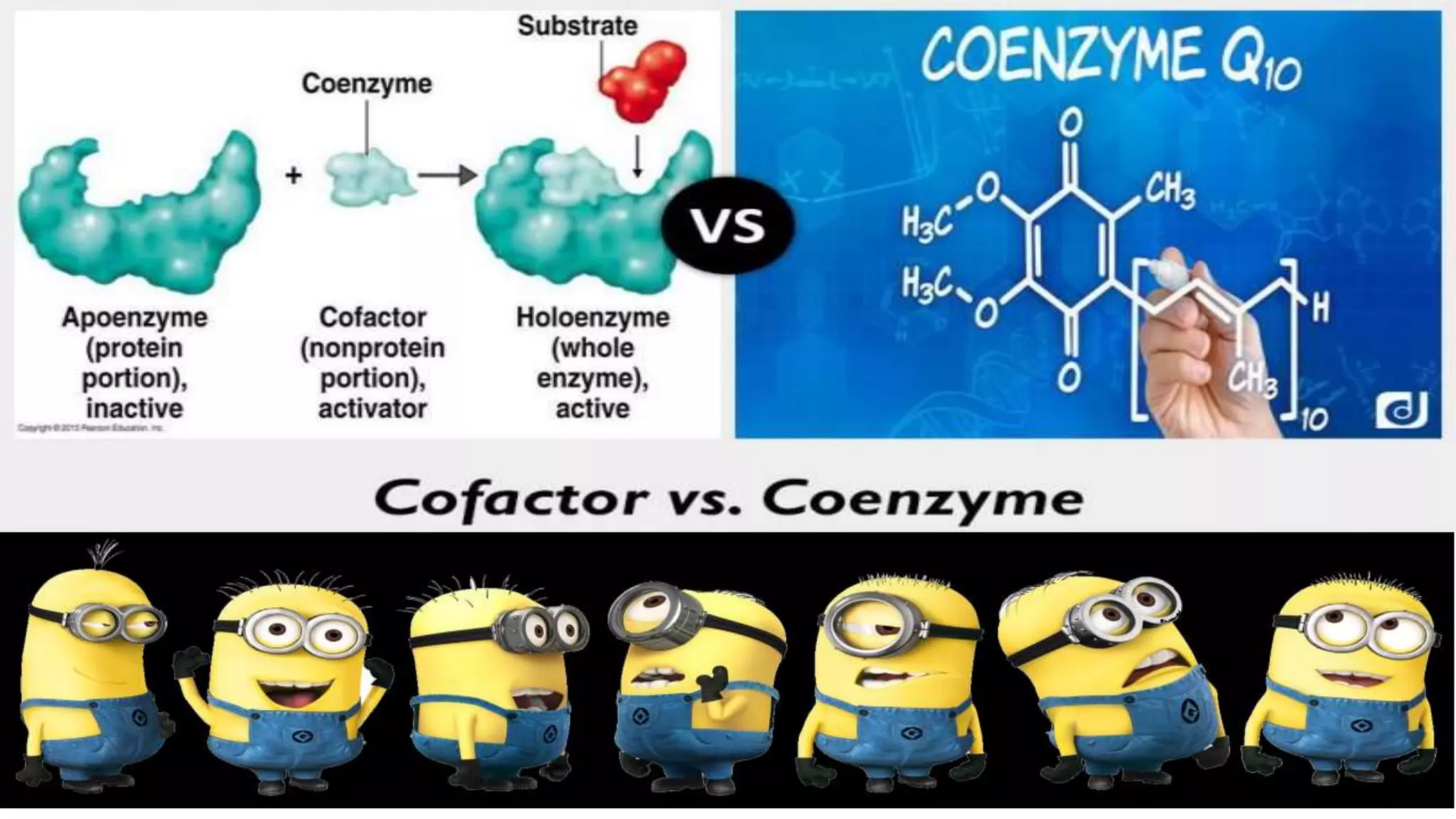
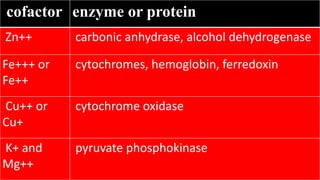
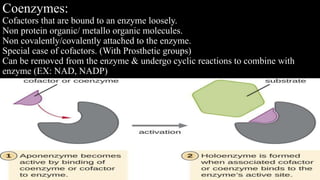
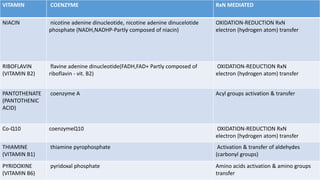
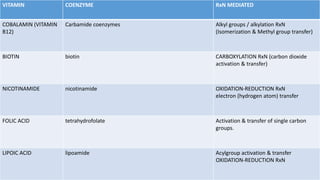
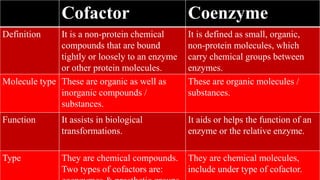
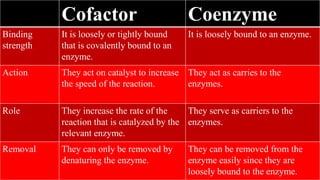
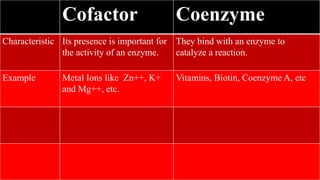
Cofactors and coenzymes are organic or inorganic molecules that assist enzymes in catalyzing biochemical reactions. There are two main types of cofactors - inorganic ions that are tightly bound and function as enzyme activators, and organic compounds that exist as coenzymes or prosthetic groups. Coenzymes are loosely bound organic molecules that serve as carriers, transferring chemical groups between enzymes and allowing redox and group transfer reactions. Many coenzymes are derived from vitamins and help mediate important metabolic reactions.