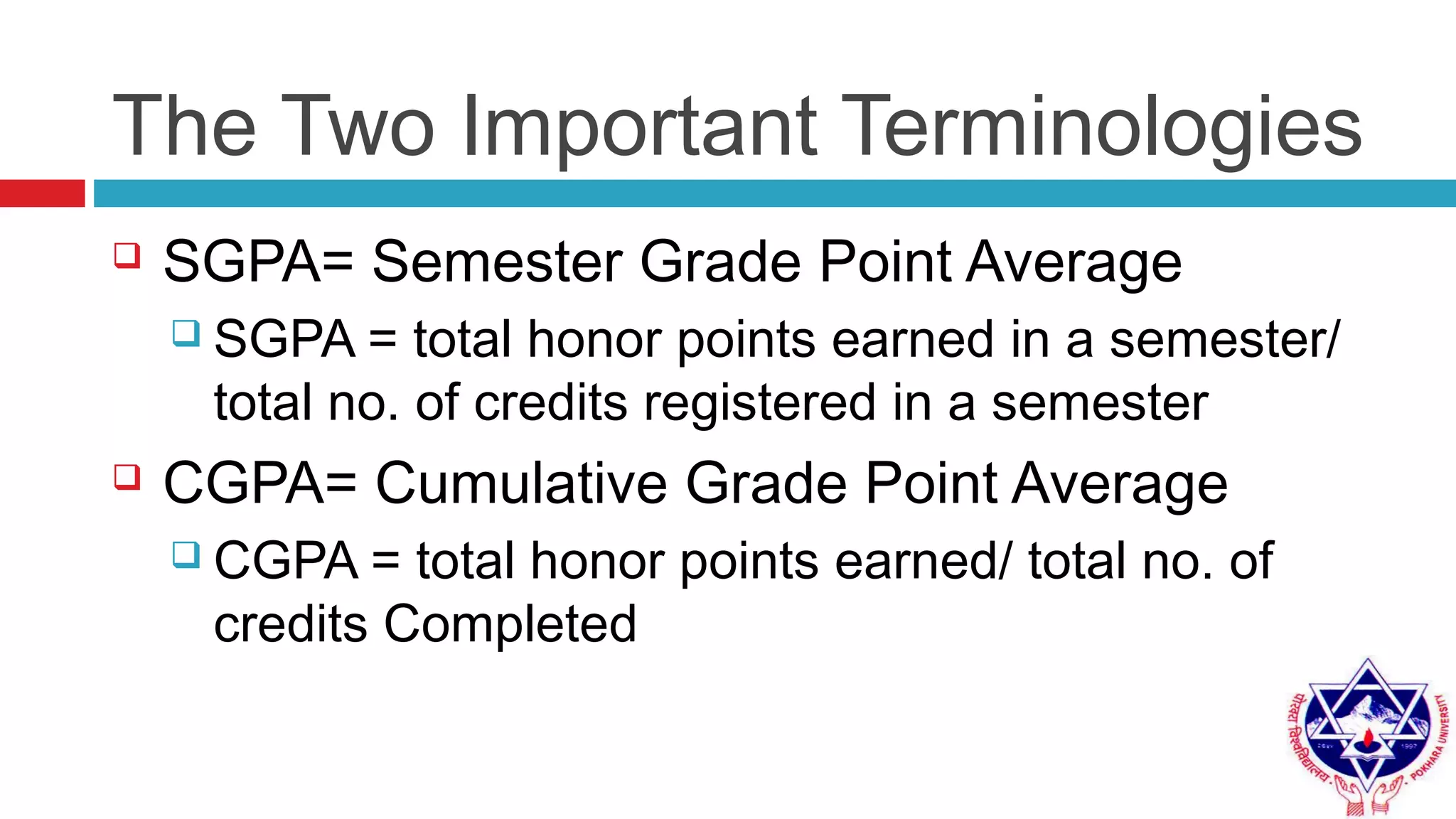
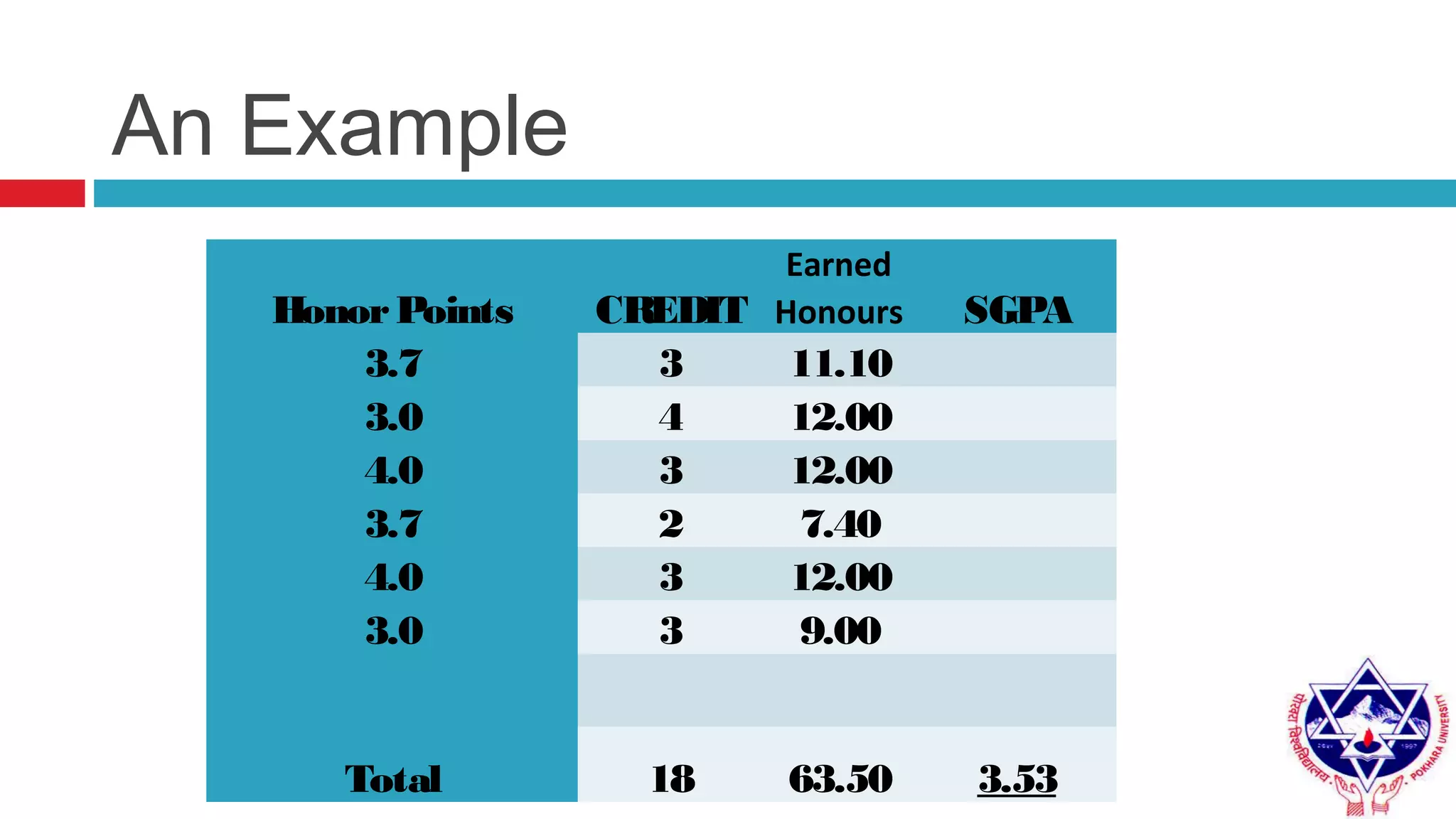
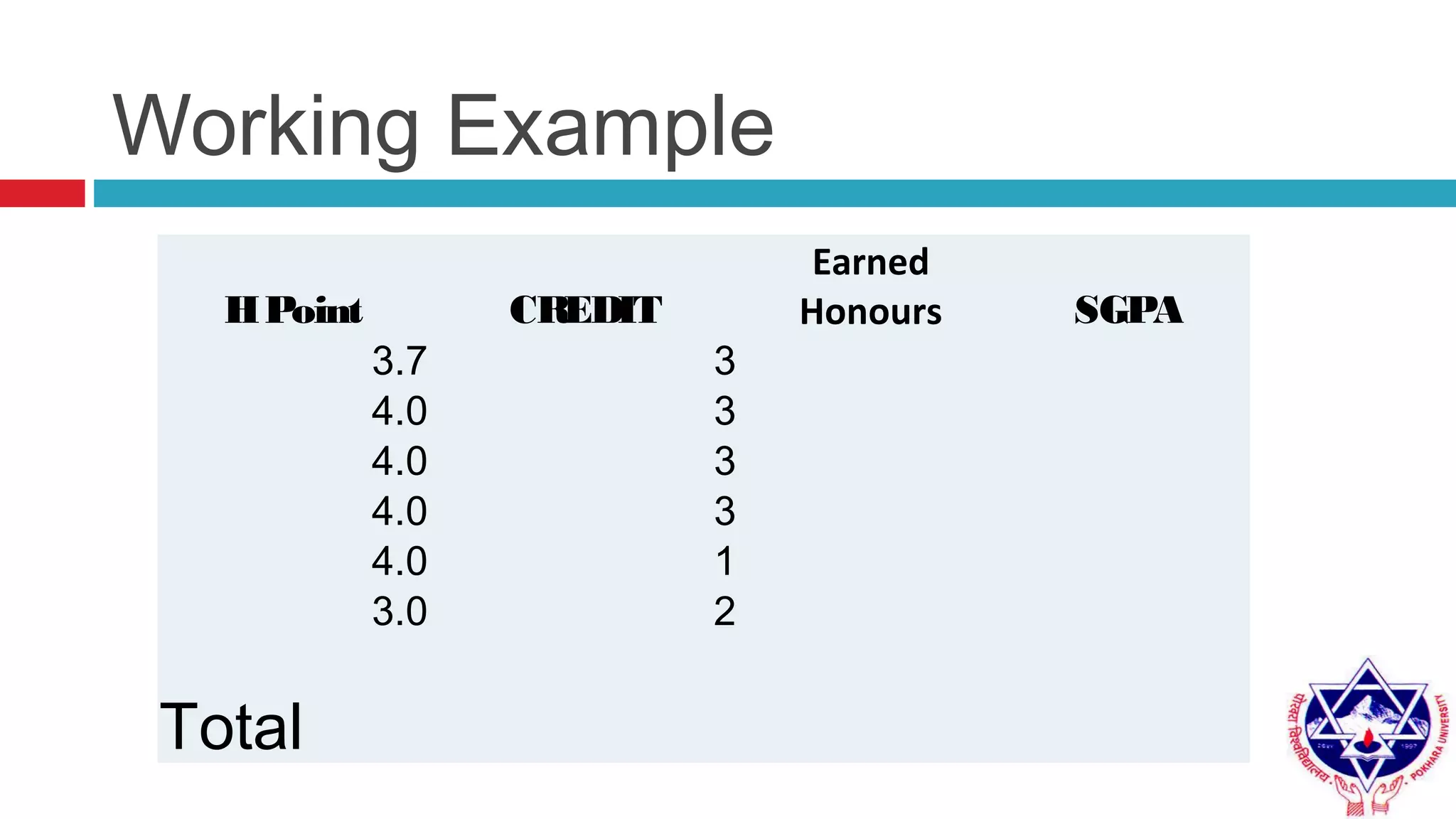
