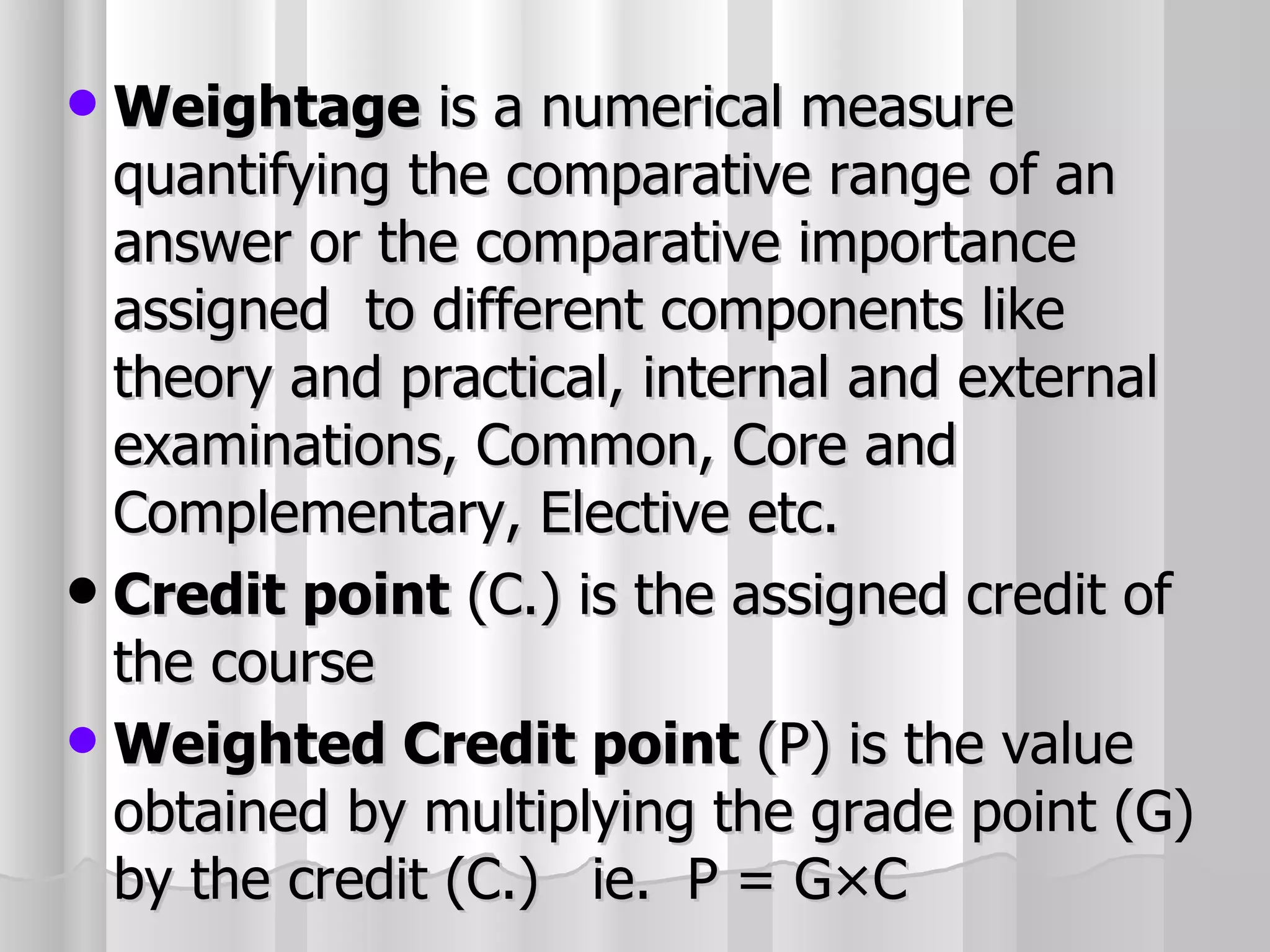
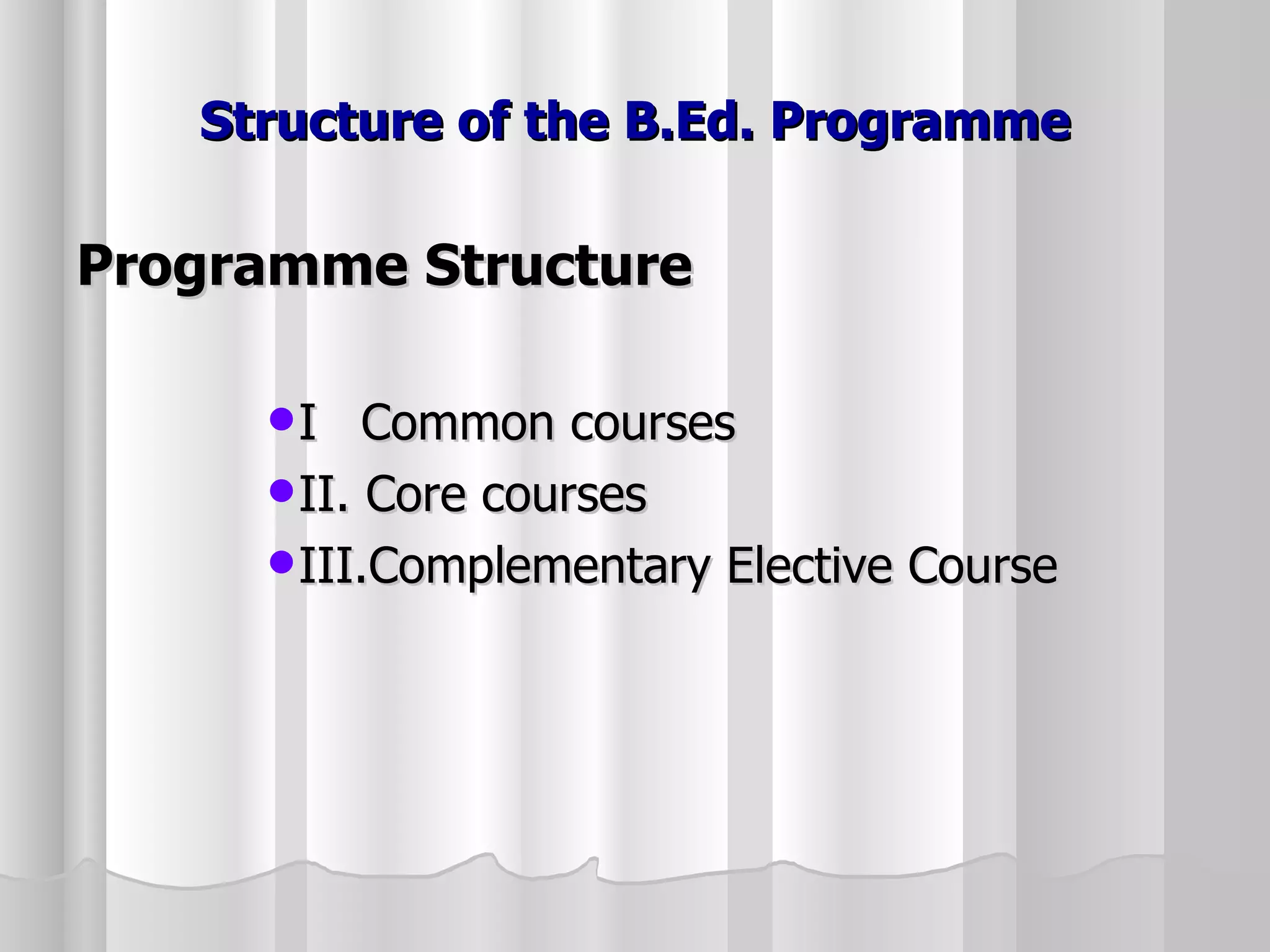
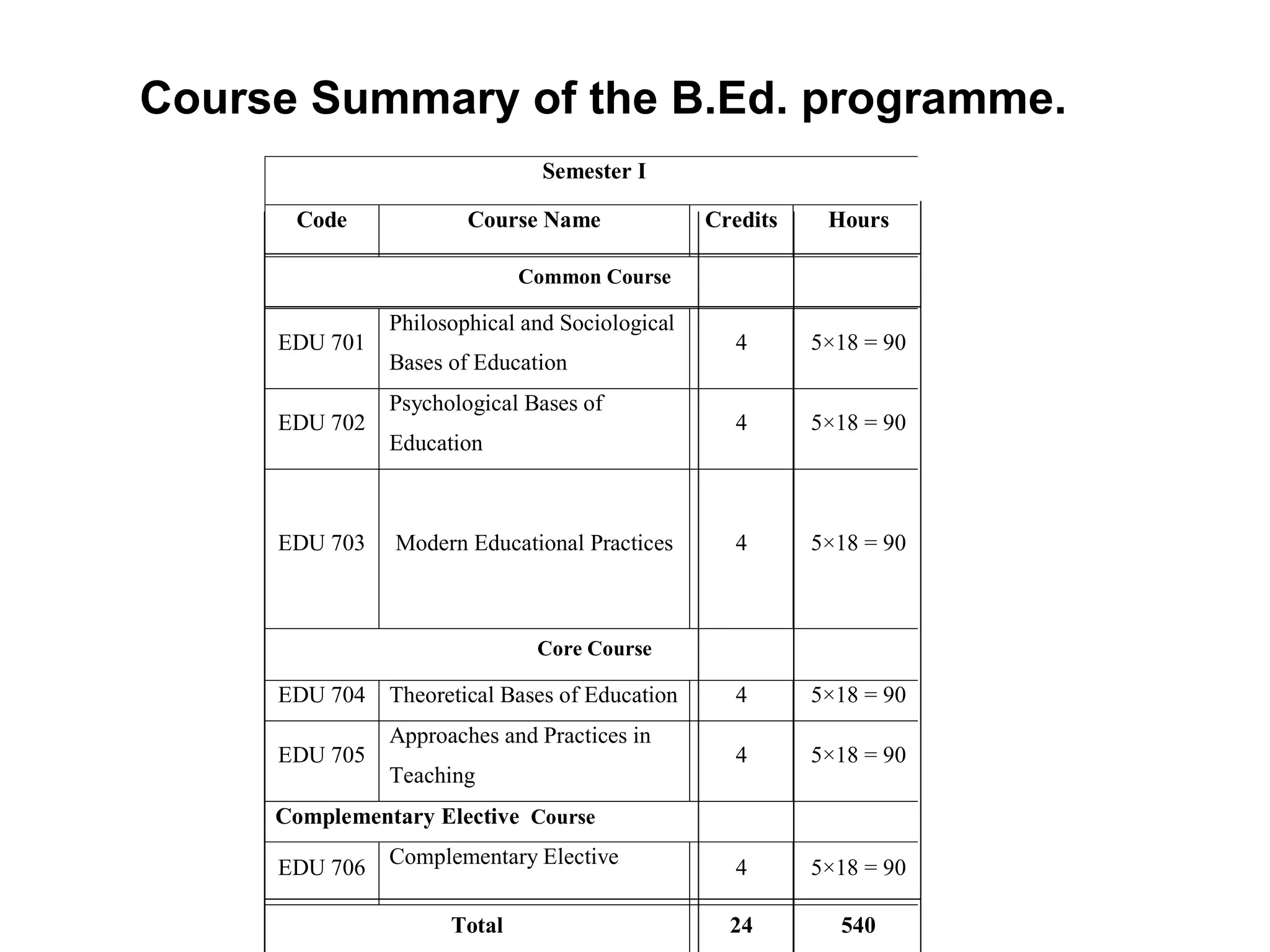
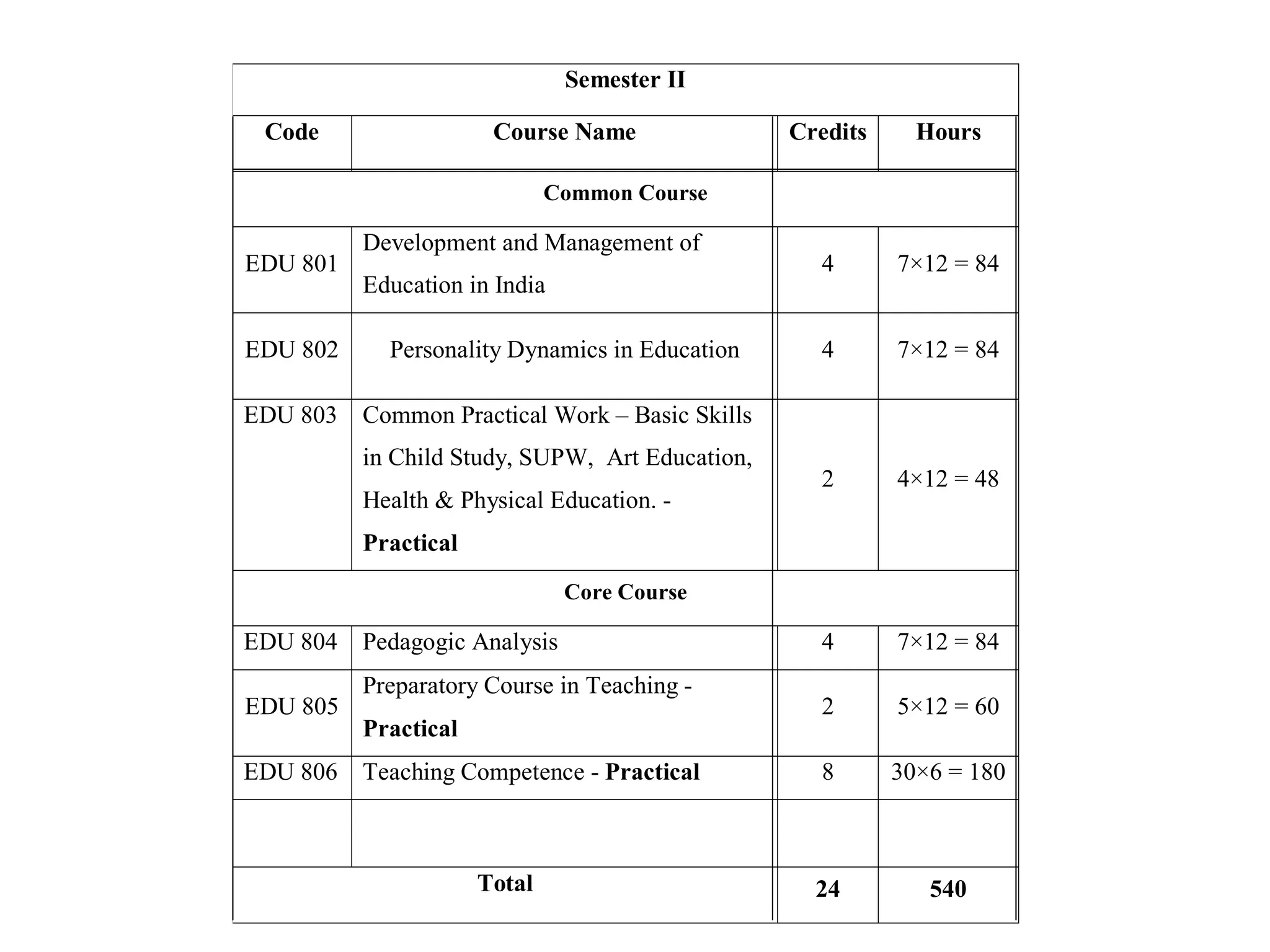
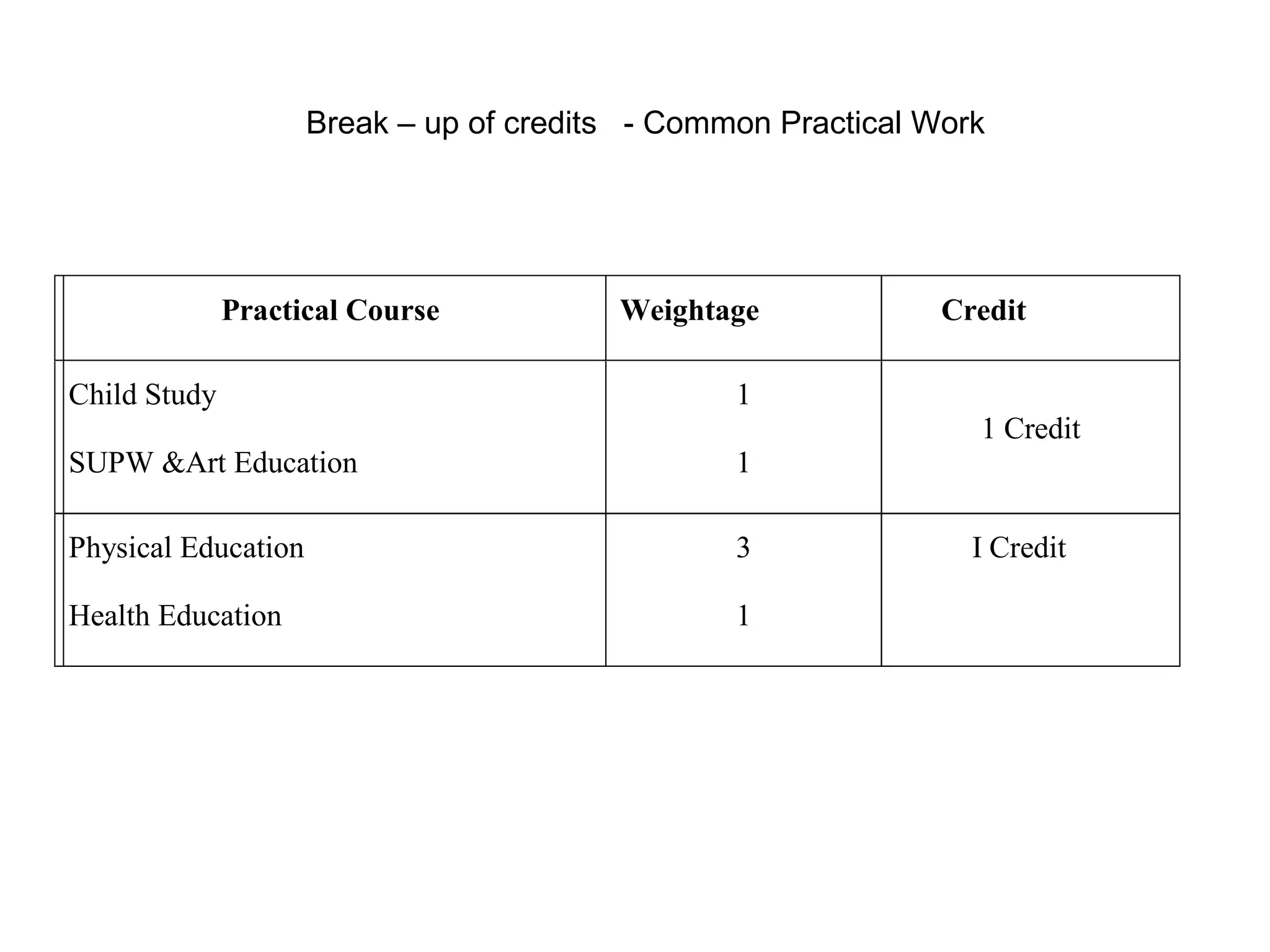
