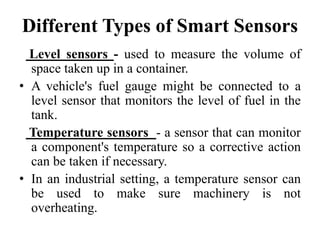
Smart sensors are devices that collect environmental data using microprocessors and wireless communication. They have four main functions: measurement, configuration, verification, and communication. Smart sensors take physical signals and convert them to electrical signals to measure things like temperature, traffic, and industrial applications. They are configured to detect errors and continuously monitor their own behavior. Smart sensors communicate data to other devices and are used in applications like flood monitoring, agriculture, traffic control, and industrial equipment monitoring. Common types of smart sensors include level, temperature, pressure, infrared, and proximity sensors. Smart sensors differ from basic sensors by including an embedded processor that allows onboard data processing before communication.