Embed presentation
Downloaded 96 times





This document discusses symmetric multiprocessing (SMP). It defines SMP as processing programs using multiple processors that share common operating system and memory. The key aspects of SMP are: - Processors share memory and I/O bus or data path - A single operating system controls all processors - SMP architecture allows processors to access same memory simultaneously - Advantages of SMP include improved performance, availability, ability to incrementally grow, and scaling - Limitations include additional complexity in operating system and potential bottlenecking of master CPU.
Presentation by Mohammad Ali Khan, Jakir Hossain, and Jannatul Ferdaus on Symmetric Multiprocessing in the Computer Science field.
Parallel computing involves simultaneous calculations to solve large problems efficiently through division into smaller tasks.
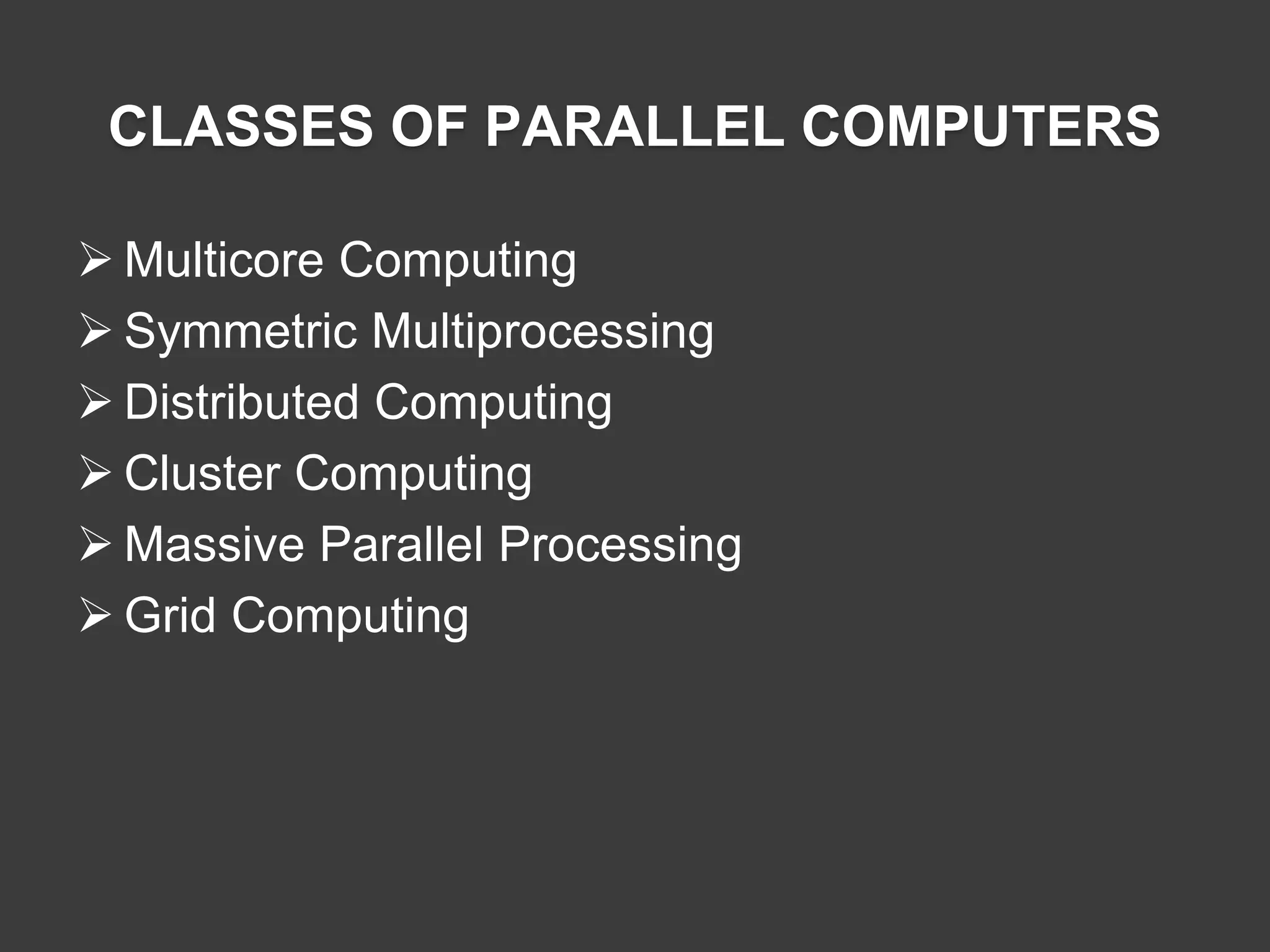
Various classes of parallel computers include Multicore Computing, SMP, Distributed Computing, Cluster, Massive Parallel Processing, and Grid Computing.