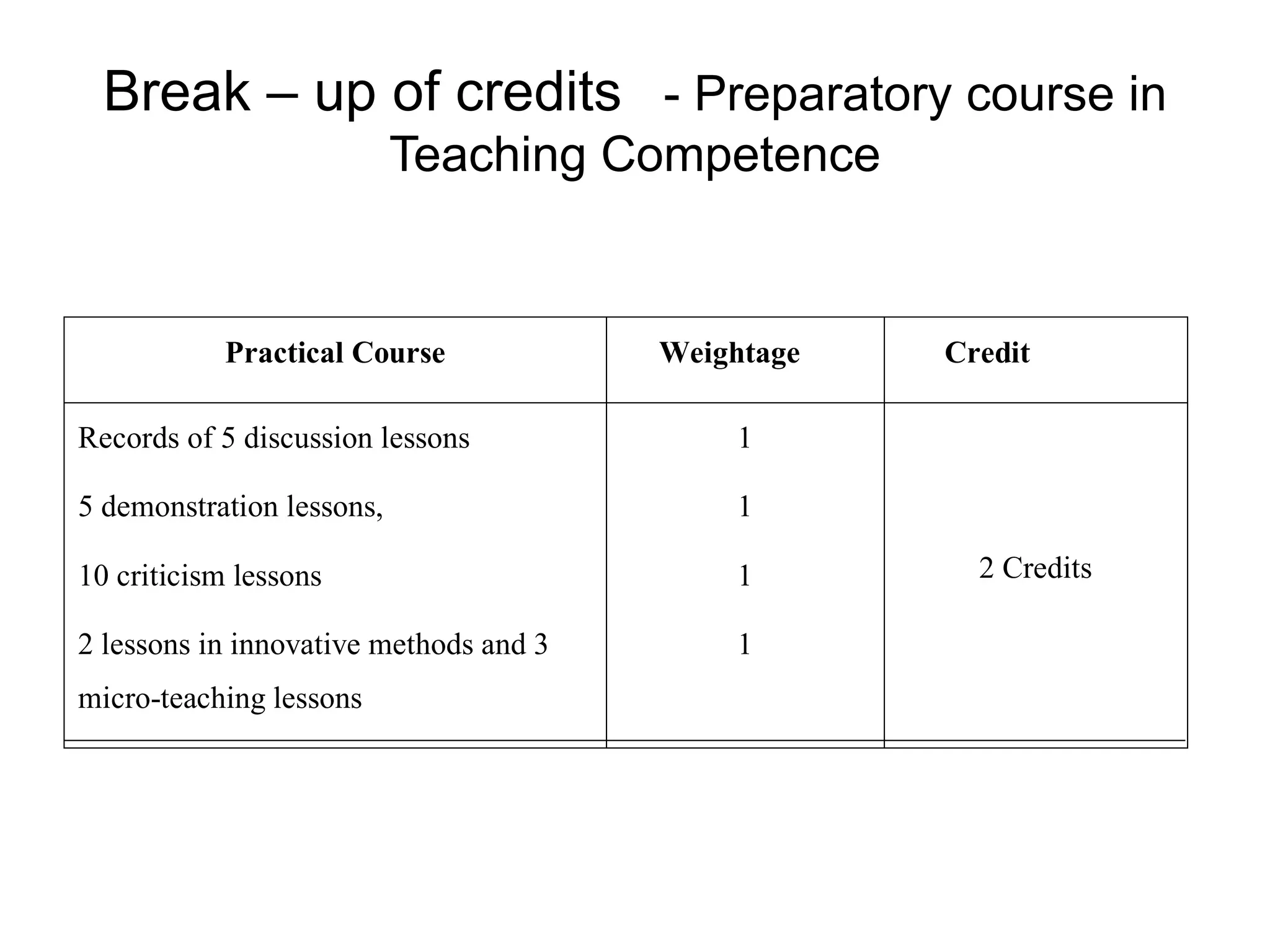
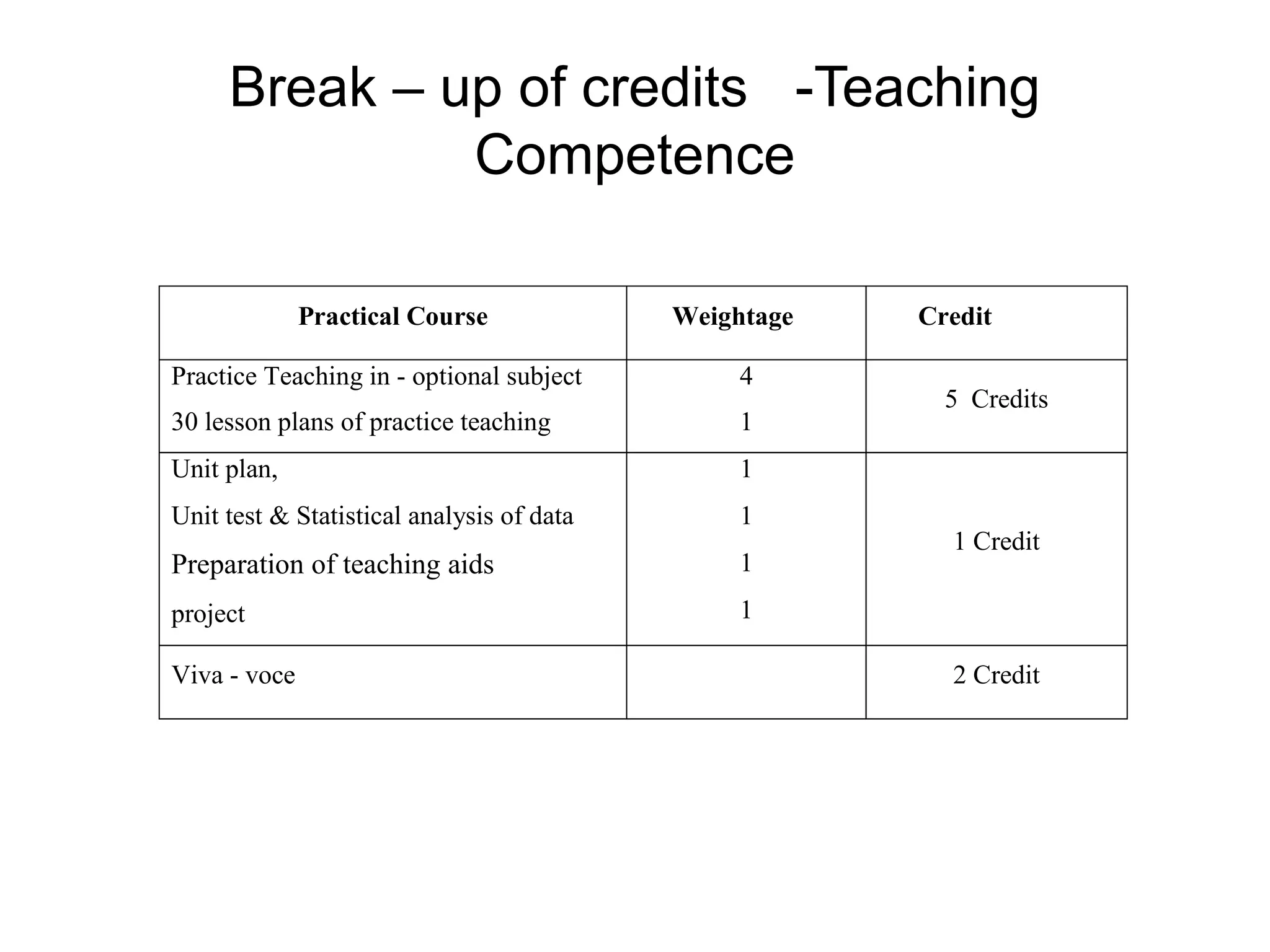
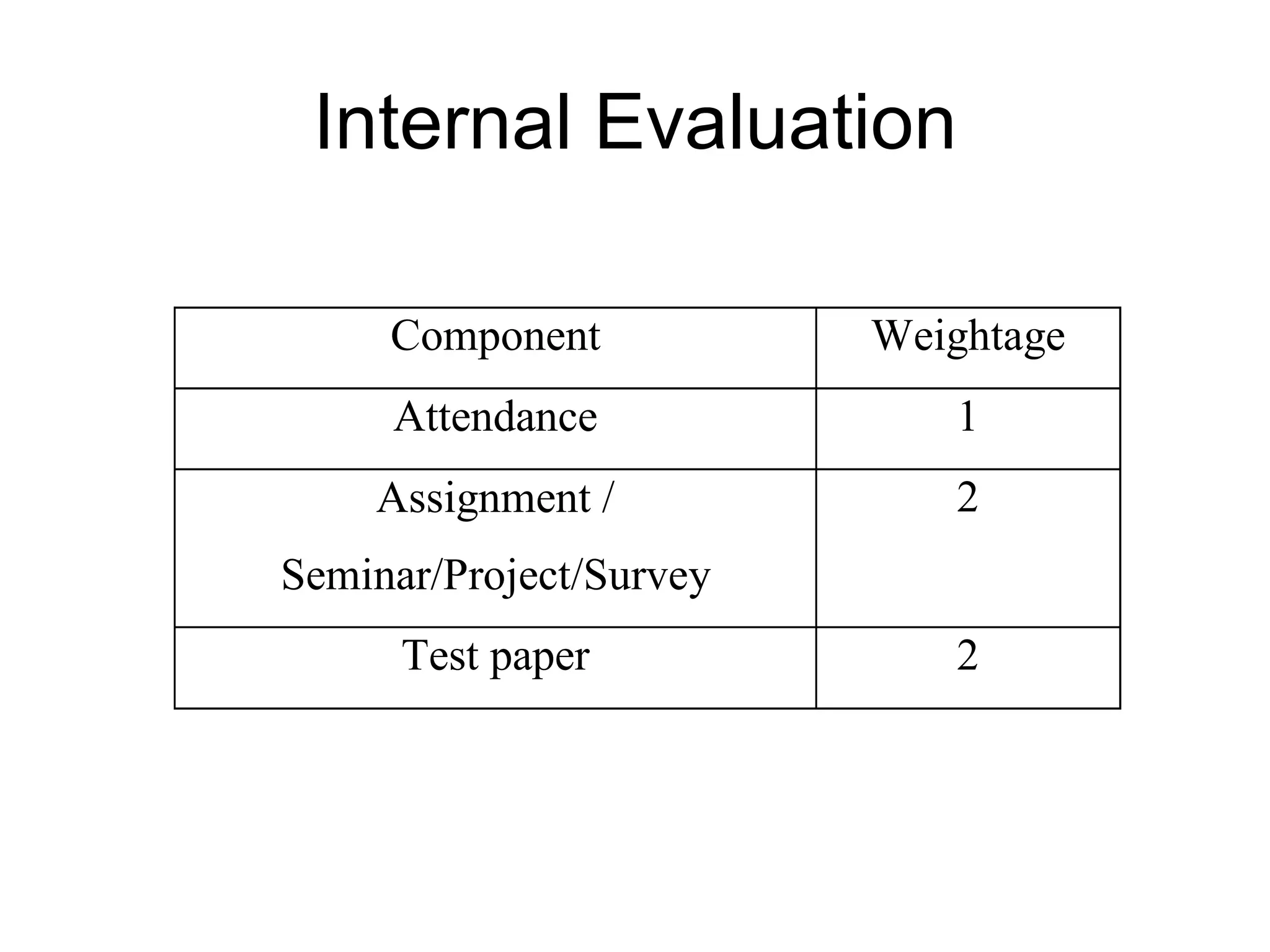
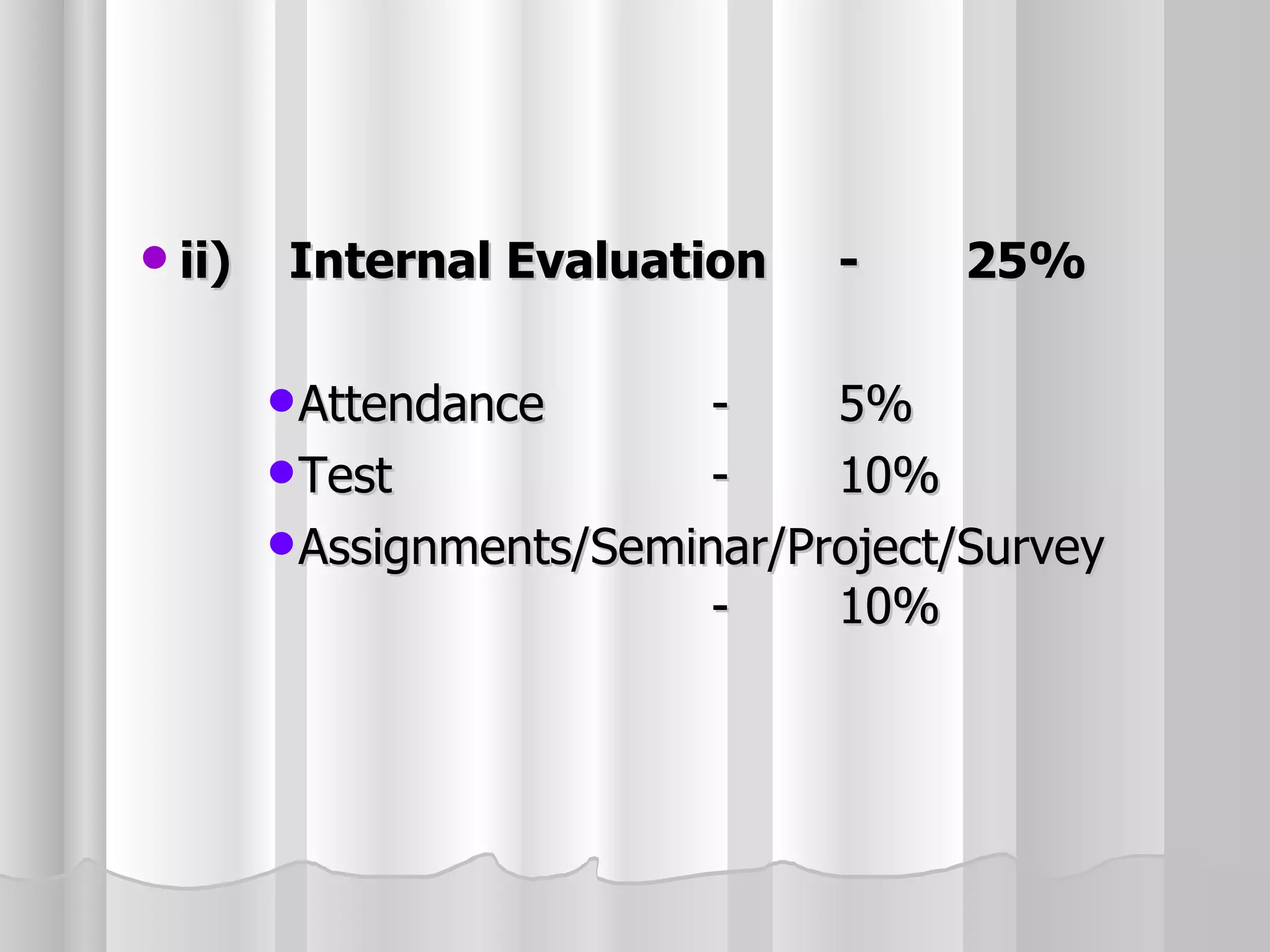
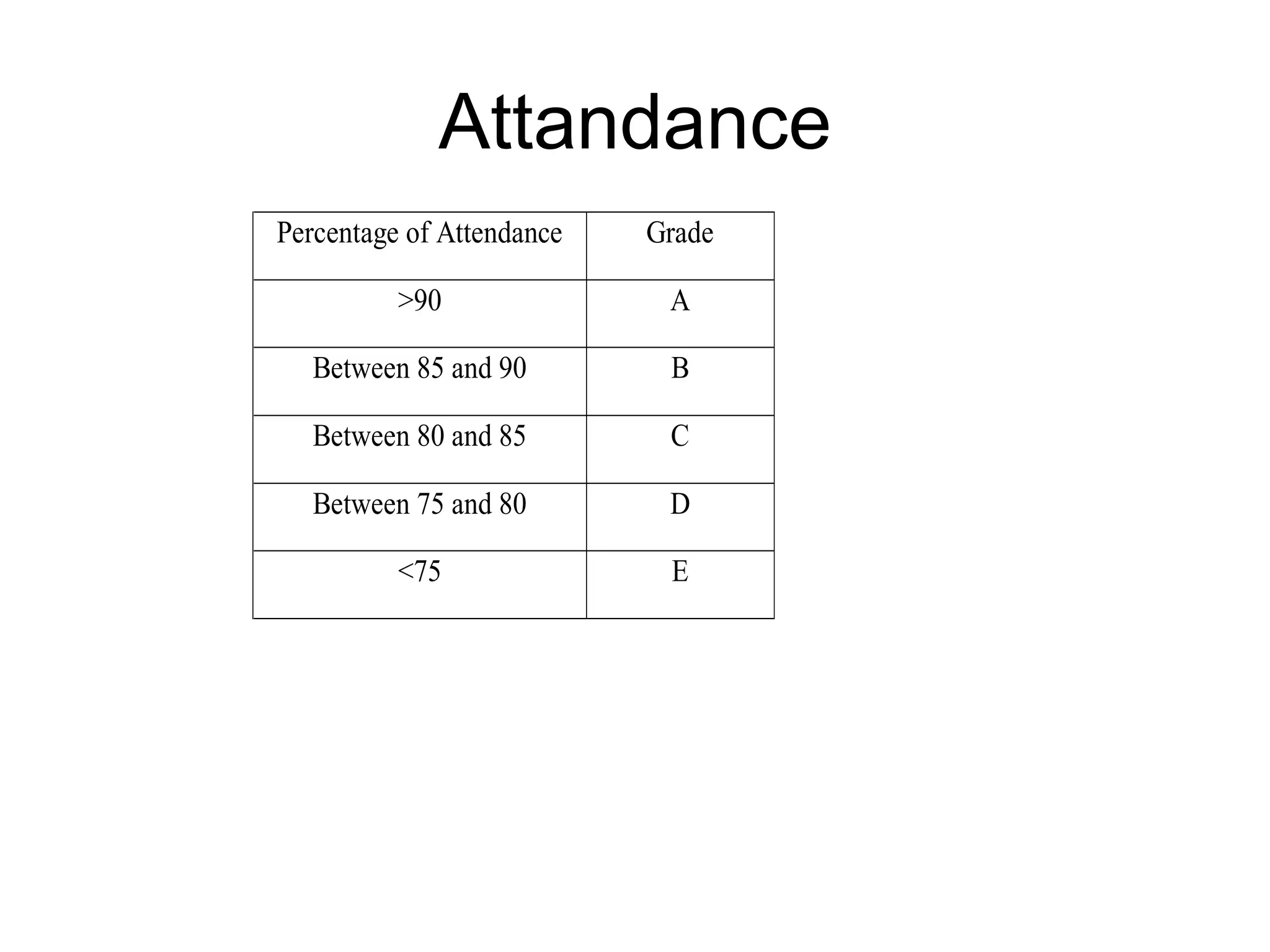