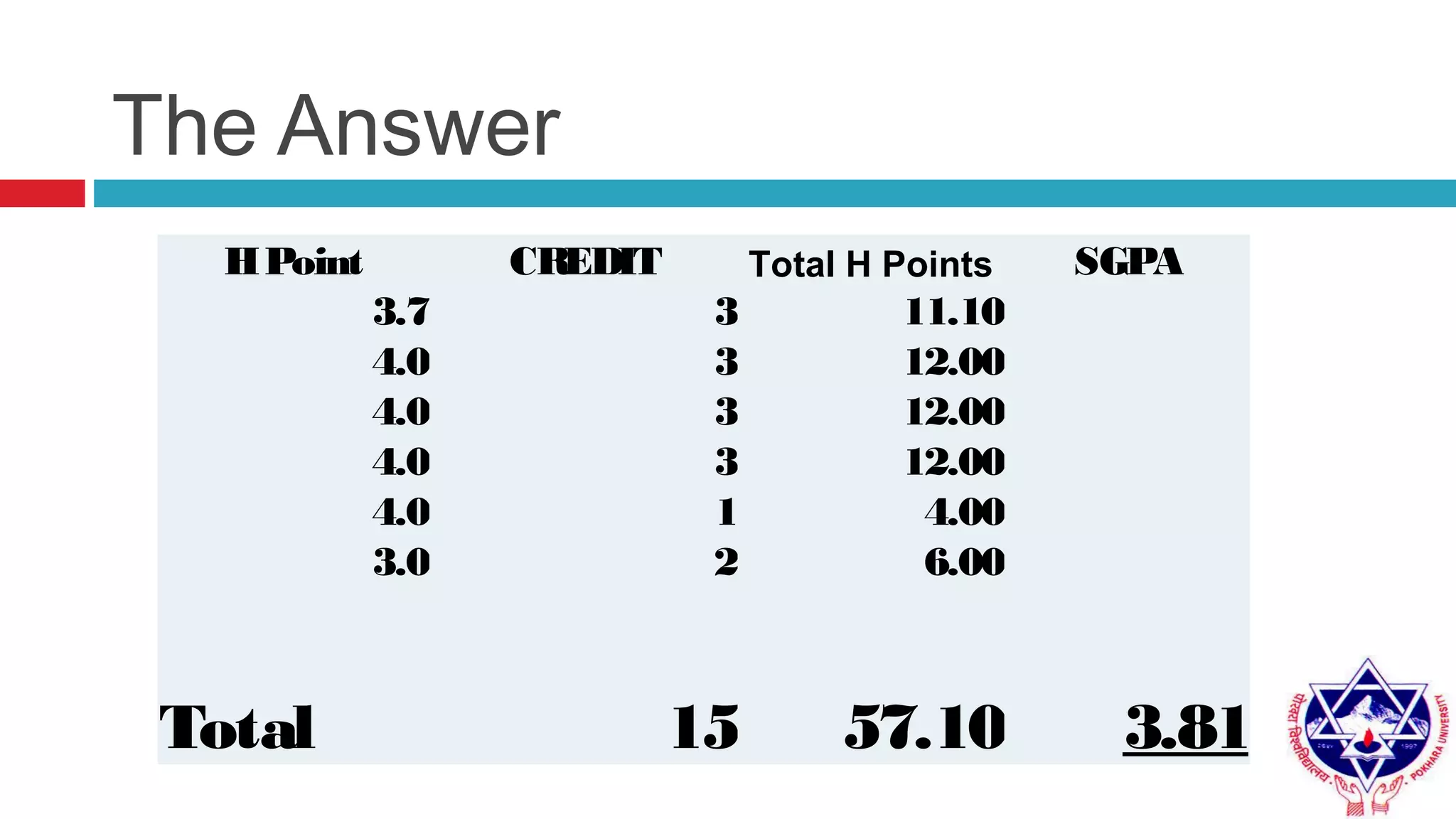
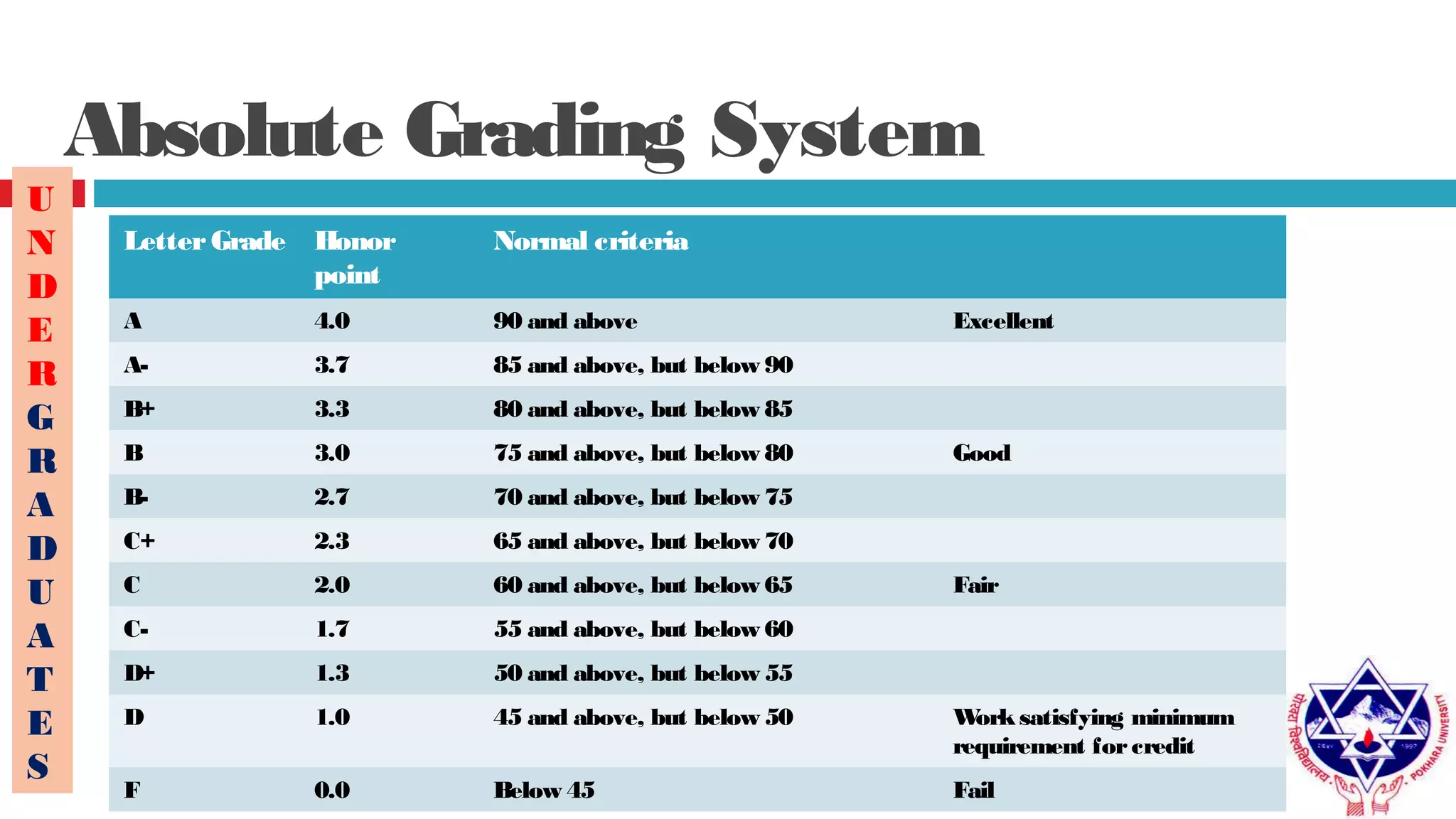
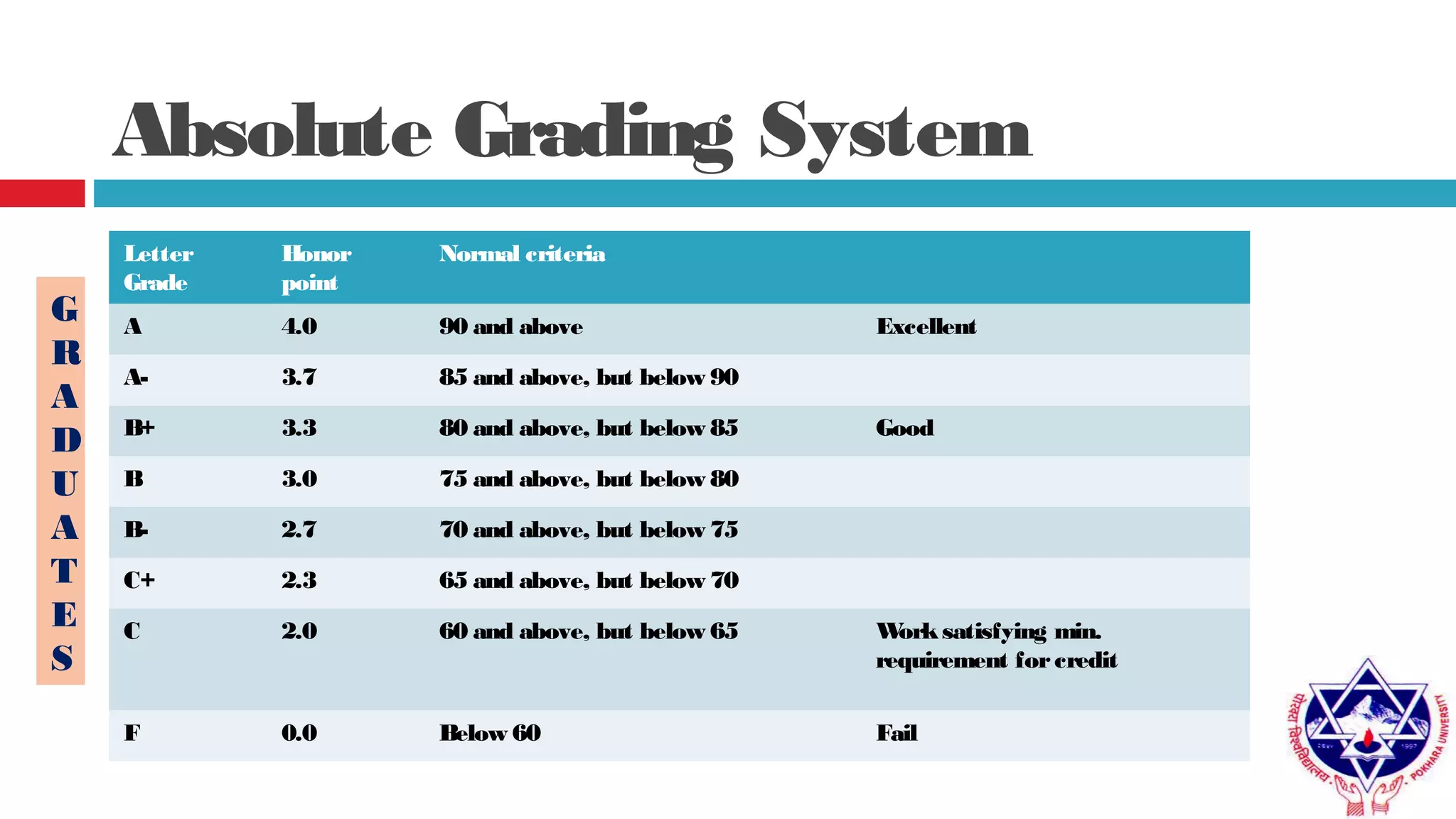
