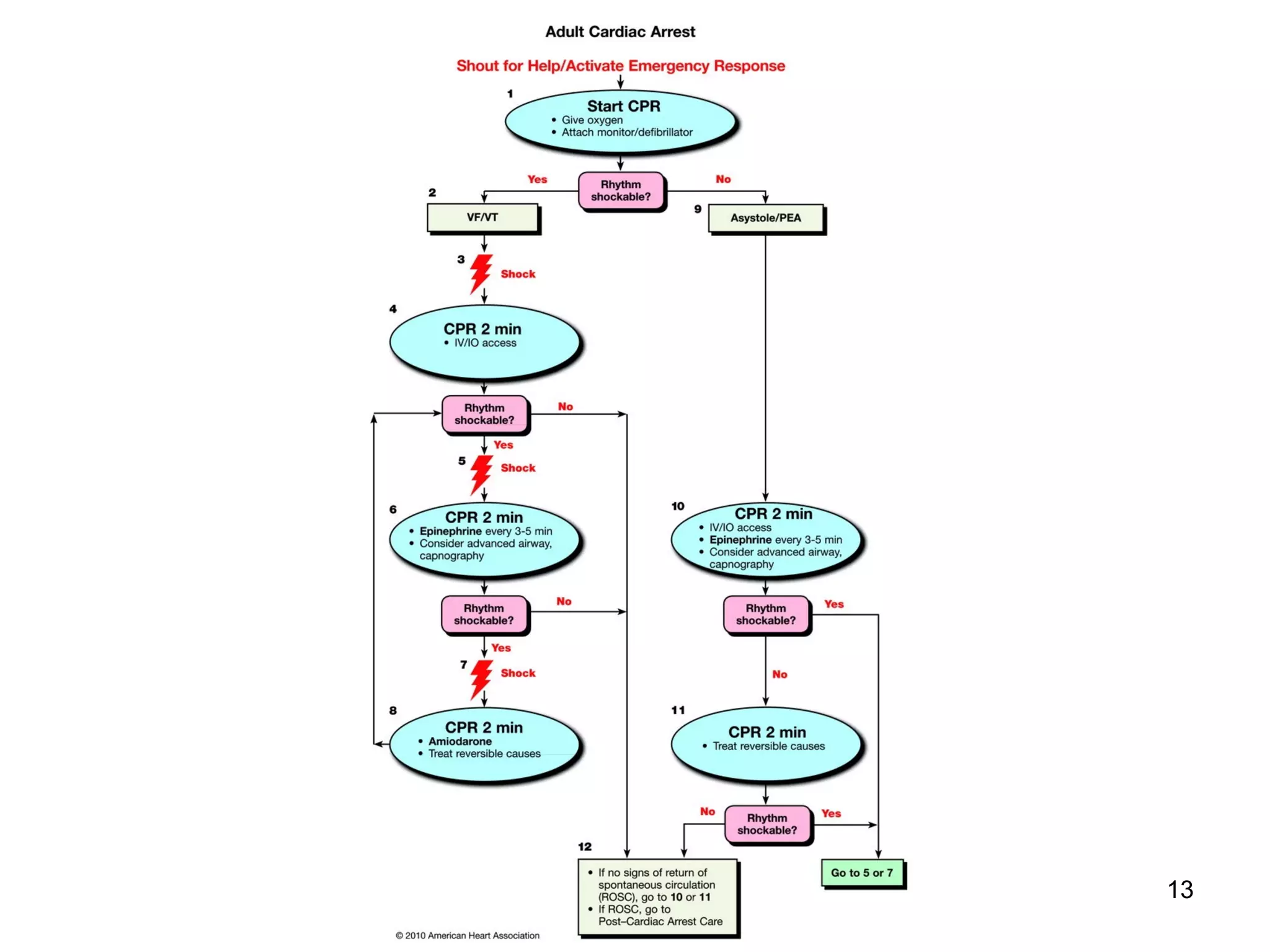
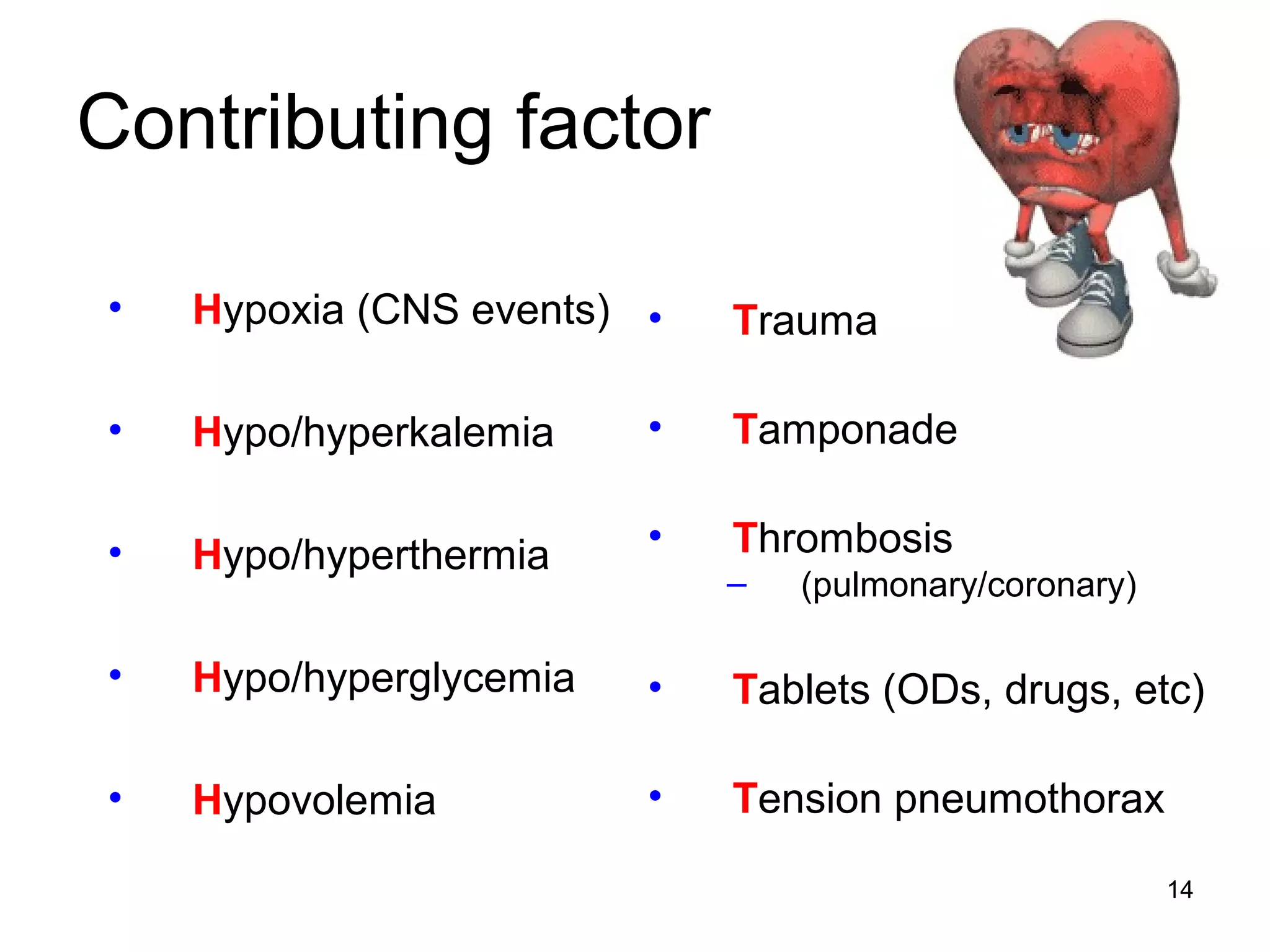
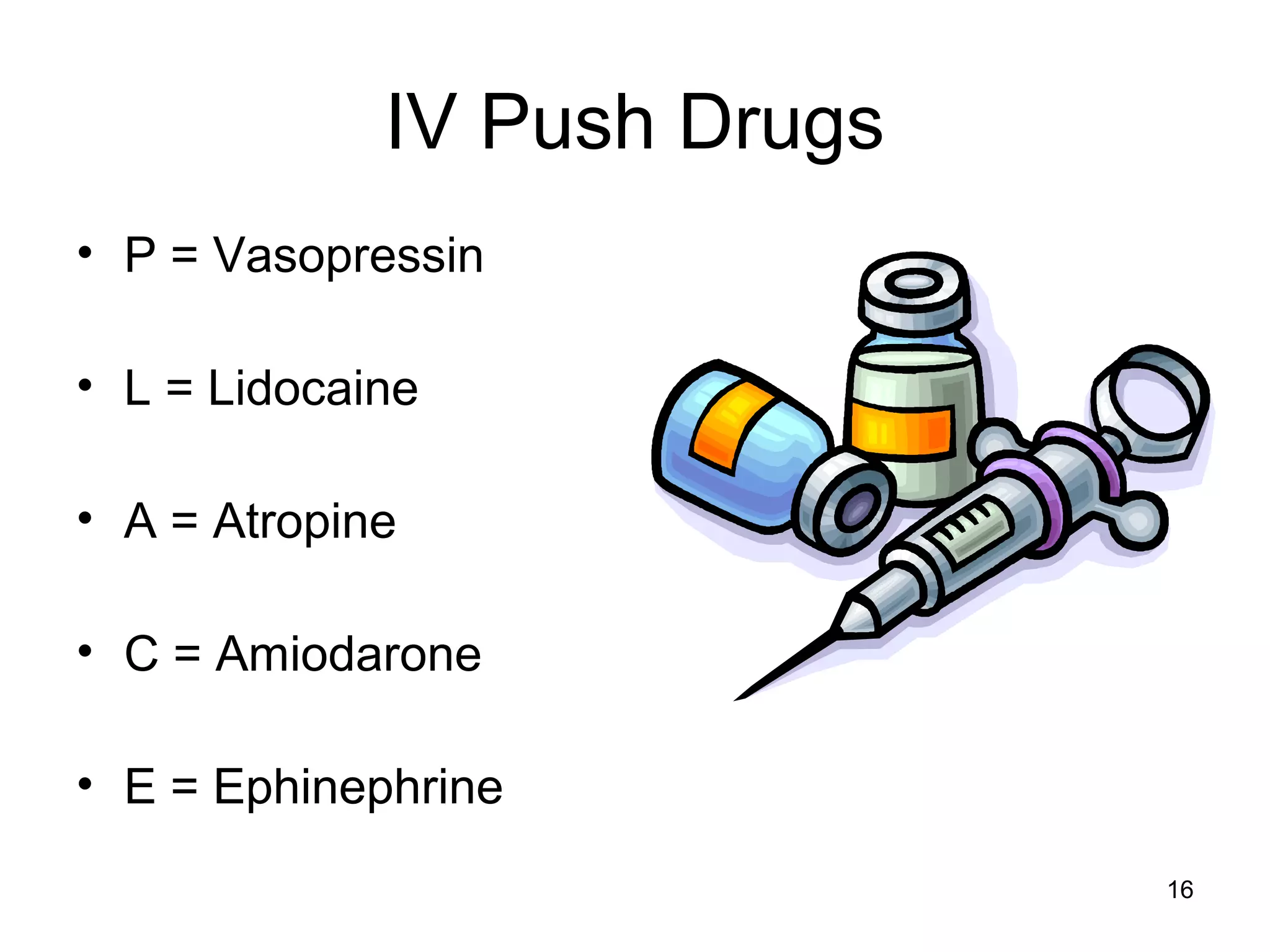
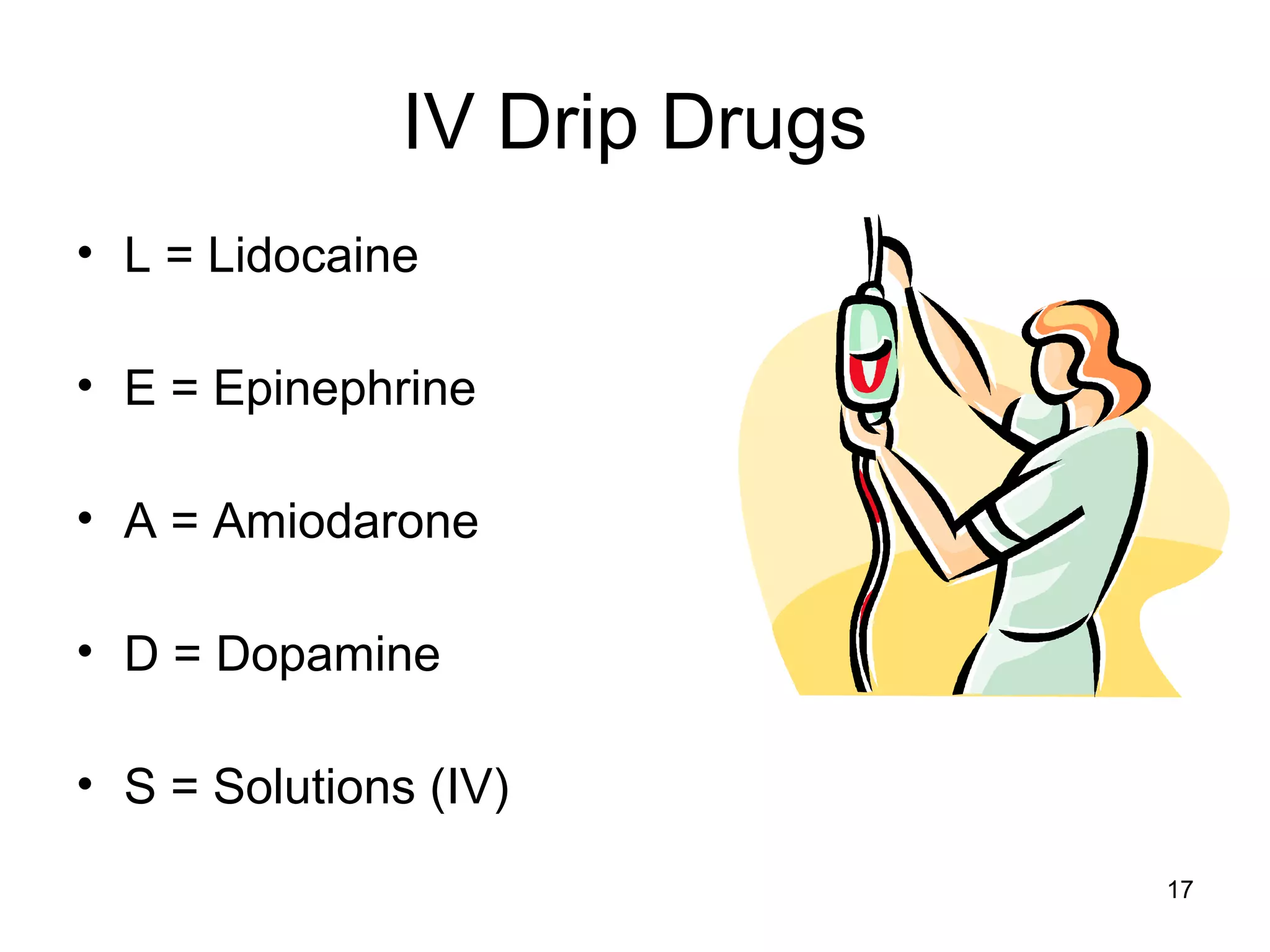