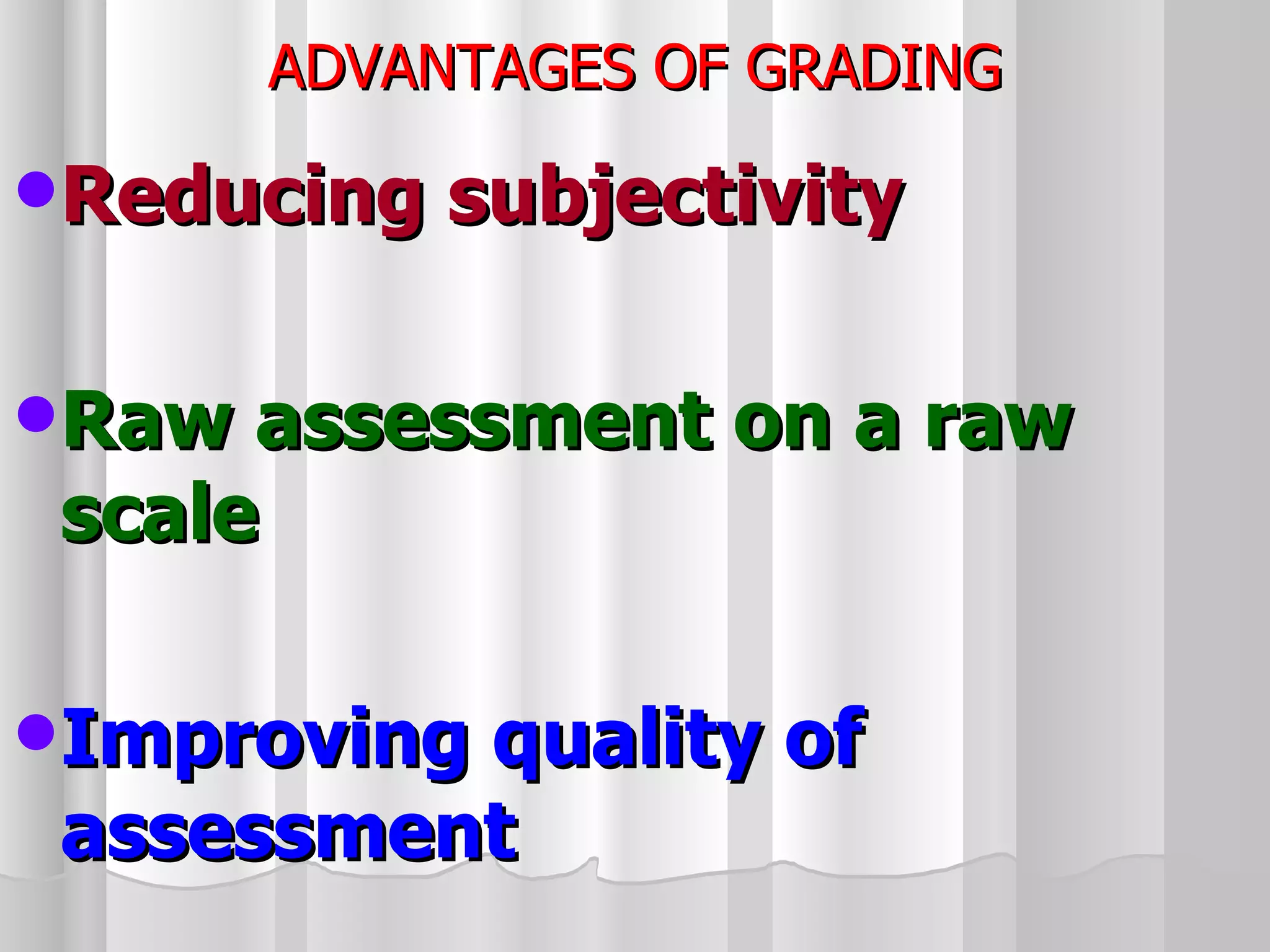
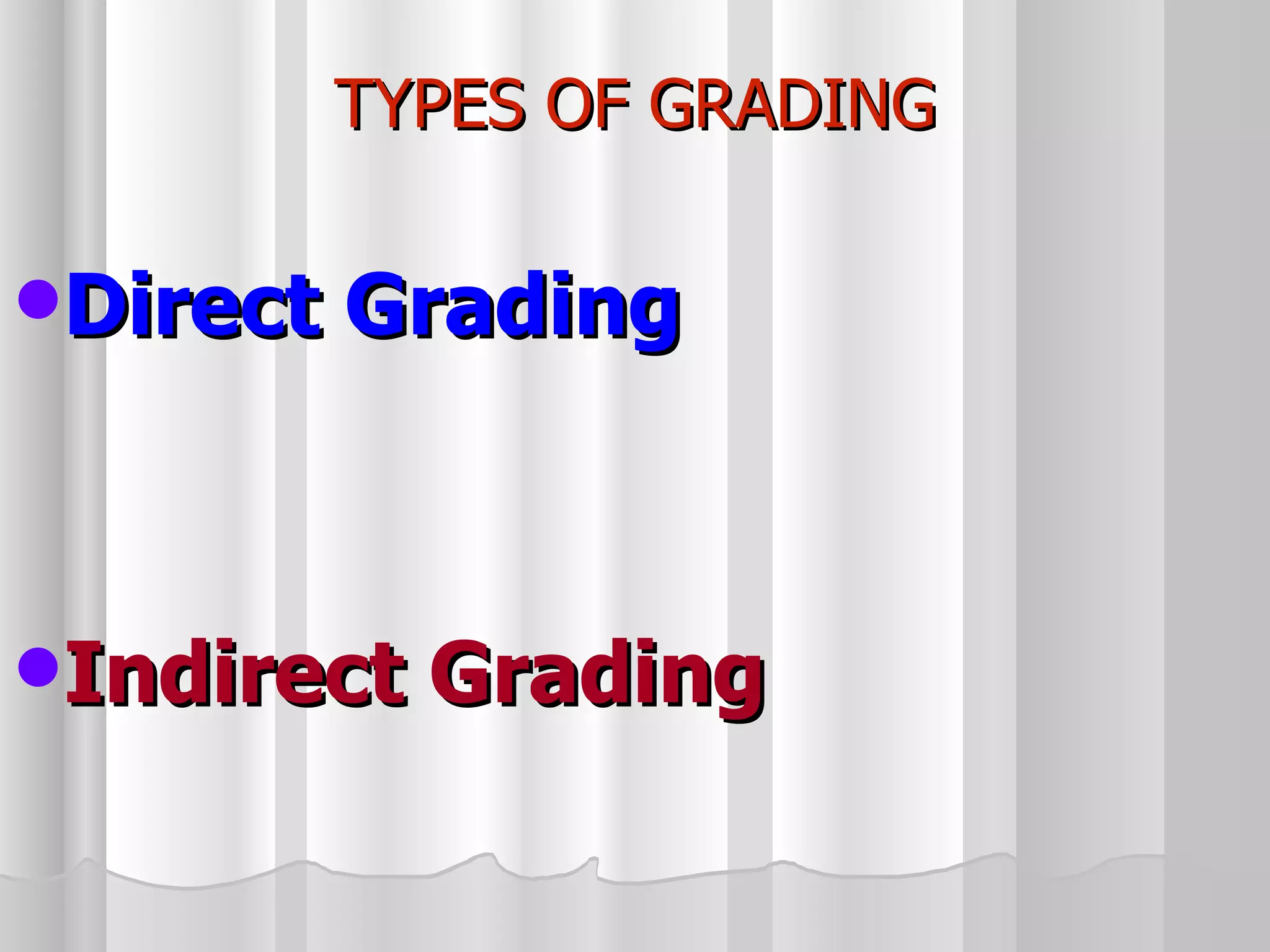
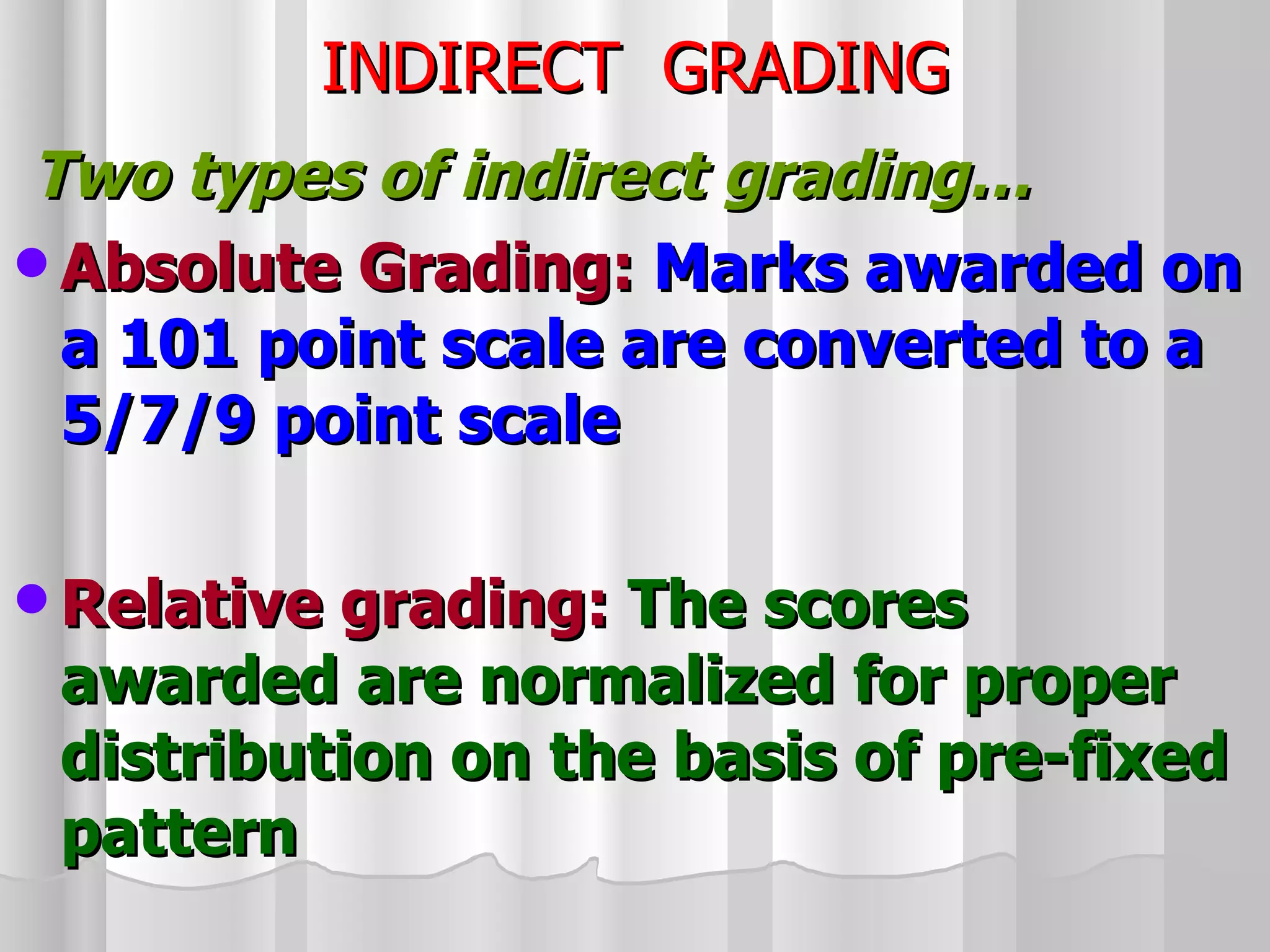
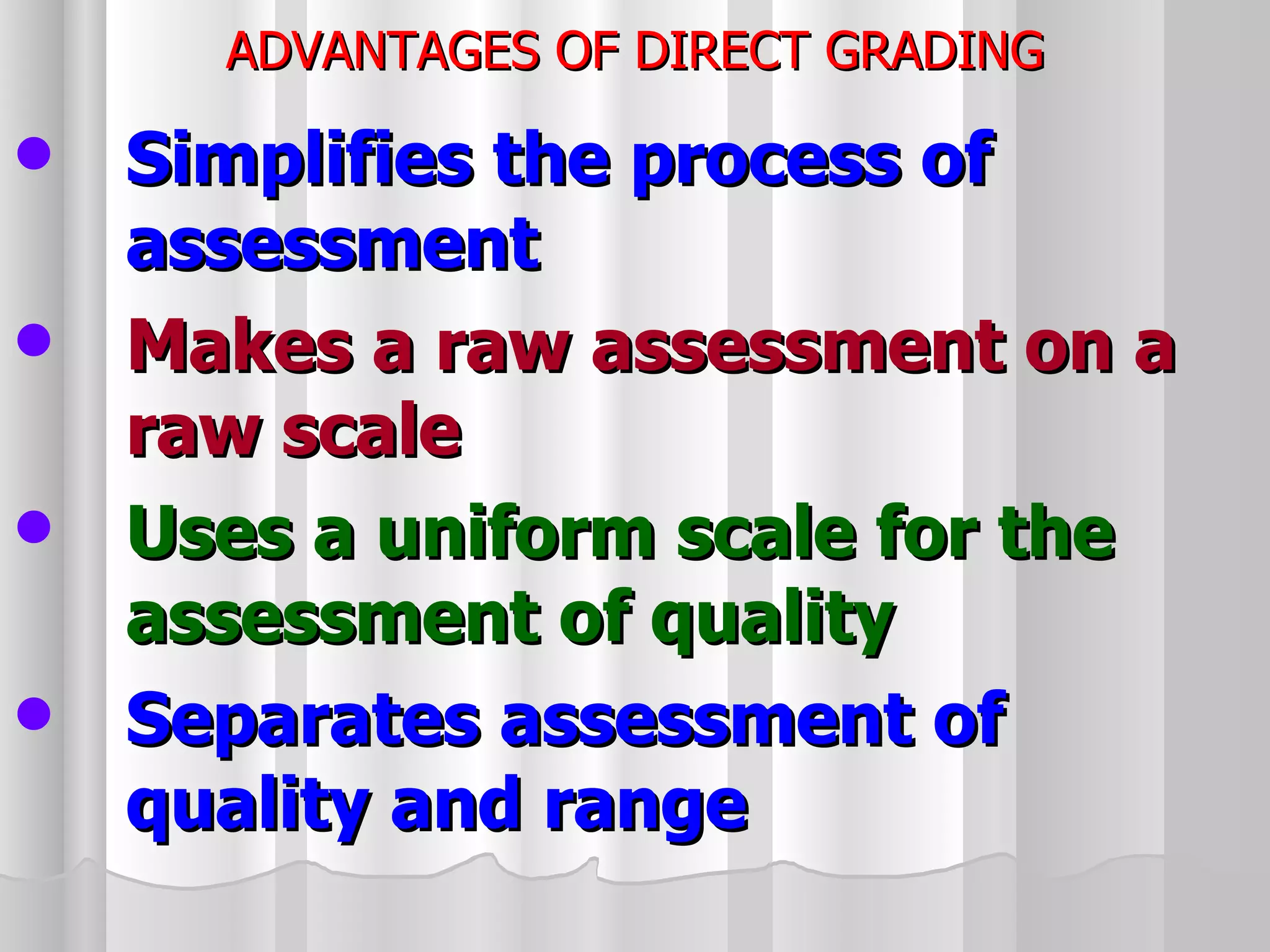
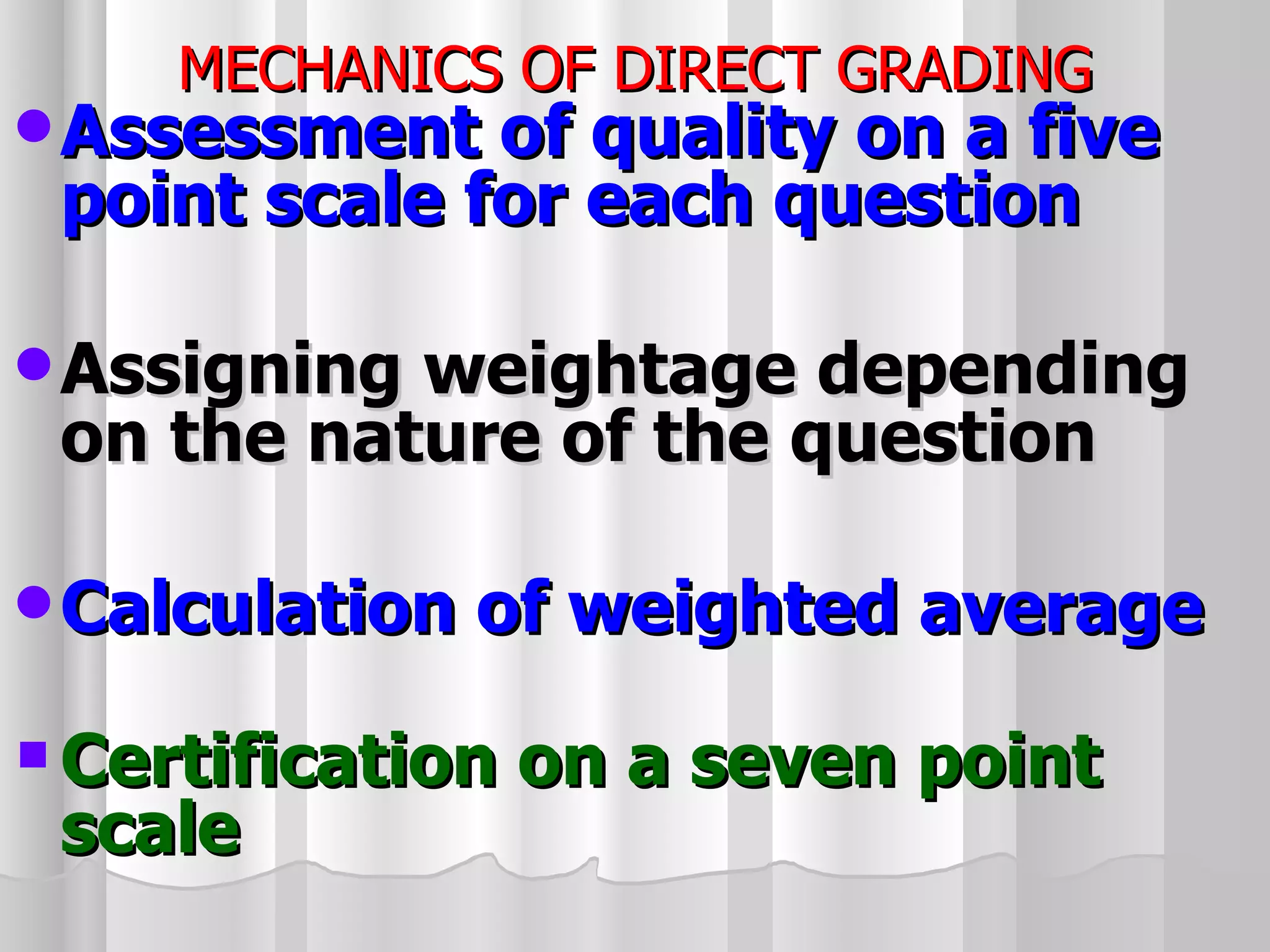