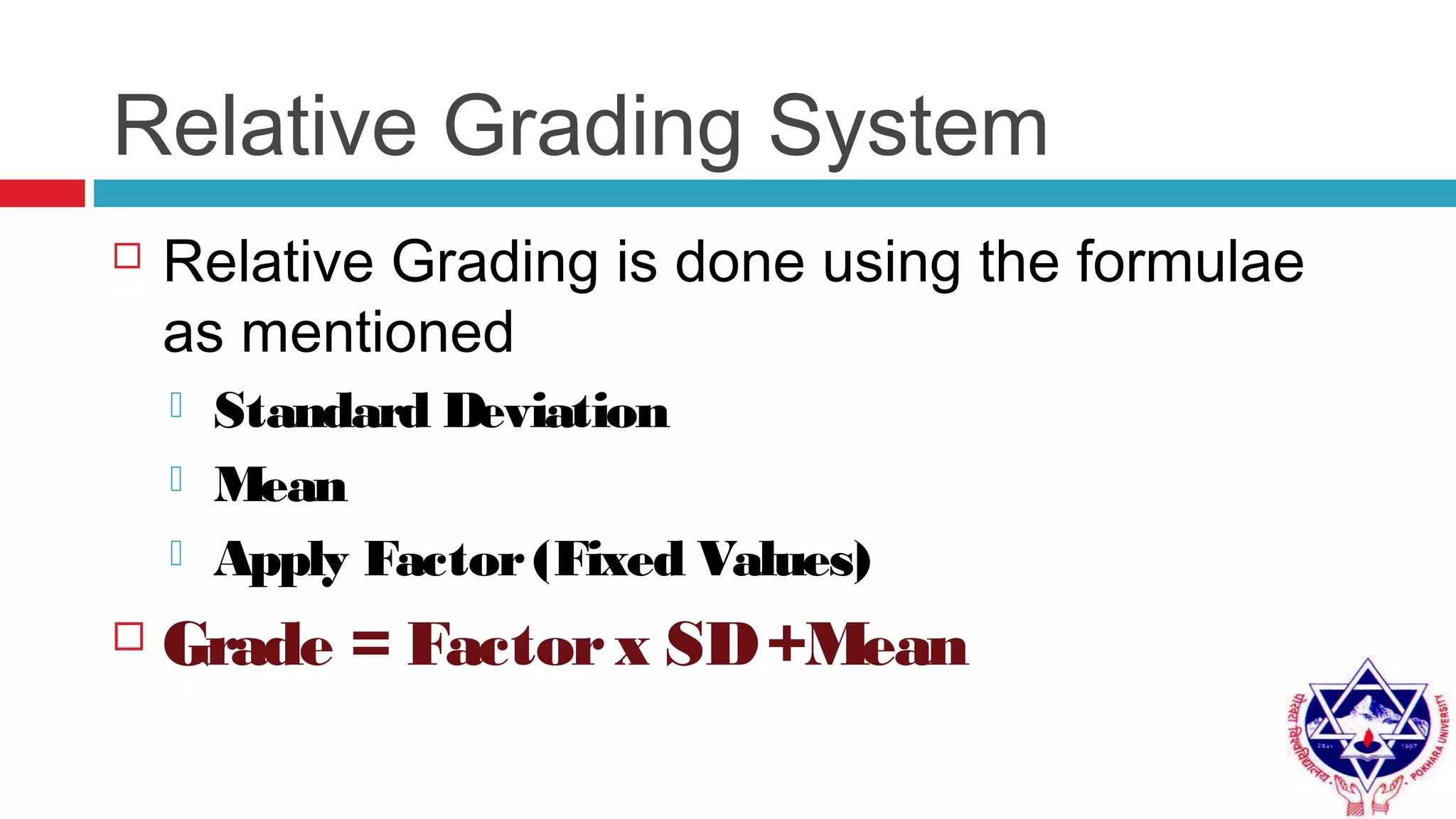
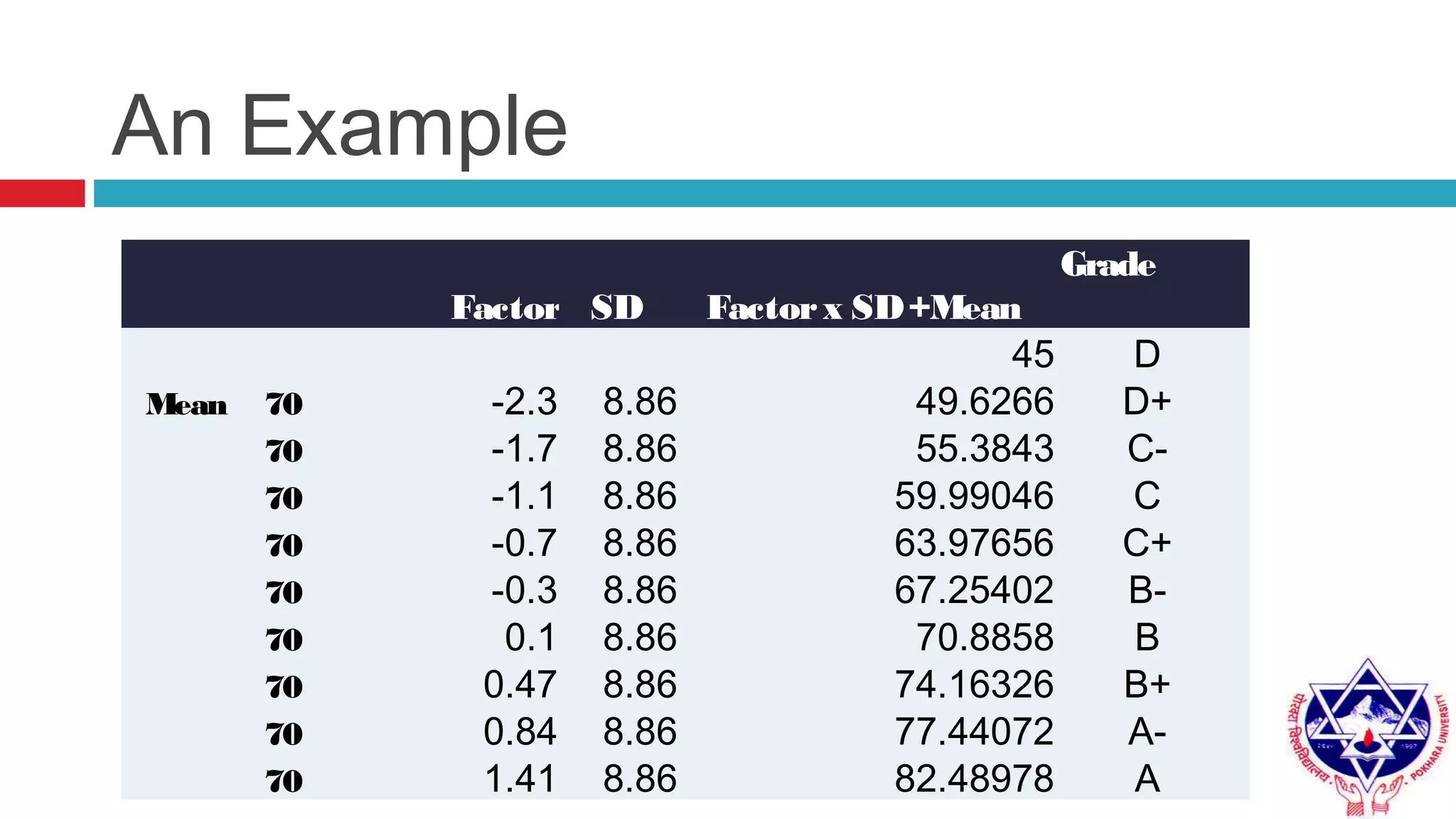
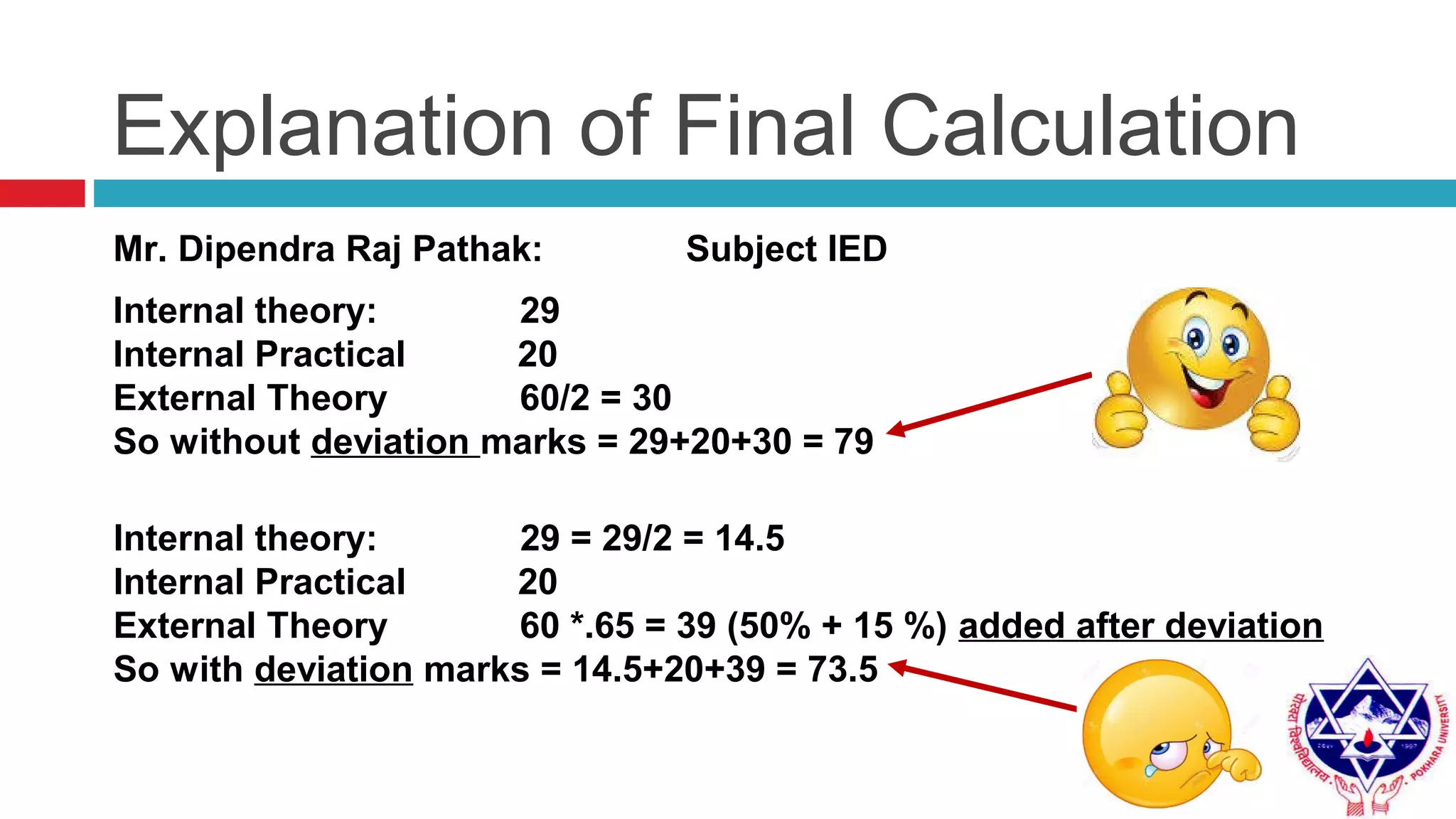