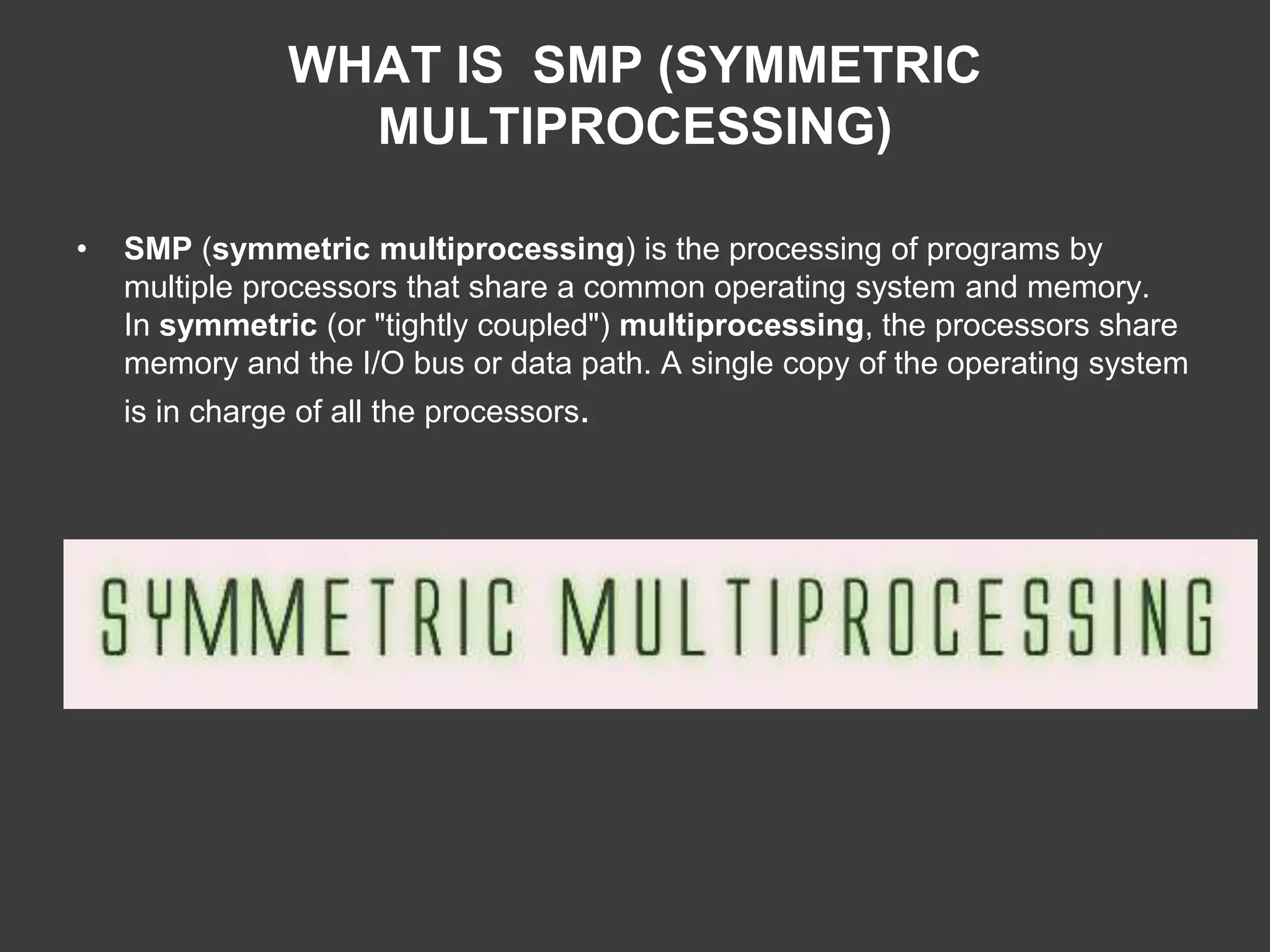
SMP (Symmetric Multiprocessing) involves multiple processors sharing a common OS and memory for efficient program execution.