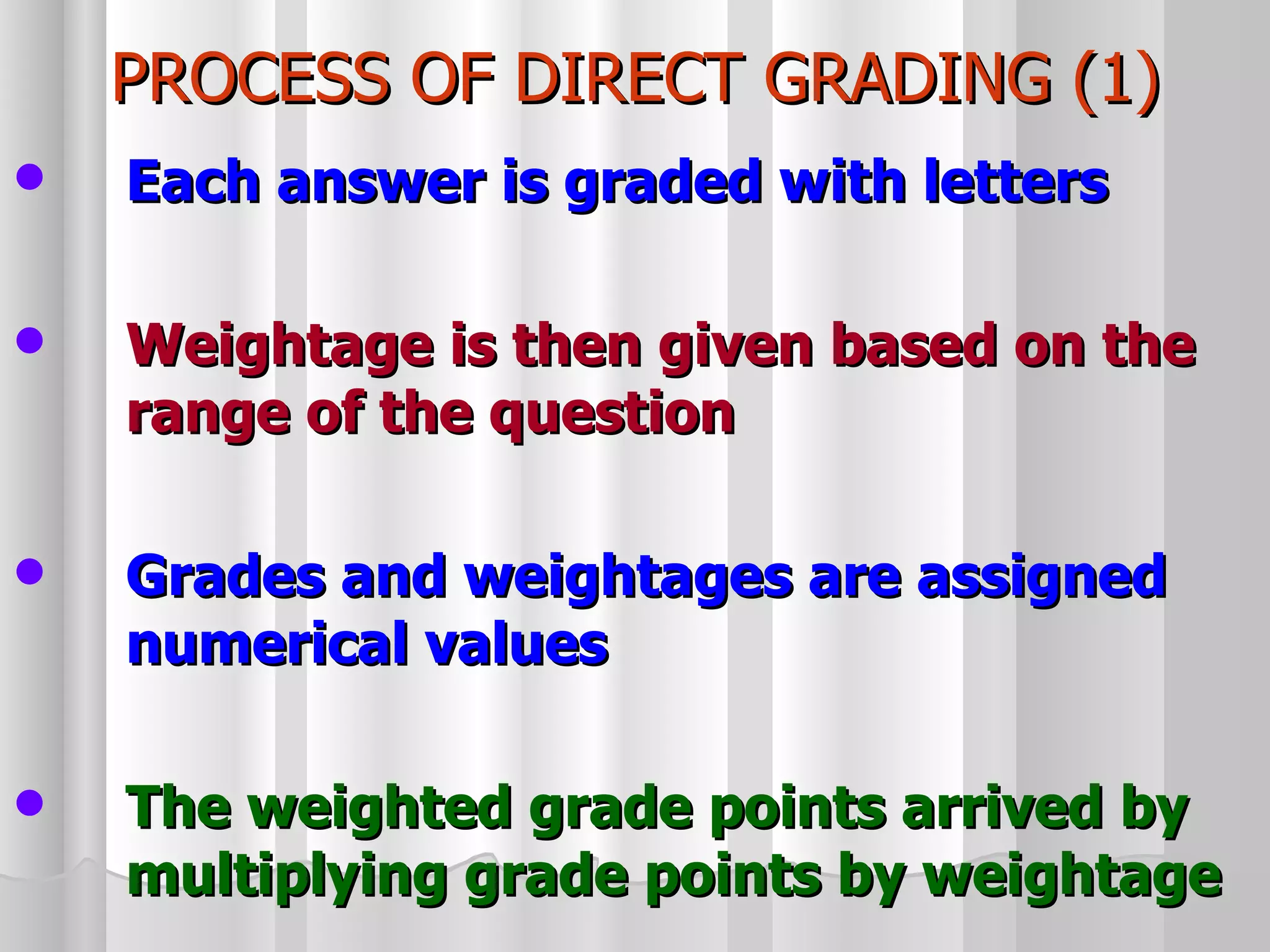
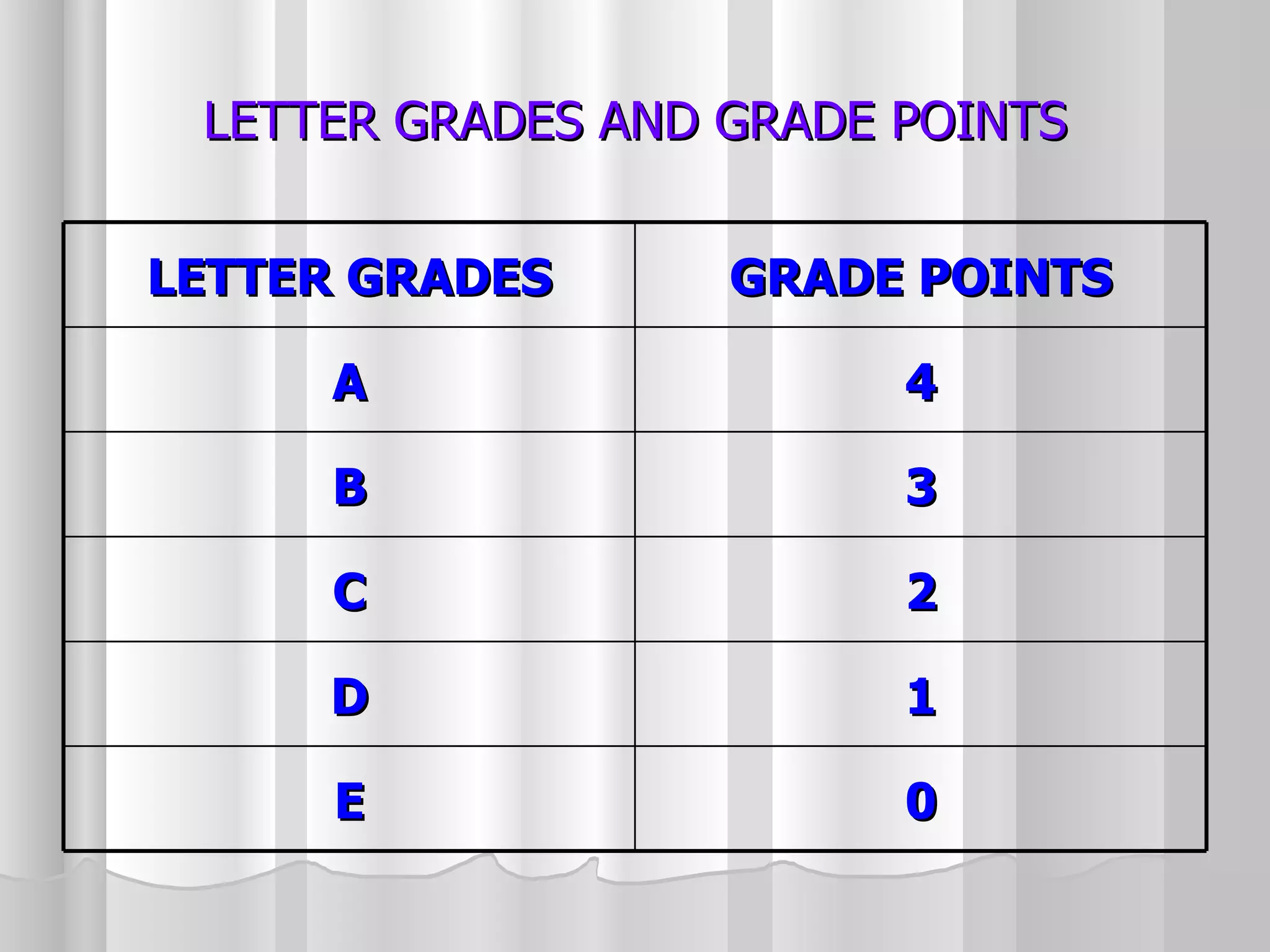
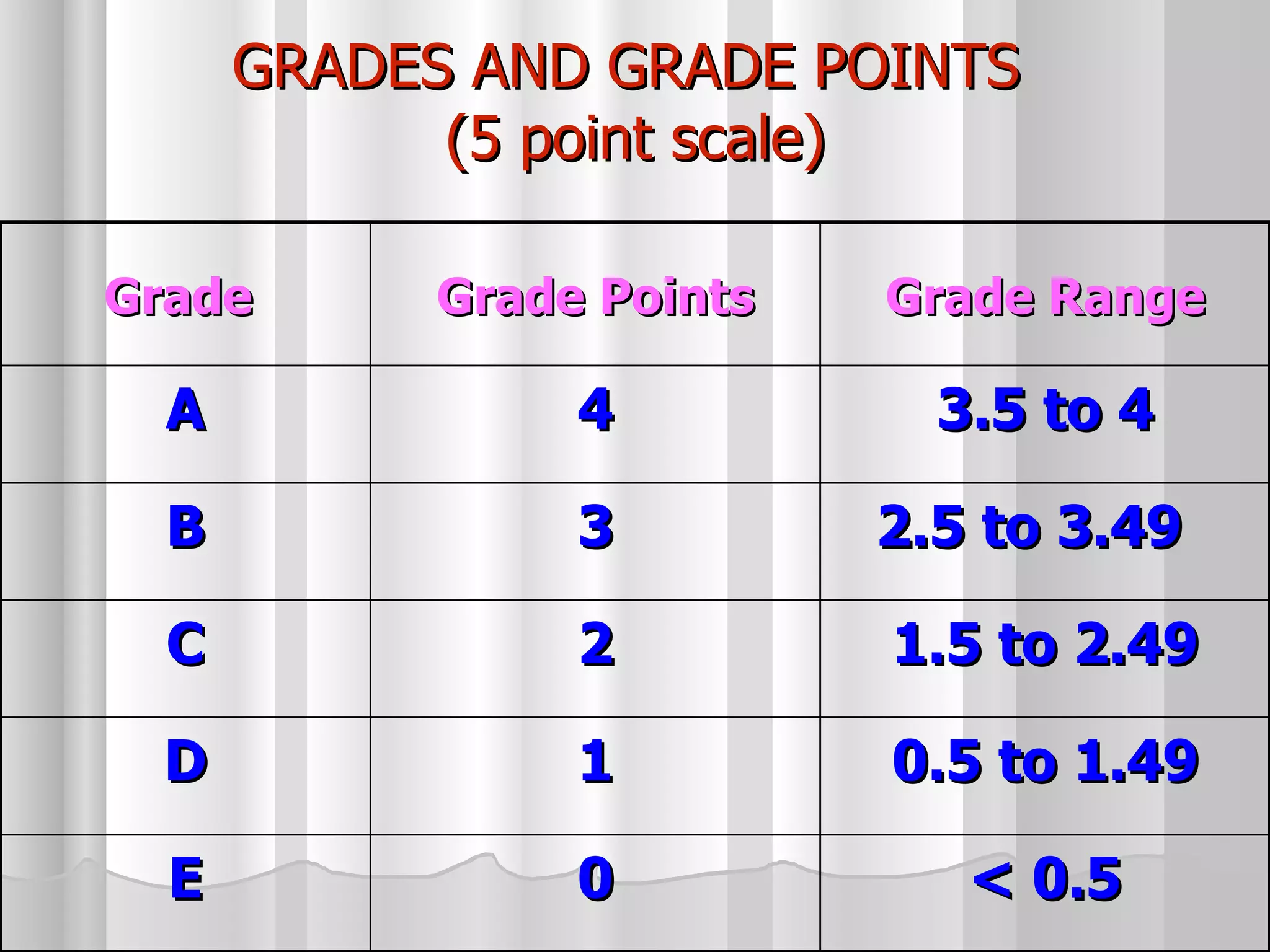
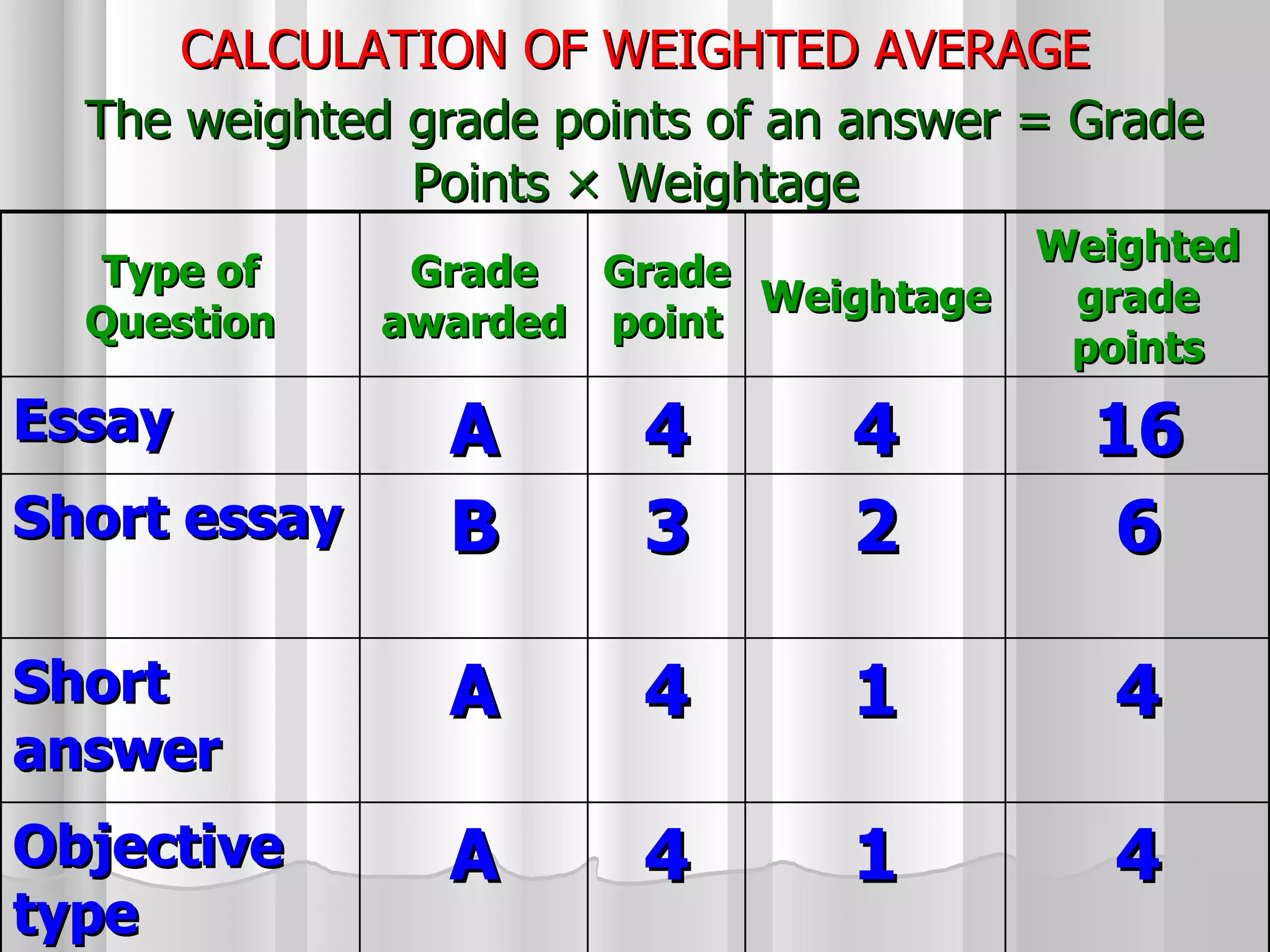
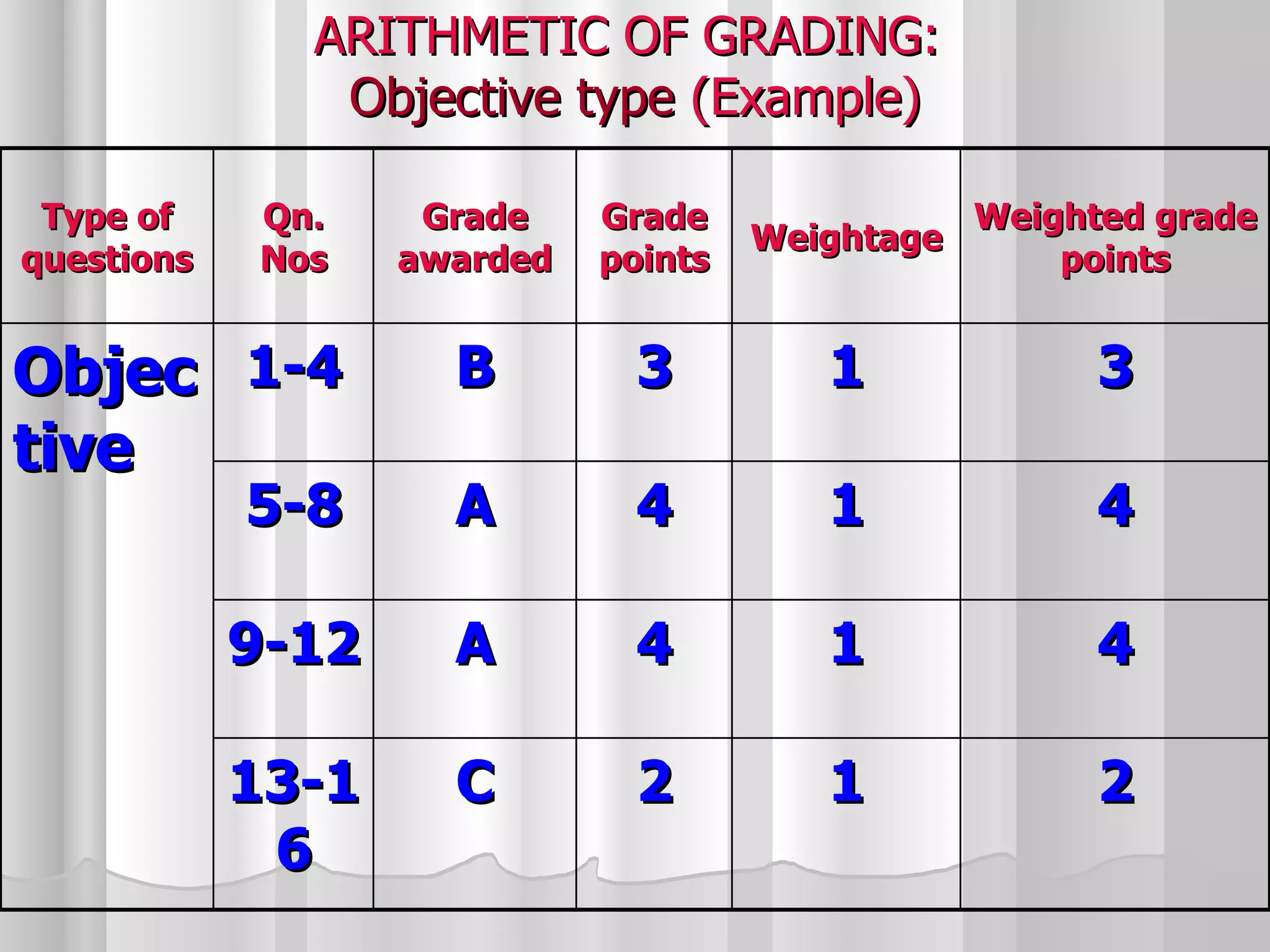