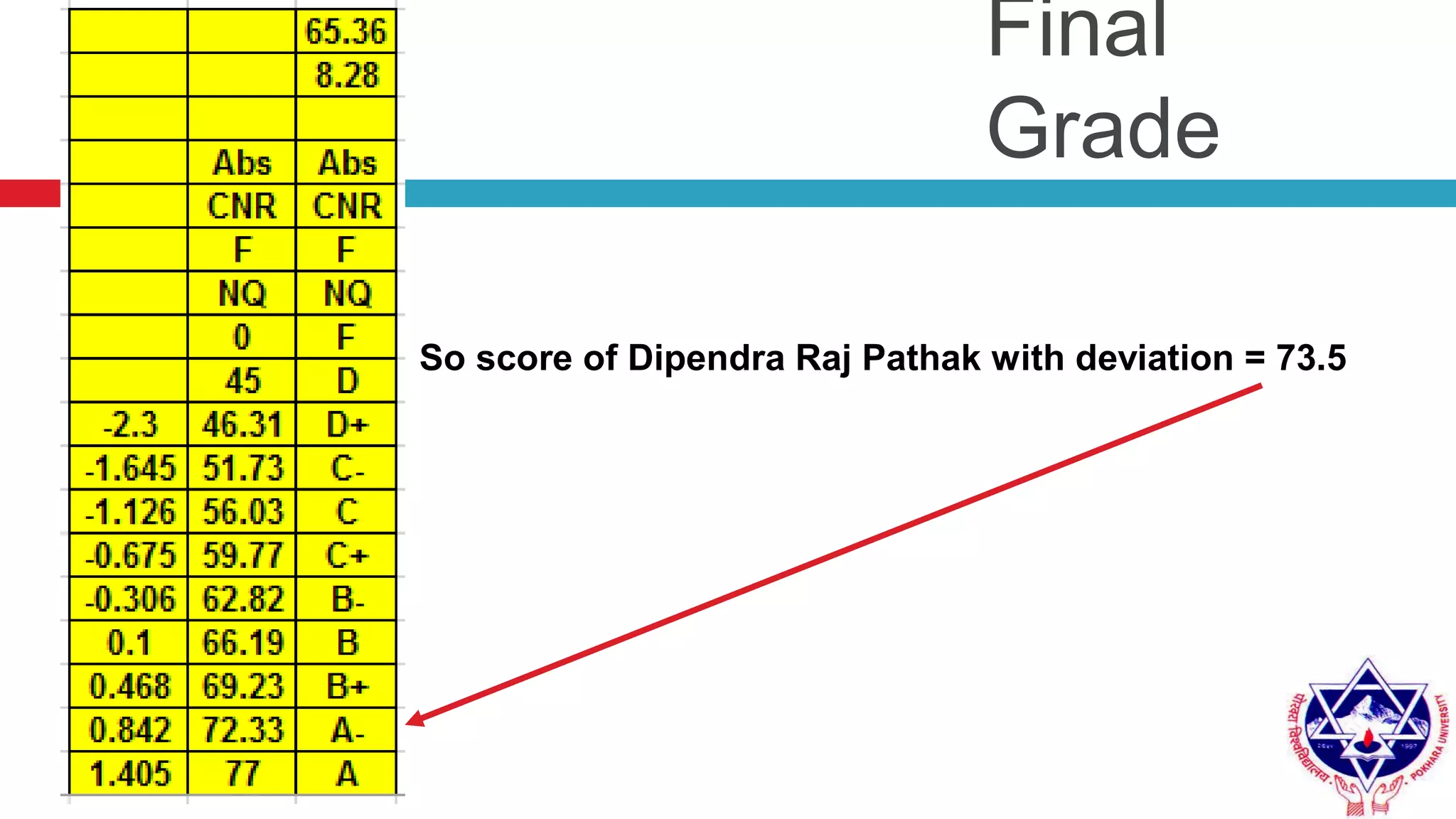
Pokhara University uses three grading systems: relative grading, absolute grading, and percentile grading for nursing programs. The relative grading system calculates grades using standard deviation, mean, and fixed factor values. Absolute grading assigns letter grades from A to F based on percentage scores. Grades are calculated using internal exam, external exam, and sometimes deviation is applied if the difference between internal and external marks is more than 25 for undergraduates or 30 for graduates. Final grades are determined using semester grade point average and cumulative grade point average.