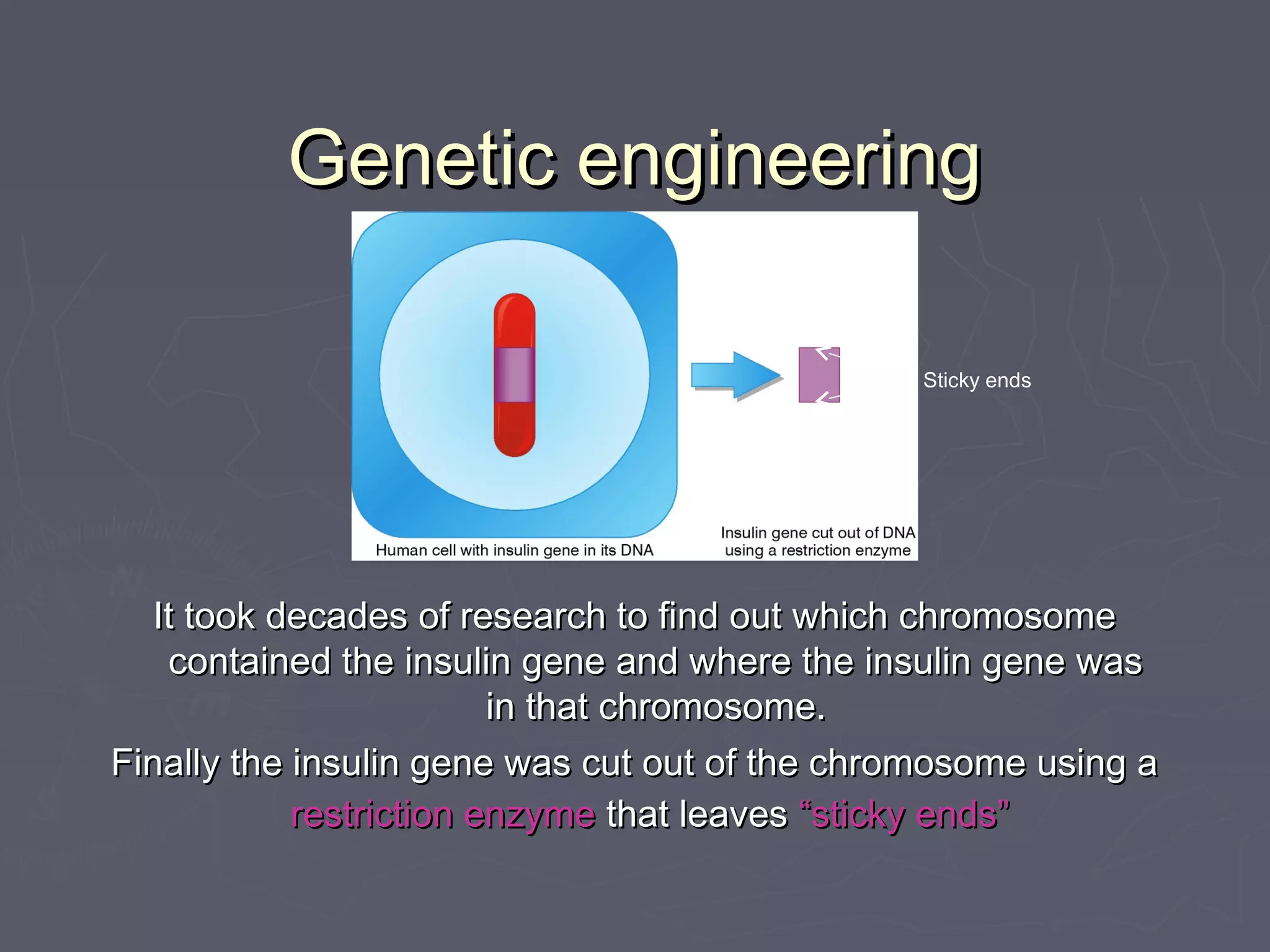
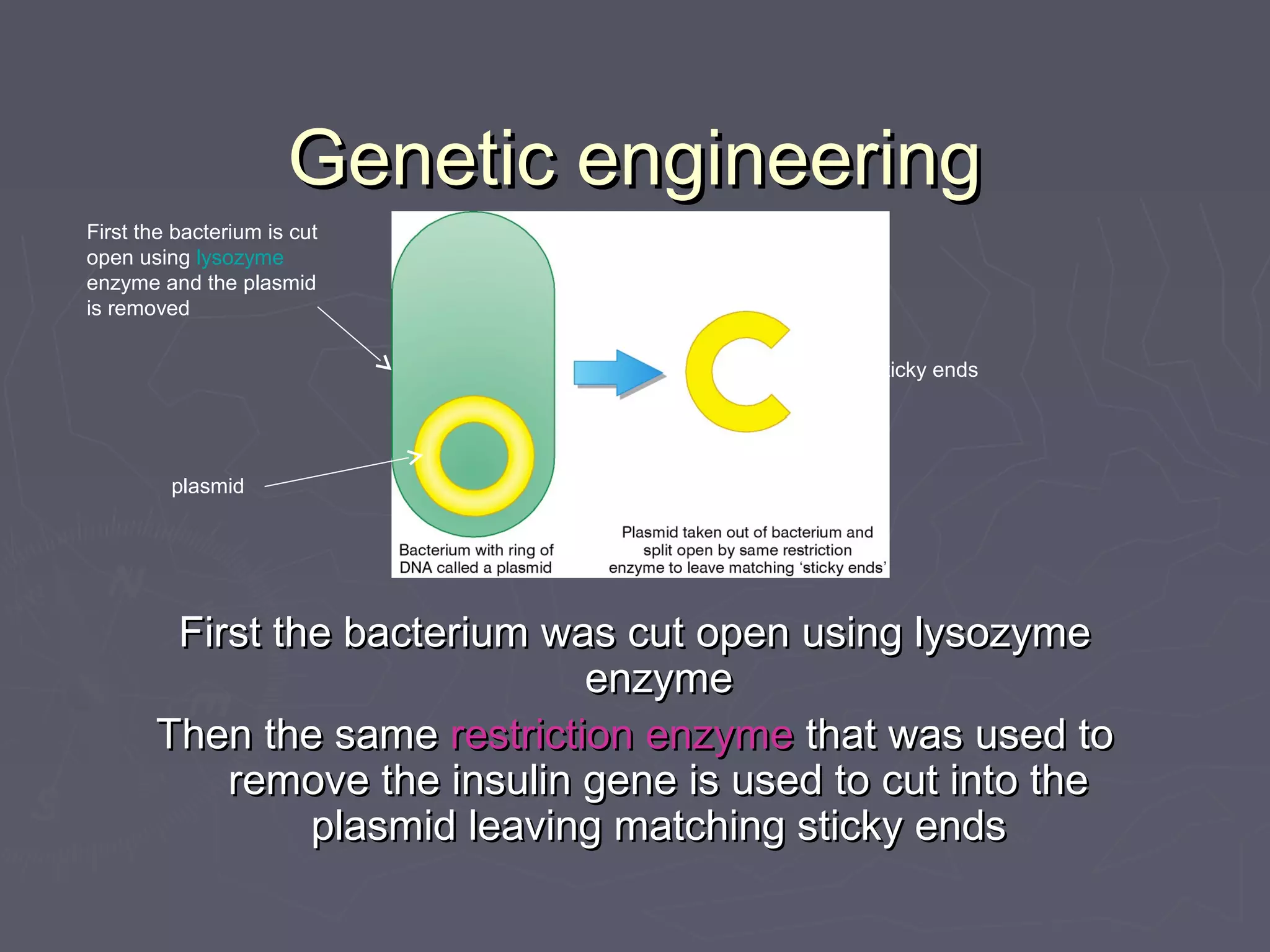
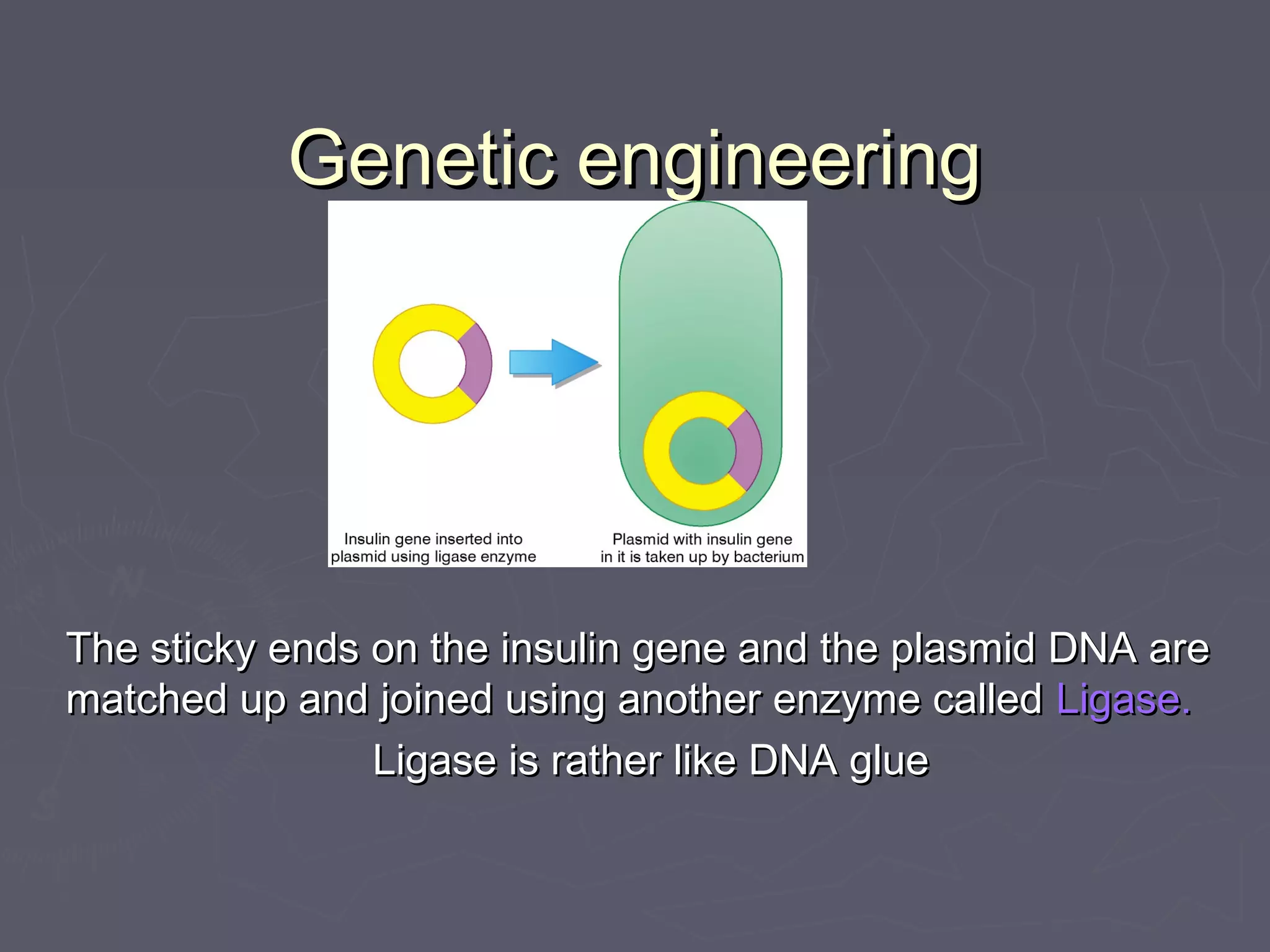
Selective breeding and genetic engineering are techniques used to produce offspring with desirable traits. Selective breeding involves selecting animals with desired traits and breeding them, while genetic engineering transfers genes between organisms. Both techniques have benefits like increased crop yields or disease resistance, but also risks like loss of genetic diversity, animal health issues, or unintended effects. Genetic engineering in particular raises ethical concerns about manipulating natural organisms.