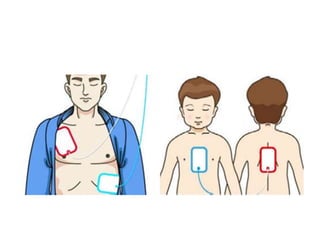
An automated external defibrillator (AED) delivers an electric shock to the heart to stop ventricular fibrillation and allow a normal rhythm to resume following sudden cardiac arrest; AEDs guide lay rescuers through the process of applying pads to the patient's chest, analyzing their heart rhythm, and delivering a shock if needed to restore a normal rhythm; It is critical to place AED pads correctly on the patient's chest, follow all prompts, and continue CPR between shocks to improve chances of survival from sudden cardiac arrest.