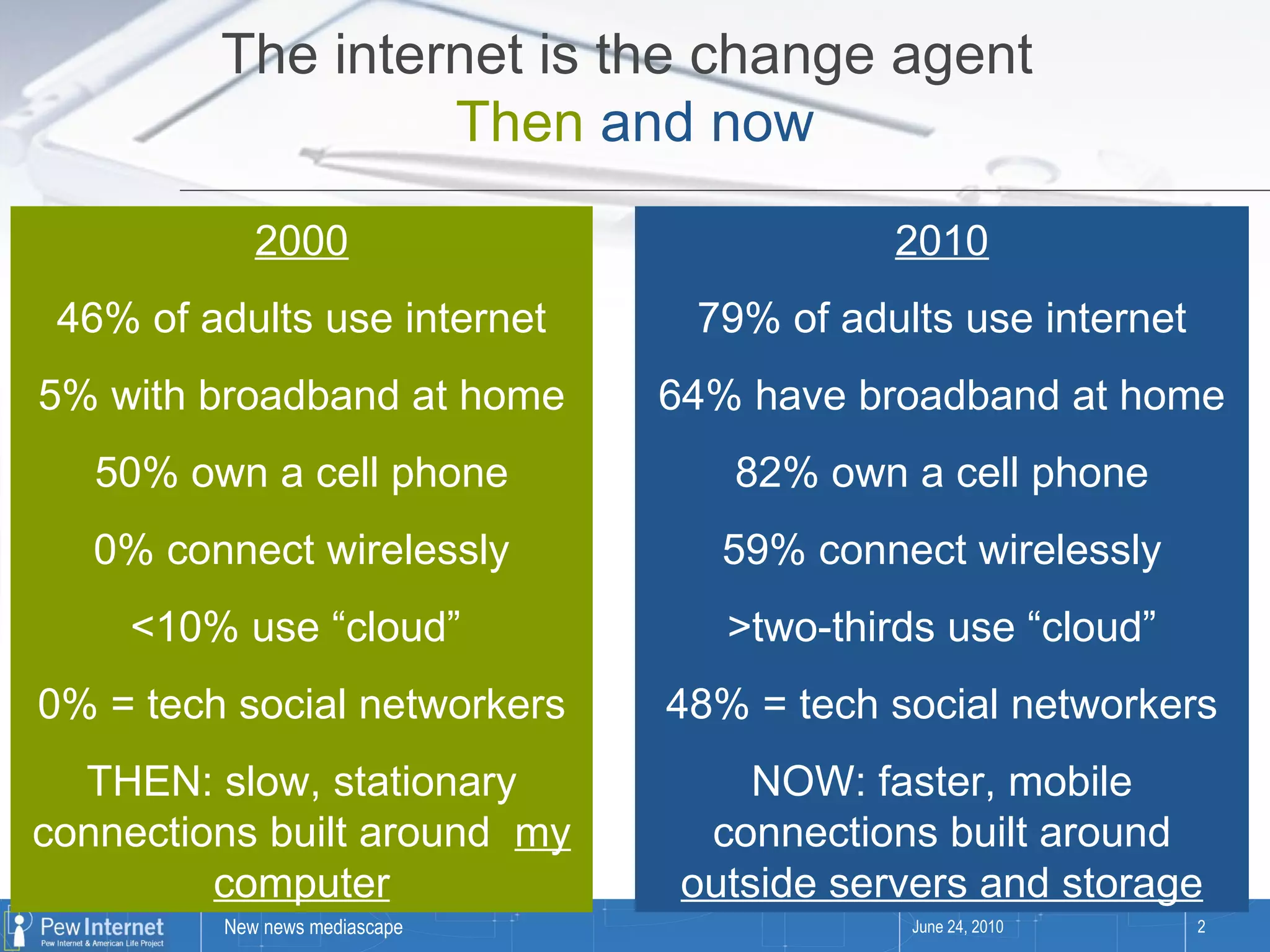
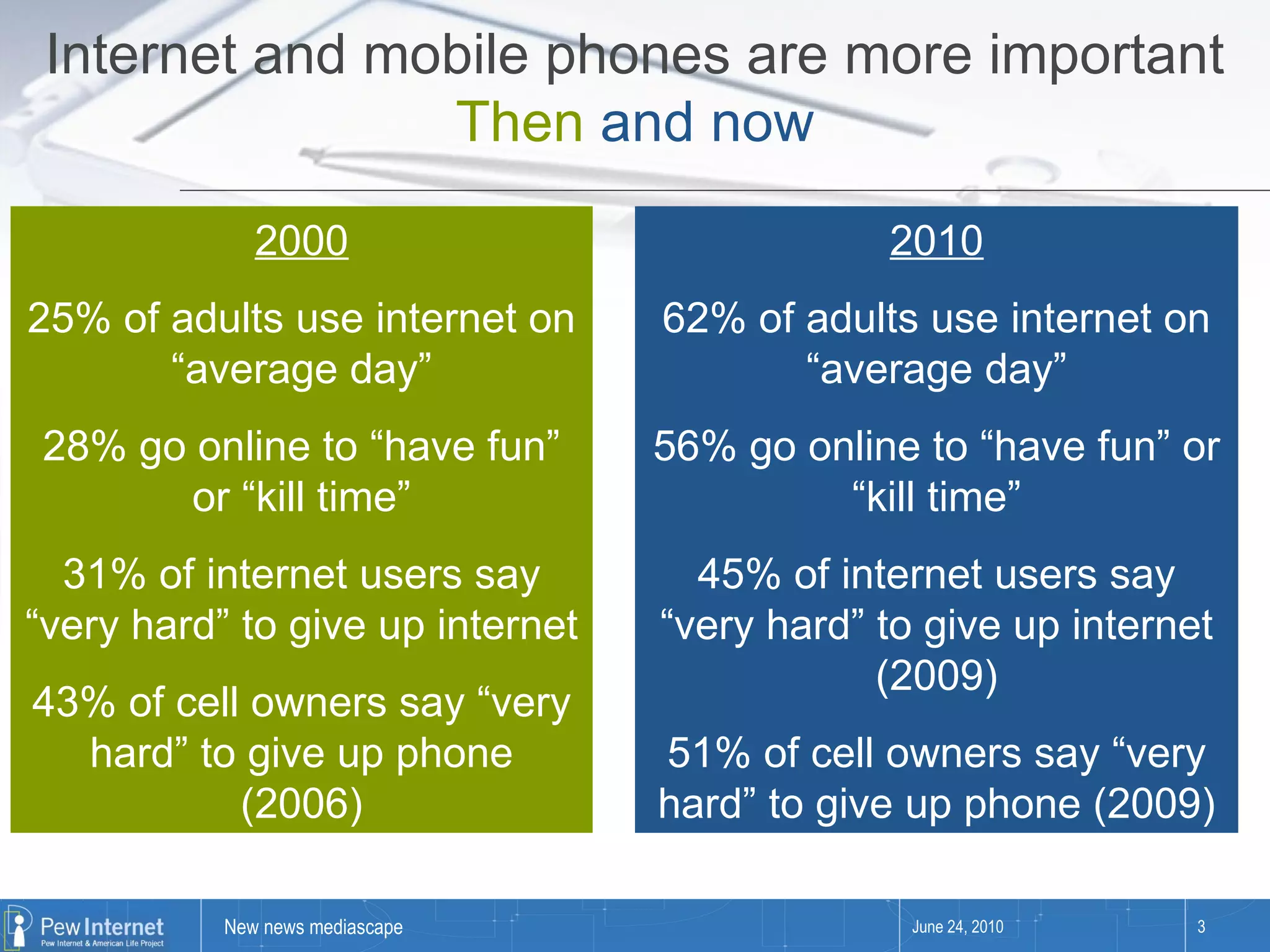
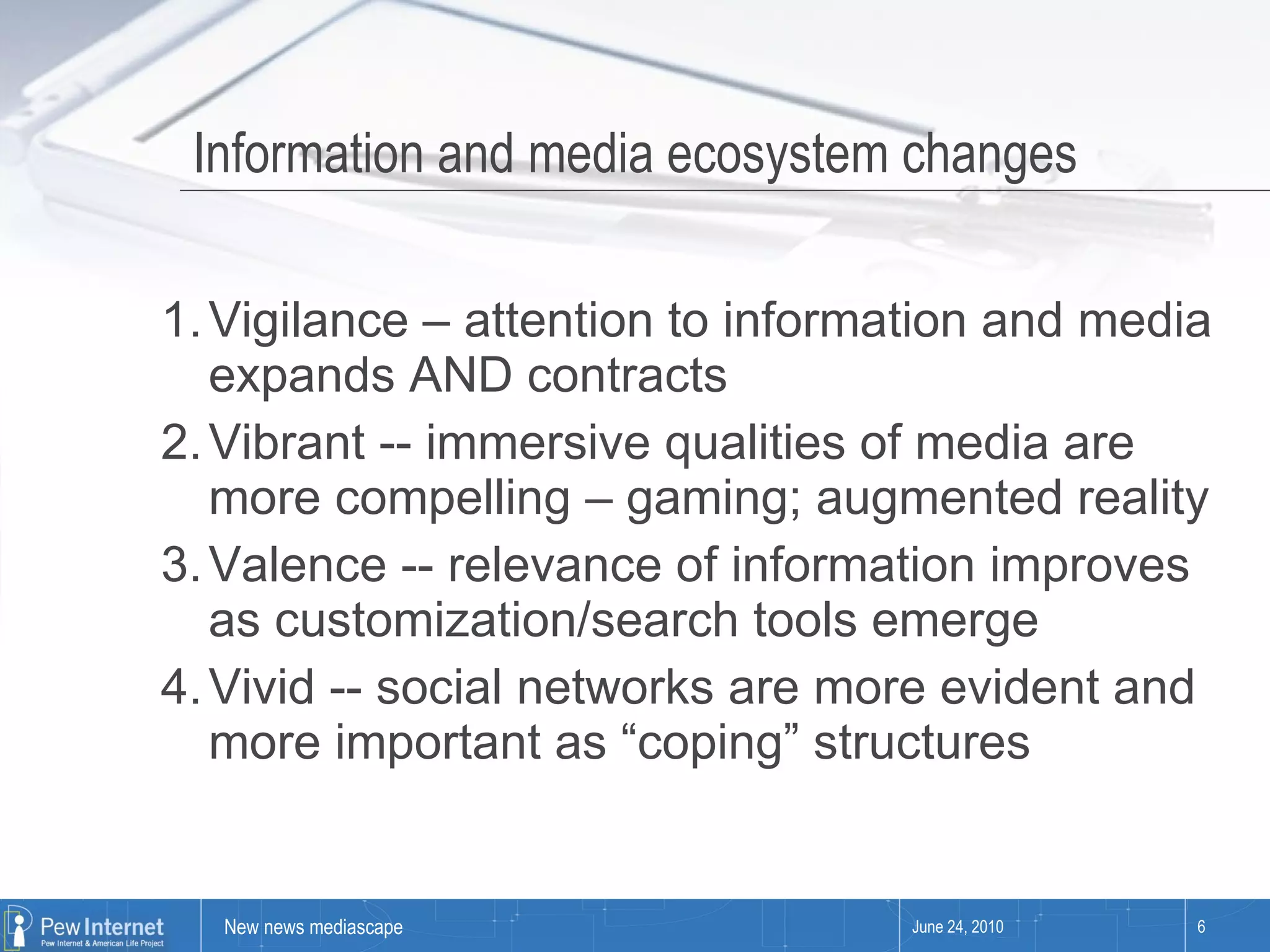
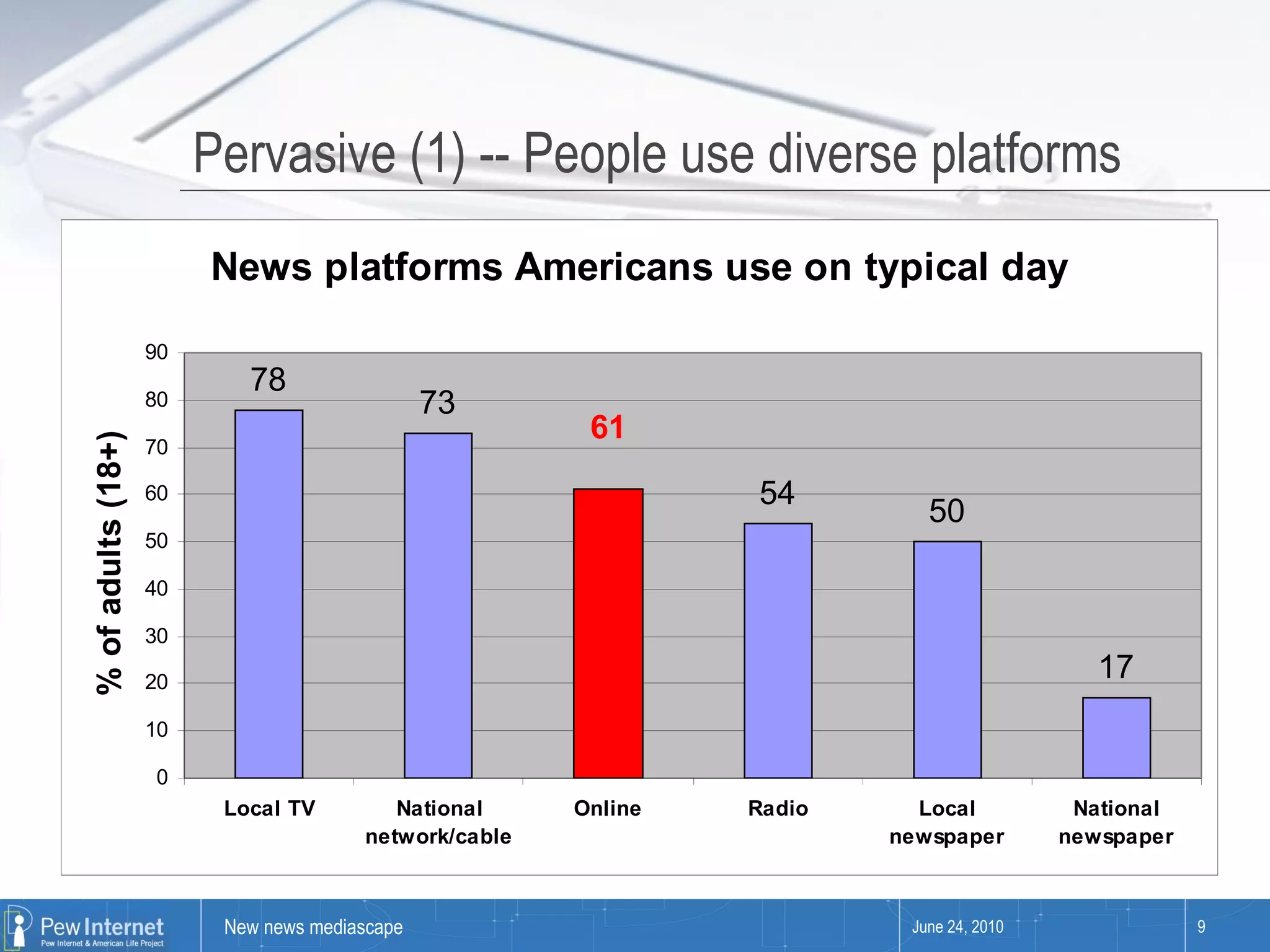