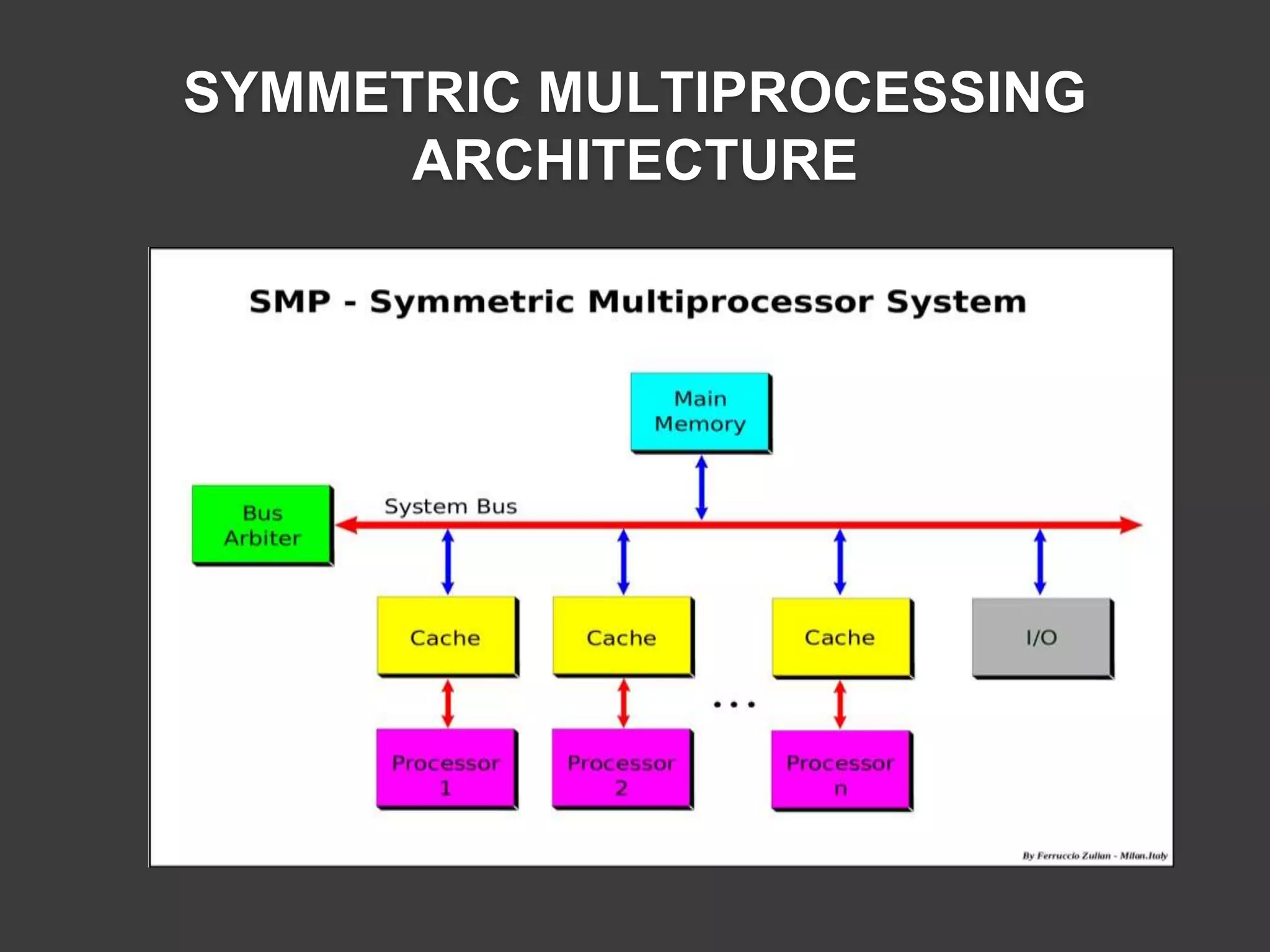
Discusses the structural layout and technology behind Symmetric Multiprocessing systems.
