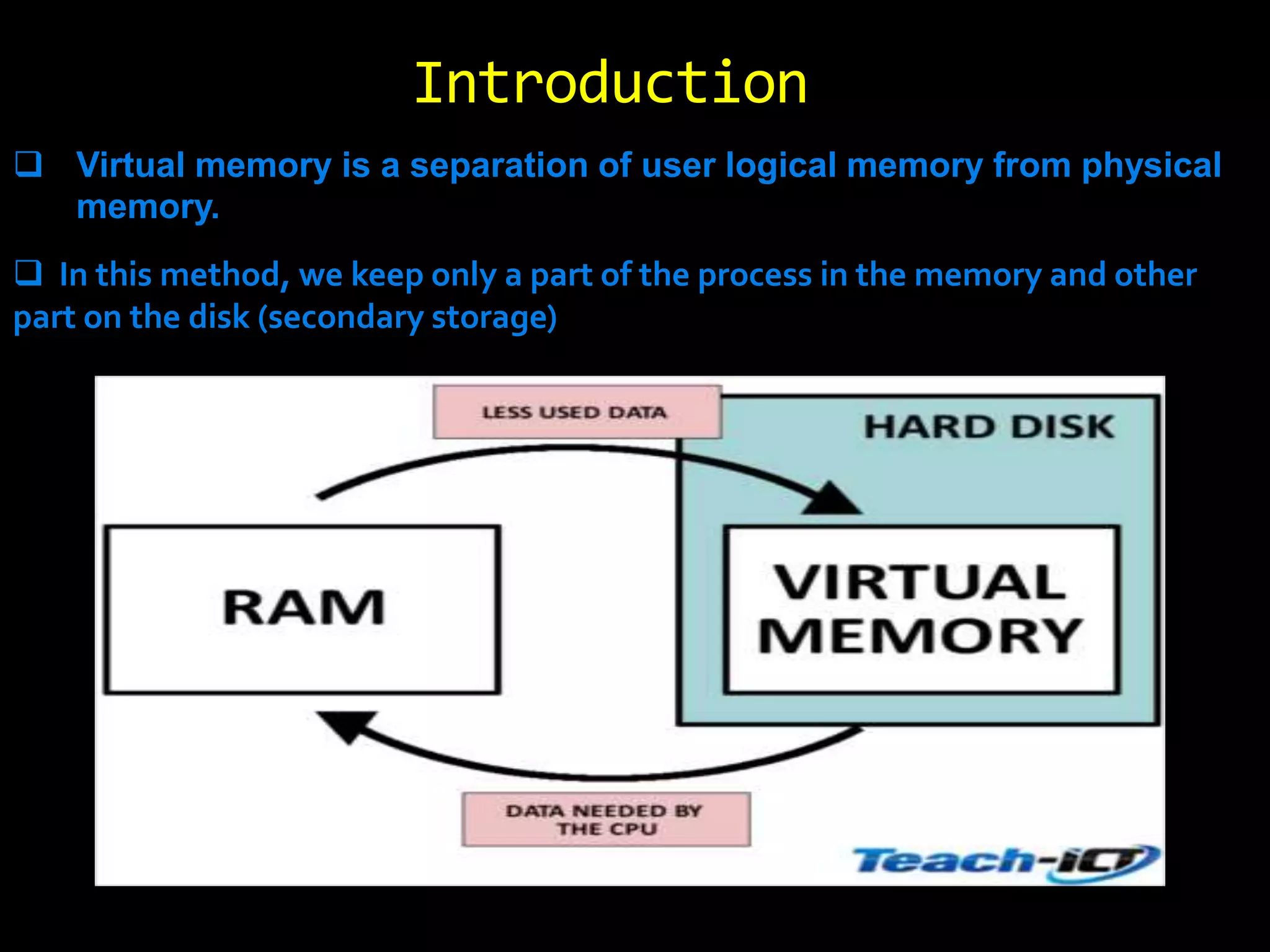
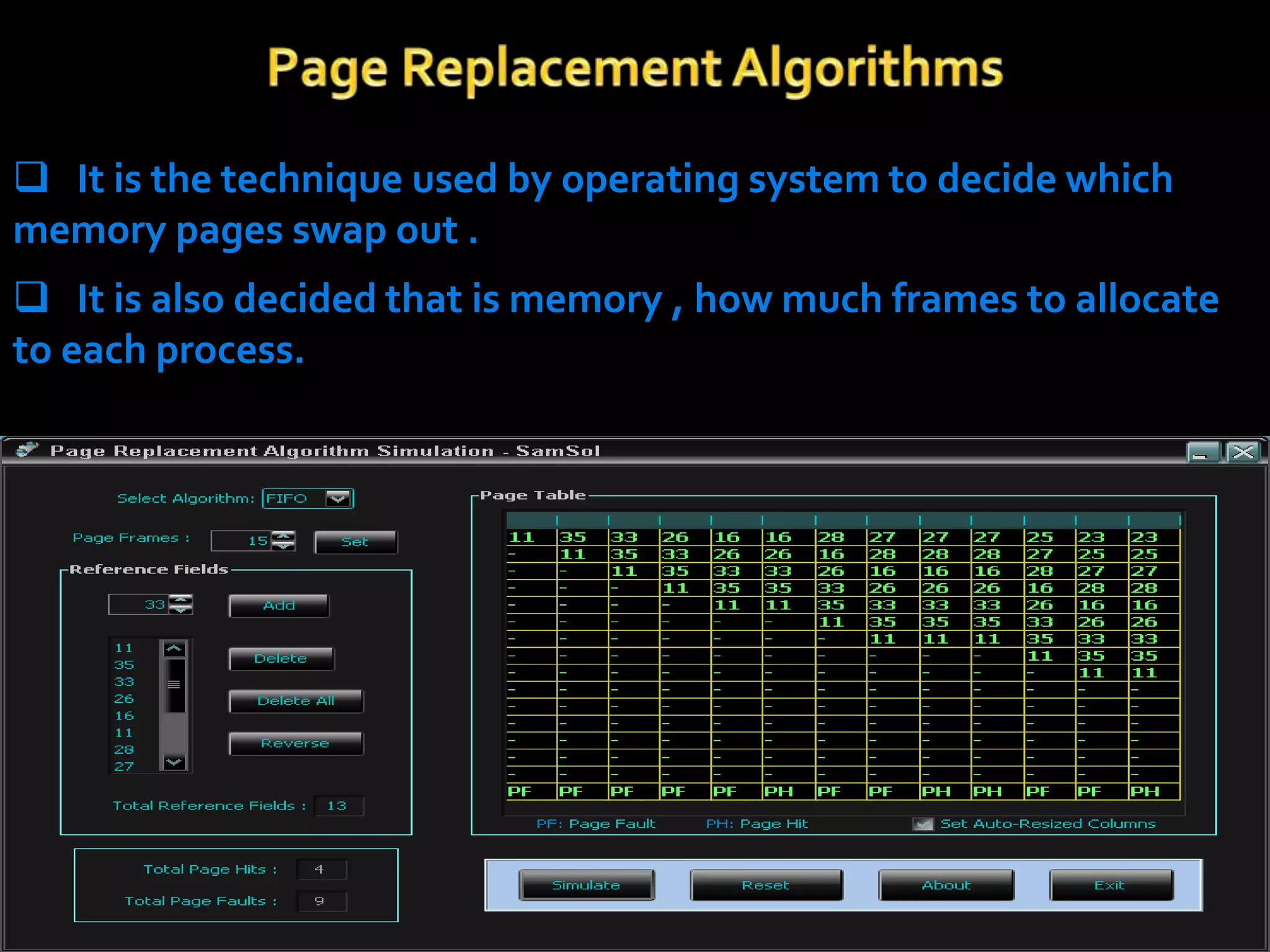
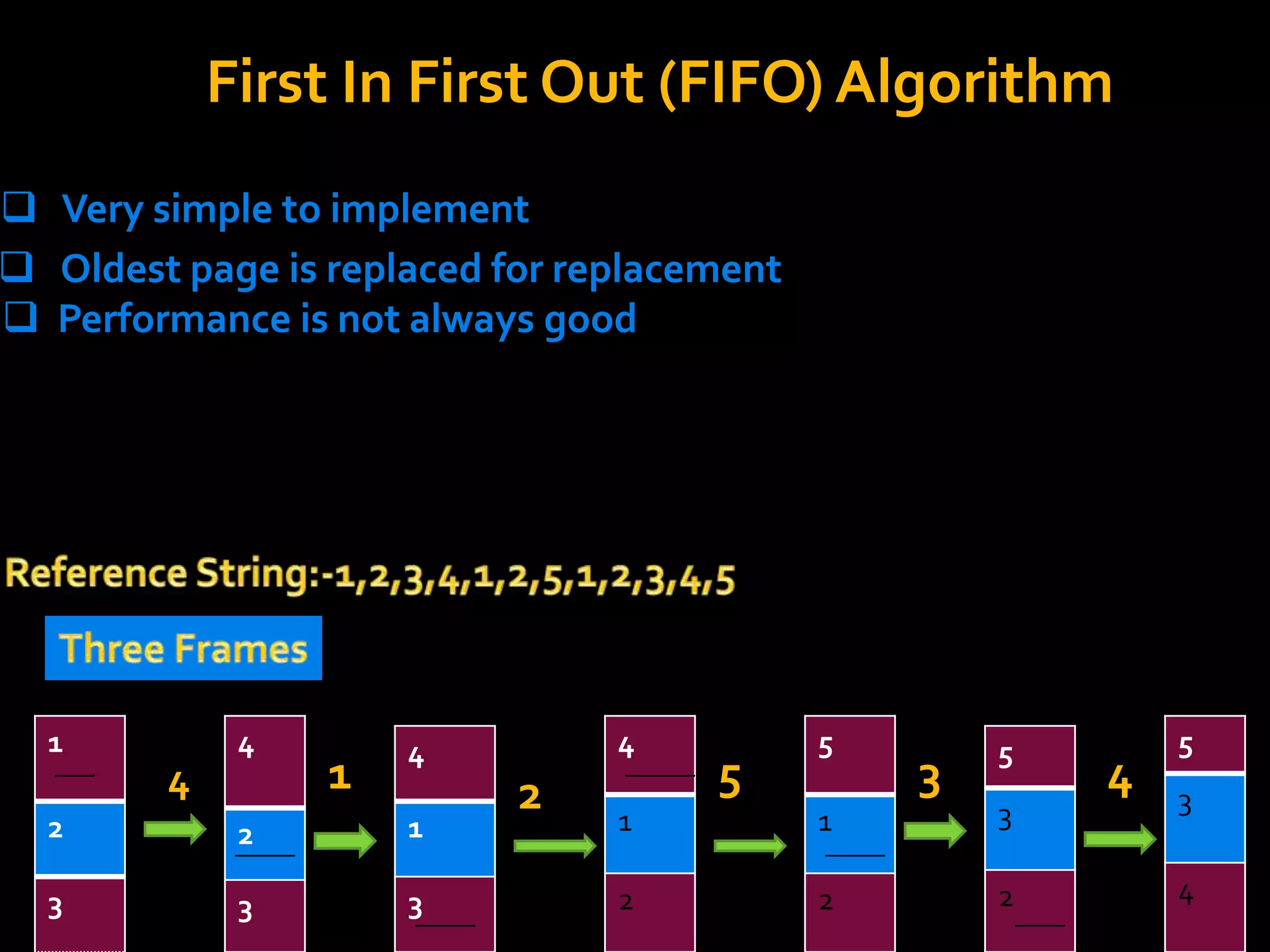
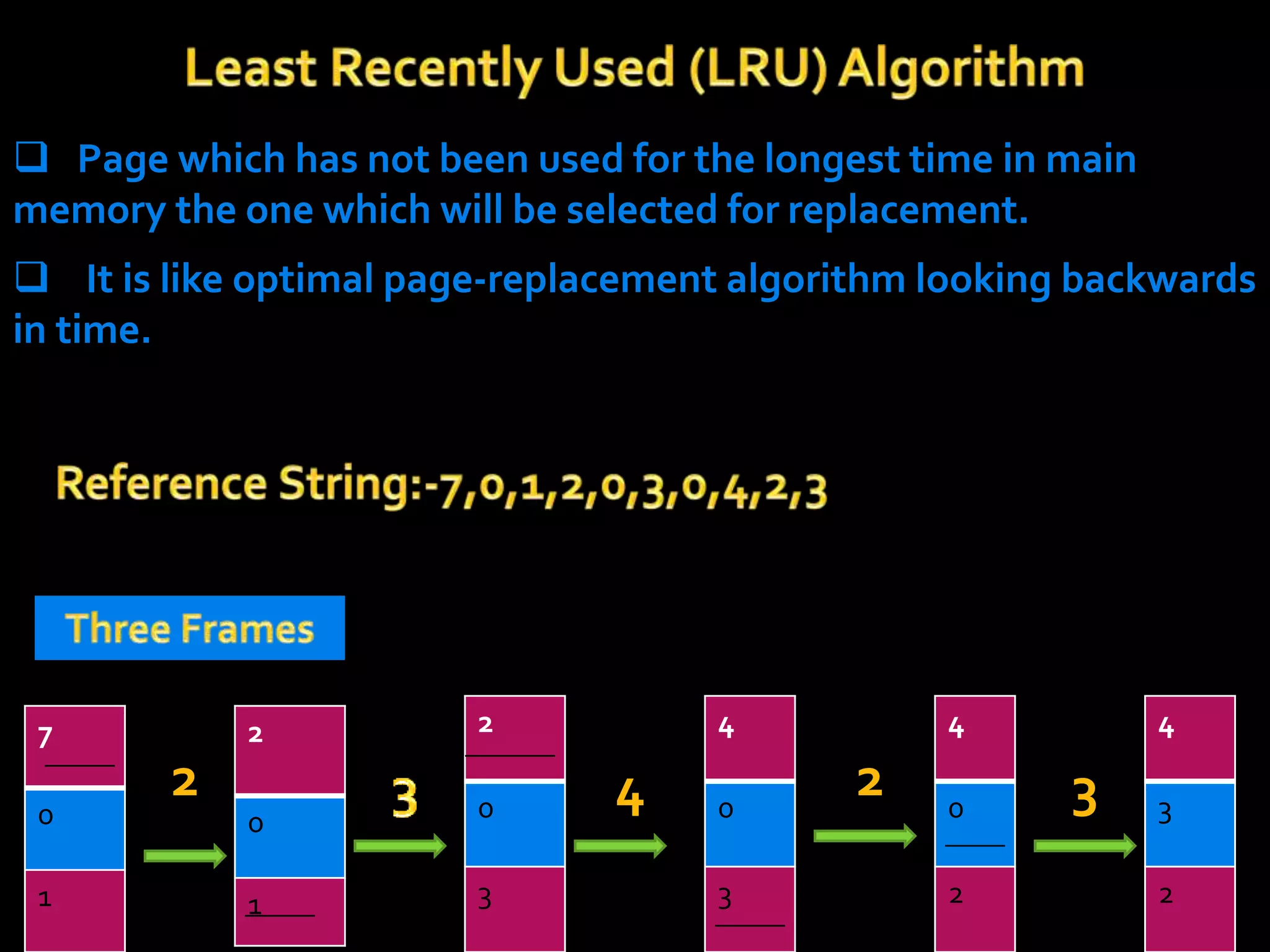
The document discusses virtual memory, which separates user logical memory from physical memory, allowing only a portion of a process to reside in memory while the rest is stored on disk. It outlines the advantages, such as improved processing speed and support for multiprogramming, as well as disadvantages, including decreased performance and system stability. Various page replacement algorithms like FIFO and LRU are explained, highlighting their mechanisms and effectiveness.