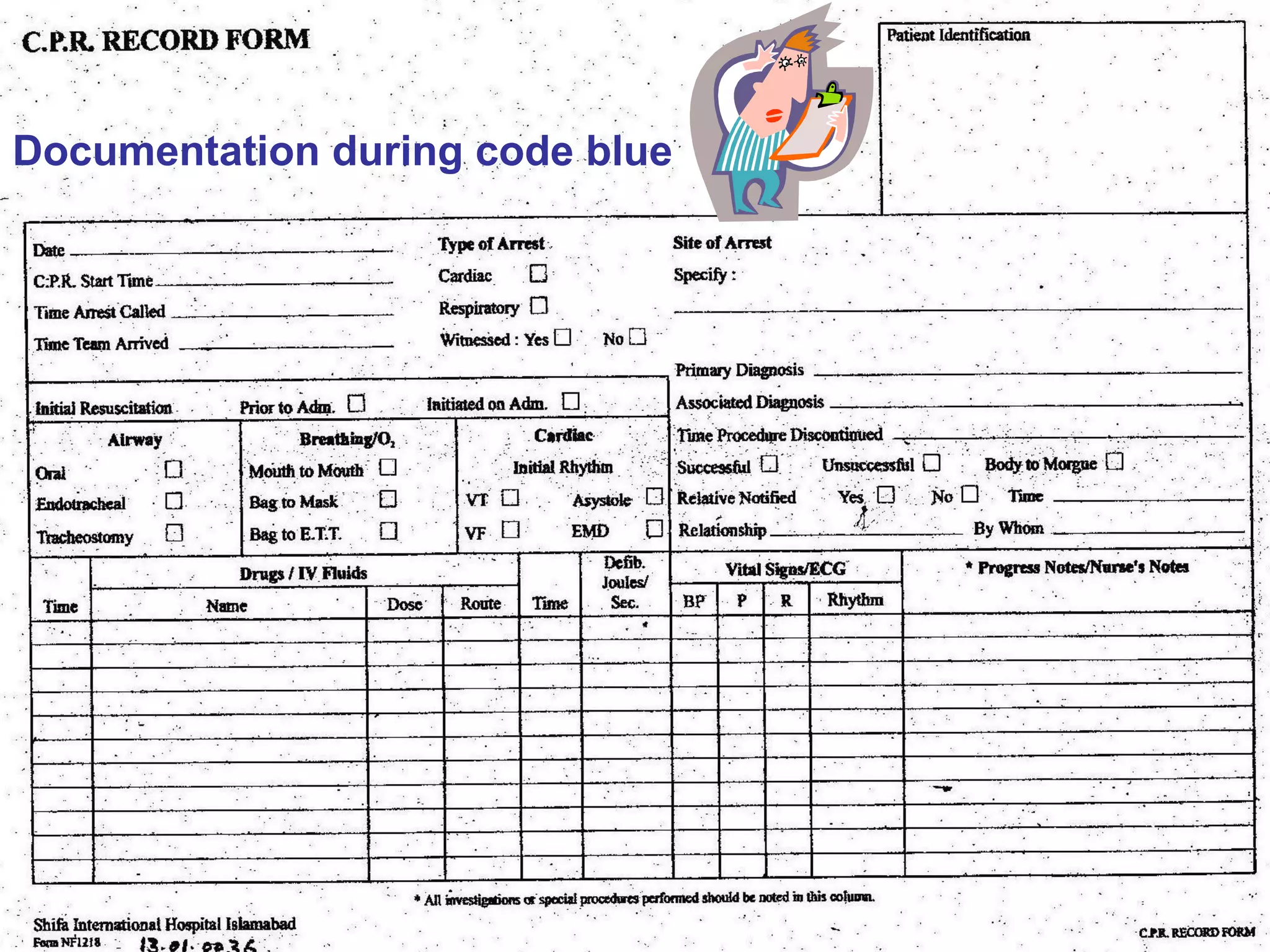
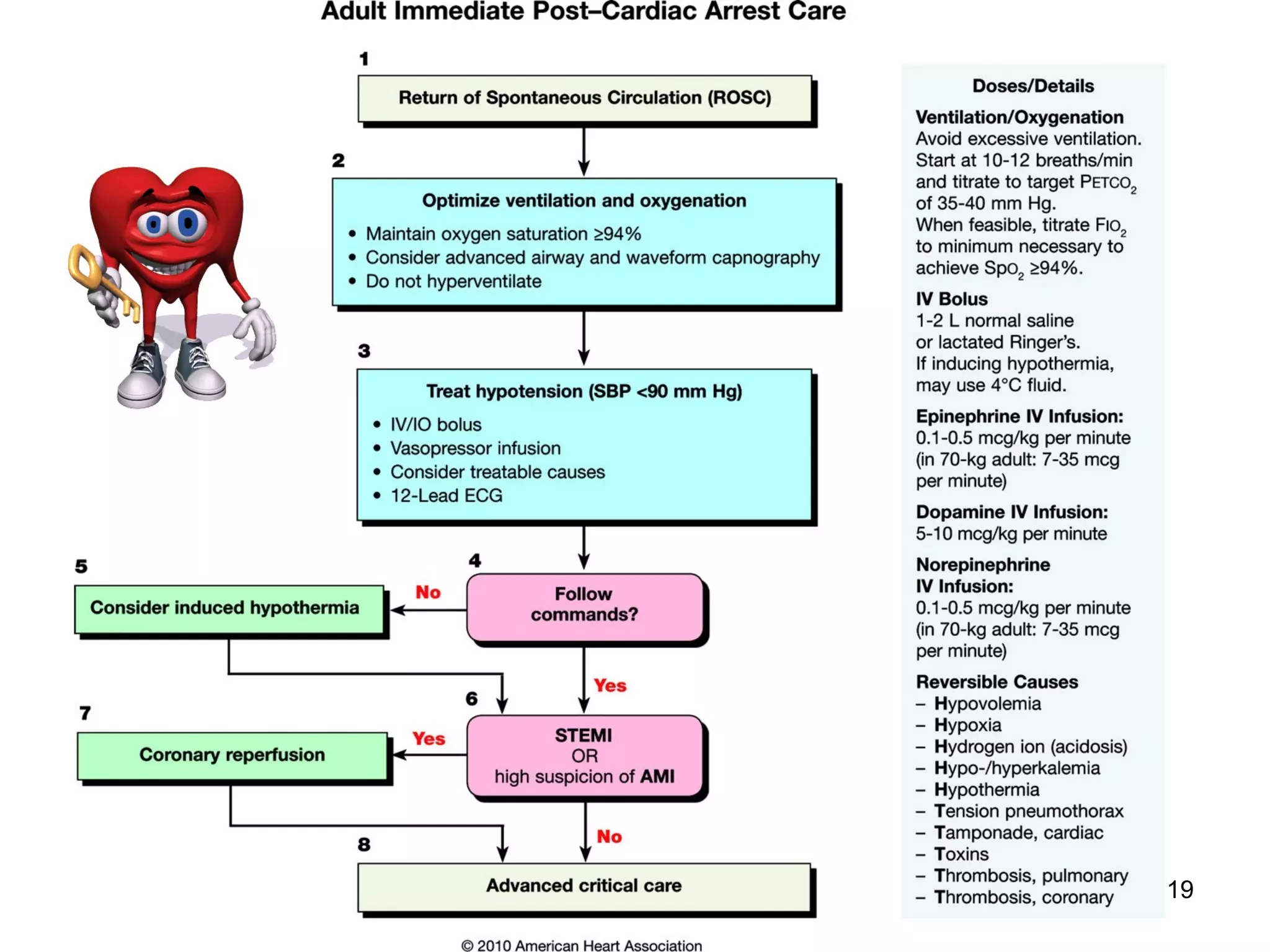
The document provides information about code blue cardiac nursing care. It outlines the objectives of presenting code blue protocols which include describing the purpose of code language, mechanisms of cardiac arrest, and the treatment hierarchy. It then details the primary components of responding to a code blue including performing CABD (Circulation, Airway, Breathing, Defibrillation) surveys and administering appropriate medications. The document provides details on cardiac arrest mechanisms, contributing factors, medications used, documentation, and post-resuscitation care with the goal of successful resuscitation.