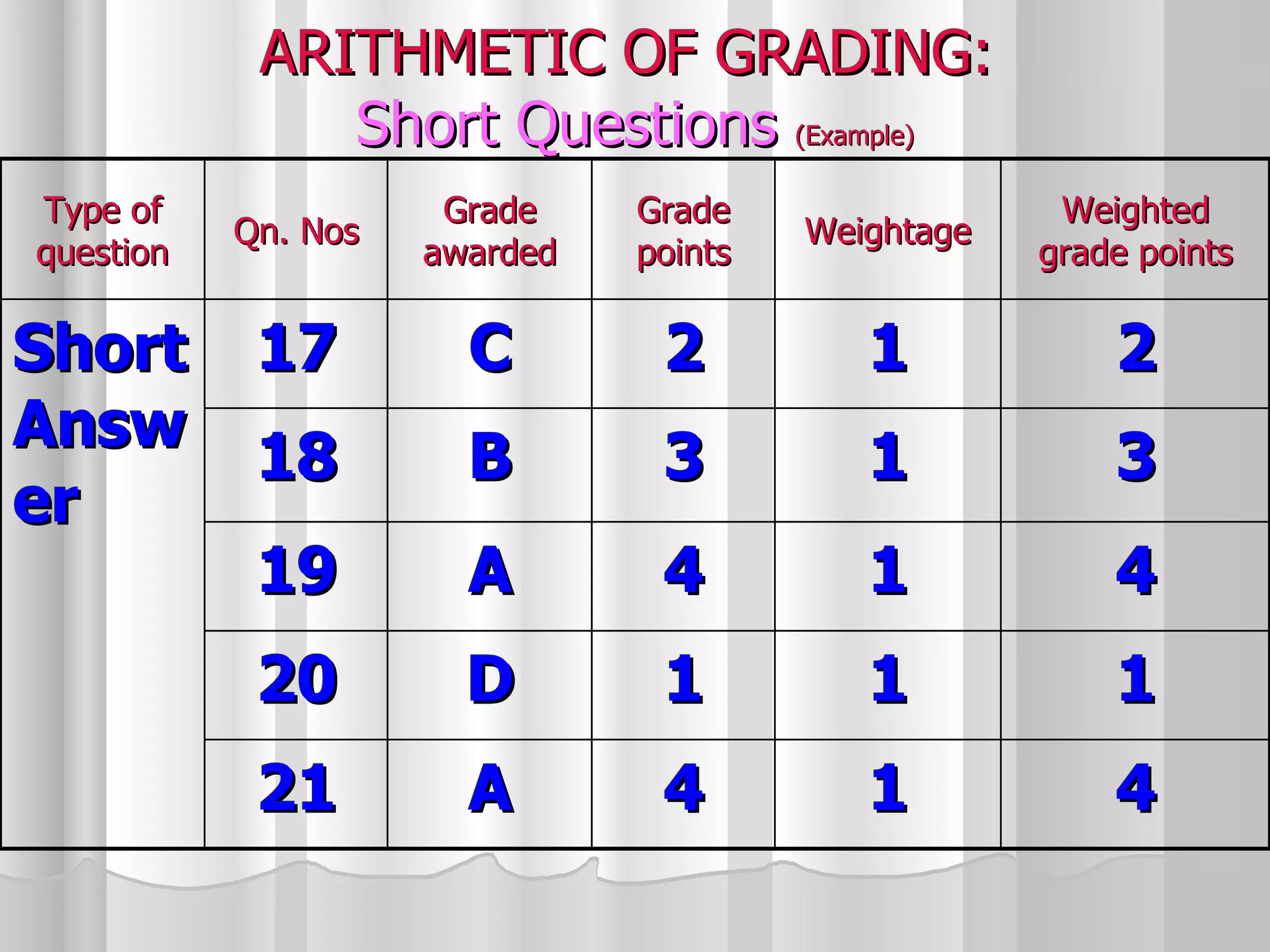
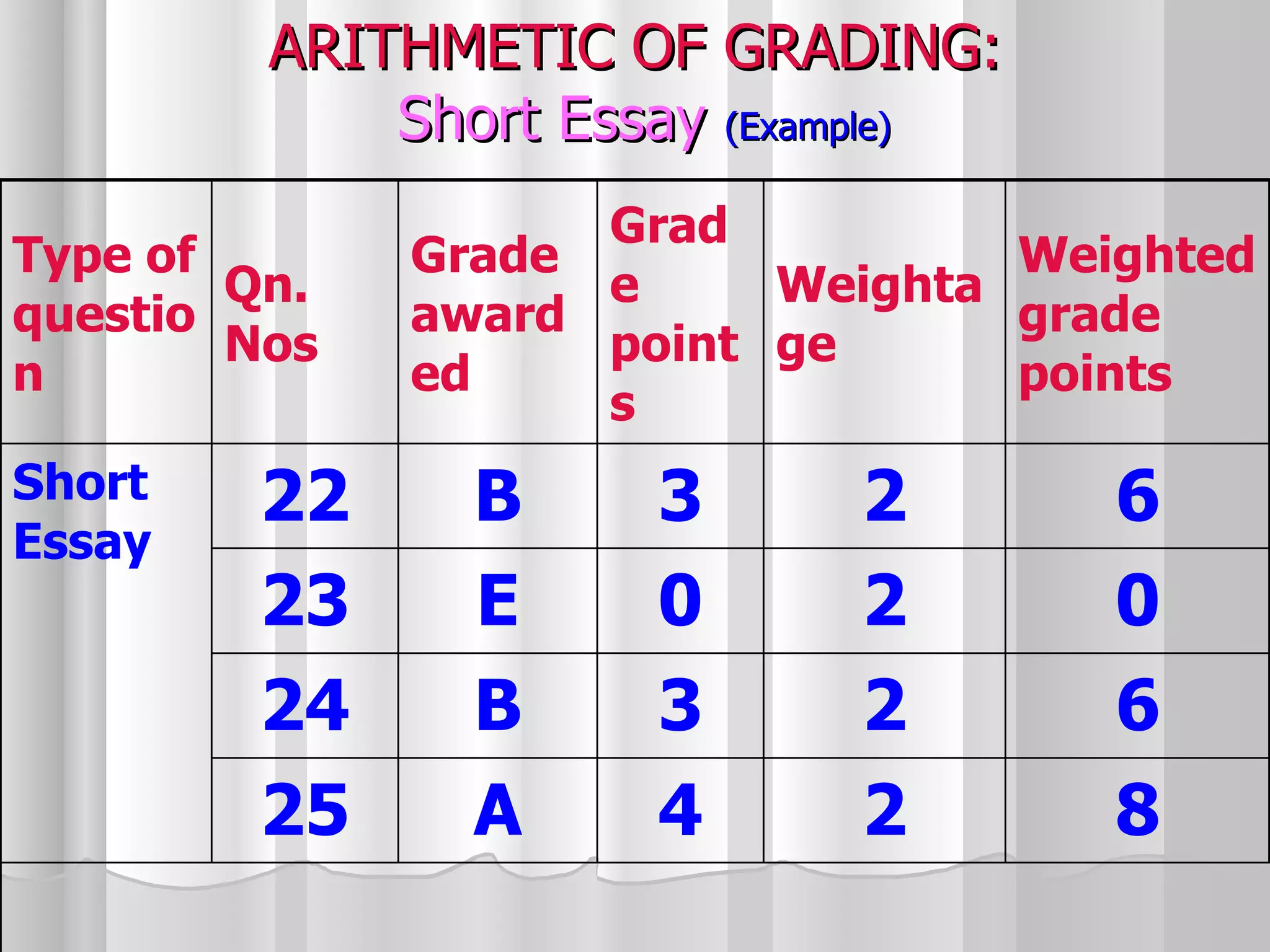
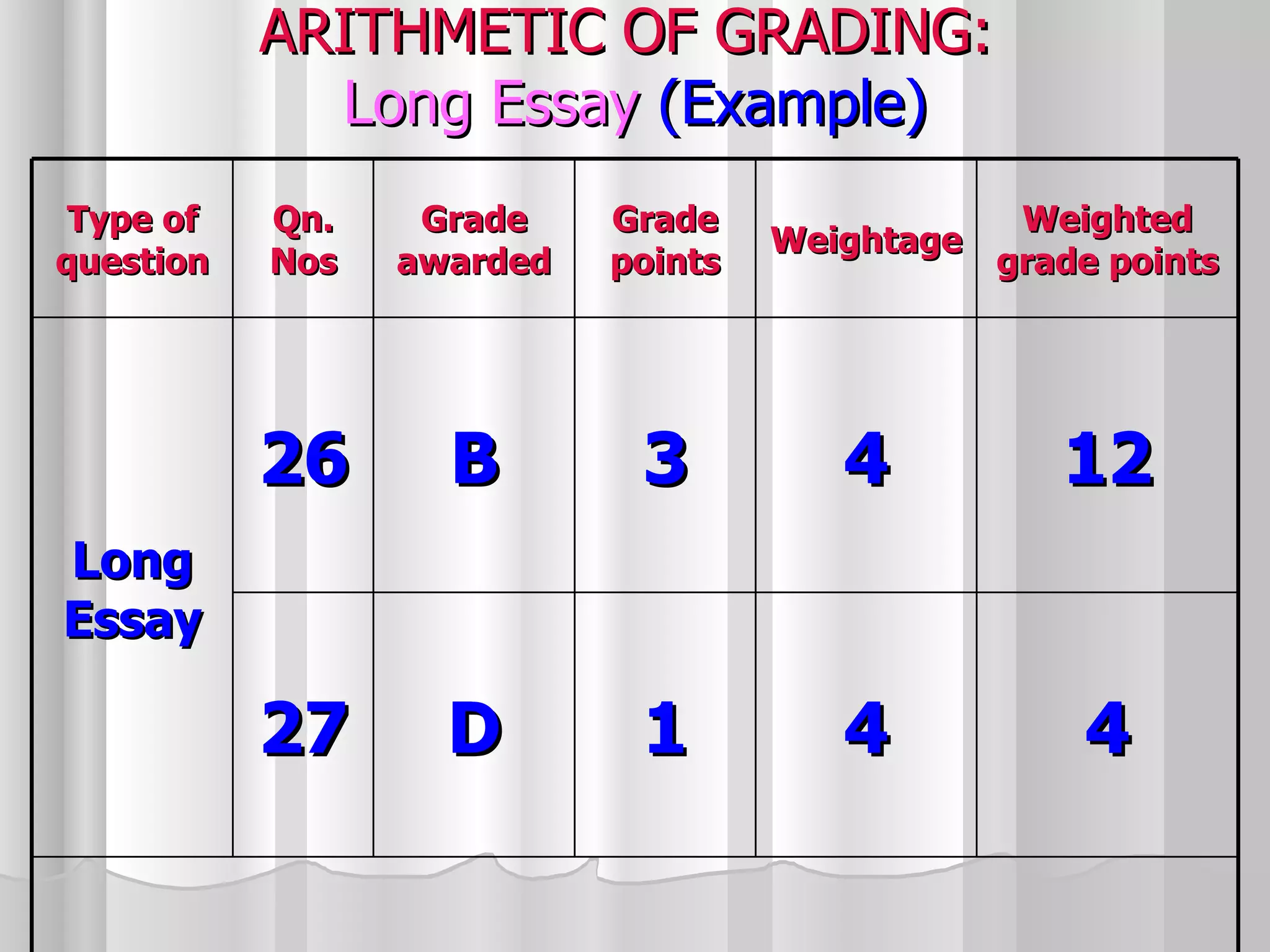
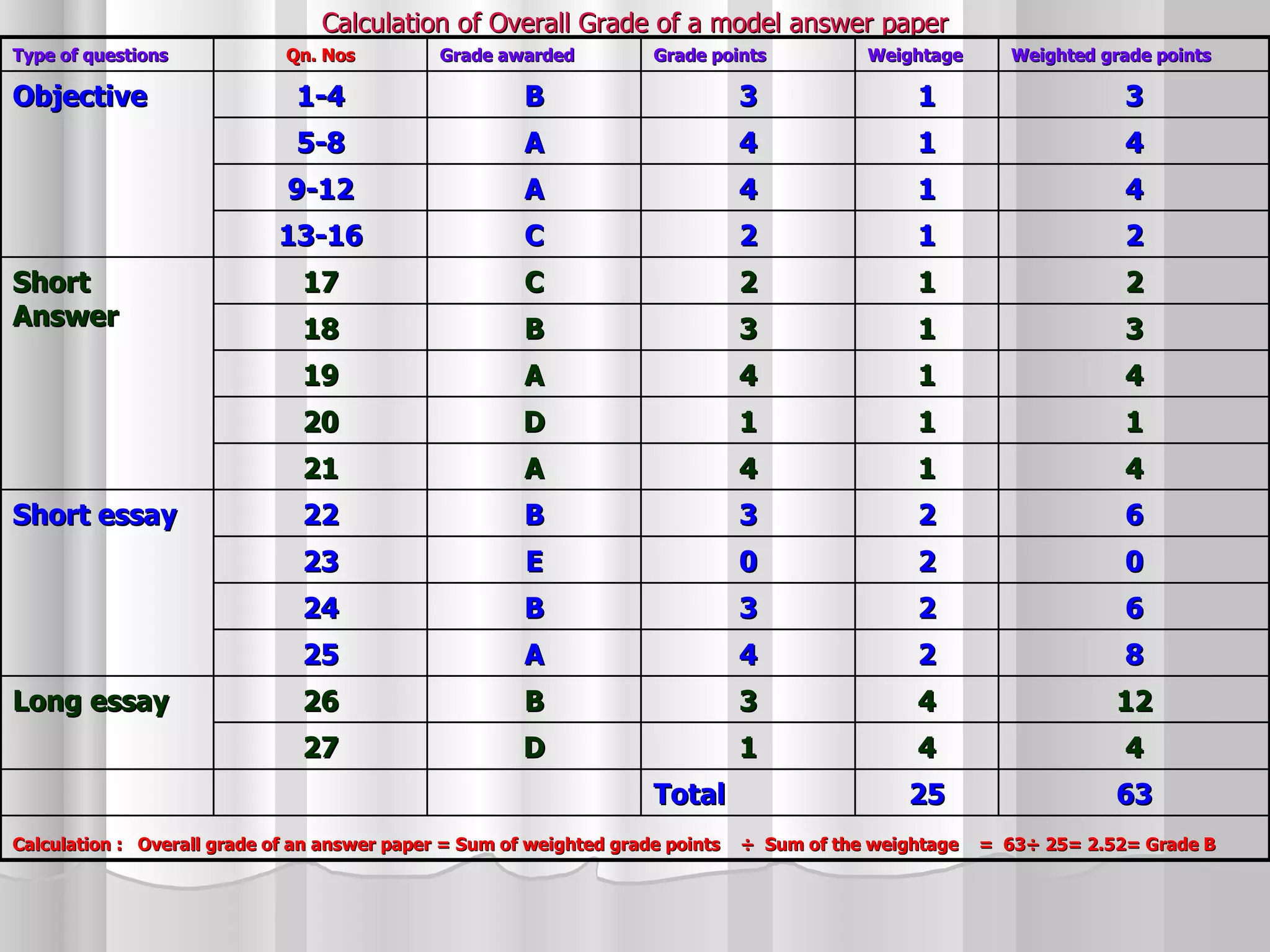
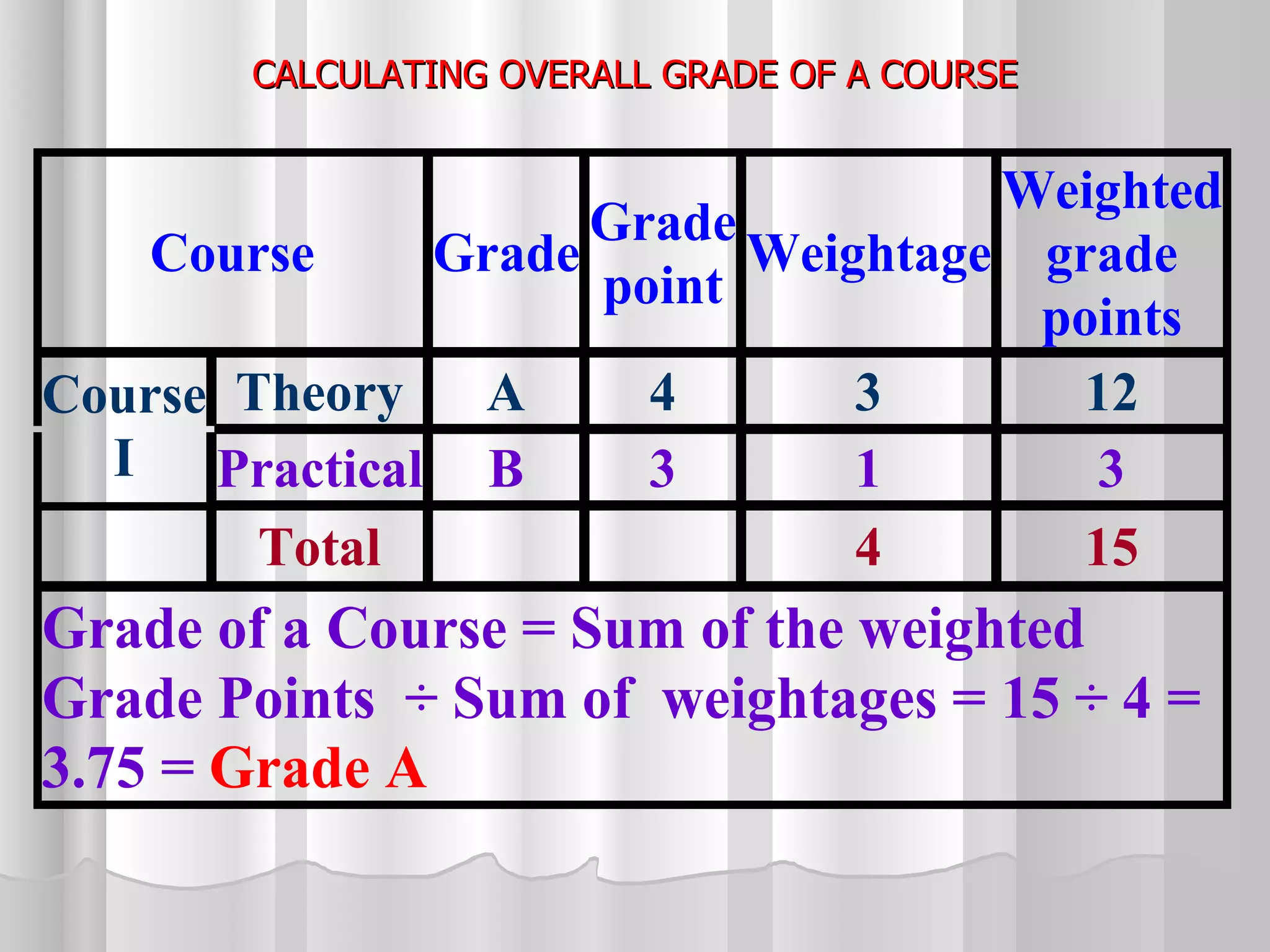
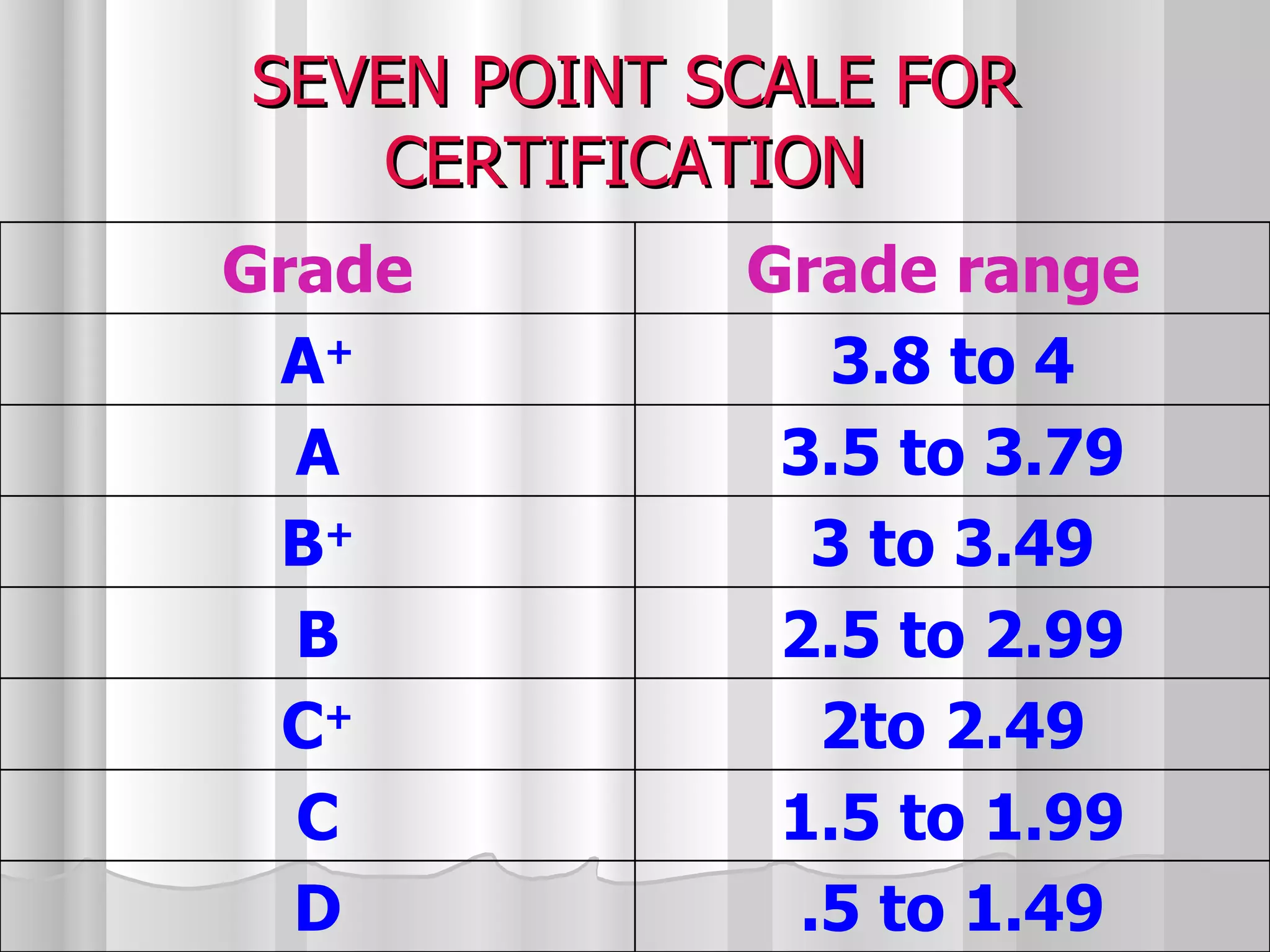
