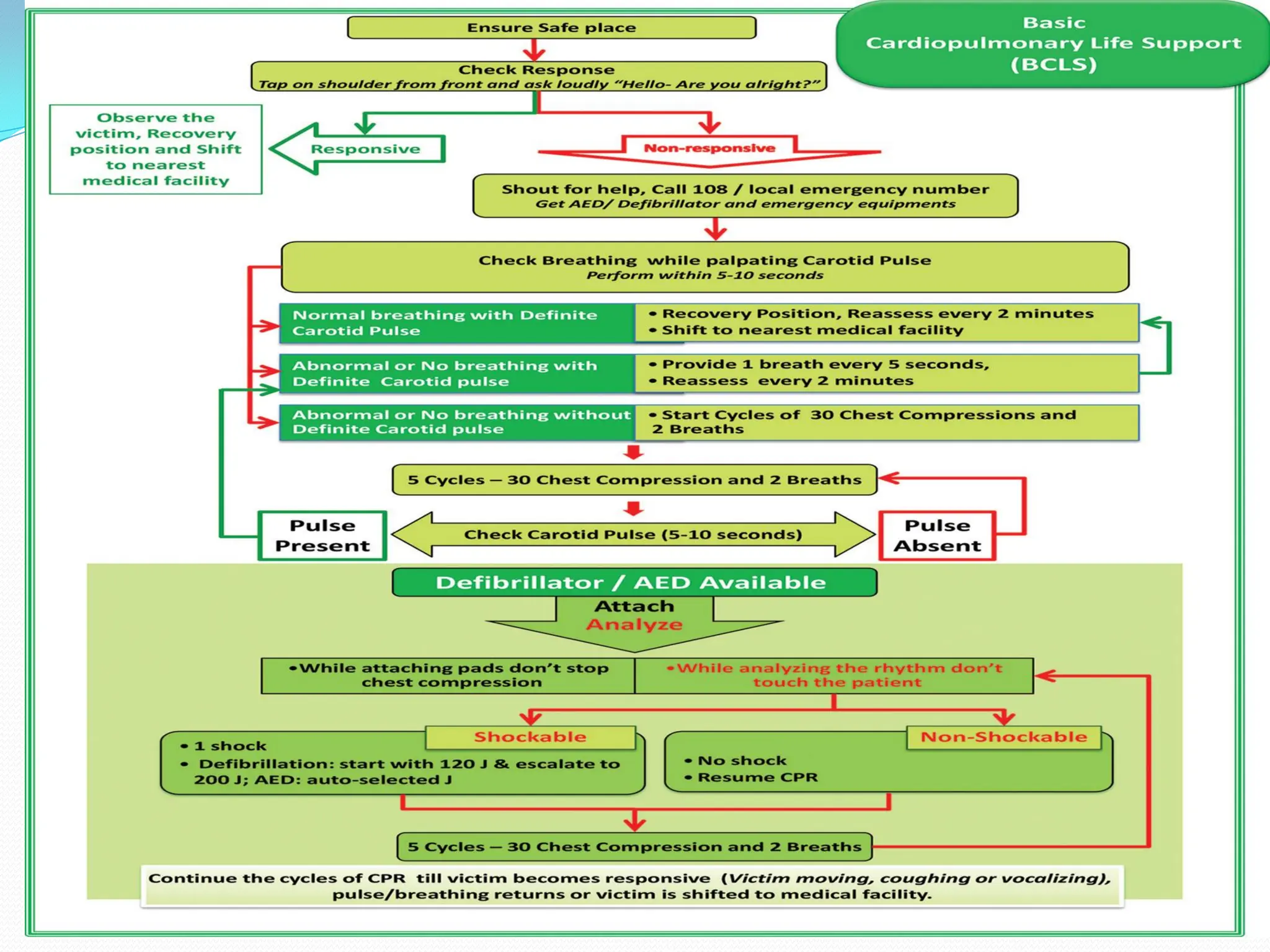
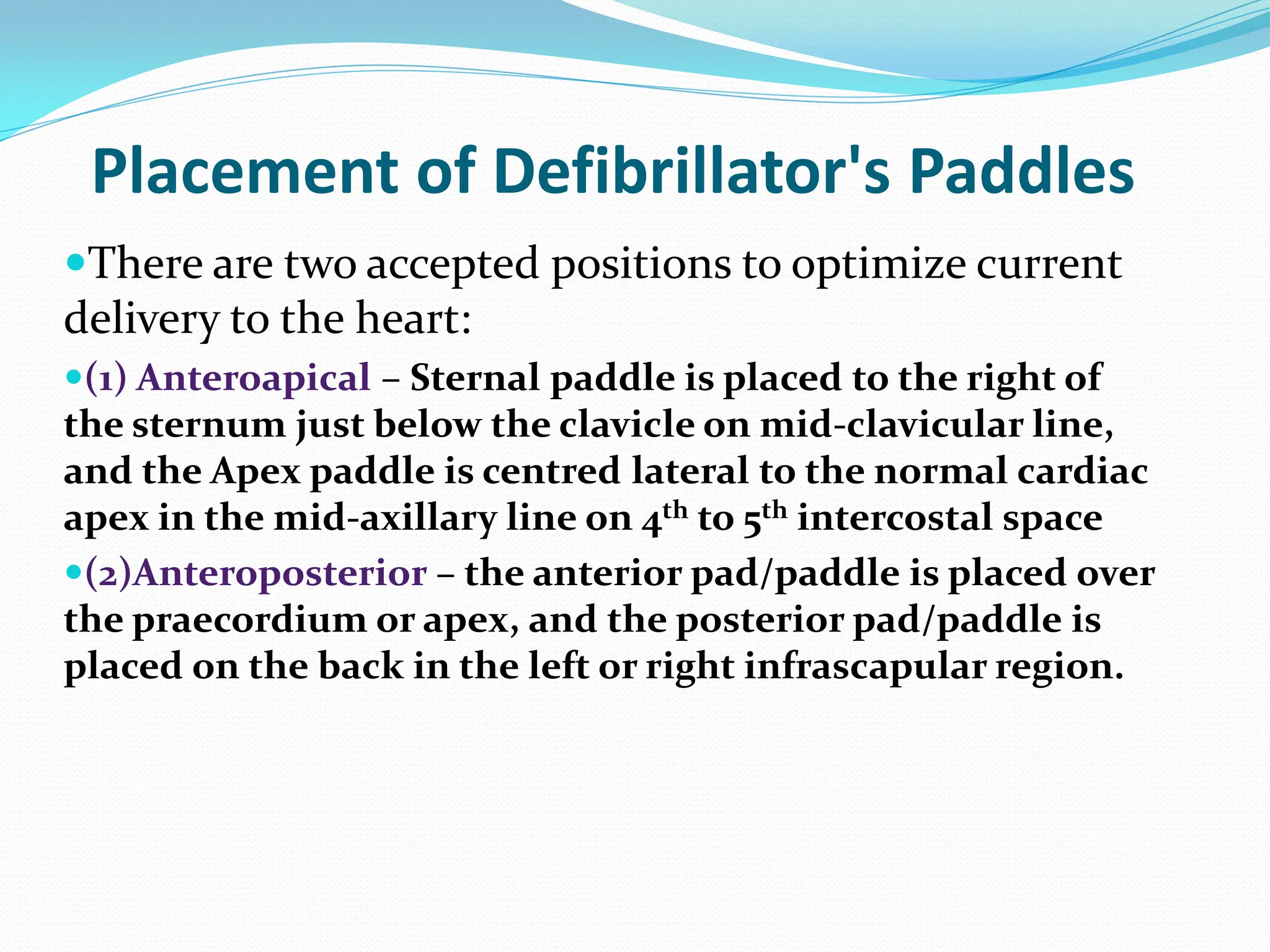
Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively due to problems with its electrical system. Basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) involves chest compressions and rescue breathing to provide oxygen to the brain and vital organs until definitive medical treatment can restore normal heart function. High quality CPR includes compressing the chest at a rate of 120 times per minute to a depth of 2-2.4 inches, minimizing interruptions, and providing rescue breaths every 5 seconds. Defibrillation, applying an electrical shock, may help restore an effective heart rhythm for shockable rhythms like ventricular fibrillation.




![REVERSABLE CAUSES
‘HIT THE TARGET’
H – Hypoxia
I – Increased H Ions [Acidosis],
T – Tension Pneumothorax,
T – Toxins/Poisons,
H – Hypovolaemia,
E – Electrolyte Imbalance [Hypo-/Hyperkalaemia],
T – TamponadeCardiac,
A – Acute Coronary Syndrome,
R – Raised Intracranial Pressure [SubarachnoidHaemorrhage]
G – Glucose [Hypo-/hyperglycaemia],
E – Embolism (Pulmonary Thrombosis),
T – Temperature [Hypothermia]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprdemonstration1-240413170643-b0f95b80/75/CPR-DEMONSTRATION-for-nursing-students-and-stafff-5-2048.jpg)