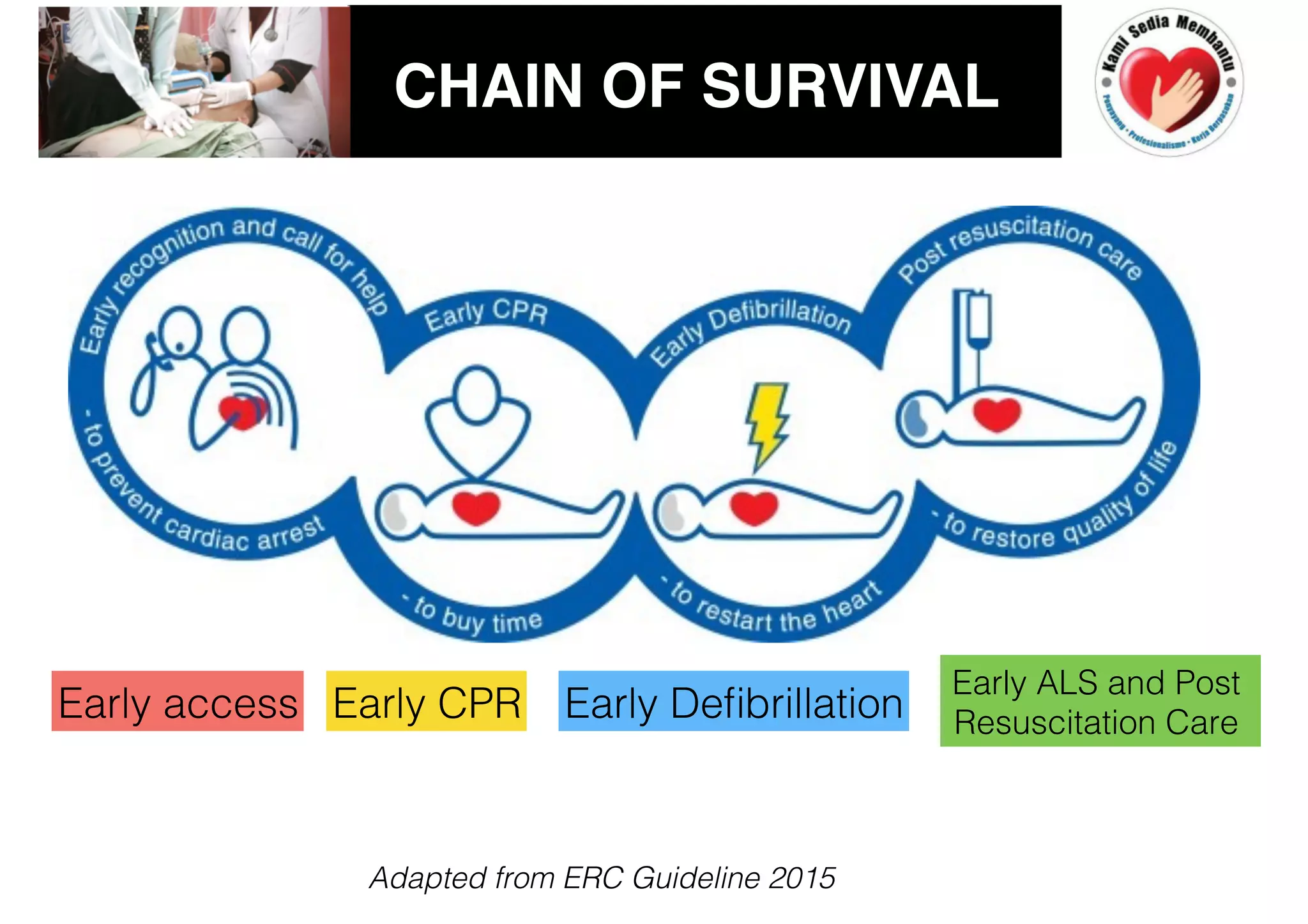
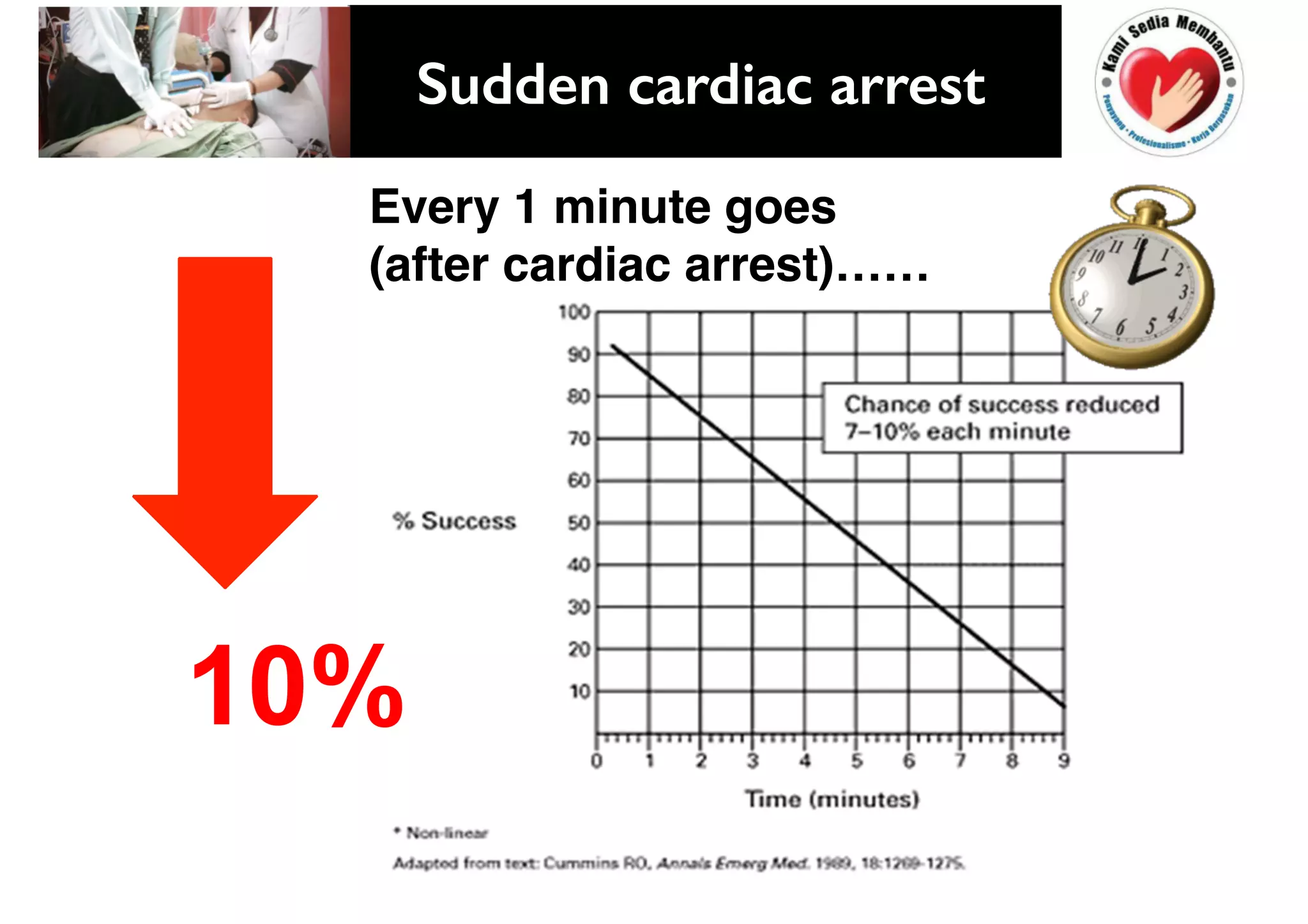
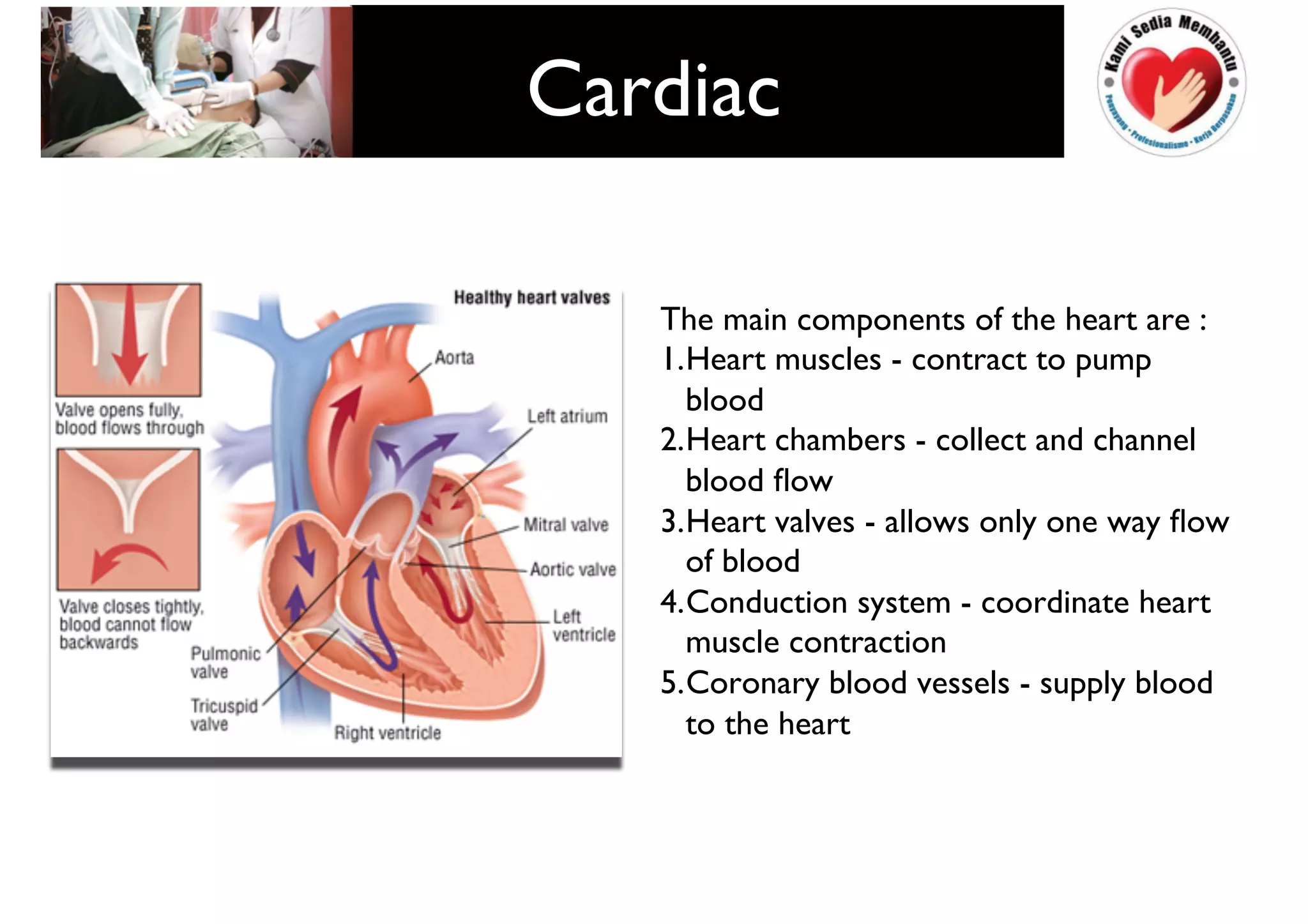