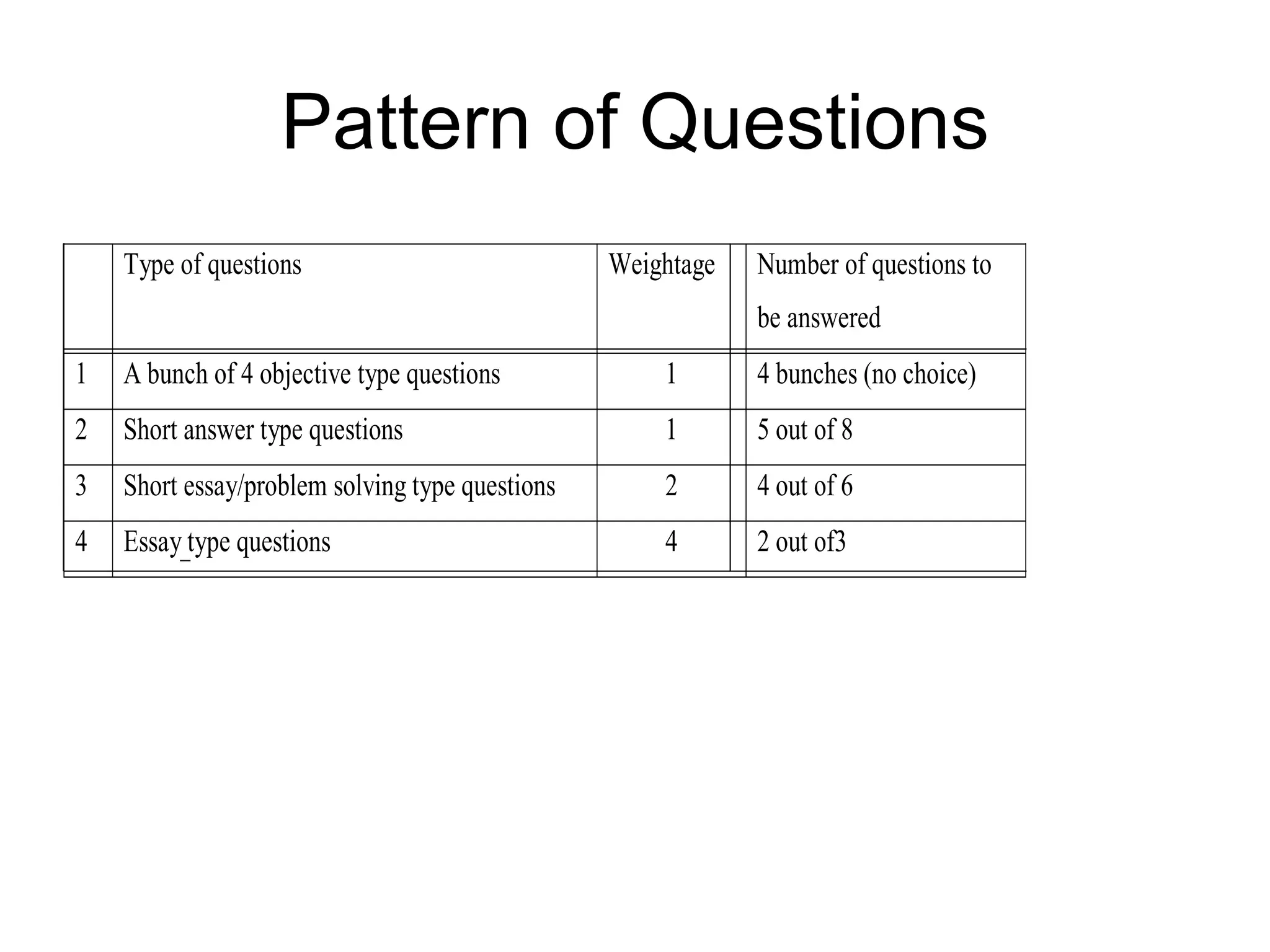
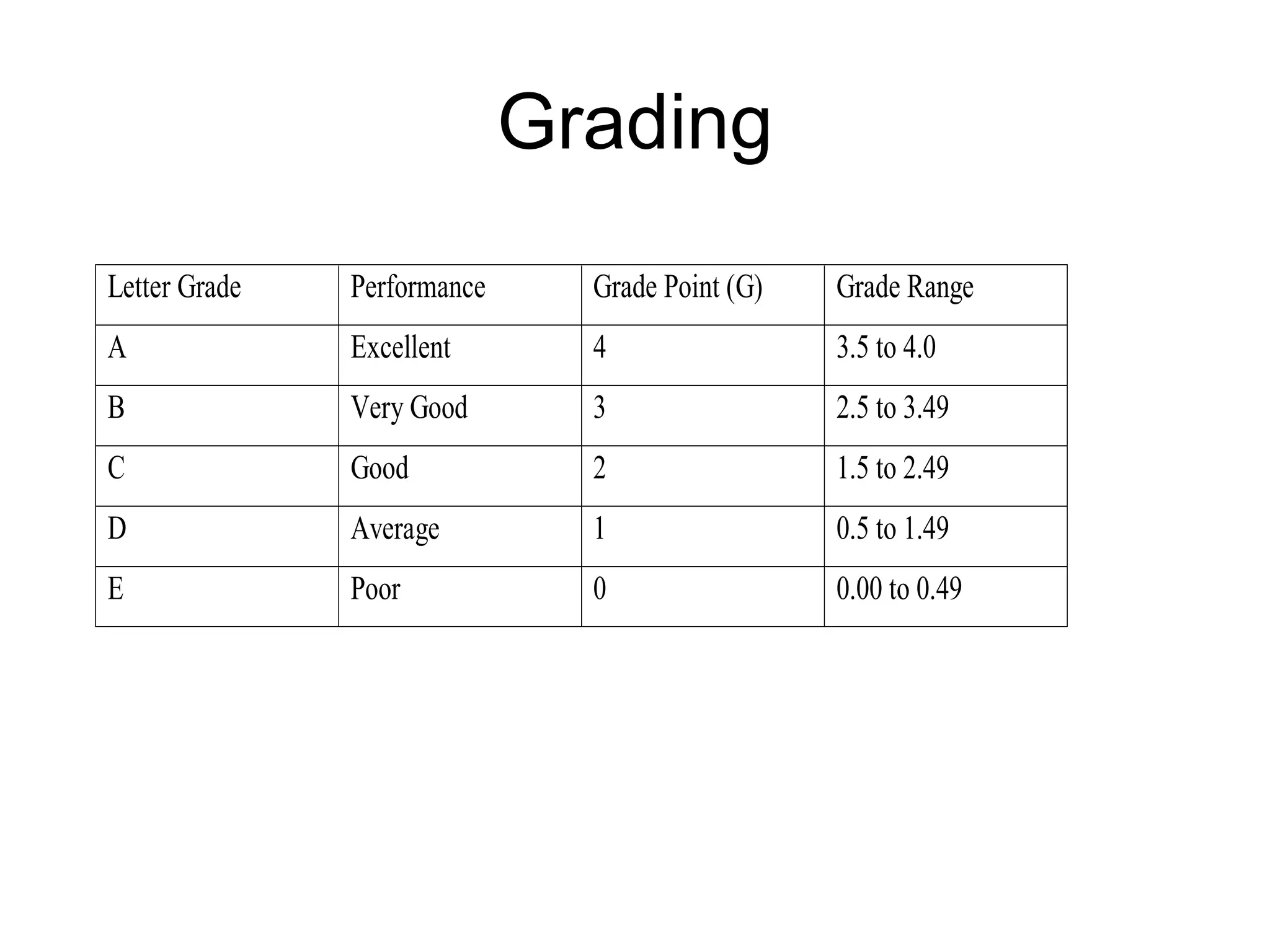
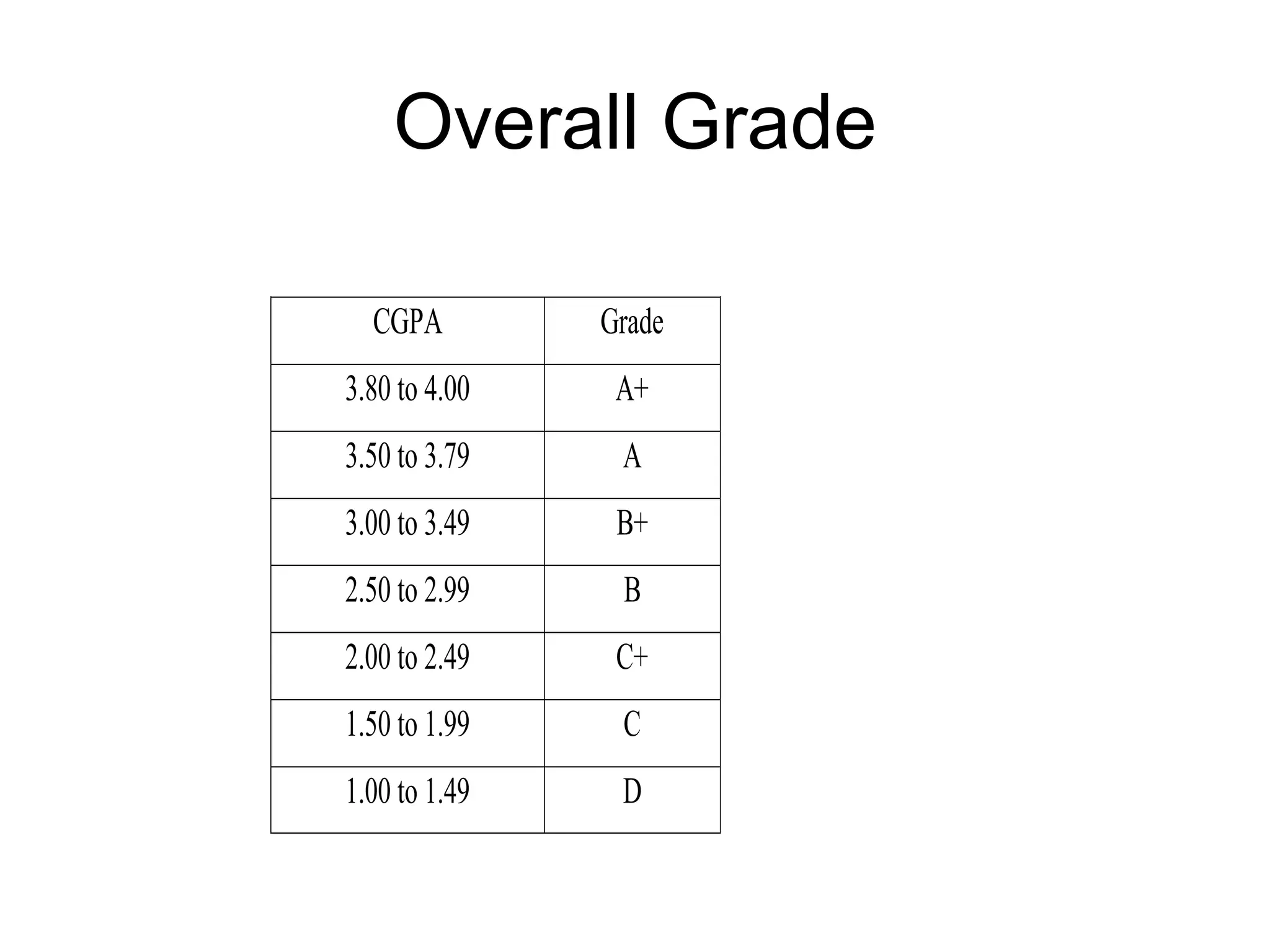
The document summarizes the key aspects of the newly implemented Bachelor of Education (B.Ed.) degree program in India, including the credit and semester system, grading, and course structure. The B.Ed. is a 2-semester program with common, core, and elective courses totaling 90 credits. Student performance is evaluated through continuous internal and end-semester external assessments. Grades are awarded based on the Cumulative Grade Point Average across all courses taken in the program.