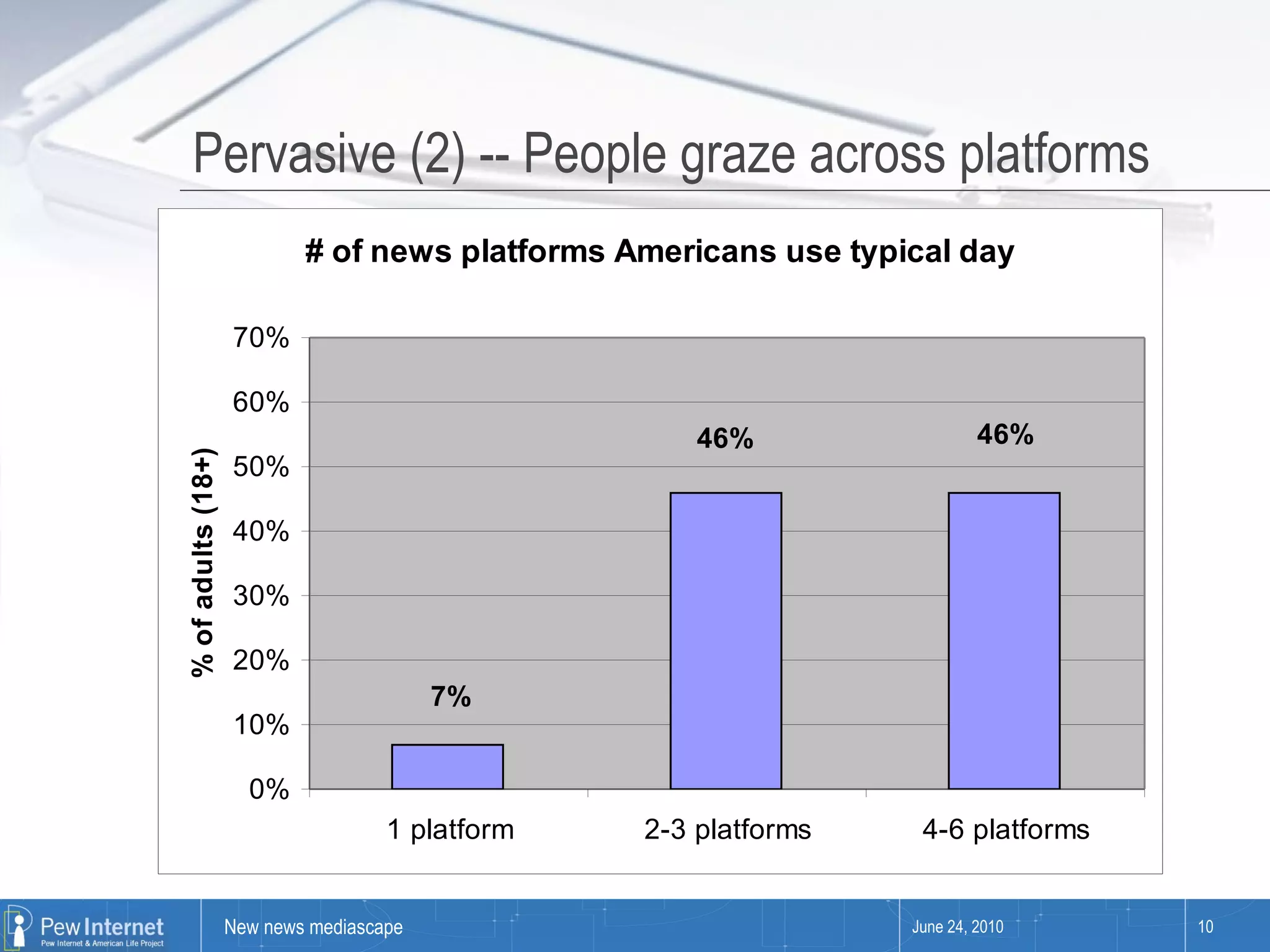
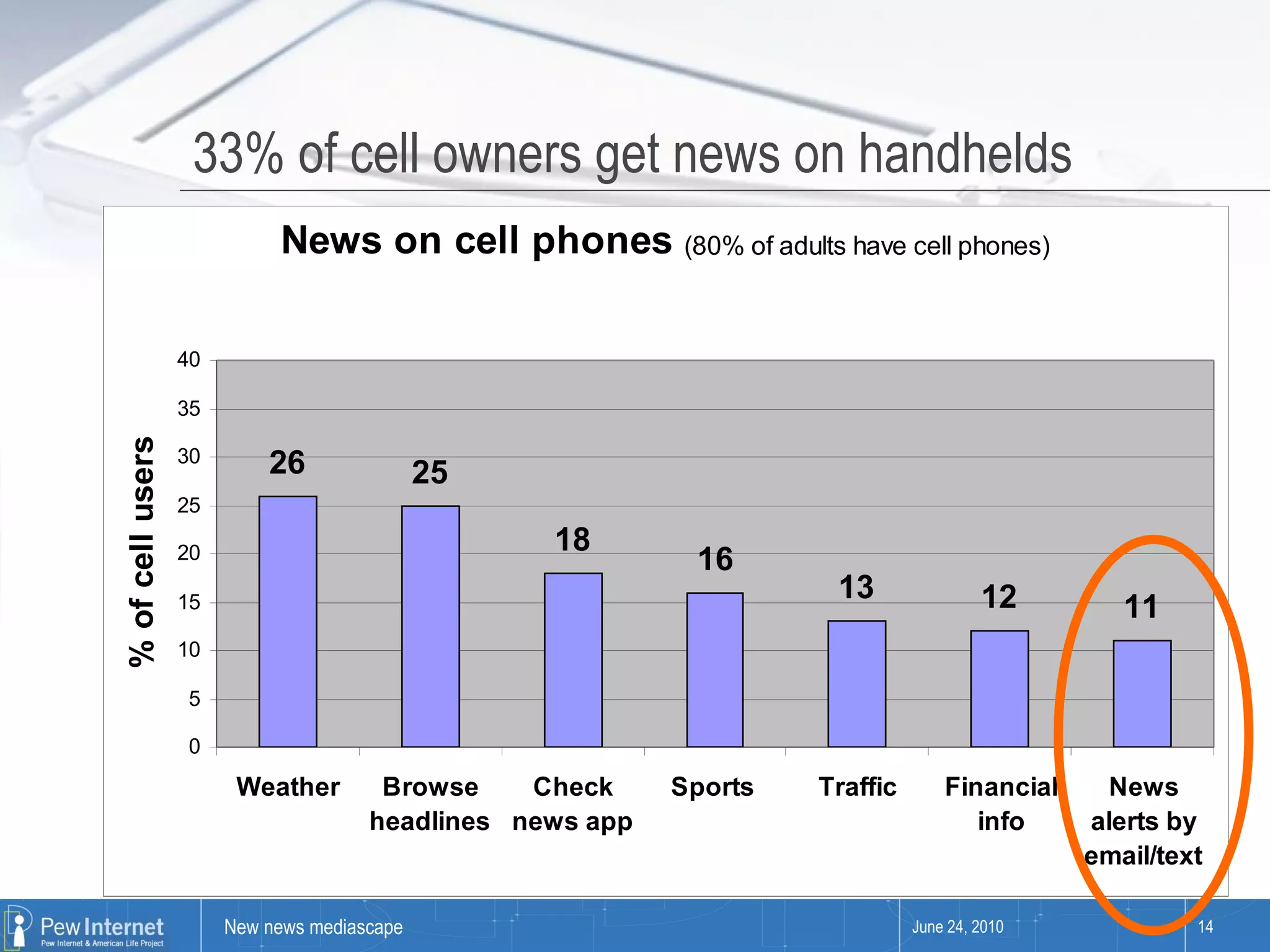
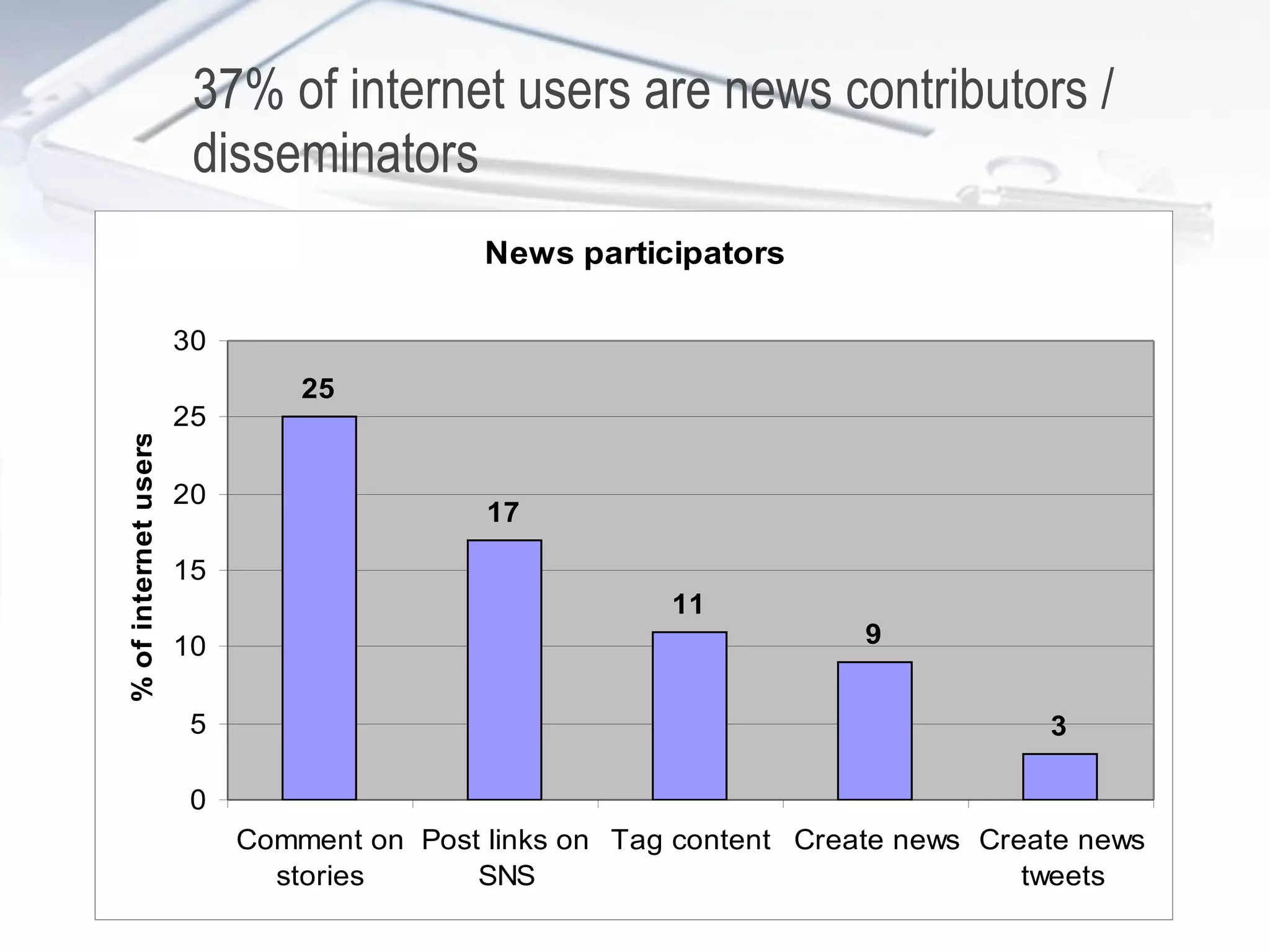
