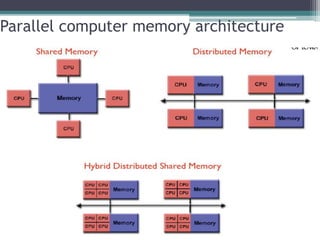
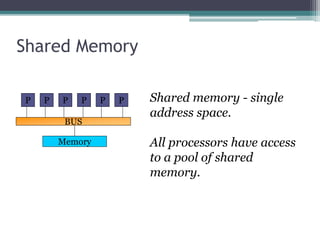
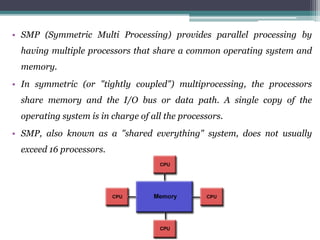
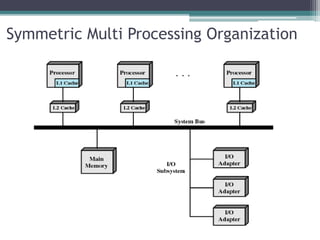
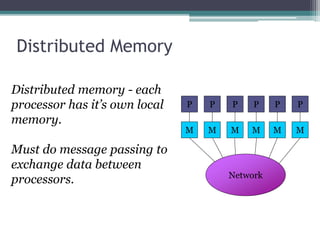
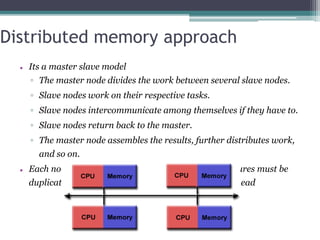
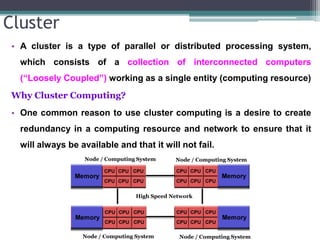
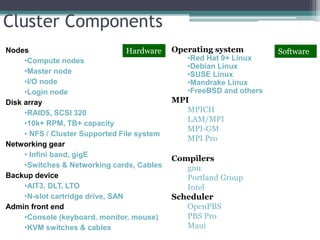
This document discusses high performance computing (HPC) and parallel computing. It defines HPC as aggregating computing power to solve large problems. Parallel computing uses multiple processors working together on common tasks. There are three main approaches to parallel computing: shared memory, where all processors access a common pool of memory; distributed memory, where each processor has its own local memory; and hybrid distributed shared memory. Parallel computers enable solving problems that require fast solutions or large amounts of memory, like weather forecasting.