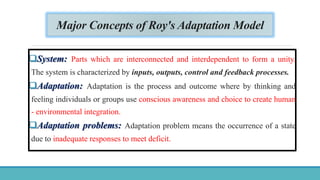
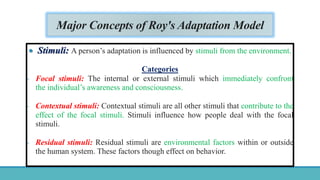
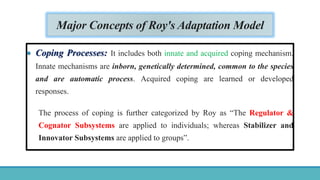
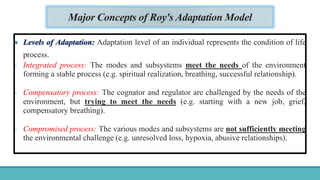
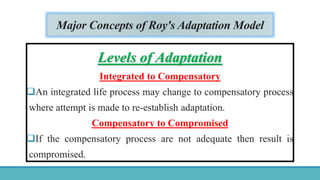
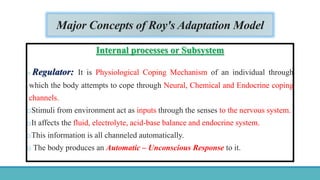
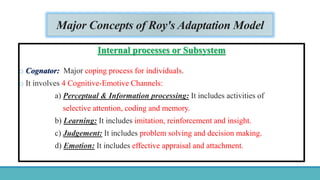
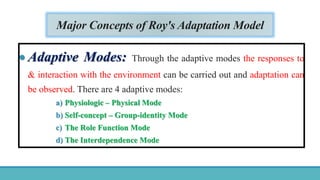
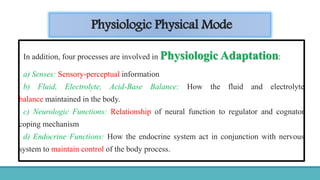
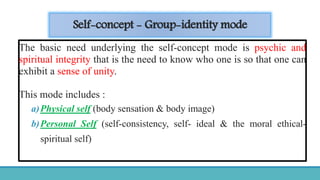
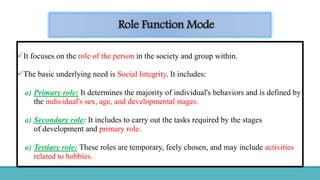
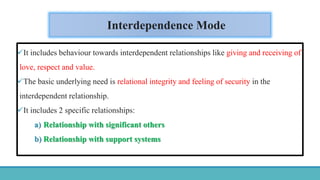
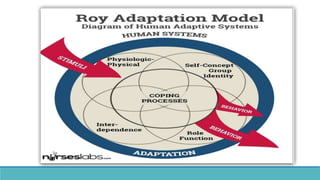
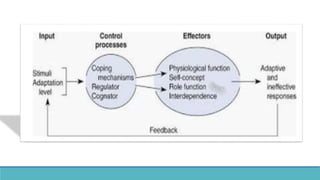
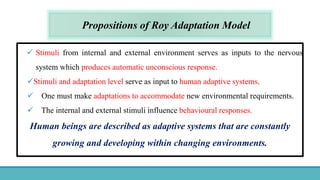
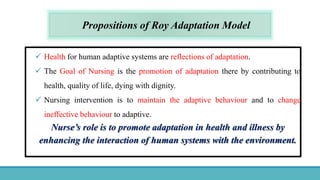
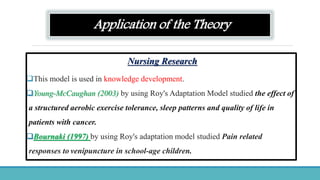
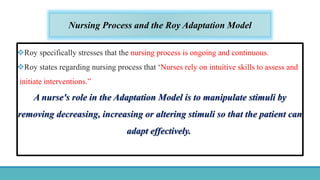
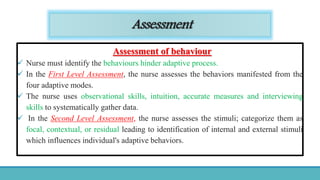
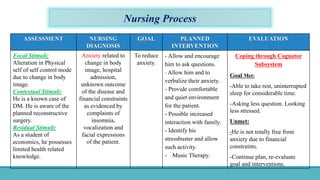
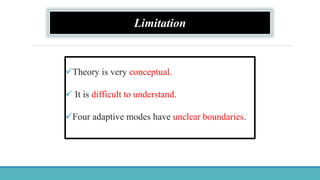
Roy Adaptation Theory is a nursing theory developed by Sister Callista Roy that views humans as adaptive systems. The theory proposes that people constantly interact with a changing environment and strive for adaptation in four modes: physiological, self-concept, role function, and interdependence. Nursing aims to promote positive adaptation through assessing a patient's behaviors and environmental interactions to enhance coping and remove ineffective responses.