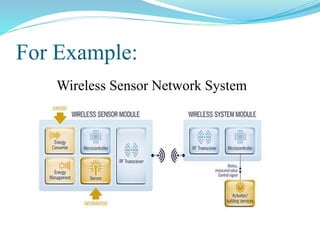
The document provides an overview of sensors, including their types, criteria for selection, applications, and drawbacks. It emphasizes the importance of sensors in engineering, the need for smart sensors with integrated processing capabilities, and outlines various sensor types such as temperature and proximity sensors. Additionally, it discusses the challenges faced by sensors and outlines their essential features for effective performance in various applications.