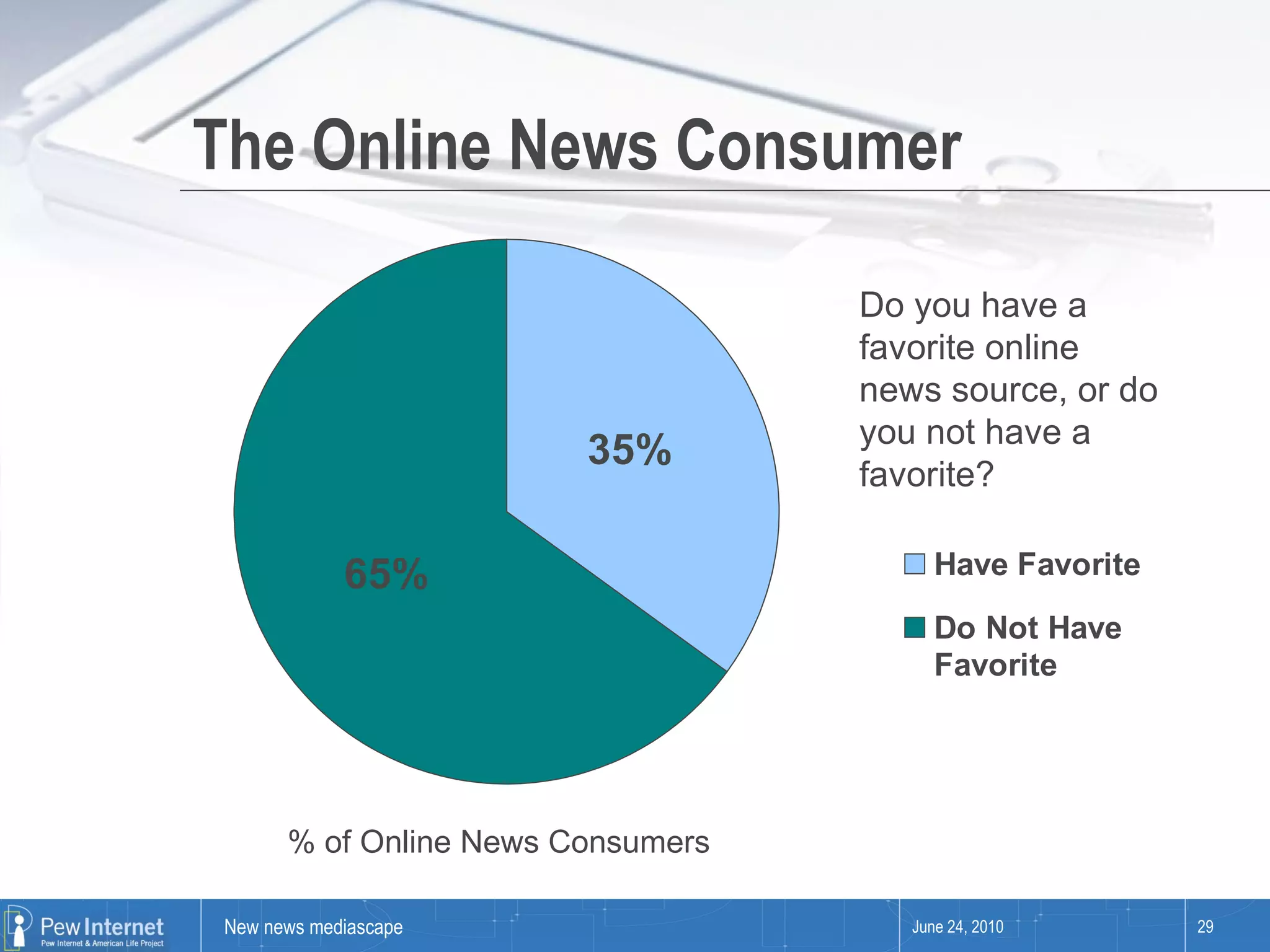
Since 2000, media consumption has become more pervasive, portable, personalized, and participatory, with a significant increase in internet access and mobile usage among adults. The audience now engages with news across diverse platforms, blending old and new media, and often participates in news creation and distribution. However, this shift presents paradoxes such as increased information availability coupled with decreased trust and loyalty to news sources.
























![Thank you! Lee Rainie Director Pew Internet & American Life Project 1615 L Street NW Suite 700 Washington, DC 20036 Email: [email_address] Twitter: http://twitter.com/lrainie 202-419-4500 June 24, 2010](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2010-062410-syracusenewhousemobconfnyc-100624104749-phpapp01/75/How-Media-Consumption-Has-Changed-Since-2000-35-2048.jpg)