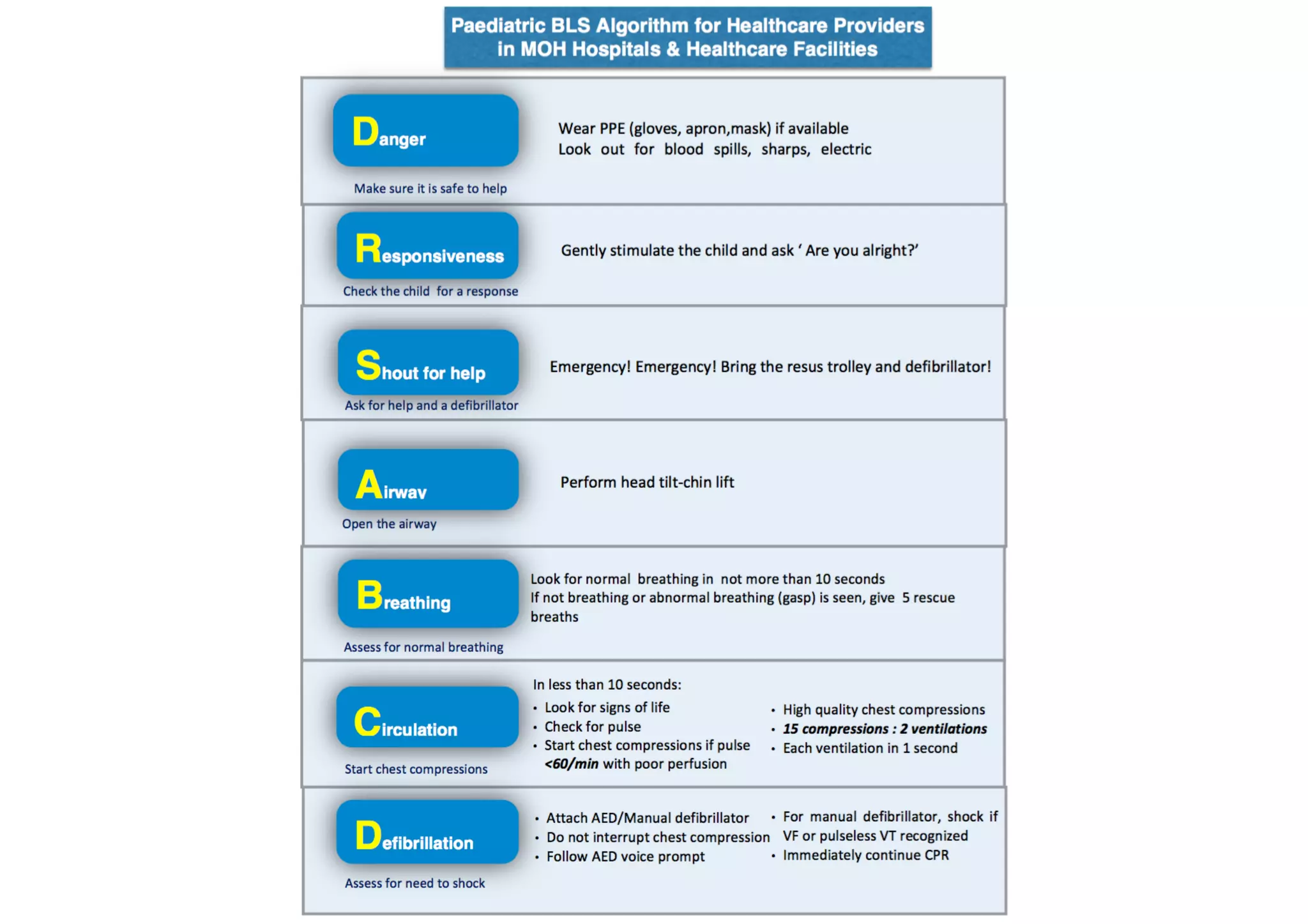
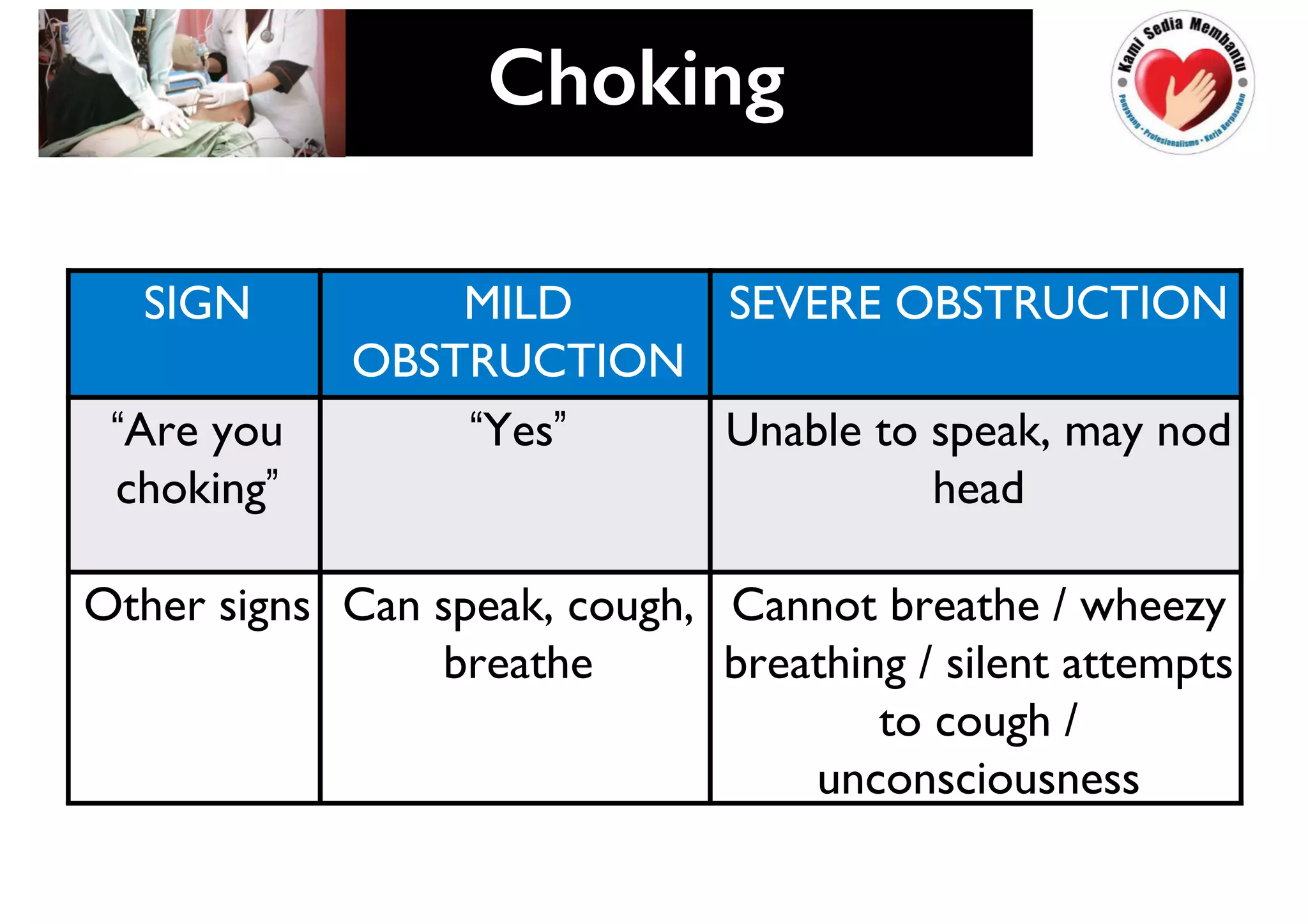
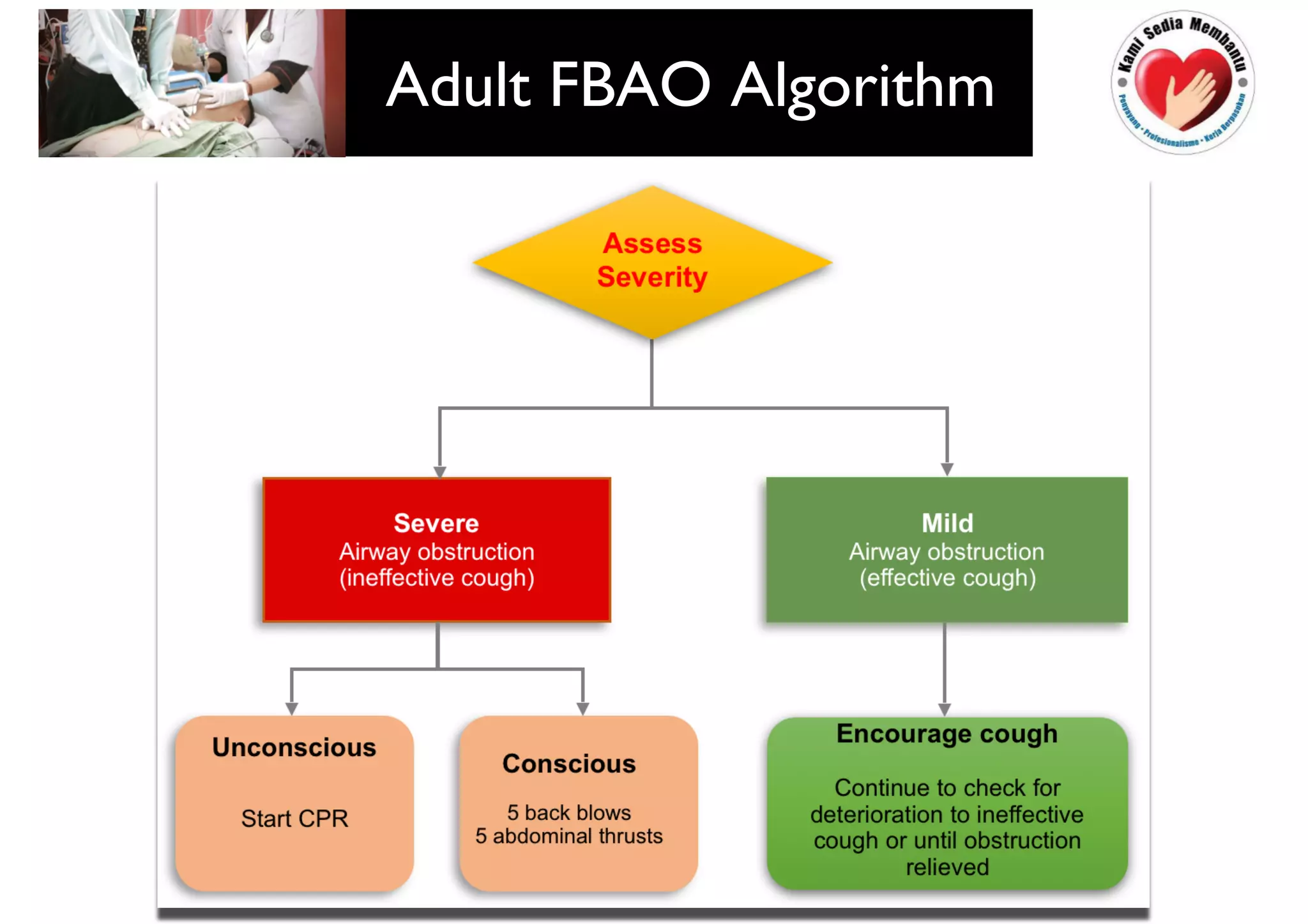
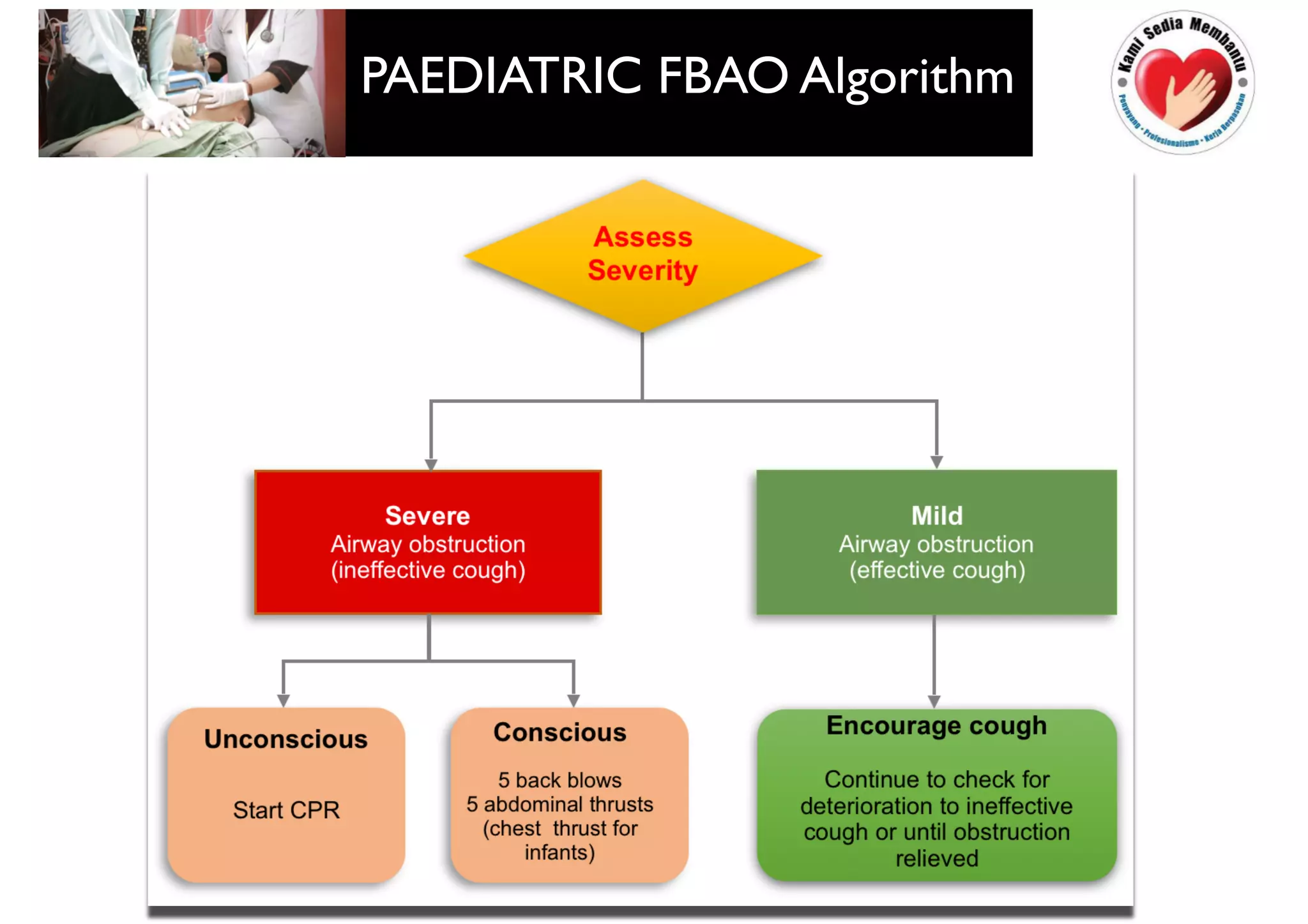
This document provides guidelines for basic life support (BLS) for healthcare workers. It describes the key components of BLS, including airway, breathing, circulation, use of an automated external defibrillator, and managing choking. The chain of survival is outlined as early access, early CPR, early defibrillation, early advanced life support, and post-resuscitation care. Guidelines are provided for performing chest compressions, rescue breathing, and defibrillation for adults, children, and infants. Defibrillators are described as devices that can terminate ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia to restore an effective heart rhythm.