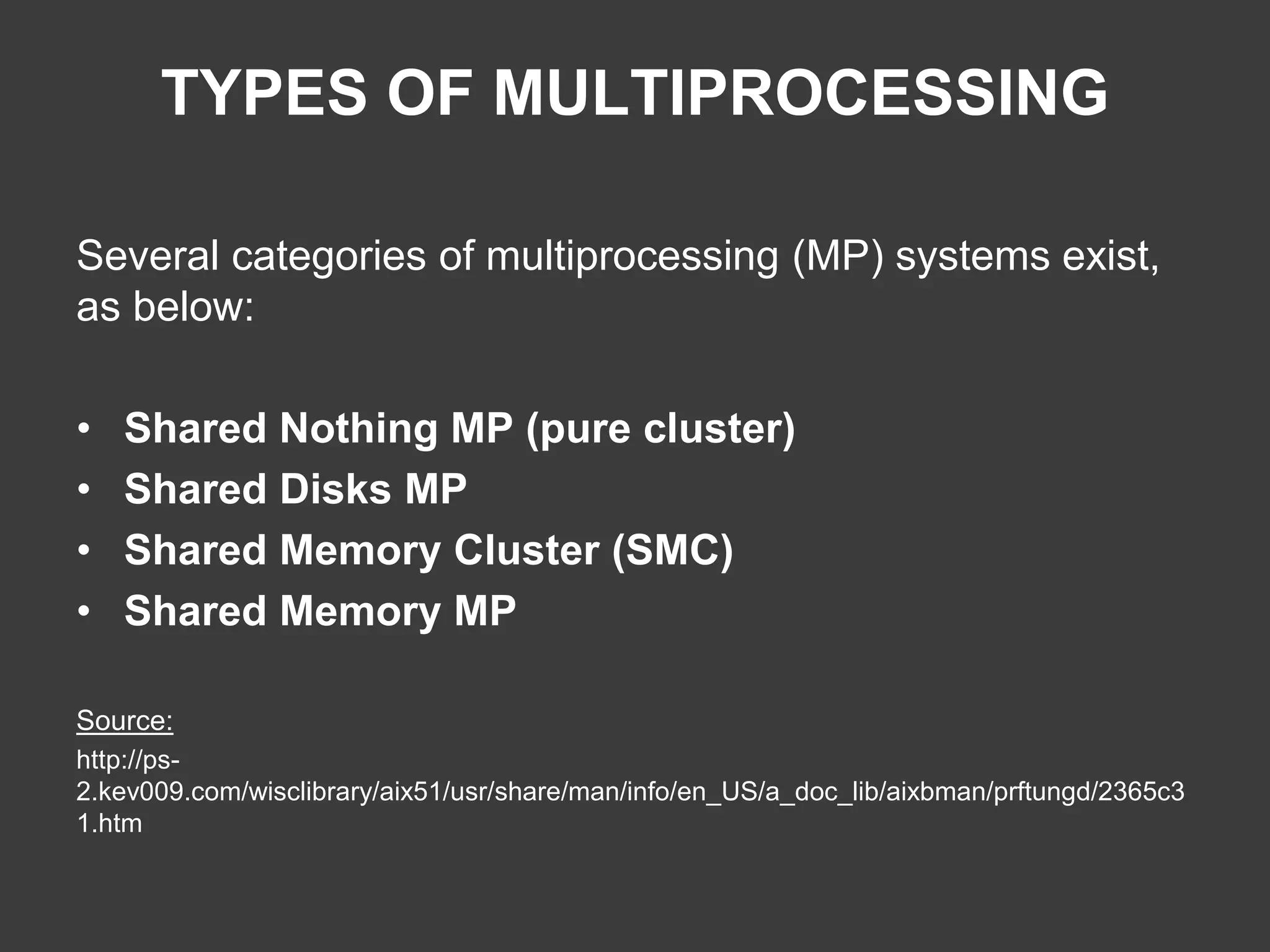
Different categories of multiprocessing systems: Shared Nothing, Shared Disks, Shared Memory Clusters, and Shared Memory MP.
