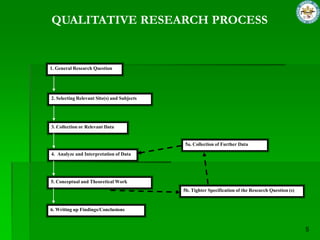
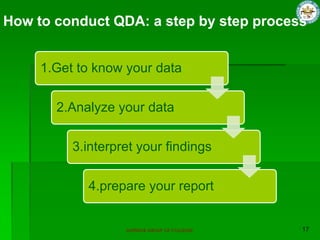
Qualitative research focuses on words rather than numbers, generates theories rather than generalizing, and aims to understand participant views without claiming to generalize. Qualitative researchers are influenced by interpretivism and seek to understand social life through the eyes of participants by emphasizing context and flexibility over rigid structures. The qualitative research process involves generating questions, selecting sites and subjects, collecting and analyzing data, developing concepts and theories, and writing conclusions. Reliability and validity are ensured through methods like member checking and triangulation. Qualitative sampling uses non-probability methods like convenience sampling. Data collection methods include interviews, focus groups, document analysis, and observation.










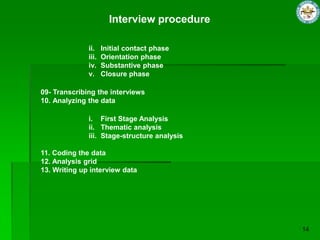




![EXAMPLE
Excerpt
First of all I would like to say few things before I give an answer to it. This is an organization which
gives you a plenty of (0.2) you see! Opportunities in which you can participate in decision making. I
always:::: been allowed by top management to participate in decision making. Like (0.2) if there are
anything regarding hiring faculty or there is any matter regarding curriculum improvement. They
have always asked me to participate in decision making and I have always give then decisions and
they have always cater those decisions implemented in their systems.
Substantive Statement
This is an organization which gives you a plenty opportunities in which you can participate in
decision making. I always:::: been allowed by top management to participate in decision making.
[For example] if there are anything regarding hiring faculty or there is any matter regarding
curriculum improvement. [The management] always asked me to participate in decision making and
then decisions and they have always catered those decisions implemented in their systems.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/qualitativeresearchprocesslec6-130211163755-phpapp01/85/QUALITATIVE-RESEARCH-PROCESS-20-320.jpg)