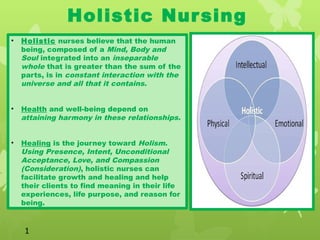
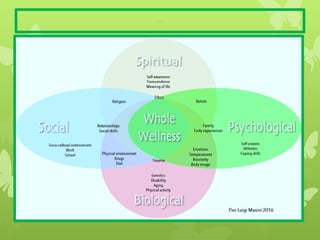
Holistic nursing encompasses an approach to healthcare that addresses the whole person, integrating mind, body, and spirit for optimal well-being. It promotes the idea that healing is a journey and emphasizes the importance of compassionate care, self-care, and the interdependence of all aspects of a person's life. Established with roots in the philosophies of Florence Nightingale, holistic nursing has gained recognition as a specialty practice that incorporates complementary and alternative therapies alongside traditional medical practices.









![What is Holistic Nursing?
Florence Nightingale
Florence
Nightingale, byname
Lady with the Lamp,
(born May 12,
1820, Florence [Italy]—died
August 13, 1910, London,
England), British nurse,
statistician, and social
reformer who was the
foundational philosopher of
modern nursing.
Who believed in care that
focused on unity, wellness,
and the interrelationship of
human beings and their
environment, is considered to
be one of the first holistic
nurses.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/holisticnursing-190201130004/85/Holistic-nursing-12-320.jpg)


















