Analyzes the differences between Symmetric and Asymmetric Multiprocessing.
Key advantages of SMP include enhanced performance, availability, incremental growth, and scalability.
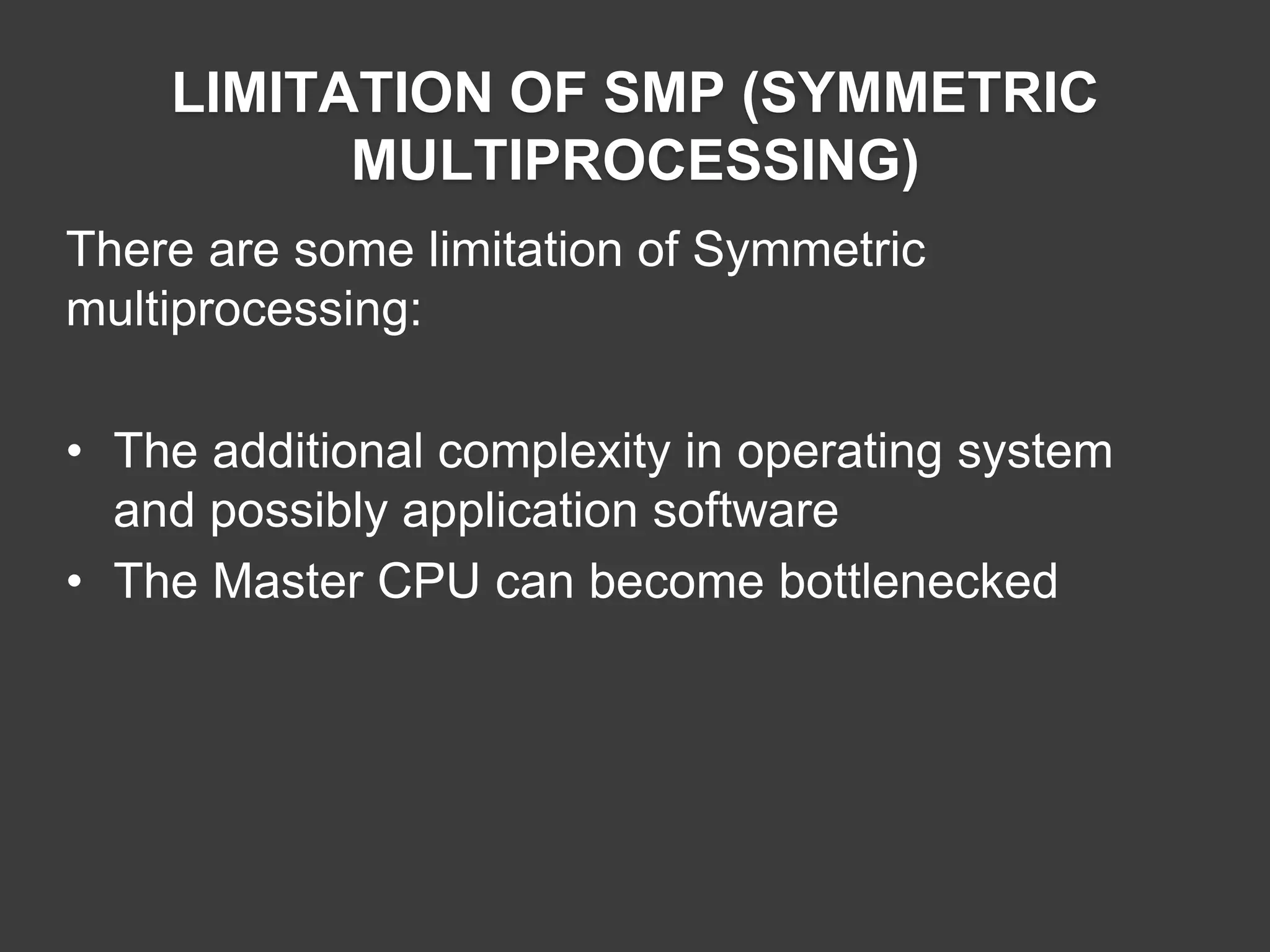
Limitations of SMP include increased system complexity and the risk of bottlenecks from the Master CPU.









